Deep Learning with TensorFlow
IBM Cognitive Class ML0120EN
Module 5 - Autoencoders
使用DBN识别手写体
传统的多层感知机或者神经网络的一个问题: 反向传播可能总是导致局部最小值。
当误差表面(error surface)包含了多个凹槽,当你做梯度下降时,你找到的并不是最深的凹槽。 下面你将会看到DBN是怎么解决这个问题的。
深度置信网络
深度置信网络可以通过额外的预训练规程解决局部最小值的问题。 预训练在反向传播之前做完,这样可以使错误率离最优的解不是那么远,也就是我们在最优解的附近。再通过反向传播慢慢地降低错误率。
深度置信网络主要分成两部分。第一部分是多层玻尔兹曼感知机,用于预训练我们的网络。第二部分是前馈反向传播网络,这可以使RBM堆叠的网络更加精细化。
1. 加载必要的深度置信网络库
#urllib is used to download the utils file from deeplearning.net
import urllib
response = urllib.urlopen('http://deeplearning.net/tutorial/code/utils.py')
content = response.read()
target = open('utils.py', 'w')
target.write(content)
target.close()
#Import the math function for calculations
import math
#Tensorflow library. Used to implement machine learning models
import tensorflow as tf
#Numpy contains helpful functions for efficient mathematical calculations
import numpy as np
#Image library for image manipulation
from PIL import Image
#import Image
#Utils file
from utils import tile_raster_images2. 构建RBM层
RBM的细节参考【这里】
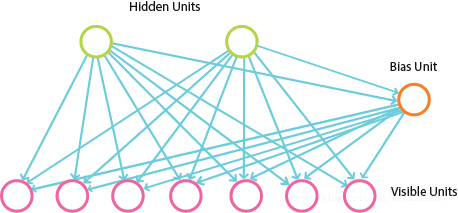
为了在Tensorflow中应用DBM, 下面创建一个RBM的类
#Class that defines the behavior of the RBM
class RBM(object):
def __init__(self, input_size, output_size):
#Defining the hyperparameters
self._input_size = input_size #Size of input
self._output_size = output_size #Size of output
self.epochs = 5 #Amount of training iterations
self.learning_rate = 1.0 #The step used in gradient descent
self.batchsize = 100 #The size of how much data will be used for training per sub iteration
#Initializing weights and biases as matrices full of zeroes
self.w = np.zeros([input_size, output_size], np.float32) #Creates and initializes the weights with 0
self.hb = np.zeros([output_size], np.float32) #Creates and initializes the hidden biases with 0
self.vb = np.zeros([input_size], np.float32) #Creates and initializes the visible biases with 0
#Fits the result from the weighted visible layer plus the bias into a sigmoid curve
def prob_h_given_v(self, visible, w, hb):
#Sigmoid
return tf.nn.sigmoid(tf.matmul(visible, w) + hb)
#Fits the result from the weighted hidden layer plus the bias into a sigmoid curve
def prob_v_given_h(self, hidden, w, vb):
return tf.nn.sigmoid(tf.matmul(hidden, tf.transpose(w)) + vb)
#Generate the sample probability
def sample_prob(self, probs):
return tf.nn.relu(tf.sign(probs - tf.random_uniform(tf.shape(probs))))
#Training method for the model
def train(self, X):
#Create the placeholders for our parameters
_w = tf.placeholder("float", [self._input_size, self._output_size])
_hb = tf.placeholder("float", [self._output_size])
_vb = tf.placeholder("float", [self._input_size])
prv_w = np.zeros([self._input_size, self._output_size], np.float32) #Creates and initializes the weights with 0
prv_hb = np.zeros([self._output_size], np.float32) #Creates and initializes the hidden biases with 0
prv_vb = np.zeros([self._input_size], np.float32) #Creates and initializes the visible biases with 0
cur_w = np.zeros([self._input_size, self._output_size], np.float32)
cur_hb = np.zeros([self._output_size], np.float32)
cur_vb = np.zeros([self._input_size], np.float32)
v0 = tf.placeholder("float", [None, self._input_size])
#Initialize with sample probabilities
h0 = self.sample_prob(self.prob_h_given_v(v0, _w, _hb))
v1 = self.sample_prob(self.prob_v_given_h(h0, _w, _vb))
h1 = self.prob_h_given_v(v1, _w, _hb)
#Create the Gradients
positive_grad = tf.matmul(tf.transpose(v0), h0)
negative_grad = tf.matmul(tf.transpose(v1), h1)
#Update learning rates for the layers
