标准库:标准库头文件与名字空间
字符串
I/O流:输入、输出、用户自定义类型的I/O
容器:vector list map unordered_map 容器概述
算法:使用迭代器、迭代器类型、流迭代器、谓词、算法概述、容器算法
标准库
在学习C++的过程中,应努力探寻标准库的相关知识,尽量使用已有的标准库设施而不是自己再做一份。
标准库概述
标准库提供的设施:
1.运行时语言支持

2. C标准库
3.字符串【国际字符集和本地化的支持】和I/O流 【输入输出框架】
4.一个包含容器(vector map)和算法(find() sort() merge())的框架,习惯上称呼该框架为 标准模板库(STL) .用户可向其中添加自己定义的容器和算法。
5.对数值计算的支持 (标准数学函数 复数 支持算术运算的向量 随机数发生器)
6.对正则表达式匹配的支持
7.对并发程序设计的支持,如thread lock机制。
8.一系列工具,模板元编程 、 STL-风格的泛型程序设计 及 通用程序设计。
9.用于资源管理的“智能指针” ,unique_ptr shared_ptr 和垃圾收集器接口。
10. 特殊用途容器 array bitset tuple【元组】。
标准库头文件和名字空间
每一个标准库设施都是通过若干标准库头文件提供的。
要在程序中使用string list,必须
#include <string>
#include <list>
标准库定义在一个名为std的名字空间中。
字符串
compose 连接操作
= += 下标操作[] 子串操作substr() replace() toupper()大写
I/O流
iostream标准库设施
输出
cout标准输出流 cerr报告错误的标准流 ostream类型
输入
istream类型
getline(cin,str)读取一整行
用户自定义类型的I/O
iostream标准库设施还允许程序员为自己的类型定义I/O操作。
在字符流中识别模式的更系统的方法(正则表达式匹配)。
容器
vector 一个给定类型元素的序列 元素在内存中是连续存储的。 push_back() 在末尾追加一个元素。
元素:vector<T> 当插入一个新元素时它的值被拷贝到容器中。
范围检查:异常处理
list 双向链表
主要用于添加insert()和删除erase()元素。
当数据量较少时,遍历、排序和搜索,vector的性能都由于list.
每一个标准库容器都提供begin()和end()函数,因此可以用范围for循环。
map
标准库提供了一个名为map的搜索树(红黑树)。
标准库map是值对的容器,通过特殊优化来提高搜索性能。
unordered_map
标准库哈希容器
容器概述
一般情况下,推荐将标准库vector作为存储元素序列的默认类型,除非有足够的理由选择其他的容器。
算法
标准库在提供最常用的容器类型之外,还为这些容器提供了最常用的算法。比如排序、打印、抽取子集、删除元素、搜索。
标准库算法都描述为元素序列上的操作,序列由一对迭代器表示,分别指向首元素位置和尾后位置,begin() end()。
!!!!!!!迭代器string::iterator的一个重要作用是分离算法和容器,算法通过迭代器来处理数据,但它对存储元素的容器一无所知,反之亦然,容器对处理其元素的算法也是一无所知,它所做的事就是按需求提供迭代器(如begin()和end())。这种数据存储和算法分离的模型催生出非常通用和灵活的软件。
迭代器类型
vector:指针 索引
list:指向下一个元素的链接
所有迭代器类型的语义及其操作的命名都是相似的。对任何迭代器,使用++运算符,会得到一个指向下一个元素的迭代器,而*运算符则得到迭代器所指的元素。
iterator const_iterator list<Entry>::iterator
流迭代器
元素序列在输入流和输出流中。
因此将迭代器的概念应用到输入输出也是很有用的。
ostream_iterator
istream_iterator
谓词
pair<const string, int> 函数对象 lambda表达式
算法概述
算法就是一个对元素序列进行操作的函数模板。
标准库提供了很多算法,定义在头文件<algorithm>中,属于名字空间std。
find count replace copy sort merge
这些算法以及其他很多算法,可以用于容器、string和内置数组。
容器算法
序列是通过一对迭代器定义的,begin() end()
C++概览:并发与实用功能
资源管理
锁: 成对的构造函数和析构函数,通过抛出和捕获异常来进行错误处理。
资源获取即初始化 RAII 是C++处理资源的基础。
unique_ptr与shared_ptr
自由存储 标准库<memory>中提供了两种智能指针。
unique_ptr-----所有权唯一 能很好地释放对象,避免忘记!
