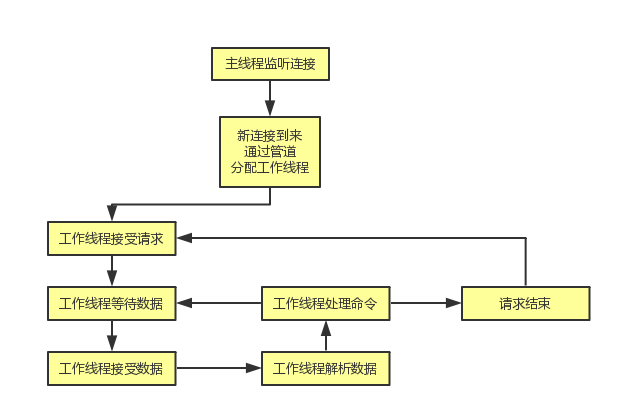
整体流程的介绍
memcached的整体结构采用的是多线程框架,这也是为什么memcached中很多锁的原因,我个人对这一点不是很喜欢,一是因为看起来很复杂,二是感觉性能也会因此而受到影响;memcached的多线程框架采用的是一对多的策略,其中主线程主要用来监听新的网络连接,工作线程用来处理请求,主线程和工作线程是通过管道pipe来实现的。
在每个请求过程中,请求以及响应的过程都是通过一个状态机来实现的(这里面应该强调下,由于网络部分不是我想学习的重点,但是还是应该说明memcached的网络部分仍然是一个不错的开源代码学习,这里面涉及的协议类型,网络数据的读取和发送等等,都是很好的参考材料)。
同时,还应该说明下memcached所有状态的更新都是通过libevent的事件模型来驱动的,这个通过与前面提到的状态机结合显得更加有意义;每个工作线程都会有自己的事件驱动。
运转流程图
整体流程细分
下面主要是结合代码仔细介绍下整体的流程:
监听新请求
在main函数中,会调用server_sockets函数来初始化监听端口,设置监听socket,同时通过conn_new函数创建一个listen_conn_add连接, 其初始状态是conn_listening, 事件驱动是main_base, 并且是永久设置,用于一直监听新的连接。
main函数中:
errno = 0;
if (settings.port && server_sockets(settings.port, tcp_transport,
portnumber_file)) { //main函数中调用设置
vperror("failed to listen on TCP port %d", settings.port);
exit(EX_OSERR);
}server_socket中:
if (IS_UDP(transport)) {
int c;
for (c = 0; c < settings.num_threads_per_udp; c++) {
/* Allocate one UDP file descriptor per worker thread;
* this allows "stats conns" to separately list multiple
* parallel UDP requests in progress.
*
* The dispatch code round-robins new connection requests
* among threads, so this is guaranteed to assign one
* FD to each thread.
*/
int per_thread_fd = c ? dup(sfd) : sfd;
dispatch_conn_new(per_thread_fd, conn_read,
EV_READ | EV_PERSIST,
UDP_READ_BUFFER_SIZE, transport);
}
} else {
if (!(listen_conn_add = conn_new(sfd, conn_listening,
EV_READ | EV_PERSIST, 1,
transport, main_base))) {
fprintf(stderr, "failed to create listening connection\n");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
listen_conn_add->next = listen_conn;
listen_conn = listen_conn_add;
}分配新连接
在conn_new函数中,主要是获取一个连接,然后对conn结构体进行初始化,初始化完成后,注册监听事件,事件回调函数为event_handler函数。
conn *conn_new(const int sfd, enum conn_states init_state,
const int event_flags,
const int read_buffer_size, enum network_transport transport,
struct event_base *base) {
conn *c;
assert(sfd >= 0 && sfd < max_fds);
c = conns[sfd]; //从连接池获取,没有则新建
if (NULL == c) {
if (!(c = (conn *)calloc(1, sizeof(conn)))) {
STATS_LOCK();
stats.malloc_fails++;
STATS_UNLOCK();
fprintf(stderr, "Failed to allocate connection object\n");
return NULL;
}
MEMCACHED_CONN_CREATE(c);
//以下是初始化conn结构体
c->rbuf = c->wbuf = 0;
c->ilist = 0;
c->suffixlist = 0;
c->iov = 0;
c->msglist = 0;
c->hdrbuf = 0;
c->rsize = read_buffer_size;
c->wsize = DATA_BUFFER_SIZE;
c->isize = ITEM_LIST_INITIAL;
c->suffixsize = SUFFIX_LIST_INITIAL;
c->iovsize = IOV_LIST_INITIAL;
c->msgsize = MSG_LIST_INITIAL;
c->hdrsize = 0;
c->rbuf = (char *)malloc((size_t)c->rsize);
c->wbuf = (char *)malloc((size_t)c->wsize);
c->ilist = (item **)malloc(sizeof(item *) * c->isize);
c->suffixlist = (char **)malloc(sizeof(char *) * c->suffixsize);
c->iov = (struct iovec *)malloc(sizeof(struct iovec) * c->iovsize);
