1、Vector介绍
Vector简介
(1)Vector 是矢量队列,它是JDK1.0版本添加的类。继承AbstractList,实现了List, RandomAccess, Cloneable接口。
(2)Vector 继承了AbstractList,实现了List;所以,它是一个队列,支持相关的添加、删除、修改、遍历等功能。
(3)Vector实现了RandmoAccess接口,即提供了随机访问功能。RandmoAccess是java中用来被List实现,为List提供快速访问功能的。在Vector中,我们即可以通过元素的序号快速获取元素对象;这就是快速随机访问。
(4)Vector 实现了Cloneable接口,即实现clone()函数。它能被克隆。
和ArrayList不同,Vector中的操作是线程安全的。
Vector的构造函数
Constructor and Description
Vector()
构造一个空向量,使其内部数据数组的大小为 10 ,标准容量增量为零。
Vector(Collection<? extends E> c)
构造一个包含指定集合元素的向量,按照集合的迭代器返回的顺序。
Vector(int initialCapacity)
构造具有指定初始容量并且其容量增量等于零的空向量。
Vector(int initialCapacity, int capacityIncrement)
构造具有指定的初始容量和容量增量的空向量。
Vector的API
boolean add(E e)
将指定的元素追加到此Vector的末尾。
void add(int index, E element)
在此Vector中的指定位置插入指定的元素。
boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c)
将指定集合中的所有元素追加到该向量的末尾,按照它们由指定集合的迭代器返回的顺序。
boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c)
将指定集合中的所有元素插入到此向量中的指定位置。
void addElement(E obj)
将指定的组件添加到此向量的末尾,将其大小增加1。
int capacity()
返回此向量的当前容量。
void clear()
从此Vector中删除所有元素。
Object clone()
返回此向量的克隆。
boolean contains(Object o)
如果此向量包含指定的元素,则返回 true 。
boolean containsAll(Collection<?> c)
如果此向量包含指定集合中的所有元素,则返回true。
void copyInto(Object[] anArray)
将此向量的组件复制到指定的数组中。
E elementAt(int index)
返回指定索引处的组件。
Enumeration<E> elements()
返回此向量的组件的枚举。
void ensureCapacity(int minCapacity)
如果需要,增加此向量的容量,以确保它可以至少保存最小容量参数指定的组件数。
boolean equals(Object o)
将指定的对象与此向量进行比较以获得相等性。
E firstElement()
返回此向量的第一个组件(索引号为 0的项目)。
void forEach(Consumer<? super E> action)
对 Iterable的每个元素执行给定的操作,直到所有元素都被处理或动作引发异常。
E get(int index)
返回此向量中指定位置的元素。
int hashCode()
返回此Vector的哈希码值。
int indexOf(Object o)
返回此向量中指定元素的第一次出现的索引,如果此向量不包含元素,则返回-1。
int indexOf(Object o, int index)
返回此向量中指定元素的第一次出现的索引,从 index向前 index ,如果未找到该元素,则返回-1。
void insertElementAt(E obj, int index)
在指定的index插入指定对象作为该向量中的一个 index 。
boolean isEmpty()
测试此矢量是否没有组件。
Iterator<E> iterator()
以正确的顺序返回该列表中的元素的迭代器。
E lastElement()
返回向量的最后一个组件。
int lastIndexOf(Object o)
返回此向量中指定元素的最后一次出现的索引,如果此向量不包含元素,则返回-1。
int lastIndexOf(Object o, int index)
返回此向量中指定元素的最后一次出现的索引,从 index ,如果未找到元素,则返回-1。
ListIterator<E> listIterator()
返回列表中的列表迭代器(按适当的顺序)。
ListIterator<E> listIterator(int index)
从列表中的指定位置开始,返回列表中的元素(按正确顺序)的列表迭代器。
E remove(int index)
删除此向量中指定位置的元素。
boolean remove(Object o)
删除此向量中指定元素的第一个出现如果Vector不包含元素,则它不会更改。
boolean removeAll(Collection<?> c)
从此Vector中删除指定集合中包含的所有元素。
void removeAllElements()
从该向量中删除所有组件,并将其大小设置为零。
boolean removeElement(Object obj)
从此向量中删除参数的第一个(最低索引)出现次数。
void removeElementAt(int index)
删除指定索引处的组件。
boolean removeIf(Predicate<? super E> filter)
删除满足给定谓词的此集合的所有元素。
protected void removeRange(int fromIndex, int toIndex)
从此列表中删除所有索引为 fromIndex (含)和 toIndex之间的元素。
void replaceAll(UnaryOperator<E> operator)
将该列表的每个元素替换为将该运算符应用于该元素的结果。
boolean retainAll(Collection<?> c)
仅保留此向量中包含在指定集合中的元素。
E set(int index, E element)
用指定的元素替换此Vector中指定位置的元素。
void setElementAt(E obj, int index)
设置在指定的组件 index此向量的要指定的对象。
void setSize(int newSize)
设置此向量的大小。
int size()
返回此向量中的组件数。
void sort(Comparator<? super E> c)
使用提供的 Comparator对此列表进行排序以比较元素。
Spliterator<E> spliterator()
