学习目标:
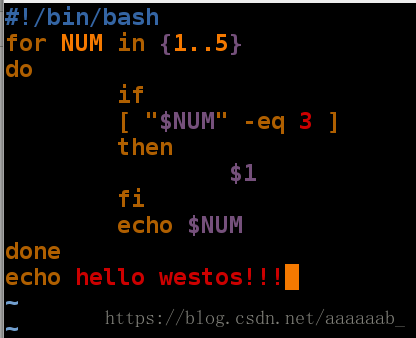
for 语句
while 语句
if 语句
case 语句
expect 语句exit break continue退出命令的区别:
exit直接退出当前脚本
break仅仅退出本次循环
continue 退出本次循环进行下一次循环效果演示:
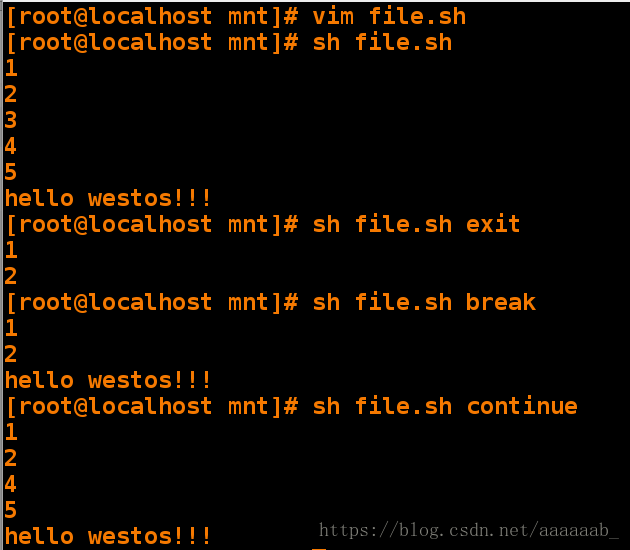
[root@localhost mnt]# vim file.sh 编写脚本[root@localhost mnt]# sh file.sh 直接调用脚本
1
2
3
4
5
hello westos!!!
[root@localhost mnt]# sh file.sh exit exit直接退出当前脚本
1
2
[root@localhost mnt]# sh file.sh break break仅仅退出本次循环
1
2
hello westos!!!
[root@localhost mnt]# sh file.sh continue continue 退出本次循环进行下一次循环
1
2
4
5
hello westos!!!for语句:
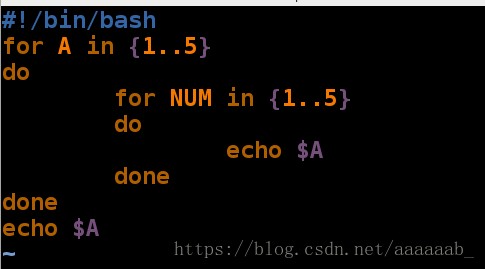
`seq 1 5`可以设置步长,可以有变量{1..5}不可以设置步长。
for语句参数可以传到循环以外,是嵌套关系,总共执行m*n次
for语句的变量仅仅最后变量被使用,循环定义变量依次执行,进行批处理。简单的for语句:
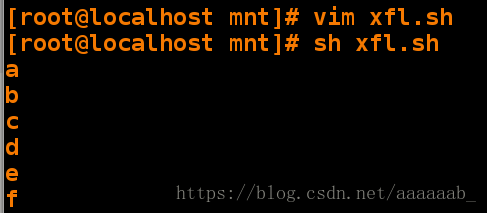
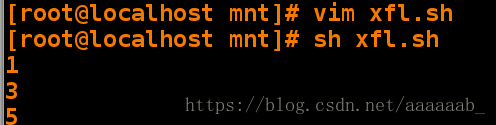
[root@localhost mnt]# vim xfl.sh 编写脚本
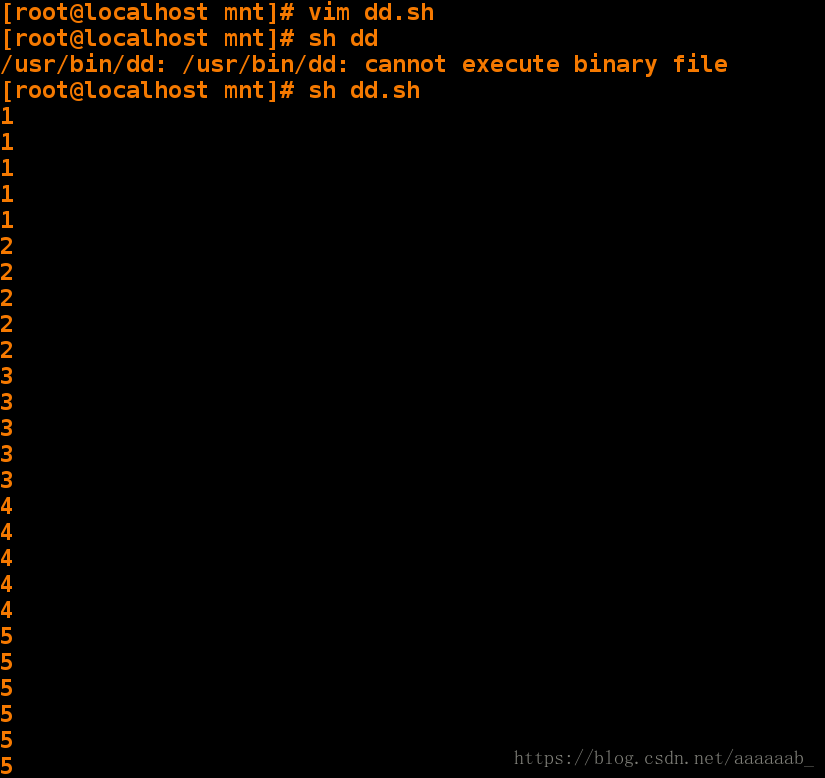
[root@localhost mnt]# sh xfl.sh 调用脚本[root@localhost mnt]# vim xfl.sh 编写脚本加入步长[root@localhost mnt]# sh xfl.sh 调用脚本查看[root@localhost mnt]# vim dd.sh 编辑脚本实现for嵌套[root@localhost mnt]# sh dd.sh 调用脚本输出25个数字检测教室能上网的机子:
[root@localhost mnt]# vim check_host.sh 编辑脚本[root@localhost mnt]# sh check_host.sh 调用没有效果呈现因为我的真机IP是172.25.254.84,我检测的是0到50所以就出不来结果
[root@localhost mnt]# cat check_host.sh
#!/bin/bash
for A in {0..50}或者用for((A=0;A<50;A++)) 必须是双层括号
do
ping -c1 -w1 172.25.254.$A &> /dev/null && echo 172.25.254.$A
done建立两个数据库两个数据表插入字段进行备份操作:
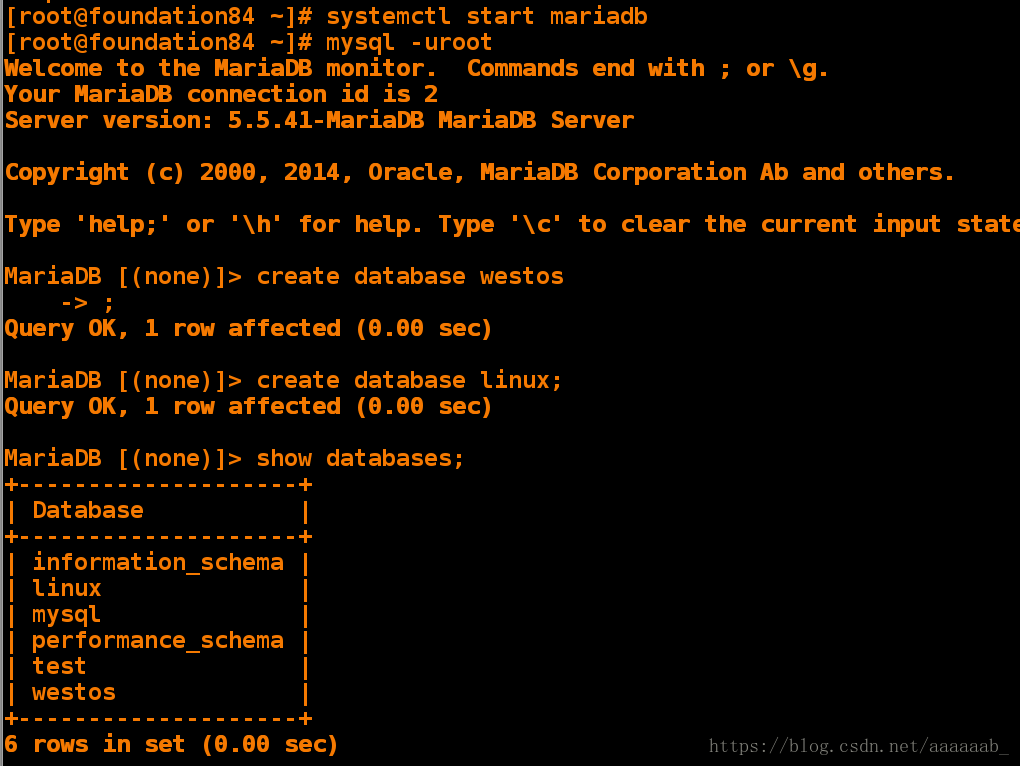
[root@foundation84 ~]# yum install mariadb-server.x86_64 -y 安装数据库[root@foundation84 ~]# systemctl start mariadb 开启数据库服务
[root@foundation84 ~]# mysql -uroot 登陆数据库
MariaDB [(none)]> create database westos 创建数据库westos
-> ;
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
MariaDB [(none)]> create database linux; 创建数据库linux
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
MariaDB [(none)]> show databases; 显示所有数据库
+--------------------+
| Database |
+--------------------+
| information_schema |
| linux |
| mysql |
| performance_schema |
| test |
| westos |
+--------------------+