c->msglist = (struct msghdr *)malloc(sizeof(struct msghdr) * c->msgsize);
if (c->rbuf == 0 || c->wbuf == 0 || c->ilist == 0 || c->iov == 0 ||
c->msglist == 0 || c->suffixlist == 0) {
conn_free(c);
STATS_LOCK();
stats.malloc_fails++;
STATS_UNLOCK();
fprintf(stderr, "Failed to allocate buffers for connection\n");
return NULL;
}
STATS_LOCK();
stats.conn_structs++;
STATS_UNLOCK();
c->sfd = sfd;
conns[sfd] = c;
}
c->transport = transport;
c->protocol = settings.binding_protocol;
/* unix socket mode doesn't need this, so zeroed out. but why
* is this done for every command? presumably for UDP
* mode. */
if (!settings.socketpath) {
c->request_addr_size = sizeof(c->request_addr);
} else {
c->request_addr_size = 0;
}
if (transport == tcp_transport && init_state == conn_new_cmd) { //这里面是工作线程处理新连接的初始状态
if (getpeername(sfd, (struct sockaddr *) &c->request_addr,
&c->request_addr_size)) {
perror("getpeername");
memset(&c->request_addr, 0, sizeof(c->request_addr));
}
}
if (settings.verbose > 1) {
if (init_state == conn_listening) { //主线程初始状态
fprintf(stderr, "<%d server listening (%s)\n", sfd,
prot_text(c->protocol));
} else if (IS_UDP(transport)) {
fprintf(stderr, "<%d server listening (udp)\n", sfd);
} else if (c->protocol == negotiating_prot) {
fprintf(stderr, "<%d new auto-negotiating client connection\n",
sfd);
} else if (c->protocol == ascii_prot) {
fprintf(stderr, "<%d new ascii client connection.\n", sfd);
} else if (c->protocol == binary_prot) {
fprintf(stderr, "<%d new binary client connection.\n", sfd);
} else {
fprintf(stderr, "<%d new unknown (%d) client connection\n",
sfd, c->protocol);
assert(false);
}
}
c->state = init_state;
c->rlbytes = 0;
c->cmd = -1;
c->rbytes = c->wbytes = 0;
c->wcurr = c->wbuf;
c->rcurr = c->rbuf;
c->ritem = 0;
c->icurr = c->ilist;
c->suffixcurr = c->suffixlist;
c->ileft = 0;
c->suffixleft = 0;
c->iovused = 0;
c->msgcurr = 0;
c->msgused = 0;
c->authenticated = false;
c->write_and_go = init_state;
c->write_and_free = 0;
c->item = 0;
c->noreply = false;
event_set(&c->event, sfd, event_flags, event_handler, (void *)c); //注册时间,回调函数是event_handler
event_base_set(base, &c->event);
c->ev_flags = event_flags;
if (event_add(&c->event, 0) == -1) {
perror("event_add");
return NULL;
}
STATS_LOCK();
stats.curr_conns++;
stats.total_conns++;
STATS_UNLOCK();
MEMCACHED_CONN_ALLOCATE(c->sfd);
return c;
}在event_handler函数中,主要是调用drive_machine函数进入网络连接状态机
void event_handler(const int fd, const short which, void *arg) {
conn *c;
c = (conn *)arg;
assert(c != NULL);
c->which = which;
/* sanity */
if (fd != c->sfd) {
if (settings.verbose > 0)
fprintf(stderr, "Catastrophic: event fd doesn't match conn fd!\n");
conn_close(c);
return;
}
drive_machine(c);
/* wait for next event */
return;
}在drive_machine函数中,在这里会根据当前连接的状态进行对应的处理,前面提过当前的初始状态是conn_listening,先分析这个状态,后面处理的命令到时再分析;连接状态是conn_listening时,首先调用accept函数接受一个新连接并获取连接socket描述符,排除异常问题后,会调用dispatch_conn_new函数将该新连接分配到对应线程上去