在此列表中的元素上创建late-binding和故障切换 Spliterator 。
List<E> subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex)
返回此列表之间的fromIndex(包括)和toIndex之间的独占视图。
Object[] toArray()
以正确的顺序返回一个包含此Vector中所有元素的数组。
<T> T[] toArray(T[] a)
以正确的顺序返回一个包含此Vector中所有元素的数组; 返回的数组的运行时类型是指定数组的运行时类型。
String toString()
返回此Vector的字符串表示形式,其中包含每个元素的String表示形式。
void trimToSize()
修改该向量的容量成为向量的当前大小。 2、Vector数据结构
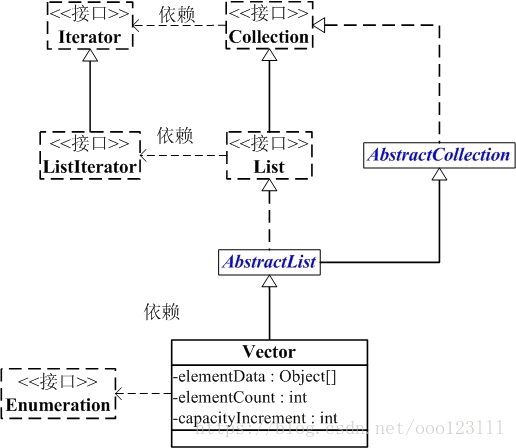
java.lang.Object
↳ java.util.AbstractCollection<E>
↳ java.util.AbstractList<E>
↳ java.util.Vector<E>
public class Vector<E>
extends AbstractList<E>
implements List<E>, RandomAccess, Cloneable, Serializable {}Vector与Collection关系如下图:
Vector的数据结构和ArrayList差不多,它包含了3个成员变量:elementData , elementCount, capacityIncrement。
(1)elementData是”Object[]类型的数组”,它保存了添加到Vector中的元素。elementData是个动态数组,如果初始化Vector时,没指定动态数组的大小,则使用默认大小10。随着Vector中元素的增加,Vector的容量也会动态增长,capacityIncrement是与容量增长相关的增长系数,具体的增长方式,请参考源码分析中的ensureCapacity()函数。
(2) elementCount 是动态数组的实际大小。
(3)capacityIncrement是动态数组的增长系数。如果在创建Vector时,指定了capacityIncrement的大小;则每次当Vector中动态数组容量增加时,增加的大小都是capacityIncrement。
3、Vector源码解析(基于JDK1.8)
为了更了解Vector的原理,下面对Vector源码代码作出分析:
package java.util;
public class Vector<E>
extends AbstractList<E>
implements List<E>, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
{
// 保存Vector中数据的数组
protected Object[] elementData;
// 实际数据的数量
protected int elementCount;
// 容量增长系数
protected int capacityIncrement;
// Vector的序列版本号
private static final long serialVersionUID = -2767605614048989439L;
// Vector构造函数。默认容量是10。
public Vector() {
this(10);
}
// 指定Vector容量大小的构造函数
public Vector(int initialCapacity) {
this(initialCapacity, 0);
}
// 指定Vector"容量大小"和"增长系数"的构造函数
public Vector(int initialCapacity, int capacityIncrement) {
super();
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+
initialCapacity);
// 新建一个数组,数组容量是initialCapacity
this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity];
// 设置容量增长系数
this.capacityIncrement = capacityIncrement;
}
// 指定集合的Vector构造函数。
public Vector(Collection<? extends E> c) {
// 获取“集合(c)”的数组,并将其赋值给elementData
elementData = c.toArray();
// 设置数组长度
elementCount = elementData.length;
// c.toArray might (incorrectly) not return Object[] (see 6260652)
if (elementData.getClass() != Object[].class)
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, elementCount, Object[].class);
}
// 将数组Vector的全部元素都拷贝到数组anArray中
public synchronized void copyInto(Object[] anArray) {
System.arraycopy(elementData, 0, anArray, 0, elementCount);
}
// 将当前容量值设为 =实际元素个数
public synchronized void trimToSize() {
modCount++;
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
if (elementCount < oldCapacity) {
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, elementCount);
}
}
// 确认“Vector容量”的帮助函数
private void ensureCapacityHelper(int minCapacity) {
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
// 当Vector的容量不足以容纳当前的全部元素,增加容量大小。
// 若 容量增量系数>0(即capacityIncrement>0),则将容量增大当capacityIncrement
// 否则,将容量增大一倍。
if (minCapacity > oldCapacity) {
Object[] oldData = elementData;
int newCapacity = (capacityIncrement > 0) ?
