Heapsort-2:堆排序-2
Animation
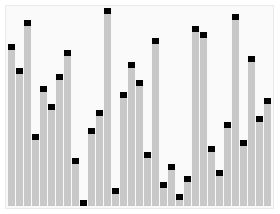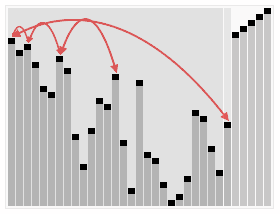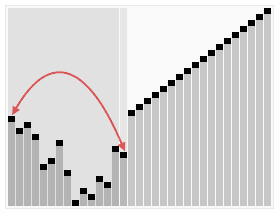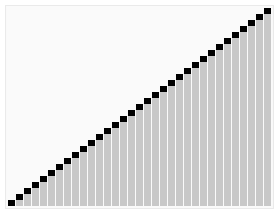
A run of the heapsort algorithm sorting an array of randomly permuted values. In the first stage of the algorithm the array elements are reordered to satisfy the heap property. Before the actual sorting takes place, the heap tree structure is shown briefly for illustration.

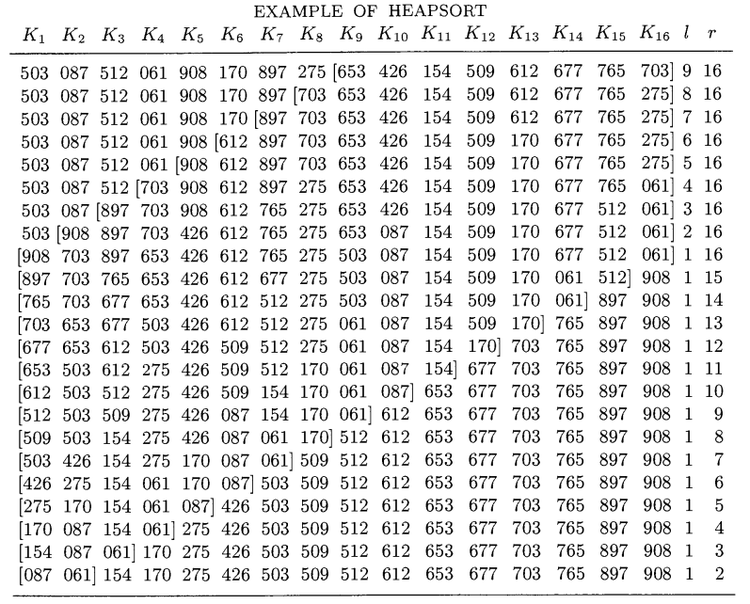
An example on heapsort.
Complexity
| Class | Sorting algorithm |
|---|---|
| Data structure | Array |
| Worst case performance |
|
| Best case performance |
|
| Average case performance |
|
| Worst case space complexity |
|
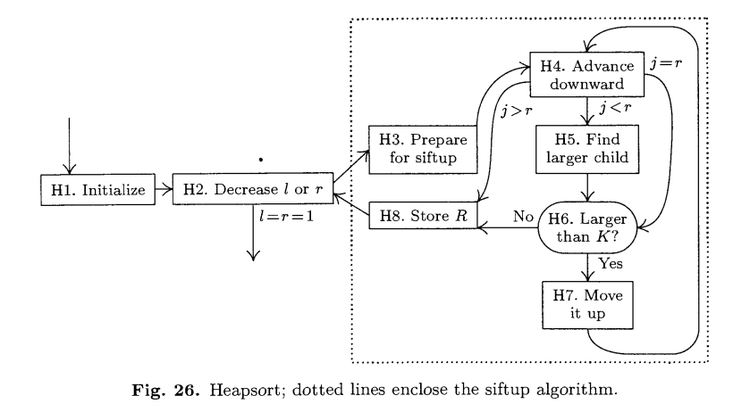
Algorithm H
Algorithm H (Heapsort). Records R1,… ,RN are rearranged in place; after
sorting is complete, their keys will be in order, K1<=…<=KN. First we
rearrange the file so that it forms a heap, then we repeatedly remove the top of
the heap and transfer it to its proper final position. Assume that N>=2.