6 rows in set (0.00 sec)MariaDB [(none)]> use westos; 进入westos数据库
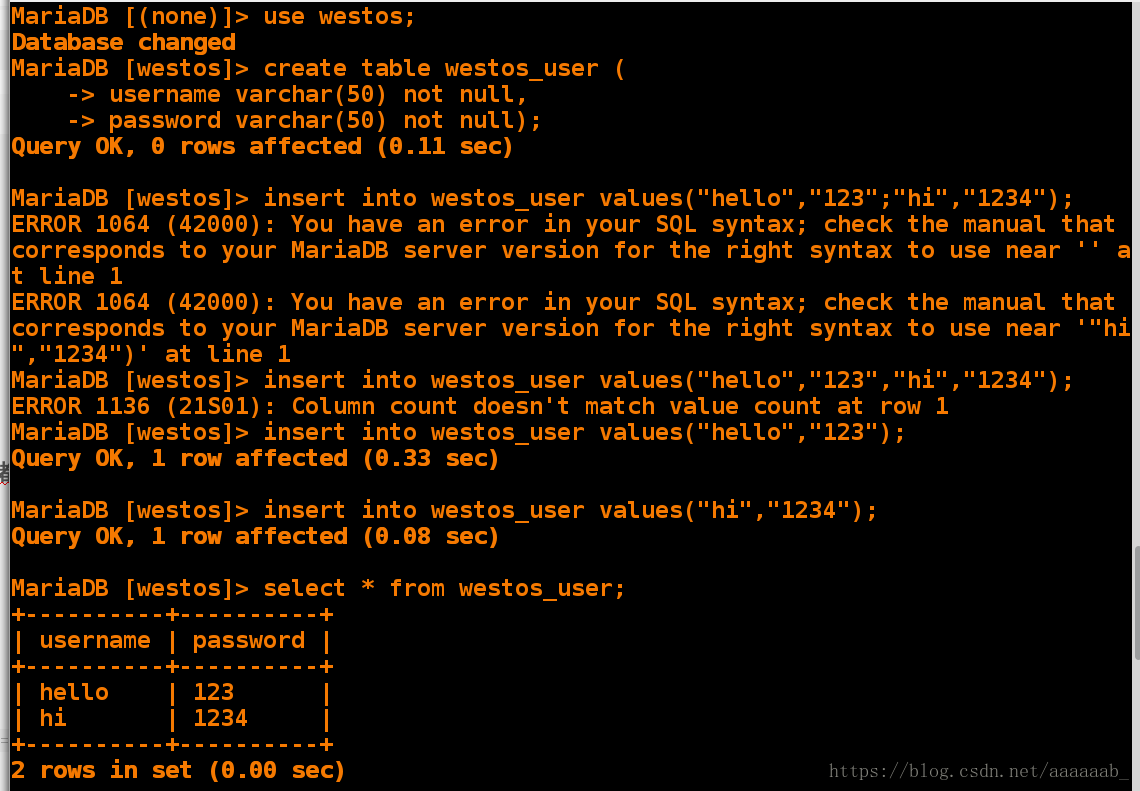
Database changed
MariaDB [westos]> create table westos_user ( 创建数据表
-> username varchar(50) not null,
-> password varchar(50) not null);
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.11 sec)
MariaDB [westos]> insert into westos_user values("hello","123"); 插入字段
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.33 sec)
MariaDB [westos]> insert into westos_user values("hi","1234"); 插入字段
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.08 sec)
MariaDB [westos]> select * from westos_user; 显示数据表信息
+----------+----------+
| username | password |
+----------+----------+
| hello | 123 |
| hi | 1234 |
+----------+----------+
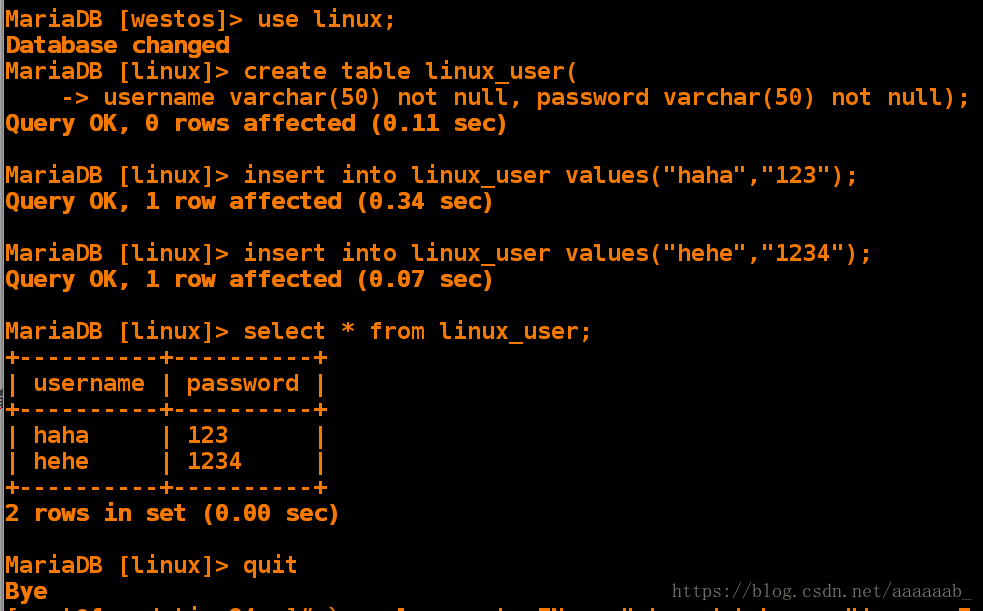
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)MariaDB [westos]> use linux; 进入linux数据库
Database changed
MariaDB [linux]> create table linux_user( 创建数据表
-> username varchar(50) not null, password varchar(50) not null);Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.11 sec)
MariaDB [linux]> insert into linux_user values("haha","123"); 插入字段
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.34 sec)
MariaDB [linux]> insert into linux_user values("hehe","1234"); 插入字段
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.07 sec)
MariaDB [linux]> select * from linux_user; 显示linux_user数据表信息
+----------+----------+
| username | password |
+----------+----------+
| haha | 123 |
| hehe | 1234 |
+----------+----------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
MariaDB [linux]> quit
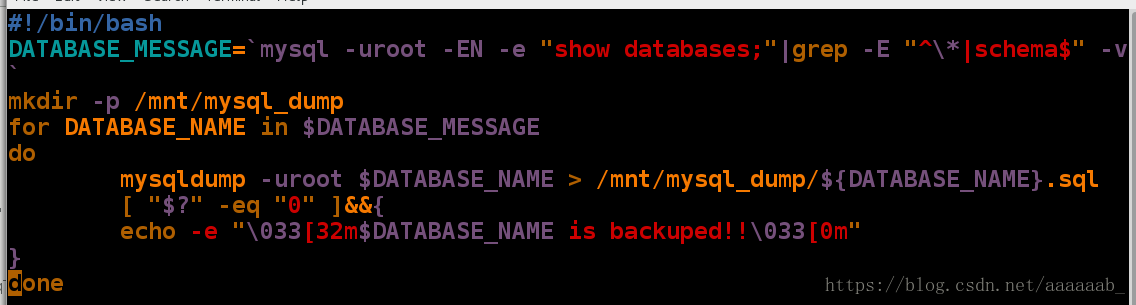
Bye对数据库做备份,每个数据库备份一个文件,例如mysql.sql将文件存储到/mnt/mysql_dump:(for 语句)
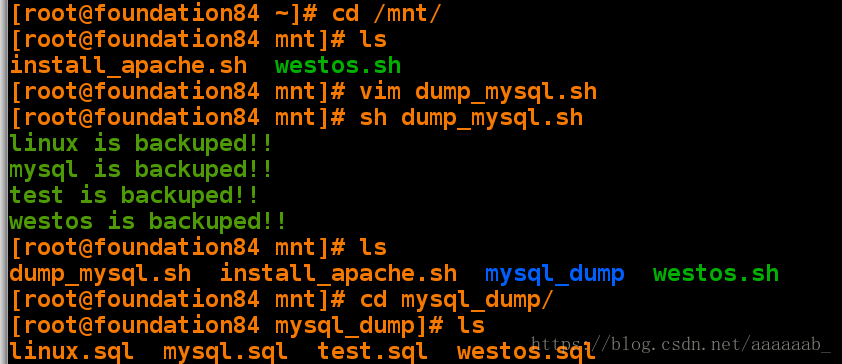
[root@foundation84 ~]# cd /mnt/
[root@foundation84 mnt]# ls
install_apache.sh westos.sh
[root@foundation84 mnt]# vim dump_mysql.sh 建立脚本[root@foundation84 mnt]# sh dump_mysql.sh 调用脚本显示已经备份
linux is backuped!!
mysql is backuped!!
test is backuped!!
westos is backuped!!