(oldCapacity + capacityIncrement) : (oldCapacity * 2);
if (newCapacity < minCapacity) {
newCapacity = minCapacity;
}
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}
}
// 确定Vector的容量。
public synchronized void ensureCapacity(int minCapacity) {
// 将Vector的改变统计数+1
modCount++;
ensureCapacityHelper(minCapacity);
}
// 设置容量值为 newSize
public synchronized void setSize(int newSize) {
modCount++;
if (newSize > elementCount) {
// 若 "newSize 大于 Vector容量",则调整Vector的大小。
ensureCapacityHelper(newSize);
} else {
// 若 "newSize 小于/等于 Vector容量",则将newSize位置开始的元素都设置为null
for (int i = newSize ; i < elementCount ; i++) {
elementData[i] = null;
}
}
elementCount = newSize;
}
// 返回“Vector的总的容量”
public synchronized int capacity() {
return elementData.length;
}
// 返回“Vector的实际大小”,即Vector中元素个数
public synchronized int size() {
return elementCount;
}
// 判断Vector是否为空
public synchronized boolean isEmpty() {
return elementCount == 0;
}
// 返回“Vector中全部元素对应的Enumeration”
public Enumeration<E> elements() {
// 通过匿名类实现Enumeration
return new Enumeration<E>() {
int count = 0;
// 是否存在下一个元素
public boolean hasMoreElements() {
return count < elementCount;
}
// 获取下一个元素
public E nextElement() {
synchronized (Vector.this) {
if (count < elementCount) {
return (E)elementData[count++];
}
}
throw new NoSuchElementException("Vector Enumeration");
}
};
}
// 返回Vector中是否包含对象(o)
public boolean contains(Object o) {
return indexOf(o, 0) >= 0;
}
// 从index位置开始向后查找元素(o)。
// 若找到,则返回元素的索引值;否则,返回-1
public synchronized int indexOf(Object o, int index) {
if (o == null) {
// 若查找元素为null,则正向找出null元素,并返回它对应的序号
for (int i = index ; i < elementCount ; i++)
if (elementData[i]==null)
return i;
} else {
// 若查找元素不为null,则正向找出该元素,并返回它对应的序号
for (int i = index ; i < elementCount ; i++)
if (o.equals(elementData[i]))
return i;
}
return -1;
}
// 查找并返回元素(o)在Vector中的索引值
public int indexOf(Object o) {
return indexOf(o, 0);
}
// 从后向前查找元素(o)。并返回元素的索引
public synchronized int lastIndexOf(Object o) {
return lastIndexOf(o, elementCount-1);
}
// 从后向前查找元素(o)。开始位置是从前向后的第index个数;
// 若找到,则返回元素的“索引值”;否则,返回-1。
public synchronized int lastIndexOf(Object o, int index) {
if (index >= elementCount)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(index + " >= "+ elementCount);
if (o == null) {
// 若查找元素为null,则反向找出null元素,并返回它对应的序号
for (int i = index; i >= 0; i--)
if (elementData[i]==null)
return i;
} else {
// 若查找元素不为null,则反向找出该元素,并返回它对应的序号
for (int i = index; i >= 0; i--)
if (o.equals(elementData[i]))
return i;
}
return -1;
}
// 返回Vector中index位置的元素。
// 若index月结,则抛出异常
public synchronized E elementAt(int index) {
if (index >= elementCount) {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index + " >= " + elementCount);
}
return (E)elementData[index];
}
// 获取Vector中的第一个元素。
// 若失败,则抛出异常!