H1. [Initialize.] Set l <– floor(N/2)+1, r<– N.
H2. [Decrease l or r.] If l>1, set I <– I-1, R <– Rl, K <– Kl (If I > 1, we are
in the process of transforming the input file into a heap; on the other hand
if I = 1, the keys K1 K2 … Kr presently constitute a heap.) Otherwise set
R <– Rr, K <– Kr, Rr <– R1, and r <– r-1; if this makes r = 1, set
R1 <– R and terminate the algorithm.
H3. [Prepare for siftup.] Set j <– I. (At this point we have
Kfloor(k/2) >= Kk for I< floor(k/2)< k<=r; (6)
and record Rk is in its final position for r < k <= N. Steps H3-H8 are called
the siftup algorithm; their effect is equivalent to setting Rl <– R and then
rearranging Rl,… ,Rr so that condition (6) holds also for I = floor(k/2).)
H4. [Advance downward.] Set i <– j and j <– 2j. (In the following steps we
have i = floor(j/2).) If j < r, go right on to step H5; if j = r, go to step H6;
and if j > r, go to H8.
H5. [Find larger child.] If Kj < Kj+1, then set j <– j+1.
H6. [Larger than K?] If K>=Kj, then go to step H8.
H7. [Move it up.] Set Ri <– Rj, and go back to step H4.
H8. [Store R.] Set Ri <– R. (This terminates the siftup algorithm initiated in
step H3.) Return to step H2. |
Flow diagram
Data table
Java program
In this program, R1,…,RN were simplified to K1,…,KN.
/**
* Created with IntelliJ IDEA.
* User: 1O1O
* Date: 12/3/13
* Time: 10:01 PM
* :)~
* Heapsort-2:Sorting by Selection:Internal Sorting
*/
public class Main {
public static void ADJUST_TO_MAX_HEAP(int[] K, int j, int r, int Key){
do{
int i = j;
j = 2*j;
if(j < r){
if(K[j] < K[j+1]){
j++;
}
if(Key >= K[j]){
K[i] = Key;
break;
}else {
K[i] = K[j];
}
}else if(j == r){
if(Key >= K[j]){
K[i] = Key;
break;
}else {
K[i] = K[j];
}
}else {
K[i] = Key;
break;
}
}while (true);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int N = 16;
int[] K = new int[17];
int Key = -1;
/*Prepare the data*/
K[1] = 503;
K[2] = 87;
K[3] = 512;
K[4] = 61;
K[5] = 908;
K[6] = 170;
K[7] = 897;
K[8] = 275;
K[9] = 653;
K[10] = 426;
K[11] = 154;
K[12] = 509;
K[13] = 612;
K[14] = 677;
K[15] = 765;
K[16] = 703;
/*Output unsorted Ks*/
System.out.println("Unsorted Ks:");
for(int i=1; i<=N; i++){
System.out.println(i+":"+K[i]);
}
System.out.println();
/*Kernel of the Algorithm!*/
int l = (int)Math.floor((double)N/2)+1;
int r = N;
while (l > 1){
l--;
Key = K[l];
int j = l;
ADJUST_TO_MAX_HEAP(K, j, r, Key);
}
while (r > 1){
Key = K[r];
K[r] = K[1];
r--;
int j = l;
ADJUST_TO_MAX_HEAP(K, j, r, Key);
}
K[1] = Key;
/*Output sorted Ks*/
System.out.println("Sorted Ks:");
for(int i=1; i<=N; i++){
System.out.println(i+":"+K[i]);
}
}
}Outputs
Unsorted Ks:
1:503
2:87
3:512
4:61
5:908
6:170
7:897
8:275
9:653
10:426
11:154
12:509
13:612
14:677
15:765
16:703
Sorted Ks:
1:61
2:87
3:154
4:170
5:275
6:426
7:503
8:509
9:512
10:612
11:653
12:677
13:703
14:765
15:897
16:908 Reference
<< The art of computer programming: Sorting and Searching >> VOLUME 3, DONALD E. KNUTH
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Heapsort