[root@foundation84 mnt]# ls
dump_mysql.sh install_apache.sh mysql_dump westos.sh
[root@foundation84 mnt]# cd mysql_dump/ 进入目录
[root@foundation84 mysql_dump]# ls 查看备份是以.sql后缀结尾
linux.sql mysql.sql test.sql westos.sql简单的while语句:
while true 条件为真就执行
do
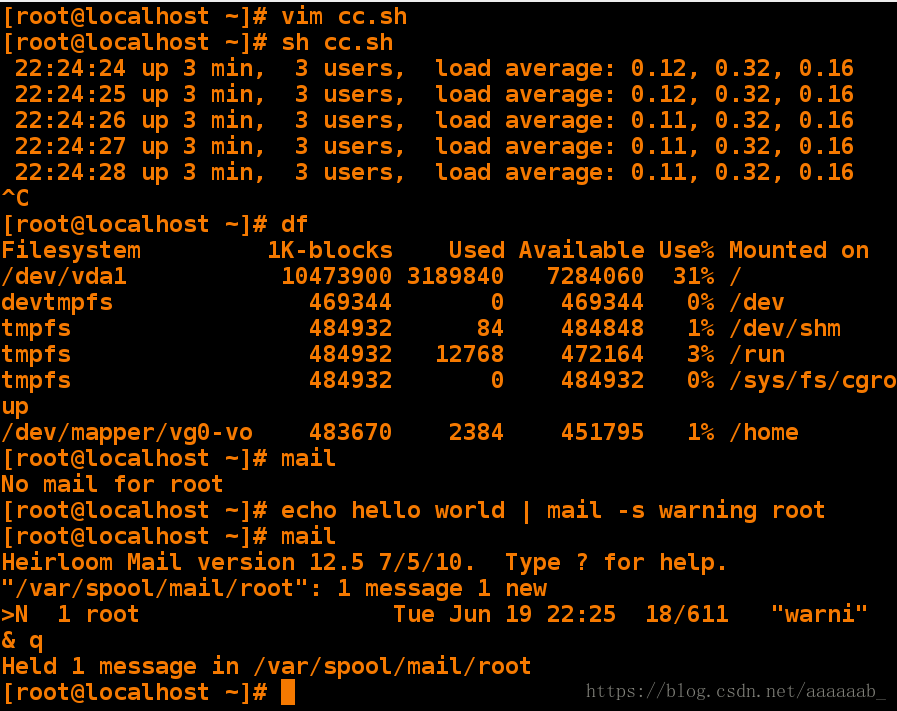
done[root@localhost mysql_dump]# vim cc.sh 简单的每隔一秒打印占用负载以及时间while语句[root@localhost mysql_dump]# sh cc.sh 调用脚本
04:44:38 up 7:42, 2 users, load average: 0.00, 0.01, 0.05
04:44:39 up 7:42, 2 users, load average: 0.00, 0.01, 0.05
04:44:40 up 7:42, 2 users, load average: 0.00, 0.01, 0.05
[root@localhost mysql_dump]# df 查看负载
Filesystem 1K-blocks Used Available Use% Mounted on
/dev/vda1 10473900 3329740 7144160 32% /
devtmpfs 469344 0 469344 0% /dev
tmpfs 484932 80 484852 1% /dev/shm
tmpfs 484932 12768 472164 3% /run
tmpfs 484932 0 484932 0% /sys/fs/cgroup
/dev/mapper/vg0-vo 483670 2384 451795 1% /home
[root@localhost mysql_dump]# mail 查看没有邮件
No mail for root
[root@localhost mysql_dump]# echo hello world | mail -s warning root发送邮件
[root@localhost ~]# mail 查看邮件
No mail for root
[root@localhost ~]# echo hello world | mail -s warning root
[root@localhost ~]# mail
Heirloom Mail version 12.5 7/5/10. Type ? for help.
"/var/spool/mail/root": 1 message 1 new
>N 1 root Tue Jun 19 22:25 18/611 "warni"
& q q退出
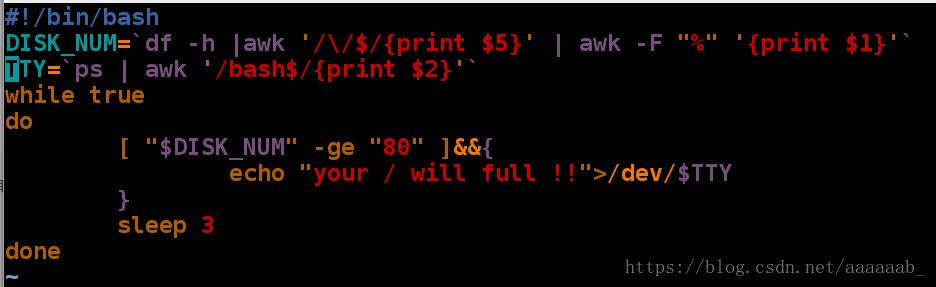
Held 1 message in /var/spool/mail/root编写脚本利用while语句检测当负载超过80%时发送邮件给超级用户:
[root@localhost mnt]# df 查看负载情况
Filesystem 1K-blocks Used Available Use% Mounted on
/dev/vda1 10473900 3124404 7349496 30% /
devtmpfs 469344 0 469344 0% /dev
tmpfs 484932 84 484848 1% /dev/shm
tmpfs 484932 12760 472172 3% /run
tmpfs 484932 0 484932 0% /sys/fs/cgroup
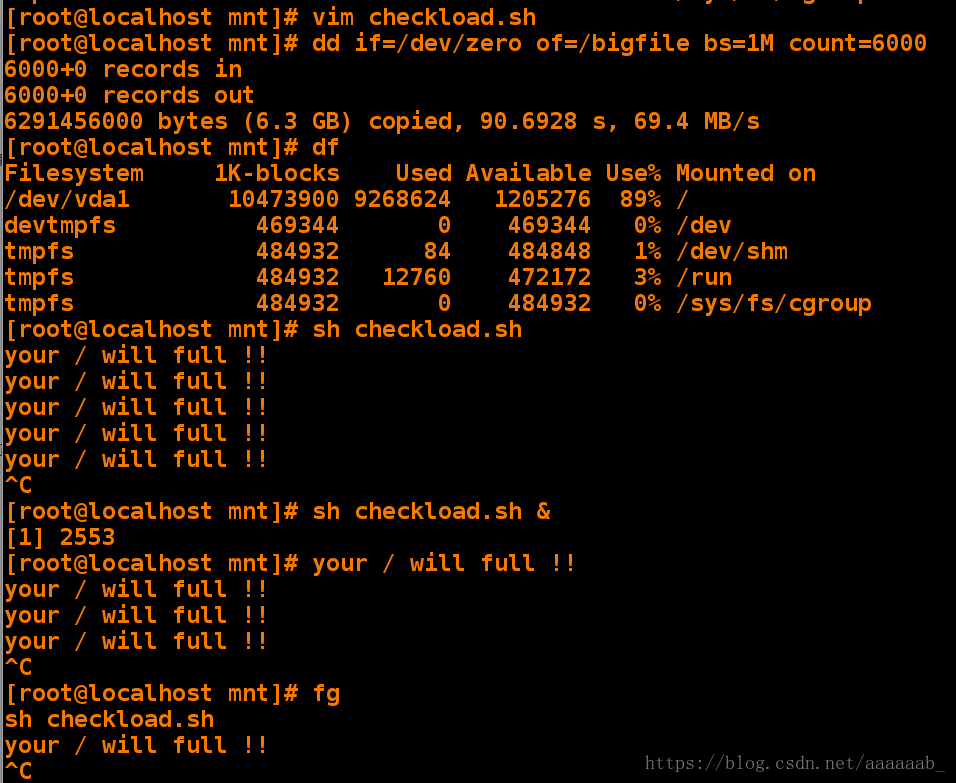
[root@localhost mnt]# vim checkload.sh 编写检测脚本[root@localhost mnt]# dd if=/dev/zero of=/bigfile bs=1M count=6000 截取命令保证负载超过80%来进行实验查看
6000+0 records in
6000+0 records out
6291456000 bytes (6.3 GB) copied, 90.6928 s, 69.4 MB/s
[root@localhost mnt]# df 查看负载已经超过80%
Filesystem 1K-blocks Used Available Use% Mounted on
/dev/vda1 10473900 9268624 1205276 89% /
devtmpfs 469344 0 469344 0% /dev
tmpfs 484932 84 484848 1% /dev/shm
tmpfs 484932 12760 472172 3% /run
tmpfs 484932 0 484932 0% /sys/fs/cgroup
[root@localhost mnt]# sh checkload.sh 调用脚本每隔3秒会提示你的负载将要满了信息
your / will full !!
your / will full !!
your / will full !!
your / will full !!
your / will full !!
^C
[root@localhost mnt]# sh checkload.sh & 当把脚本打入后台之后
[1] 2553
[root@localhost mnt]# your / will full !! 依旧会每隔三秒进行提示
your / will full !!
your / will full !!
your / will full !!