public synchronized E firstElement() {
if (elementCount == 0) {
throw new NoSuchElementException();
}
return (E)elementData[0];
}
// 获取Vector中的最后一个元素。
// 若失败,则抛出异常!
public synchronized E lastElement() {
if (elementCount == 0) {
throw new NoSuchElementException();
}
return (E)elementData[elementCount - 1];
}
// 设置index位置的元素值为obj
public synchronized void setElementAt(E obj, int index) {
if (index >= elementCount) {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index + " >= " +
elementCount);
}
elementData[index] = obj;
}
// 删除index位置的元素
public synchronized void removeElementAt(int index) {
modCount++;
if (index >= elementCount) {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index + " >= " +
elementCount);
} else if (index < 0) {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index);
}
int j = elementCount - index - 1;
if (j > 0) {
System.arraycopy(elementData, index + 1, elementData, index, j);
}
elementCount--;
elementData[elementCount] = null; /* to let gc do its work */
}
// 在index位置处插入元素(obj)
public synchronized void insertElementAt(E obj, int index) {
modCount++;
if (index > elementCount) {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index
+ " > " + elementCount);
}
ensureCapacityHelper(elementCount + 1);
System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + 1, elementCount - index);
elementData[index] = obj;
elementCount++;
}
// 将“元素obj”添加到Vector末尾
public synchronized void addElement(E obj) {
modCount++;
ensureCapacityHelper(elementCount + 1);
elementData[elementCount++] = obj;
}
// 在Vector中查找并删除元素obj。
// 成功的话,返回true;否则,返回false。
public synchronized boolean removeElement(Object obj) {
modCount++;
int i = indexOf(obj);
if (i >= 0) {
removeElementAt(i);
return true;
}
return false;
}
// 删除Vector中的全部元素
public synchronized void removeAllElements() {
modCount++;
// 将Vector中的全部元素设为null
for (int i = 0; i < elementCount; i++)
elementData[i] = null;
elementCount = 0;
}
// 克隆函数
public synchronized Object clone() {
try {
Vector<E> v = (Vector<E>) super.clone();
// 将当前Vector的全部元素拷贝到v中
v.elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, elementCount);
v.modCount = 0;
return v;
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
// this shouldn't happen, since we are Cloneable
throw new InternalError();
}
}
// 返回Object数组
public synchronized Object[] toArray() {
return Arrays.copyOf(elementData, elementCount);
}
// 返回Vector的模板数组。所谓模板数组,即可以将T设为任意的数据类型
public synchronized <T> T[] toArray(T[] a) {
// 若数组a的大小 < Vector的元素个数;
// 则新建一个T[]数组,数组大小是“Vector的元素个数”,并将“Vector”全部拷贝到新数组中
if (a.length < elementCount)
return (T[]) Arrays.copyOf(elementData, elementCount, a.getClass());
// 若数组a的大小 >= Vector的元素个数;
// 则将Vector的全部元素都拷贝到数组a中。
System.arraycopy(elementData, 0, a, 0, elementCount);
if (a.length > elementCount)
a[elementCount] = null;
return a;
}
// 获取index位置的元素
public synchronized E get(int index) {
if (index >= elementCount)
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index);
return (E)elementData[index];
}
// 设置index位置的值为element。并返回index位置的原始值
public synchronized E set(int index, E element) {
if (index >= elementCount)
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index);
Object oldValue = elementData[index];
elementData[index] = element;
return (E)oldValue;
}
// 将“元素e”添加到Vector最后。
public synchronized boolean add(E e) {
modCount++;
ensureCapacityHelper(elementCount + 1);
elementData[elementCount++] = e;
return true;
}
// 删除Vector中的元素o
public boolean remove(Object o) {
return removeElement(o);
}
// 在index位置添加元素element
public void add(int index, E element) {
insertElementAt(element, index);
}
// 删除index位置的元素,并返回index位置的原始值
public synchronized E remove(int index) {
modCount++;
if (index >= elementCount)
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index);