shared_ptr-----所有权共享 某个对象的多个shared_ptr共享该对象的所有权
并发
腾讯课堂C++11 多线程 黄棒清。
进程和线程
并发编程:
1.多进程 应用于分布式系统 文件、管道、消息队列进行进程间通信。
2.多线程。
实际项目是两者的混合使用。
#include <iostream>
#include <thread>
using namespace std;
void function_1(){
cout << "hello hello" << endl;
}
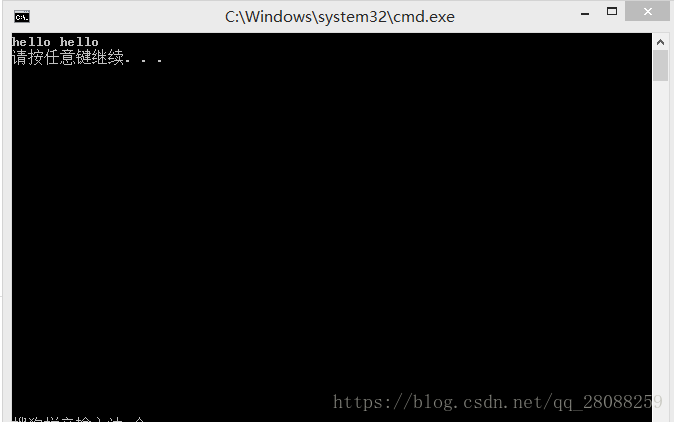
int main(){
thread t1(function_1);
t1.join(); //join()的作用是主线程会等待这里的t1线程结束后,再运行
return 0;
}
#include <iostream>
#include <thread>
using namespace std;
void function_1(){
cout << "hello hello" << endl;
}
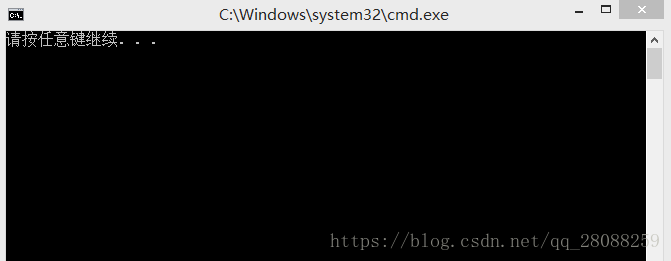
int main(){
thread t1(function_1);
t1.detach(); //detach()的作用是分离t1和主线程,结果是无法输出hello hello,主线程没等t1完成就结束了
return 0;
}
#include <iostream>
#include <thread>
using namespace std;
void function_1(){
cout << "hello hello" << endl;
}
int main(){
thread t1(function_1);
try{
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++){
cout << "from main:" << i << endl;
}
}
catch (...){ //如果在try部分捕获了异常,仍然可以在此join()
t1.join();
throw;
}
t1.join();
return 0;
}
#include <iostream>
#include <thread>
using namespace std;
void function_1(){
cout << "hello hello" << endl;
}
//thread不单单可以通过函数构造
//还可以根据任意对象构造
class Fctor{
public:
void operator()(){ //第二个()表示无参
for (int i = 0; i > -100; i--)
cout << "from t1:" << i << endl;
}
};
int main(){
Fctor fct;
thread t1(fct); //这就是通过一个类构造一个线程
try{
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++){
cout << "from main:" << i << endl;
}
}
catch (...){ //如果在try部分捕获了异常,仍然可以在此join()
t1.join();
throw;
}
t1.join();
return 0;
}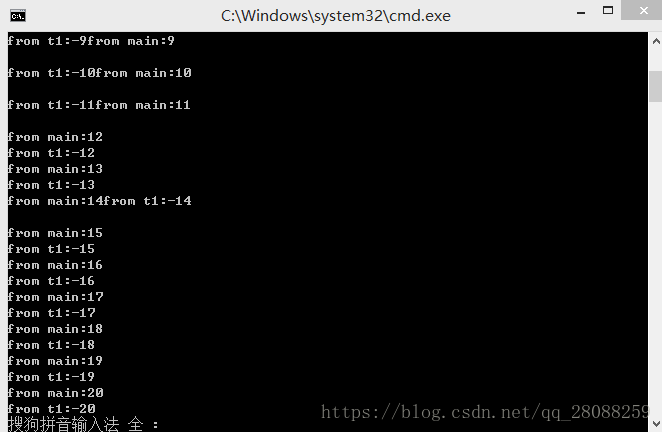
t1 和 main()交替出现
#include <iostream>
#include <thread>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
void function_1(){
cout << "hello hello" << endl;
}
//thread不单单可以通过函数构造
//还可以根据任意对象构造
class Fctor{
public:
void operator()(string msg){ //现在加入参数msg
for (int i = 0; i > -100; i--)
cout << "from t1:" << msg << endl;
}
};
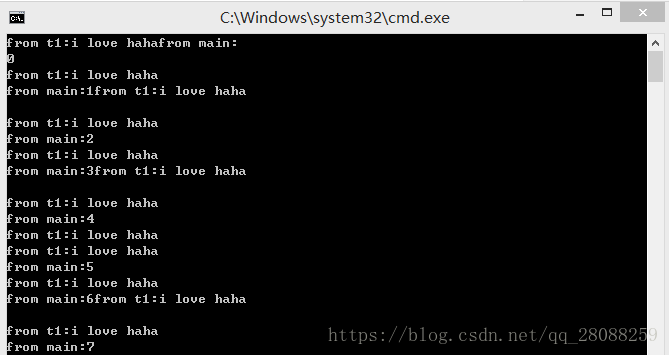
int main(){
//Fctor fct;
//thread t1(fct); //这就是通过一个类构造一个线程