^C
[root@localhost mnt]# fg 调回进程
sh checkload.sh
your / will full !!
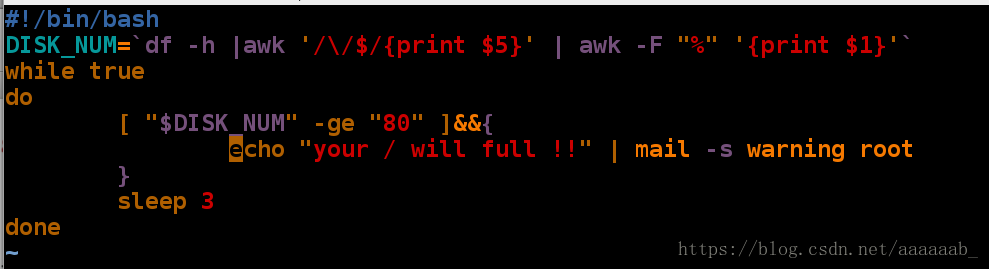
^C 结束进程用发送邮件方式检测负载超过80%提示警告(while 语句)
[root@localhost mnt]# dd if=/dev/zero of=/bigfile bs=1M count=6000 截取命令保证负载超过80%来进行实验查看
6000+0 records in
6000+0 records out
6291456000 bytes (6.3 GB) copied, 90.6928 s, 69.4 MB/s
[root@localhost mnt]# df 查看负载已经超过80%
Filesystem 1K-blocks Used Available Use% Mounted on
/dev/vda1 10473900 9268624 1205276 89% /
devtmpfs 469344 0 469344 0% /dev
tmpfs 484932 84 484848 1% /dev/shm
tmpfs 484932 12760 472172 3% /run
tmpfs 484932 0 484932 0% /sys/fs/cgroup
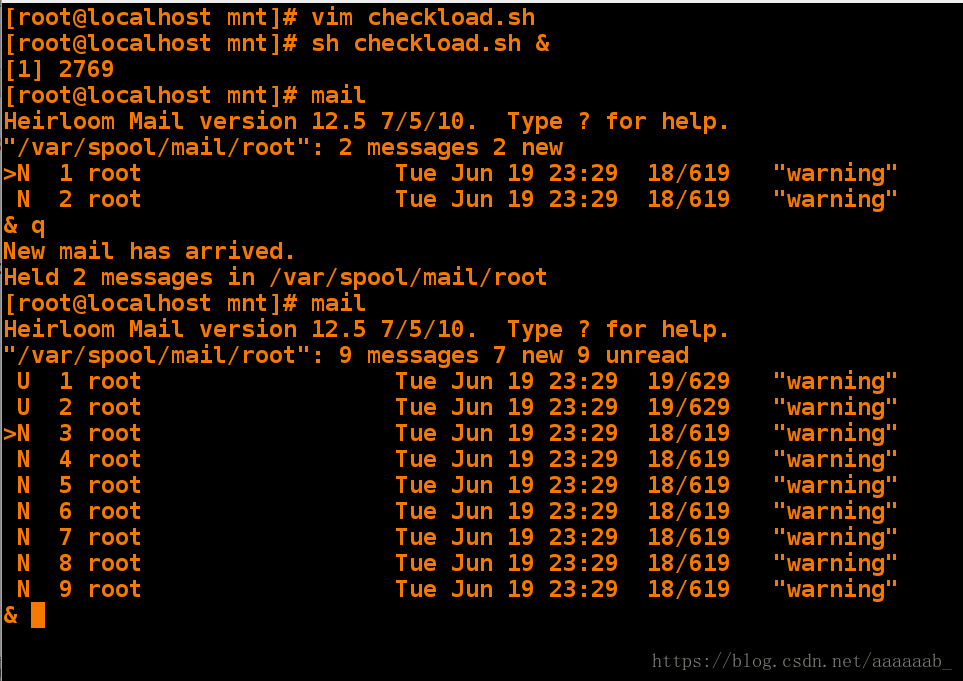
[root@localhost mnt]# vim checkload.sh 编写脚本[root@localhost mnt]# sh checkload.sh & 在后台运行脚本
[1] 2769
[root@localhost mnt]# mail 查看邮件
Heirloom Mail version 12.5 7/5/10. Type ? for help.
"/var/spool/mail/root": 2 messages 2 new
>N 1 root Tue Jun 19 23:29 18/619 "warning"
N 2 root Tue Jun 19 23:29 18/619 "warning"
& q 退出
New mail has arrived.
Held 2 messages in /var/spool/mail/root
[root@localhost mnt]# mail 查看邮件每隔3秒就会以root用户身份发送一份邮件
Heirloom Mail version 12.5 7/5/10. Type ? for help.
"/var/spool/mail/root": 9 messages 7 new 9 unread
U 1 root Tue Jun 19 23:29 19/629 "warning"
U 2 root Tue Jun 19 23:29 19/629 "warning"
>N 3 root Tue Jun 19 23:29 18/619 "warning"
N 4 root Tue Jun 19 23:29 18/619 "warning"
N 5 root Tue Jun 19 23:29 18/619 "warning"
N 6 root Tue Jun 19 23:29 18/619 "warning"
N 7 root Tue Jun 19 23:29 18/619 "warning"
N 8 root Tue Jun 19 23:29 18/619 "warning"
N 9 root Tue Jun 19 23:29 18/619 "warning"
& q
New mail has arrived.
Held 9 messages in /var/spool/mail/rootif语句:
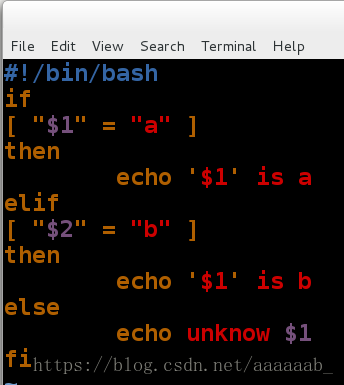
简单的if脚本:
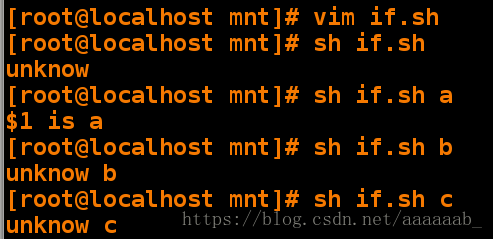
[root@localhost mnt]# vim if.sh 简单的if脚本[root@localhost mnt]# sh if.sh 调用if脚本
unknow
[root@localhost mnt]# sh if.sh a
$1 is a
[root@localhost mnt]# sh if.sh b
$1 is b
[root@localhost mnt]# sh if.sh c
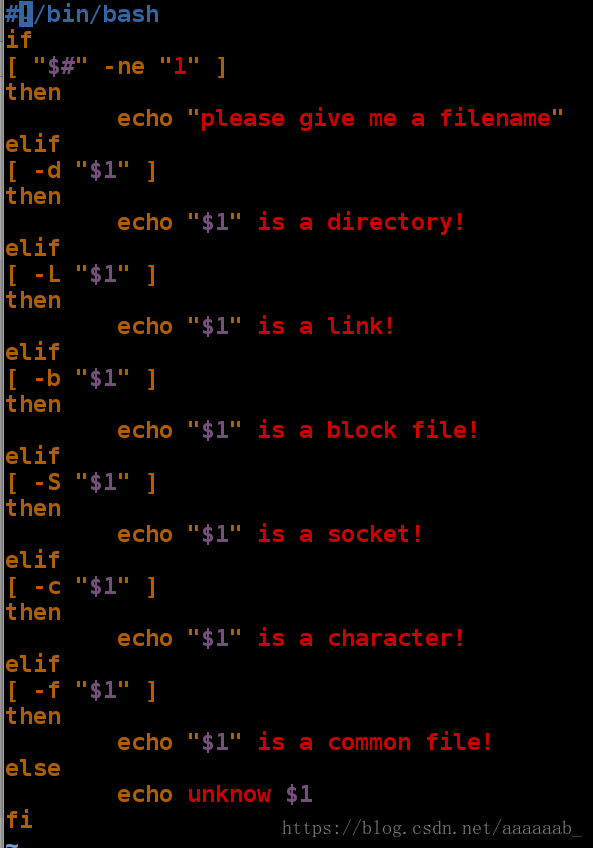
unknow c编写脚本用if判断文件是否存在并判断文件类型:
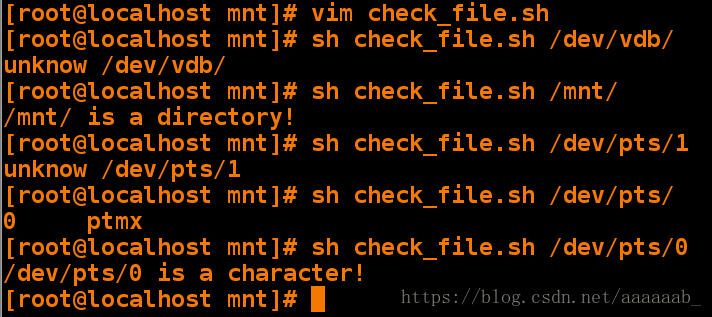
[root@localhost mnt]# vim check_file.sh 编写脚本[root@localhost mnt]# sh check_file.sh /dev/vdb/ 调用文件检测脚本功能
unknow /dev/vdb/
[root@localhost mnt]# sh check_file.sh /mnt/
/mnt/ is a directory!