Object oldValue = elementData[index];
int numMoved = elementCount - index - 1;
if (numMoved > 0)
System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index,
numMoved);
elementData[--elementCount] = null; // Let gc do its work
return (E)oldValue;
}
// 清空Vector
public void clear() {
removeAllElements();
}
// 返回Vector是否包含集合c
public synchronized boolean containsAll(Collection<?> c) {
return super.containsAll(c);
}
// 将集合c添加到Vector中
public synchronized boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) {
modCount++;
Object[] a = c.toArray();
int numNew = a.length;
ensureCapacityHelper(elementCount + numNew);
// 将集合c的全部元素拷贝到数组elementData中
System.arraycopy(a, 0, elementData, elementCount, numNew);
elementCount += numNew;
return numNew != 0;
}
// 删除集合c的全部元素
public synchronized boolean removeAll(Collection<?> c) {
return super.removeAll(c);
}
// 删除“非集合c中的元素”
public synchronized boolean retainAll(Collection<?> c) {
return super.retainAll(c);
}
// 从index位置开始,将集合c添加到Vector中
public synchronized boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) {
modCount++;
if (index < 0 || index > elementCount)
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index);
Object[] a = c.toArray();
int numNew = a.length;
ensureCapacityHelper(elementCount + numNew);
int numMoved = elementCount - index;
if (numMoved > 0)
System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + numNew, numMoved);
System.arraycopy(a, 0, elementData, index, numNew);
elementCount += numNew;
return numNew != 0;
}
// 返回两个对象是否相等
public synchronized boolean equals(Object o) {
return super.equals(o);
}
// 计算哈希值
public synchronized int hashCode() {
return super.hashCode();
}
// 调用父类的toString()
public synchronized String toString() {
return super.toString();
}
// 获取Vector中fromIndex(包括)到toIndex(不包括)的子集
public synchronized List<E> subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
return Collections.synchronizedList(super.subList(fromIndex, toIndex), this);
}
// 删除Vector中fromIndex到toIndex的元素
protected synchronized void removeRange(int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
modCount++;
int numMoved = elementCount - toIndex;
System.arraycopy(elementData, toIndex, elementData, fromIndex,
numMoved);
// Let gc do its work
int newElementCount = elementCount - (toIndex-fromIndex);
while (elementCount != newElementCount)
elementData[--elementCount] = null;
}
// java.io.Serializable的写入函数
private synchronized void writeObject(java.io.ObjectOutputStream s)
throws java.io.IOException {
s.defaultWriteObject();
}
}总结:
(1)Vector实际上是通过一个数组去保存数据的。当我们构造Vector时;若使用默认构造函数,则Vector的默认容量大小是10。
(2)当Vector容量不足以容纳全部元素时,Vector的容量会增加。若容量增加系数 >0,则将容量的值增加“容量增加系数”;否则,将容量大小增加一倍。
(3)Vector的克隆函数,即是将全部元素克隆到一个数组中。
4、Vector遍历方式
Vector支持4种遍历方式。建议使用下面的第二种去遍历Vector,因为效率问题。
(01) 第一种,通过迭代器遍历。即通过Iterator去遍历。
Integer value = null;
int size = vec.size();
for (int i=0; i<size; i++) {
value = (Integer)vec.get(i);
}(02) 第二种,随机访问,通过索引值去遍历。
由于Vector实现了RandomAccess接口,它支持通过索引值去随机访问元素。
Integer value = null;
int size = vec.size();
for (int i=0; i<size; i++) {
value = (Integer)vec.get(i);
}(03) 第三种,另一种for循环。如下:
Integer value = null;
for (Integer integ:vec) {
value = integ;
}(04) 第四种,Enumeration遍历。如下:
Integer value = null;
Enumeration enu = vec.elements();
while (enu.hasMoreElements()) {
value = (Integer)enu.nextElement();
}测试这些遍历方式效率的代码如下:
import java.util.*;
/*
* @desc Vector遍历方式和效率的测试程序。
*
* @author hackerlee
*/
public class VectorRandomAccessTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Vector vec= new Vector();
for (int i=0; i<100000; i++)
vec.add(i);
iteratorThroughRandomAccess(vec) ;
iteratorThroughIterator(vec) ;
iteratorThroughFor2(vec) ;
iteratorThroughEnumeration(vec) ;
}
private static void isRandomAccessSupported(List list) {
if (list instanceof RandomAccess) {
