运行环境 win10 / oracle(DB11g)
一、使用高效查询
1、用exists 替代 IN
- 使用exists 时更快的原因有两个:
- 如果连接列(id)上建立了索引,那么查询class_b_11时不用查实际的表,只需查索引就可以了
- 如果使用exists,那么只要查到一行数据满足条件就会终止查询,不用像使用IN时一样扫描全表
例子:
create table Class_A_11
(
id SMALLINT,
name1 varchar(10)
)
;
create table Class_B_11
(
id SMALLINT,
name1 varchar(10)
)
;
insert into Class_A_11 values(1,'田中');
insert into Class_A_11 values(2,'铃木');
insert into Class_A_11 values(3,'伊集院');
insert into Class_B_11 values(1,'田中');
insert into Class_B_11 values(2,'铃木');
insert into Class_B_11 values(4,'西园寺');
-- 慢
select *
from class_a_11
where id in (select id from Class_B_11)
;
-- 快
select *
from class_a_11 a
where exists (select *
from Class_B_11 b
where a.id = b.id)
;2、参数是子查询时,可以使用连接代替IN
select a.id, a.NAME1
from class_a_11 a inner join class_b_11 B
on a.id = b.id
;如果没有索引,和连接相比exists更胜一筹
二、避免排序
这些都会默认进行排序:
group by/ order by/ 聚合函数/ distinct/ 集合运算符(union、intersect、except)
窗口函数(rank / row_number等)
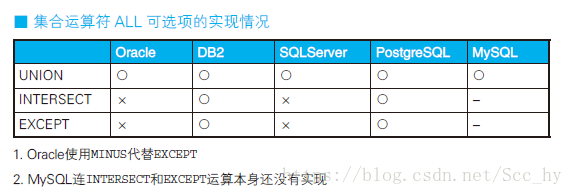
1、灵活使用集合运算符的ALL可选项
– 使用union 会默认排序去重,再不需要去重的情况下,建议使用union all
– 各个数据库all的支持的情况
2、使用exists代替distinct
为了排除重复数据,distinct也会进行排序
创表:
create table items_11
(
item_no SMALLINT,
item varchar(10)
)
;
insert into items_11 values(10, 'FD');
insert into items_11 values(20, 'CD-R');
insert into items_11 values(30, 'MO');
insert into items_11 values(40, 'DVD');
create table saleshistory_11
(
sale_date date,
item_no smallint,
quantity SMALLINT
)
;
insert into saleshistory_11 values(to_date('2007-10-01','yyyy-mm-dd'),10 ,4);
insert into saleshistory_11 values(to_date('2007-10-01','yyyy-mm-dd'),20 ,10);
insert into saleshistory_11 values(to_date('2007-10-01','yyyy-mm-dd'),30 ,3);
insert into saleshistory_11 values(to_date('2007-10-03','yyyy-mm-dd'),10 ,32);
insert into saleshistory_11 values(to_date('2007-10-03','yyyy-mm-dd'),30 ,12);
insert into saleshistory_11 values(to_date('2007-10-04','yyyy-mm-dd'),20 ,22);
insert into saleshistory_11 values(to_date('2007-10-04','yyyy-mm-dd'),30 ,7);
exists 替代 distinct
-- 一对多出现重复数据,排重需要distinct
select distinct i.item_no
from items_11 i inner join saleshistory_11 sh
on i.item_no = sh.item_no
;
-- 可以使用exists 更加快速
select i.item_no
from items_11 i
where exists
(select *
from saleshistory_11 sh
where i.item_no = sh.item_no
)
; 结果:
ITEM_NO
----------
10
20
30三、索引和减少使用子查询
1、能写在where里的子句不要写在having中
select sale_date, sum(quantity)
from saleshistory_11
group by sale_date
having sale_date = to_date('2007-10-01','yyyy-mm-dd')
;
-- 用where 会先提取子集 再做group
select sale_date, sum(quantity)
from saleshistory_11
where sale_date = to_date('2007-10-01','yyyy-mm-dd')
group by sale_date
;2、有效运用索引
当col_1 为索引列的时候
where col_1 * 1.1 >100 – 没有用到出索引的优势
where col_1 > 100/1.1 – 用到了索引
<> != not in不能用到索引
3、减少中间表,灵活使用having
select *
from (select sale_date, max(quantity) max_quantity
from saleshistory_11
group by sale_date) tmp -- 没用的中间表
where max_quantity >= 10
;
select sale_date, max(quantity)
from saleshistory_11
group by sale_date
having max(quantity) >= 10
;4、需要对多个字段使用IN时,将他们汇总到一处
-- 字段连接
select *
from address1 a1
where id || sate || city
in (select id || sate || city
from address1 a2)
;
-- 字段组合
select *
from address1 a1
where (id ,sate ,city)
in (select id, sate, city
from address1 a2)
;- 组合的优势:
- 1、不用担心连接字段时出现的类型转换问题
- 2、不对字段进行加工,可以直接使用索引
内容多来自 《SQL进阶教材》,仅做笔记。