[root@localhost mnt]# sh check_file.sh /dev/pts/1
unknow /dev/pts/1
[root@localhost mnt]# sh check_file.sh /dev/pts/
0 ptmx
[root@localhost mnt]# sh check_file.sh /dev/pts/0
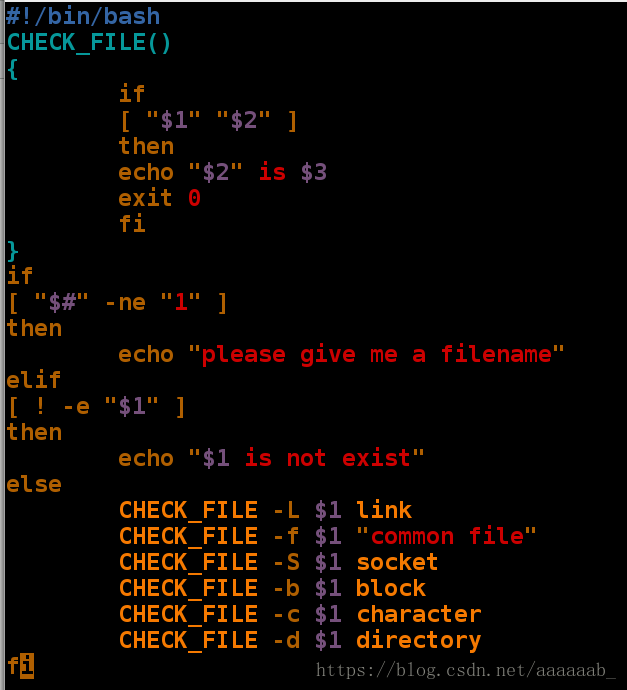
/dev/pts/0 is a character!编写脚本用if判断文件是否存在并判断文件类型:(用函数形式)
用函数可以将一些重复的代码进行简便,同时增加代码的可读性。
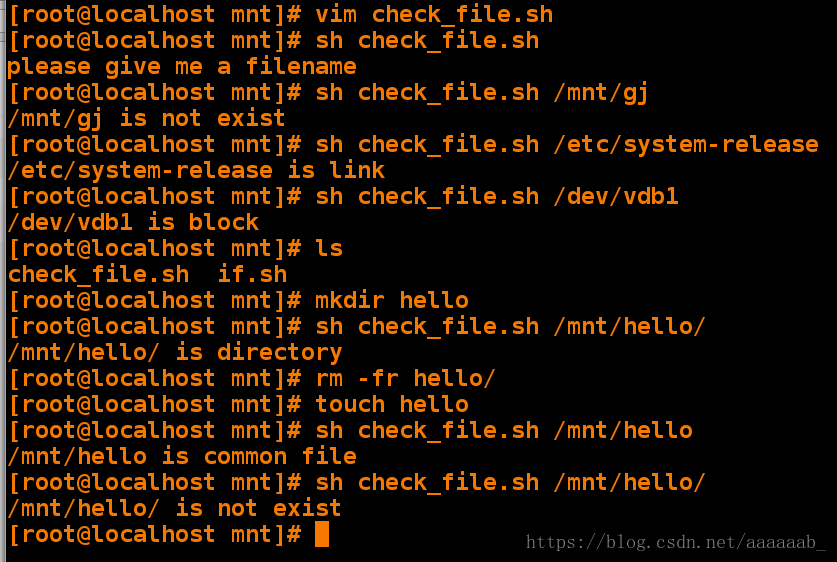
[root@localhost mnt]# vim check_file.sh 用函数编写检测文件类型脚本[root@localhost mnt]# sh check_file.sh 检测不给$1的功能
please give me a filename
[root@localhost mnt]# sh check_file.sh /mnt/gj 检测文件不存在的报错
/mnt/gj is not exist
[root@localhost mnt]# sh check_file.sh /etc/system-release 依次调用检测已有文件类型
/etc/system-release is link
[root@localhost mnt]# sh check_file.sh /dev/vdb1
/dev/vdb1 is block
[root@localhost mnt]# ls
check_file.sh if.sh
[root@localhost mnt]# mkdir hello 建立目录
[root@localhost mnt]# sh check_file.sh /mnt/hello/ 查看类型是否匹配
/mnt/hello/ is directory
[root@localhost mnt]# rm -fr hello/
[root@localhost mnt]# touch hello 建立文件
[root@localhost mnt]# sh check_file.sh /mnt/hello 查看类型是否匹配
/mnt/hello is common file
[root@localhost mnt]# sh check_file.sh /mnt/hello/
/mnt/hello/ is not exist用if,then进行字符匹配:
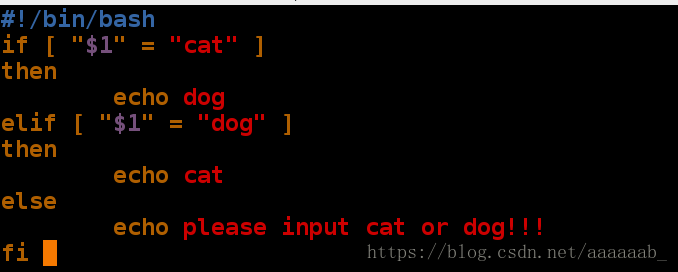
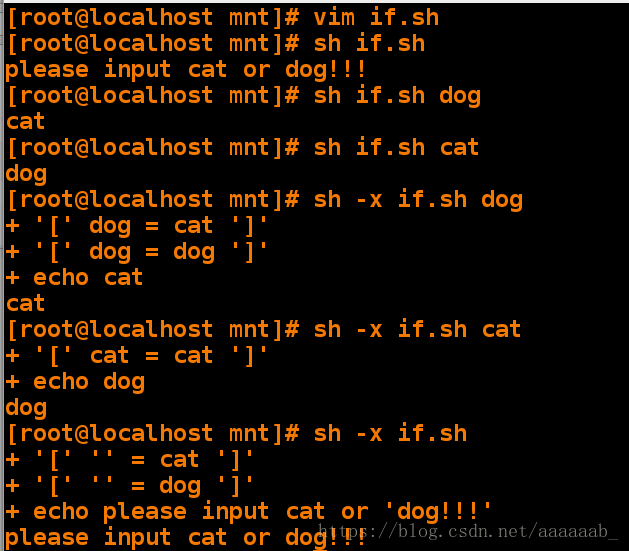
[root@localhost mnt]# vim if.sh 编写脚本[root@localhost mnt]# sh if.sh 直接调用
please input cat or dog!!!
[root@localhost mnt]# sh if.sh may 错用调用
please input cat or dog!!!
[root@localhost mnt]# sh if.sh dog
cat
[root@localhost mnt]# sh if.sh cat
dog
[root@localhost mnt]# sh -x if.sh dog 检测运行效率,进行两次比较浪费cpu
+ '[' dog = cat ']'
+ '[' dog = dog ']'
+ echo cat
cat
[root@localhost mnt]# sh -x if.sh cat 检测运行效率,进行一次比较
+ '[' cat = cat ']'
+ echo dog
dog
[root@localhost mnt]# sh -x if.sh 空输入检测
+ '[' '' = cat ']'
+ '[' '' = dog ']'
+ echo please input cat or 'dog!!!'
