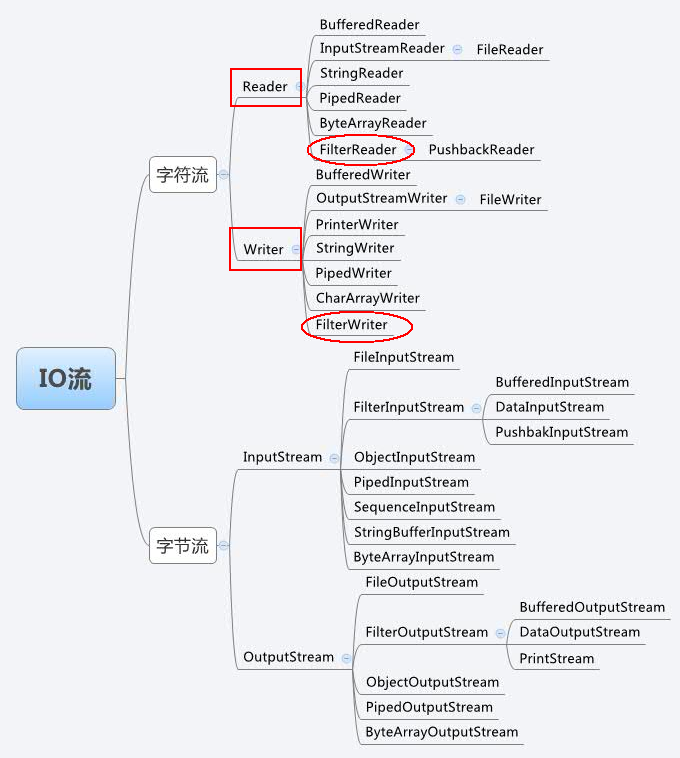
那么这篇博客我们讲的是字节输入输出流:Reader、Writer(下图红色长方形框内),红色椭圆框内是其典型实现(FileReader、FileWriter)
①、为什么要使用字符流?
因为使用字节流操作汉字或特殊符号语言的时候容易乱码,因为汉字不止一个字节,为了解决这个问题,建议使用字符流。
②、什么情况下使用字符流?
一般可以用记事本打开的文件,我们可以看到内容不乱码的。就是文本文件,可以使用字符流。而操作二进制文件(比如图片、音频、视频)必须使用字节流
1、字符输出流:FileWriter
|
1
2
3
|
public
abstract
class
Writer
extends
Object
implements
Appendable, Closeable, Flushable
|
用于写入字符流的抽象类
方法摘要:

下面我们用 字符输出流 Writer 的典型实现 FileWriter 来介绍这个类的用法:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
|
//1、创建源
File srcFile =
new
File(
"io"
+File.separator+
"a.txt"
);
//2、创建字符输出流对象
Writer out =
new
FileWriter(srcFile);
//3、具体的 IO 操作
/***
* void write(int c):向外写出一个字符
* void write(char[] buffer):向外写出多个字符 buffer
* void write(char[] buffer,int off,int len):把 buffer 数组中从索引 off 开始到 len个长度的数据写出去
* void write(String str):向外写出一个字符串
*/
//void write(int c):向外写出一个字符
out.write(
65
);
//将 A 写入 a.txt 文件中
//void write(char[] buffer):向外写出多个字符 buffer
out.write(
"Aa帅锅"
.toCharArray());
//将 Aa帅锅 写入 a.txt 文件中
//void write(char[] buffer,int off,int len)
out.write(
"Aa帅锅"
.toCharArray(),
0
,
2
);
//将 Aa 写入a.txt文件中
//void write(String str):向外写出一个字符串
out.write(
"Aa帅锅"
);
//将 Aa帅锅 写入 a.txt 文件中
//4、关闭流资源
/***
* 注意如果这里有一个 缓冲的概念,如果写入文件的数据没有达到缓冲的数组长度,那么数据是不会写入到文件中的
* 解决办法:手动刷新缓冲区 flush()
* 或者直接调用 close() 方法,这个方法会默认刷新缓冲区
*/
out.flush();
out.close();
|
2、字符输入流:Reader
|
1
2
3
|
public
abstract
class
Reader
extends
Object
implements
Readable, Closeable
|
用于读取字符流的抽象类。
方法摘要:
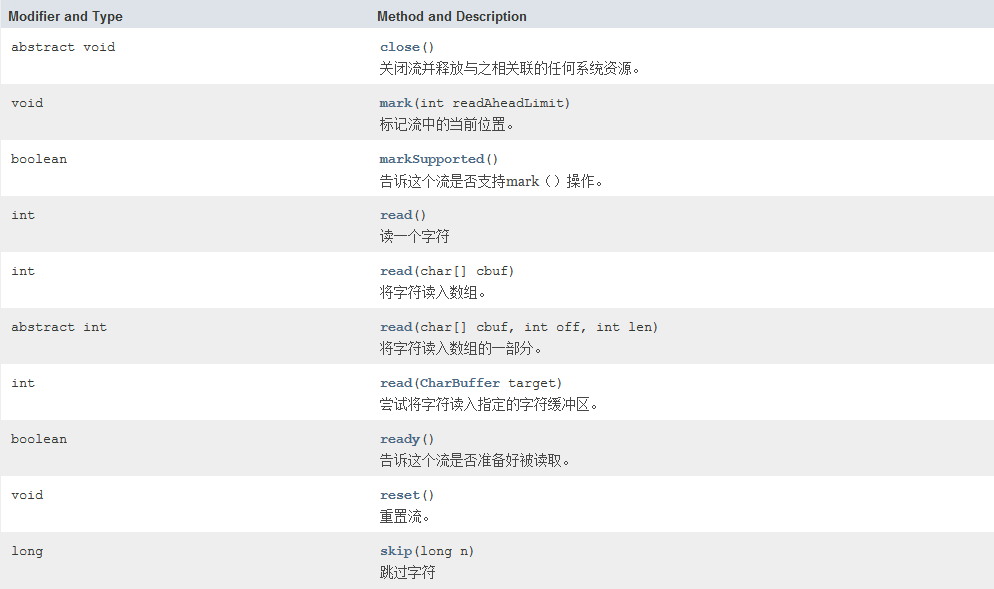
下面我们用 字符输入流 Reader 的典型实现 FileReader 来介绍这个类的用法:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
|
//1、创建源
File srcFile =
new
File(
"io"
+File.separator+
"a.txt"
);
//2、创建字符输出流对象
Reader in =
new
FileReader(srcFile);
//3、具体的 IO 操作
/***
* int read():每次读取一个字符,读到最后返回 -1
* int read(char[] buffer):将字符读进字符数组,返回结果为读取的字符数
* int read(char[] buffer,int off,int len):将读取的字符存储进字符数组 buffer,返回结果为读取的字符数,从索引 off 开始,长度为 len
*
*/
//int read():每次读取一个字符,读到最后返回 -1
int
len = -
1
;
//定义当前读取字符的数量
while
((len = in.read())!=-
1
){
//打印 a.txt 文件中所有内容
System.out.print((
char
)len);
}
//int read(char[] buffer):将字符读进字符数组
char
[] buffer =
new
char
[
10
];
//每次读取 10 个字符
while
((len=in.read(buffer))!=-
1
){
System.out.println(
new
String(buffer,
0
,len));
}
//int read(char[] buffer,int off,int len)
while
((len=in.read(buffer,
0
,
10
))!=-
1
){
System.out.println(
new
String(buffer,
0
,len));
}
//4、关闭流资源
in.close();
|
3、用字符流完成文件的复制
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
/**
* 将 a.txt 文件 复制到 b.txt 中
*/
//1、创建源和目标
File srcFile =
new
File(
"io"
+File.separator+
"a.txt"
);
File descFile =
new
File(
"io"
+File.separator+
"b.txt"
);
//2、创建字符输入输出流对象
Reader in =
new
FileReader(srcFile);
Writer out =
new
FileWriter(descFile);
//3、读取和写入操作
char
[] buffer =
new
char
[
10
];
//创建一个容量为 10 的字符数组,存储已经读取的数据
int
len = -
1
;
//表示已经读取了多少个字节,如果是 -1,表示已经读取到文件的末尾
while
((len=in.read(buffer))!=-
1
){
out.write(buffer,
0
, len);
}
//4、关闭流资源
out.close();
in.close();
|