string s = "i love haha";
thread t1((Fctor()),s); //s作为参数,也可以通过这种方式构造线程
try{
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++){
cout << "from main:" << i << endl;
}
}
catch (...){ //如果在try部分捕获了异常,仍然可以在此join()
t1.join();
throw;
}
t1.join();
return 0;
}
针对上述string类型的这个参数,刚才是通过值传递方式的,现在想用引用的方式,通过引用能节省很多的复制操作。
引用是可以改变值的。
#include <iostream>
#include <thread>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
void function_1(){
cout << "hello hello" << endl;
}
//thread不单单可以通过函数构造
//还可以根据任意对象构造
class Fctor{
public:
void operator()(string& msg){ //注意现在是引用传递了,是会改变值的
msg = "i love gaga";
cout<< "from t1:" << msg << endl;
}
};
int main(){
//Fctor fct;
//thread t1(fct); //这就是通过一个类构造一个线程
string s = "i love haha";
thread t1((Fctor()),s); //s作为参数,也可以通过这种方式构造线程
try{
cout << "from main:" << s << endl;
}
catch (...){ //如果在try部分捕获了异常,仍然可以在此join()
t1.join();
throw;
}
t1.join();
return 0;
}
使用另外一种方式传递参数,move。
#include <iostream>
#include <thread>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
void function_1(){
cout << "hello hello" << endl;
}
//thread不单单可以通过函数构造
//还可以根据任意对象构造
class Fctor{
public:
void operator()(string& msg){ //注意现在是引用传递了,是会改变值的
msg = "i love gaga";
cout<< "from t1:" << msg << endl;
}
};
int main(){
//Fctor fct;
//thread t1(fct); //这就是通过一个类构造一个线程
string s = "i love haha";
thread t1((Fctor()),move(s)); //move(s)将s参数从主线程移动到子线程,即安全又高效
try{
cout << "from main:" << s << endl;
}
catch (...){ //如果在try部分捕获了异常,仍然可以在此join()
t1.join();
throw;
}
t1.join();
return 0;
}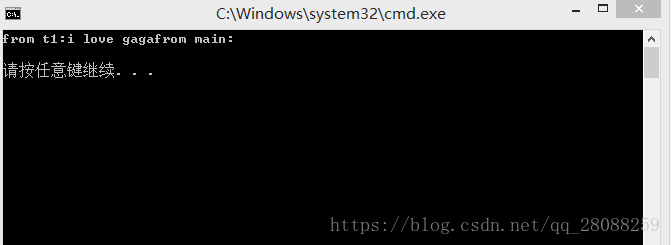
move完了之后,注意主线程中就没有了s。
线程对象只能被move,不能赋值
#include <iostream>
#include <thread>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
void function_1(){
cout << "hello hello" << endl;
}
//thread不单单可以通过函数构造
//还可以根据任意对象构造
class Fctor{
public:
void operator()(string& msg){ //注意现在是引用传递了,是会改变值的
msg = "i love wawa";
cout<< "from t1:" << msg << endl;
}
};
int main(){
//Fctor fct;
//thread t1(fct); //这就是通过一个类构造一个线程
string s = "i love haha";