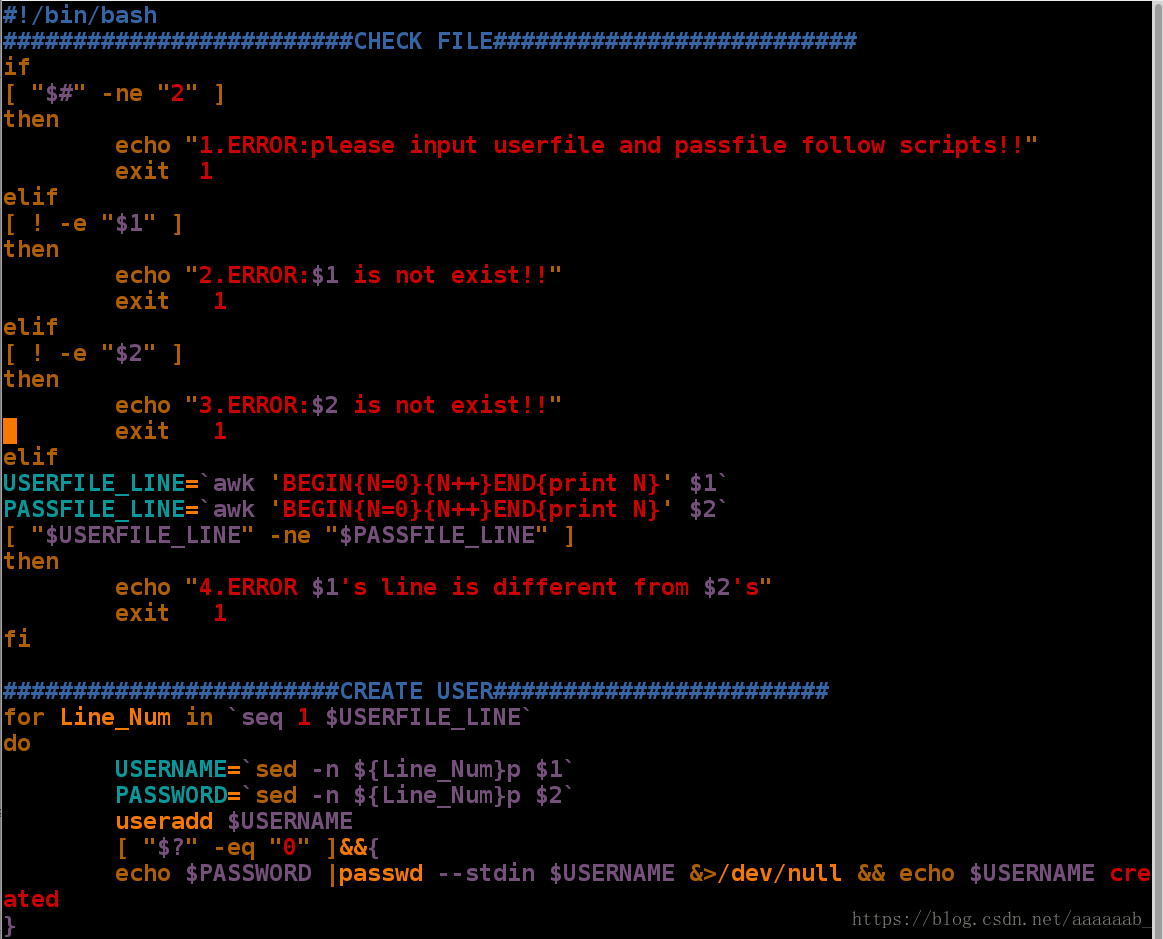
please input cat or dog!!!编写脚本智能建立用户,有如下要求:
1,文件数量不对报错。
2,文件不存在报错。
3,文件行数差异报错。
4,用户存在显示用户存在,但是不改变用户密码。
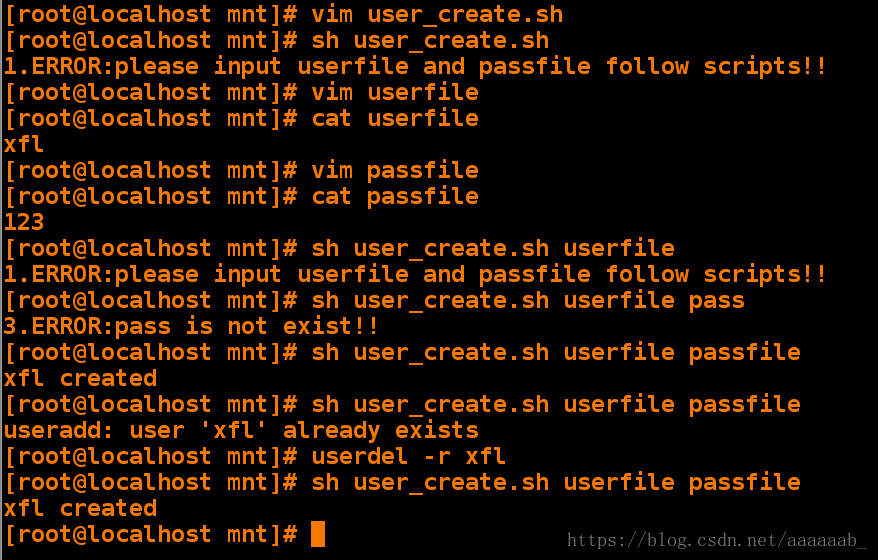
5,当用户不存在建立用户并设定相应密码。[root@localhost mnt]# vim user_create.sh 编写脚本[root@localhost mnt]# sh user_create.sh 空调用脚本
1.ERROR:please input userfile and passfile follow scripts!!
[root@localhost mnt]# vim userfile 编辑用户文件
[root@localhost mnt]# cat userfile
xfl
[root@localhost mnt]# vim passfile 编辑密码文件
[root@localhost mnt]# cat passfile
123
[root@localhost mnt]# sh user_create.sh userfile
1.ERROR:please input userfile and passfile follow scripts!!
[root@localhost mnt]# sh user_create.sh userfile pass 错误调用
3.ERROR:pass is not exist!!
[root@localhost mnt]# sh user_create.sh userfile passfile 调用成功建立用户
xfl created
[root@localhost mnt]# sh user_create.sh userfile passfile 重复建立
useradd: user 'xfl' already exists
[root@localhost mnt]# userdel -r xfl 删除用户
[root@localhost mnt]# sh user_create.sh userfile passfile 重新建立
xfl createdcase语句:
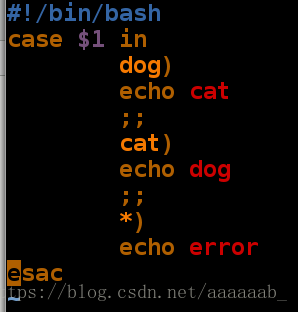
用case语句进行字符匹配:
case语句好处就是能缩短输出所进行的比较,if语句是从上到下浪费cpu。
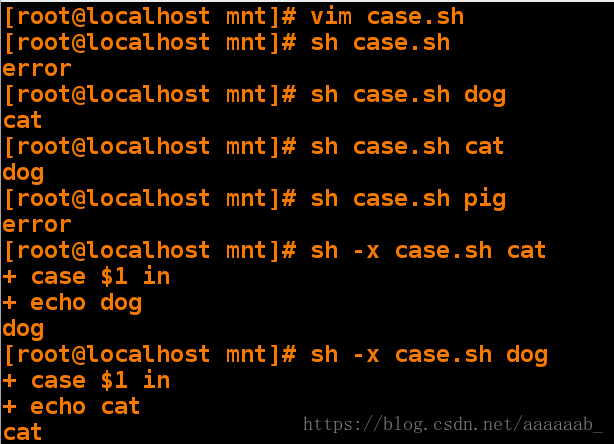
[root@localhost mnt]# vim case.sh 编写case脚本[root@localhost mnt]# sh case.sh 空输入调用
error
[root@localhost mnt]# sh case.sh dog 调用脚本检测
cat
[root@localhost mnt]# sh case.sh cat
dog
[root@localhost mnt]# sh case.sh pig 输入错误检测
error
[root@localhost mnt]# sh -x case.sh cat 每次只需要一次比较就可以得出输出结果
+ case $1 in
+ echo dog
dog
[root@localhost mnt]# sh -x case.sh dog
+ case $1 in
+ echo cat
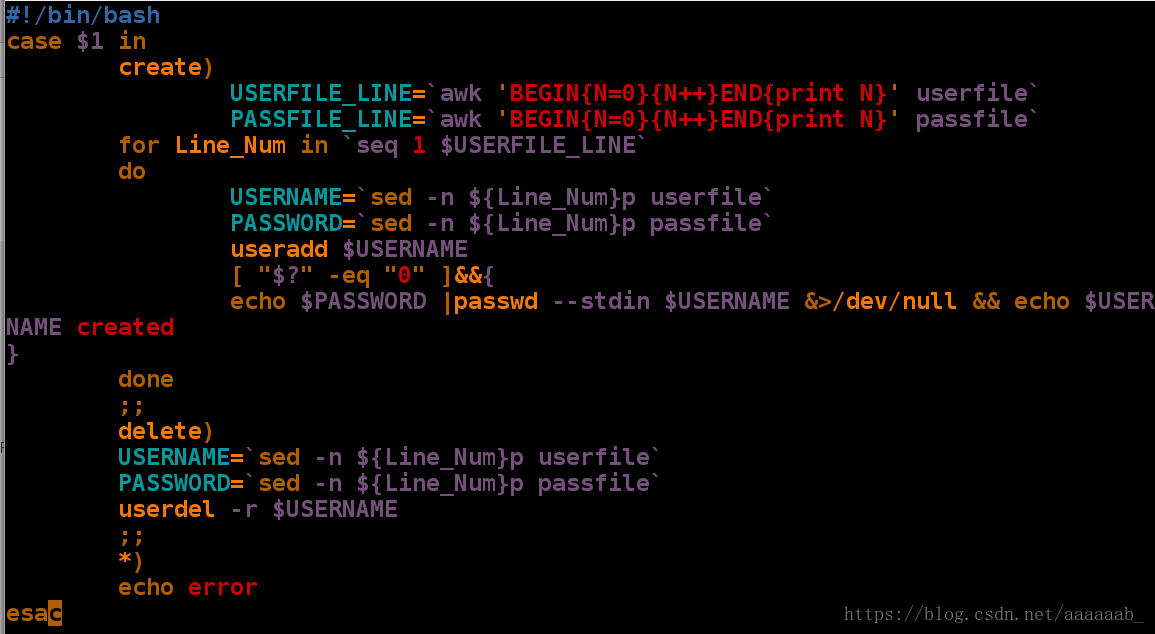
cat用case语句控制建立删除用户:
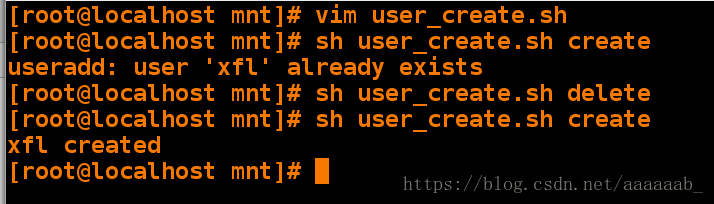
[root@localhost mnt]# vim user_create.sh 编写case脚本[root@localhost mnt]# sh user_create.sh create 调用创建用户功能
useradd: user 'xfl' already exists
[root@localhost mnt]# sh user_create.sh delete 调用删除用户功能
[root@localhost mnt]# sh user_create.sh create 再次调用创建用户
xfl created用脚本自动建立分区删除分区:
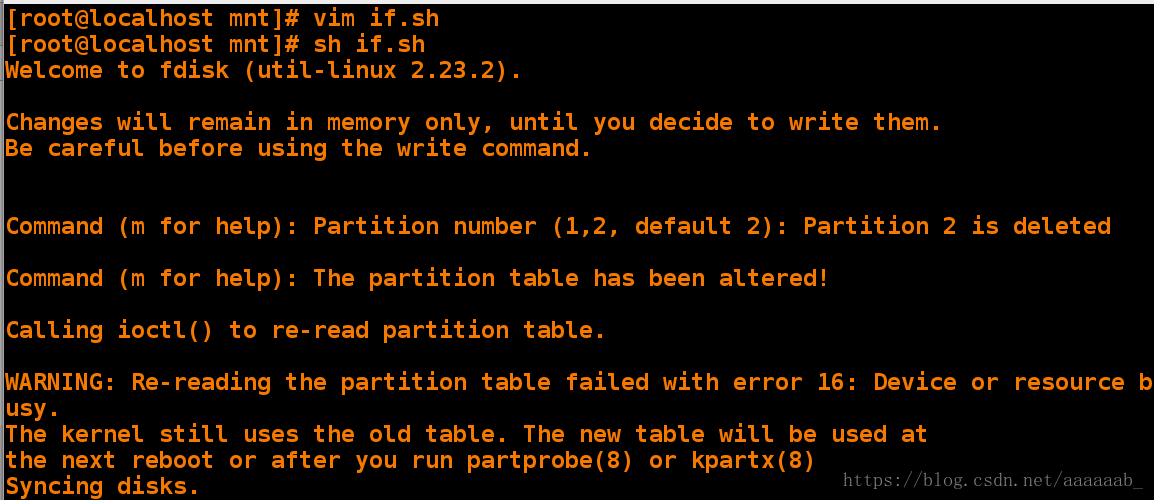
建立分区:
[root@localhost mnt]# fdisk /dev/vdb 首先查看分区[root@localhost mnt]# vim if.sh 编辑脚本[root@localhost mnt]# sh if.sh +500M 调用脚本