update_w = _w + self.learning_rate *(positive_grad - negative_grad) / tf.to_float(tf.shape(v0)[0])
update_vb = _vb + self.learning_rate * tf.reduce_mean(v0 - v1, 0)
update_hb = _hb + self.learning_rate * tf.reduce_mean(h0 - h1, 0)
#Find the error rate
err = tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(v0 - v1))
#Training loop
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(tf.initialize_all_variables())
#For each epoch
for epoch in range(self.epochs):
#For each step/batch
for start, end in zip(range(0, len(X), self.batchsize),range(self.batchsize,len(X), self.batchsize)):
batch = X[start:end]
#Update the rates
cur_w = sess.run(update_w, feed_dict={v0: batch, _w: prv_w, _hb: prv_hb, _vb: prv_vb})
cur_hb = sess.run(update_hb, feed_dict={v0: batch, _w: prv_w, _hb: prv_hb, _vb: prv_vb})
cur_vb = sess.run(update_vb, feed_dict={v0: batch, _w: prv_w, _hb: prv_hb, _vb: prv_vb})
prv_w = cur_w
prv_hb = cur_hb
prv_vb = cur_vb
error=sess.run(err, feed_dict={v0: X, _w: cur_w, _vb: cur_vb, _hb: cur_hb})
print 'Epoch: %d' % epoch,'reconstruction error: %f' % error
self.w = prv_w
self.hb = prv_hb
self.vb = prv_vb
#Create expected output for our DBN
def rbm_outpt(self, X):
input_X = tf.constant(X)
_w = tf.constant(self.w)
_hb = tf.constant(self.hb)
out = tf.nn.sigmoid(tf.matmul(input_X, _w) + _hb)
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
return sess.run(out)3. 导入MNIST数据
使用one-hot encoding标注的形式载入MNIST图像数据。
#Getting the MNIST data provided by Tensorflow
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
#Loading in the mnist data
mnist = input_data.read_data_sets("MNIST_data/", one_hot=True)
trX, trY, teX, teY = mnist.train.images, mnist.train.labels, mnist.test.images,\
mnist.test.labels
Extracting MNIST_data/train-images-idx3-ubyte.gz
Extracting MNIST_data/train-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz
Extracting MNIST_data/t10k-images-idx3-ubyte.gz
Extracting MNIST_data/t10k-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz4. 建立DBN
RBM_hidden_sizes = [500, 200 , 50 ] #create 2 layers of RBM with size 400 and 100
#Since we are training, set input as training data
inpX = trX
#Create list to hold our RBMs
rbm_list = []
#Size of inputs is the number of inputs in the training set
input_size = inpX.shape[1]
#For each RBM we want to generate
for i, size in enumerate(RBM_hidden_sizes):
print 'RBM: ',i,' ',input_size,'->', size
rbm_list.append(RBM(input_size, size))
input_size = sizeRBM: 0 784 -> 500
RBM: 1 500 -> 200
RBM: 2 200 -> 50rbm的类创建好了和数据都已经载入,可以创建DBN。 在这个例子中,我们使用了3个RBM,一个的隐藏层单元个数为500, 第二个RBM的隐藏层个数为200,最后一个为50. 我们想要生成训练数据的深层次表示形式。
5.训练RBM
我们将使用rbm.train()开始预训练步骤, 单独训练堆中的每一个RBM,并将当前RBM的输出作为下一个RBM的输入。
#For each RBM in our list
for rbm in rbm_list:
print 'New RBM:'
#Train a new one
rbm.train(inpX)
#Return the output layer
inpX = rbm.rbm_outpt(inpX)New RBM:
Epoch: 0 reconstruction error: 0.061884
Epoch: 1 reconstruction error: 0.052996
Epoch: 2 reconstruction error: 0.049414
Epoch: 3 reconstruction error: 0.047123
Epoch: 4 reconstruction error: 0.046149
New RBM:
Epoch: 0 reconstruction error: 0.035305
Epoch: 1 reconstruction error: 0.031168
Epoch: 2 reconstruction error: 0.029394
Epoch: 3 reconstruction error: 0.028474
Epoch: 4 reconstruction error: 0.027456
New RBM:
Epoch: 0 reconstruction error: 0.055896
Epoch: 1 reconstruction error: 0.053111
Epoch: 2 reconstruction error: 0.051631
Epoch: 3 reconstruction error: 0.051126
Epoch: 4 reconstruction error: 0.051245现在我们可以将输入数据的学习好的表示转换为有监督的预测,比如一个线性分类器。特别地,我们使用这个浅层神经网络的最后一层的输出对数字分类。