thread t1((Fctor()),move(s)); //move(s)将s参数从主线程移动到子线程,即安全又高效
//thread t2 = t1; //赋值的语法是错误的
thread t2 = move(t1); //move是可以的,有了t2,然后t1就是空的了
try{
cout << "from main:" << s << endl;
}
catch (...){ //如果在try部分捕获了异常,仍然可以在此join()
t2.join();
throw;
}
t2.join();
return 0;
}
每一个线程都有ID号,可以通过get_id()函数获得!
#include <iostream>
#include <thread>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
void function_1(){
cout << "hello hello" << endl;
}
//thread不单单可以通过函数构造
//还可以根据任意对象构造
class Fctor{
public:
void operator()(string& msg){ //注意现在是引用传递了,是会改变值的
msg = "i love wawa";
cout<< "from t1:" << msg << endl;
}
};
int main(){
//Fctor fct;
//thread t1(fct); //这就是通过一个类构造一个线程
string s = "i love haha";
cout << this_thread::get_id() << endl; //输出主线程的id
thread t1((Fctor()),move(s)); //move(s)将s参数从主线程移动到子线程,即安全又高效
//thread t2 = t1; //赋值的语法是错误的
thread t2 = move(t1); //move是可以的,有了t2,然后t1就是空的了
cout << t2.get_id() << endl; //输出t2线程的id
try{
cout << "from main:" << s << endl;
}
catch (...){ //如果在try部分捕获了异常,仍然可以在此join()
t2.join();
throw;
}
t2.join();
return 0;
}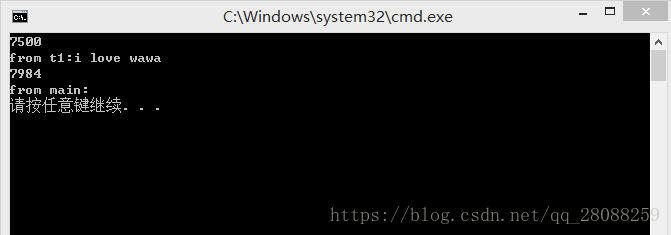
CPU核心数 设置多少个线程合适呢? thread::hardware_concurrency(); 最多可以由多少个线程
#include <iostream>
#include <thread>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
void function_1(){
cout << "hello hello" << endl;
}
//thread不单单可以通过函数构造
//还可以根据任意对象构造
class Fctor{
public:
void operator()(string& msg){ //注意现在是引用传递了,是会改变值的
msg = "i love wawa";
cout<< "from t1:" << msg << endl;
}
};
int main(){
//Fctor fct;
//thread t1(fct); //这就是通过一个类构造一个线程
string s = "i love haha";
//cout << this_thread::get_id() << endl; //输出主线程的id
thread t1((Fctor()),move(s)); //move(s)将s参数从主线程移动到子线程,即安全又高效
//thread t2 = t1; //赋值的语法是错误的
thread t2 = move(t1); //move是可以的,有了t2,然后t1就是空的了
//cout << t2.get_id() << endl; //输出t2线程的id
try{
cout << "from main:" << s << endl;
}
catch (...){ //如果在try部分捕获了异常,仍然可以在此join()
t2.join();
throw;
}
t2.join();
cout<<thread::hardware_concurrency()<<endl;
return 0;
}
说明最多可以设置8个线程。