[root@localhost mnt]# fdisk /dev/vdb 再次查看分区
Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/vdb1 2048 1026047 512000 8e Linux LVM
/dev/vdb2 1026048 2050047 512000 83 Linux删除分区:
[root@localhost mnt]# vim if.sh 编辑脚本[root@localhost mnt]# sh if.sh 调用脚本[root@localhost mnt]# fdisk /dev/vdb 查看分区
Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/vdb1 2048 1026047 512000 8e Linux LVMexpext是自动应答脚本:(解释器)
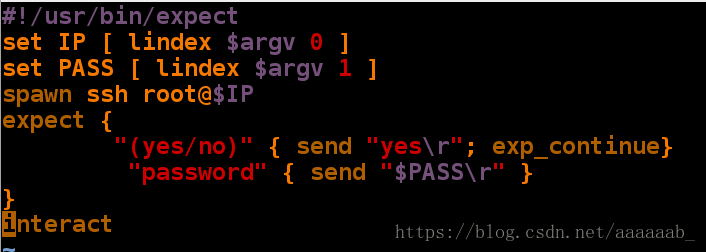
expect 是自动应答命令用于交互式命令的自动执行。
spawn是expect中的监控程序,其运行后会监控命令提出的交互问题。
send 发送问题答案给交互命令
"\r" 表示回车
exp_continue 标示当问题不存在时继续回答下面的问题
expect eof 标示问题回答完毕退出 expect 环境
interact 标示问题回答完毕留在交互界面
set NAME [ lindex $argv n ] 定义变量简单的expect应答脚本:
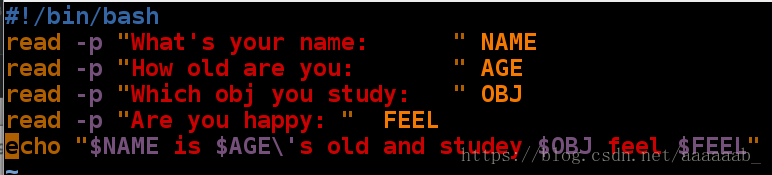
read交互式脚本:
[root@localhost mnt]# vim ask.sh 编写脚本[root@localhost mnt]# chmod +x ask.sh 赋予执行权限
[root@localhost mnt]# /mnt/ask.sh 绝对路径调用
What's your name: xuefeilong
How old are you: 20
Which obj you study: yunwei
Are you happy: happy
xuefeilong is 20\'s old and studey yunwei feel happyexpect 是自动应答命令:
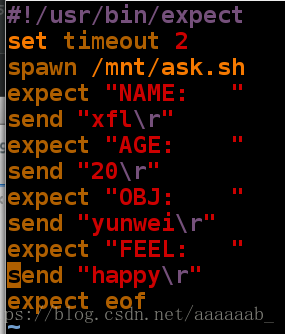
[root@localhost mnt]# vim answer.exp 编写expect脚本设置延时2s[root@localhost mnt]# expect answer.exp 调用脚本2s自动给出答案
spawn /mnt/ask.sh
What's your name: xfl
How old are you: 20
Which obj you study: yunwei
Are you happy: happy
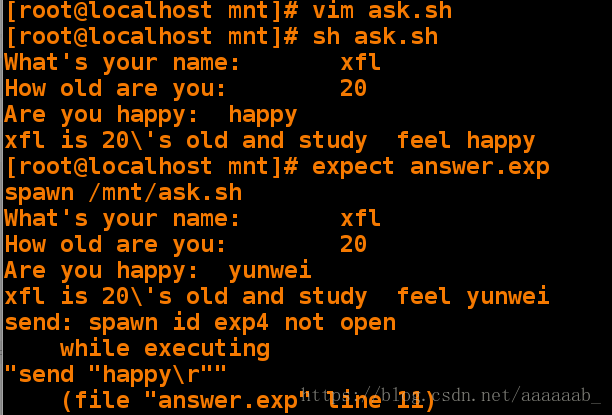
xfl is 20\'s old and studey yunwei feel happy当问题不存在时继续使用answer.exp监控就会出错:
[root@localhost mnt]# vim ask.sh 编辑问题脚本注释一行 [root@localhost mnt]# sh ask.sh 调用问题脚本不会报错
What's your name: xfl
How old are you: 20
Are you happy: happy
xfl is 20\'s old and study feel happy
[root@localhost mnt]# expect answer.exp 调用expect脚本会报错
spawn /mnt/ask.sh
What's your name: xfl
How old are you: 20
Are you happy: yunwei
xfl is 20\'s old and study feel yunwei
send: spawn id exp4 not open
while executing
"send "happy\r""
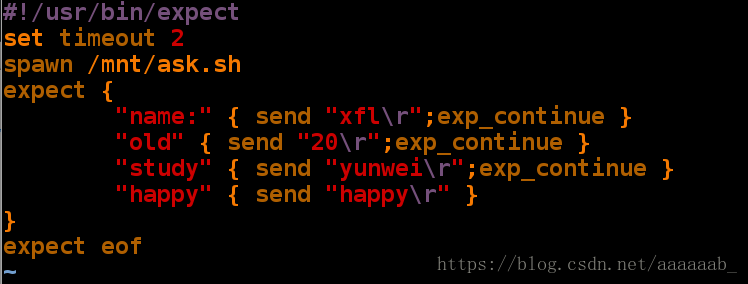
(file "answer.exp" line 11)使用exp_continue命令当问题不存在时继续回答下面的问题:
[root@localhost mnt]# vim ask.sh 将问题脚本问题注释掉[root@localhost mnt]# vim answer.exp expect脚本里面必须写入问题脚本的关键字[root@localhost mnt]# expect answer.exp 调用就不会出现问题
spawn /mnt/ask.sh