System.out.println("RandomAccess implemented!");
} else {
System.out.println("RandomAccess not implemented!");
}
}
public static void iteratorThroughRandomAccess(List list) {
long startTime;
long endTime;
startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i=0; i<list.size(); i++) {
list.get(i);
}
endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
long interval = endTime - startTime;
System.out.println("iteratorThroughRandomAccess:" + interval+" ms");
}
public static void iteratorThroughIterator(List list) {
long startTime;
long endTime;
startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for(Iterator iter = list.iterator(); iter.hasNext(); ) {
iter.next();
}
endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
long interval = endTime - startTime;
System.out.println("iteratorThroughIterator:" + interval+" ms");
}
public static void iteratorThroughFor2(List list) {
long startTime;
long endTime;
startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for(Object obj:list)
;
endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
long interval = endTime - startTime;
System.out.println("iteratorThroughFor2:" + interval+" ms");
}
public static void iteratorThroughEnumeration(Vector vec) {
long startTime;
long endTime;
startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for(Enumeration enu = vec.elements(); enu.hasMoreElements(); ) {
enu.nextElement();
}
endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
long interval = endTime - startTime;
System.out.println("iteratorThroughEnumeration:" + interval+" ms");
}
}运行结果:
iteratorThroughRandomAccess:6 ms
iteratorThroughIterator:9 ms
iteratorThroughFor2:8 ms
iteratorThroughEnumeration:7 ms总结:遍历Vector,使用索引的随机访问方式最快,使用迭代器最慢。
5、Vector示例
下面通过示例学习如何使用Vector
import java.util.Vector;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Enumeration;
/**
* @desc Vector测试函数:遍历Vector和常用API
*
* @author hackerlee
*/
public class VectorTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 新建Vector
Vector vec = new Vector();
// 添加元素
vec.add("1");
vec.add("2");
vec.add("3");
vec.add("4");
vec.add("5");
// 设置第一个元素为100
vec.set(0, "100");
// 将“500”插入到第3个位置
vec.add(2, "300");
System.out.println("vec:"+vec);
// (顺序查找)获取100的索引
System.out.println("vec.indexOf(100):"+vec.indexOf("100"));
// (倒序查找)获取100的索引
System.out.println("vec.lastIndexOf(100):"+vec.lastIndexOf("100"));
// 获取第一个元素
System.out.println("vec.firstElement():"+vec.firstElement());
// 获取第3个元素
System.out.println("vec.elementAt(2):"+vec.elementAt(2));
// 获取最后一个元素
System.out.println("vec.lastElement():"+vec.lastElement());
// 获取Vector的大小
System.out.println("size:"+vec.size());
// 获取Vector的总的容量
System.out.println("capacity:"+vec.capacity());
// 获取vector的“第2”到“第4”个元素
System.out.println("vec 2 to 4:"+vec.subList(1, 4));
// 通过Enumeration遍历Vector
Enumeration enu = vec.elements();
while(enu.hasMoreElements())
System.out.println("nextElement():"+enu.nextElement());
Vector retainVec = new Vector();
retainVec.add("100");
retainVec.add("300");
// 获取“vec”中包含在“retainVec中的元素”的集合
System.out.println("vec.retain():"+vec.retainAll(retainVec));
System.out.println("vec:"+vec);
// 获取vec对应的String数组
String[] arr = (String[]) vec.toArray(new String[0]);
for (String str:arr)
System.out.println("str:"+str);
// 清空Vector。clear()和removeAllElements()一样!
vec.clear();
// vec.removeAllElements();
// 判断Vector是否为空
System.out.println("vec.isEmpty():"+vec.isEmpty());
}
}运行结果:
vec:[100, 2, 300, 3, 4, 5]
vec.indexOf(100):0
vec.lastIndexOf(100):0
vec.firstElement():100
vec.elementAt(2):300
vec.lastElement():5
size:6
capacity:10
vec 2 to 4:[2, 300, 3]
nextElement():100
nextElement():2
nextElement():300
nextElement():3
nextElement():4
nextElement():5
vec.retain():true
vec:[100, 300]
str:100
str:300
vec.isEmpty():true