6. 神经网络
下面的类使用了上面预训练好的RBMs实现神经网络。
import numpy as np
import math
import tensorflow as tf
class NN(object):
def __init__(self, sizes, X, Y):
#Initialize hyperparameters
self._sizes = sizes
self._X = X
self._Y = Y
self.w_list = []
self.b_list = []
self._learning_rate = 1.0
self._momentum = 0.0
self._epoches = 10
self._batchsize = 100
input_size = X.shape[1]
#initialization loop
for size in self._sizes + [Y.shape[1]]:
#Define upper limit for the uniform distribution range
max_range = 4 * math.sqrt(6. / (input_size + size))
#Initialize weights through a random uniform distribution
self.w_list.append(
np.random.uniform( -max_range, max_range, [input_size, size]).astype(np.float32))
#Initialize bias as zeroes
self.b_list.append(np.zeros([size], np.float32))
input_size = size
#load data from rbm
def load_from_rbms(self, dbn_sizes,rbm_list):
#Check if expected sizes are correct
assert len(dbn_sizes) == len(self._sizes)
for i in range(len(self._sizes)):
#Check if for each RBN the expected sizes are correct
assert dbn_sizes[i] == self._sizes[i]
#If everything is correct, bring over the weights and biases
for i in range(len(self._sizes)):
self.w_list[i] = rbm_list[i].w
self.b_list[i] = rbm_list[i].hb
#Training method
def train(self):
#Create placeholders for input, weights, biases, output
_a = [None] * (len(self._sizes) + 2)
_w = [None] * (len(self._sizes) + 1)
_b = [None] * (len(self._sizes) + 1)
_a[0] = tf.placeholder("float", [None, self._X.shape[1]])
y = tf.placeholder("float", [None, self._Y.shape[1]])
#Define variables and activation functoin
for i in range(len(self._sizes) + 1):
_w[i] = tf.Variable(self.w_list[i])
_b[i] = tf.Variable(self.b_list[i])
for i in range(1, len(self._sizes) + 2):
_a[i] = tf.nn.sigmoid(tf.matmul(_a[i - 1], _w[i - 1]) + _b[i - 1])
#Define the cost function
cost = tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(_a[-1] - y))
#Define the training operation (Momentum Optimizer minimizing the Cost function)
train_op = tf.train.MomentumOptimizer(
self._learning_rate, self._momentum).minimize(cost)
#Prediction operation
predict_op = tf.argmax(_a[-1], 1)
#Training Loop
with tf.Session() as sess:
#Initialize Variables
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
#For each epoch
for i in range(self._epoches):
#For each step
for start, end in zip(
range(0, len(self._X), self._batchsize), range(self._batchsize, len(self._X), self._batchsize)):
#Run the training operation on the input data
sess.run(train_op, feed_dict={
_a[0]: self._X[start:end], y: self._Y[start:end]})
for j in range(len(self._sizes) + 1):
#Retrieve weights and biases
self.w_list[j] = sess.run(_w[j])
self.b_list[j] = sess.run(_b[j])
print "Accuracy rating for epoch " + str(i) + ": " + str(np.mean(np.argmax(self._Y, axis=1) ==
sess.run(predict_op, feed_dict={_a[0]: self._X, y: self._Y})))7. 运行
nNet = NN(RBM_hidden_sizes, trX, trY)
nNet.load_from_rbms(RBM_hidden_sizes,rbm_list)
nNet.train()Accuracy rating for epoch 0: 0.39641818181818184
Accuracy rating for epoch 1: 0.664309090909091
Accuracy rating for epoch 2: 0.7934545454545454
Accuracy rating for epoch 3: 0.8152727272727273
Accuracy rating for epoch 4: 0.8258181818181818
Accuracy rating for epoch 5: 0.8348727272727273
Accuracy rating for epoch 6: 0.8525272727272727
Accuracy rating for epoch 7: 0.889109090909091
Accuracy rating for epoch 8: 0.9079454545454545
Accuracy rating for epoch 9: 0.9158参考文献
• http://deeplearning.net/tutorial/DBN.html
• https://github.com/myme5261314/dbn_tf
本文译自 : ML0120EN-5.2-Review-DBNMNIST.ipynb