What's your name: xfl
How old are you: 20
Are you happy: happy
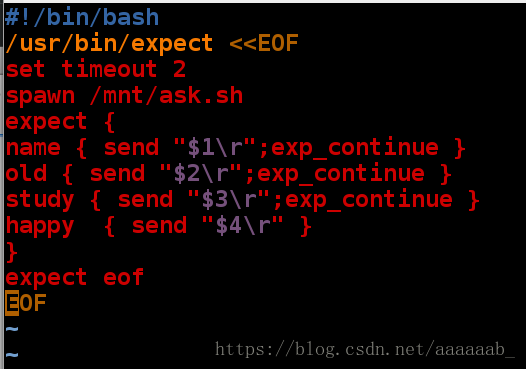
xfl is 20\'s old and study feel happy 自动跳过study问题自主调用问题答案:
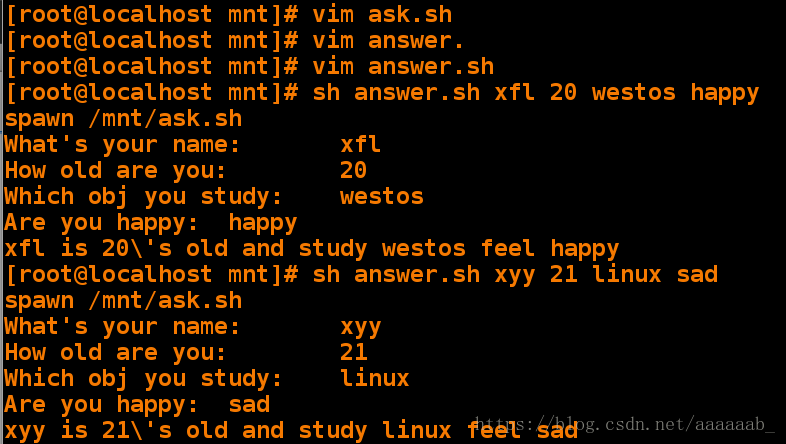
[root@localhost mnt]# vim ask.sh 编辑问题脚本[root@localhost mnt]# vim answer.sh 编辑expect脚本[root@localhost mnt]# sh answer.sh xfl 20 westos happy 根据调用自动配置答案
spawn /mnt/ask.sh
What's your name: xfl
How old are you: 20
Which obj you study: westos
Are you happy: happy
xfl is 20\'s old and study westos feel happy
[root@localhost mnt]# sh answer.sh xyy 21 linux sad
spawn /mnt/ask.sh
What's your name: xyy
How old are you: 21
Which obj you study: linux
Are you happy: sad
xyy is 21\'s old and study linux feel sad编写脚本1,直接登录设备:
[root@localhost mnt]# yum install expect -y 安装expect解释器
Loaded plugins: langpacks
Package expect-5.45-12.el7.x86_64 already installed and latest version
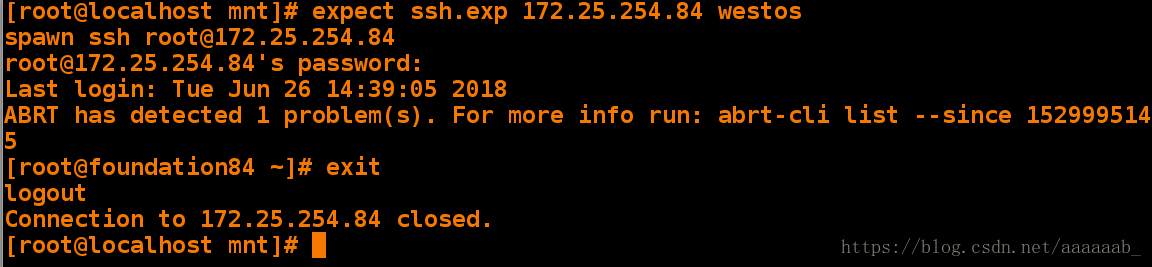
Nothing to do[root@localhost mnt]# vim ssh.exp 编写脚本[root@localhost mnt]# expect ssh.exp 172.25.254.84 westos 调用脚本加入ip,密码
spawn ssh root@172.25.254.84
root@172.25.254.84's password:
Last login: Tue Jun 26 14:39:05 2018
ABRT has detected 1 problem(s). For more info run: abrt-cli list --since 1529995145
[root@foundation84 ~]# exit 退出
logout
Connection to 172.25.254.84 closed.编写脚本2,直接登录设备:
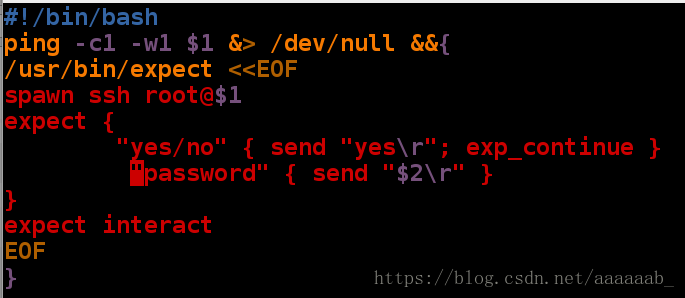
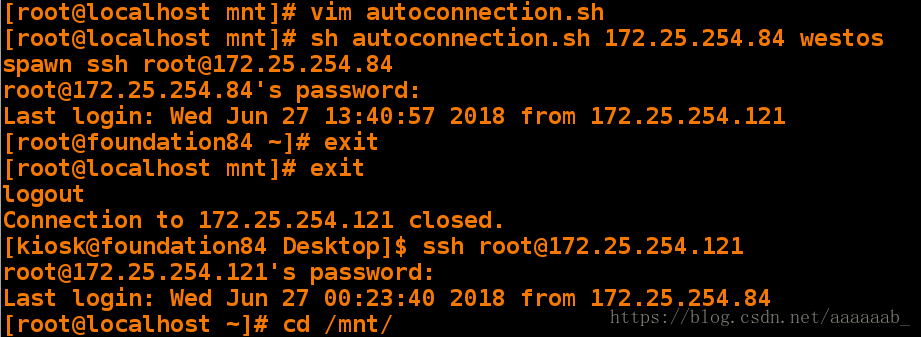
[root@localhost mnt]# vim autoconnection.sh 编写脚本[root@localhost mnt]# sh autoconnection.sh 172.25.254.84 westos 用IP和密码调用
spawn ssh root@172.25.254.84
root@172.25.254.84's password:
Last login: Wed Jun 27 13:40:57 2018 from 172.25.254.121
[root@foundation84 ~]# exit 自动登陆设备
[root@localhost mnt]# exit
logout
Connection to 172.25.254.121 closed.查看可以登陆的IP:
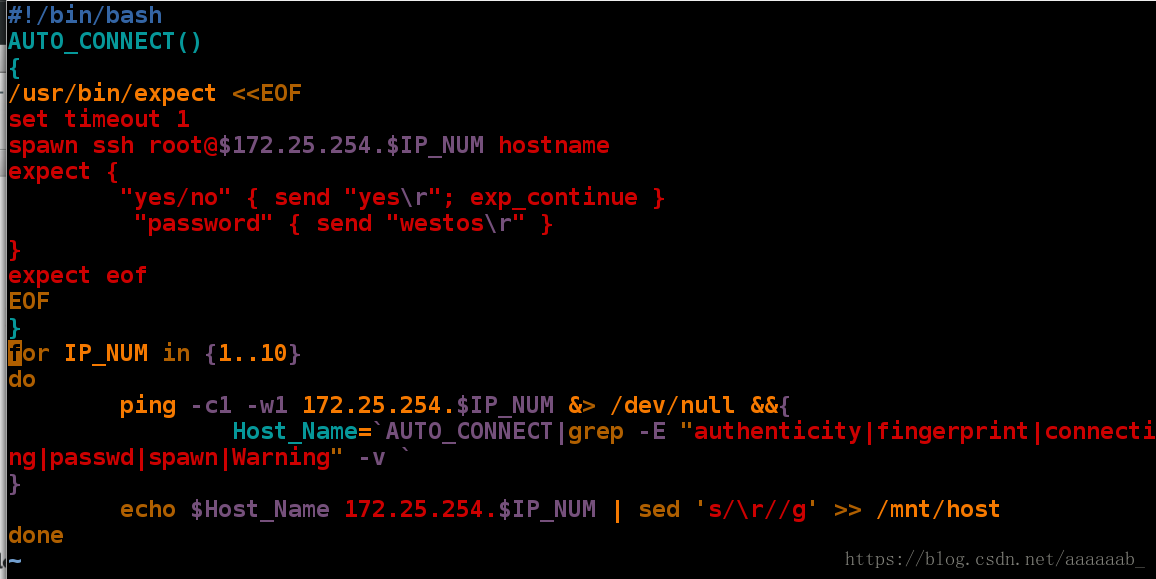
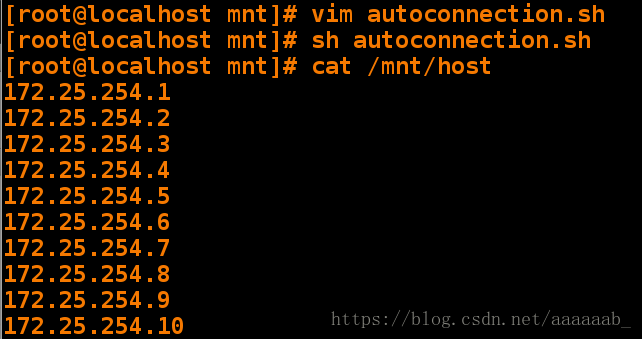
[root@localhost mnt]# vim autoconnection.sh 编写脚本[root@localhost mnt]# sh autoconnection.sh 调用脚本
[root@localhost mnt]# cat /mnt/host 查看
172.25.254.1
172.25.254.2
172.25.254.3
172.25.254.4
172.25.254.5
172.25.254.6
172.25.254.7
172.25.254.8
172.25.254.9
172.25.254.10