1.通过Thread对象开启线程
1.1函数调用
首先用new申请Thread对象,然后对象调用Start()方法启用线程。
Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId获取当前线程的ID,便于管理。
class Program
{
static void DownLoad()
{
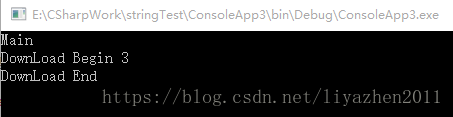
Console.WriteLine("DownLoad Begin " + Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId);
Thread.Sleep(1000);
Console.WriteLine("DownLoad End");
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//创建Thread对象
Thread thread = new Thread(DownLoad);
//启动线程
thread.Start();
Console.WriteLine("Main");
Console.ReadKey();
}
}1.2 Lambda表达式
用Lambda表达式代替函数调用,得到相同的执行结果。
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Thread thread = new Thread(() =>
{
Console.WriteLine("DownLoad Begin " + Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId);
Thread.Sleep(1000);
Console.WriteLine("DownLoad End");
});
thread.Start();
Console.WriteLine("Main");
Console.ReadKey();
}
}1.3 运行结果
2.传递参数
2.1 Start()传递
首先参数的类型必须是object,其次通过Start方法传递参数。
class Program
{
static void DownLoad(object name)
{
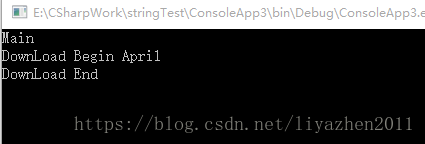
Console.WriteLine("DownLoad Begin " + name);
Thread.Sleep(1000);
Console.WriteLine("DownLoad End");
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//创建Thread对象
Thread thread = new Thread(DownLoad);
//启动线程
thread.Start("April");
Console.WriteLine("Main");
Console.ReadKey();
}
}运行结果
2.2 对象传递
通过对象的构造函数,将参数传递给对象,然后用对象的方法初始化Thread。
class Program
{
public class Download
{
private int Id;
private string Name;
public Download(int id, string name)
{
Id = id;
Name = name;
}
public void DownloadFile()
{
Console.WriteLine("DownLoad Begin " + "ID: " + Id + " Name: " + Name);
Thread.Sleep(1000);
Console.WriteLine("DownLoad End");
}
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Download download = new Download(1, "人民日报");
Thread thread = new Thread(download.DownloadFile);
thread.Start();
Console.WriteLine("Main");
Console.ReadKey();
}
}运行结果
3. 前台线程和后台线程
前台线程:只要存在有一个前台线程在运行,应用程序就在运行。
后台线程:应用程序关闭时,如果后台线程没有执行完,会被强制性的关闭
默认情况下,用Thread类创建的线程是前台线程,线程池中的线程总是后台线程。
class Program
{
static void DownLoad()
{
Console.WriteLine("DownLoad Begin " + Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId);
Thread.Sleep(1000);
Console.WriteLine("DownLoad End");
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//创建Thread对象
Thread thread = new Thread(DownLoad);
//设为后台线程
thread.IsBackground = true;
//启动线程
thread.Start();
Console.WriteLine("Main");
}
}在上例中,thread被设置为后台线程。Main执行完后,没有前台线程了,应用程序就结束,虽然后台线程thread此时尚未执行完,也被终止。
thread.Abort() 终止线程的执行。调用这个方法,会抛出一个ThreadAbortException类型的异常。
thread.Join() 将当前线程睡眠,等待thread线程执行完,然后再继续执行当前线程。