case conn_listening:
addrlen = sizeof(addr);
#ifdef HAVE_ACCEPT4
if (use_accept4) {
sfd = accept4(c->sfd, (struct sockaddr *)&addr, &addrlen, SOCK_NONBLOCK);
} else {
sfd = accept(c->sfd, (struct sockaddr *)&addr, &addrlen);
}
#else
sfd = accept(c->sfd, (struct sockaddr *)&addr, &addrlen); //从监听连接接受新请求
#endif
if (sfd == -1) {
if (use_accept4 && errno == ENOSYS) {
use_accept4 = 0;
continue;
}
perror(use_accept4 ? "accept4()" : "accept()");
if (errno == EAGAIN || errno == EWOULDBLOCK) {
/* these are transient, so don't log anything */
stop = true;
} else if (errno == EMFILE) {
if (settings.verbose > 0)
fprintf(stderr, "Too many open connections\n");
accept_new_conns(false);
stop = true;
} else {
perror("accept()");
stop = true;
}
break;
}
if (!use_accept4) {
if (fcntl(sfd, F_SETFL, fcntl(sfd, F_GETFL) | O_NONBLOCK) < 0) {
perror("setting O_NONBLOCK");
close(sfd);
break;
}
}
if (settings.maxconns_fast &&
stats.curr_conns + stats.reserved_fds >= settings.maxconns - 1) {
str = "ERROR Too many open connections\r\n";
res = write(sfd, str, strlen(str));
close(sfd);
STATS_LOCK();
stats.rejected_conns++;
STATS_UNLOCK();
} else {
dispatch_conn_new(sfd, conn_new_cmd, EV_READ | EV_PERSIST,
DATA_BUFFER_SIZE, tcp_transport); //分配新连接,初始状态改为conn_new_cmd
}
stop = true;
break;在dispatch_conn_new函数中,会调用cqi_new新建一个conn结构,并使用简单的轮询策略分配一个线程给该连接,并将连接状态conn_new_cmd写到conn结构中去,然后将该结构放到该线程的new_conn_queue中去,并通过该线程的管道发送一个’c’字符通知线程接收该连接
void dispatch_conn_new(int sfd, enum conn_states init_state, int event_flags,
int read_buffer_size, enum network_transport transport) {
CQ_ITEM *item = cqi_new(); //这个item不是之前说的数据item,是指连接队列的一个conn结构
char buf[1];
if (item == NULL) {
close(sfd);
/* given that malloc failed this may also fail, but let's try */
fprintf(stderr, "Failed to allocate memory for connection object\n");
return ;
}
//下面轮询选择一个线程用来处理新连接
int tid = (last_thread + 1) % settings.num_threads;
LIBEVENT_THREAD *thread = threads + tid;
last_thread = tid;
item->sfd = sfd;
item->init_state = init_state;
item->event_flags = event_flags;
item->read_buffer_size = read_buffer_size;
item->transport = transport;
cq_push(thread->new_conn_queue, item); //将该item加入到该线程的新连接队列中去
MEMCACHED_CONN_DISPATCH(sfd, thread->thread_id);
buf[0] = 'c'; //下面是通过管道发送一个‘c’字符给对应的工作线程
if (write(thread->notify_send_fd, buf, 1) != 1) {
perror("Writing to thread notify pipe");
}
}由于每个线程在创建的时候都会给自己的事件驱动注册一个读取管道的事件,当调度线程发送一个c字符时,对应线程的事件会被唤醒,并执行回调函数thread_libevent_process;在thread_libevent_process函数中,会从该线程的new_conn_queue获取刚才添加的那个conn结构,根据结构内容再次调用conn_new函数,这样就会再次注册了监听事件,同样回调函数是event_handler,不同的是此时的初始状态是conn_new_cmd
static void thread_libevent_process(int fd, short which, void *arg) {
LIBEVENT_THREAD *me = arg;
CQ_ITEM *item;
char buf[1];
if (read(fd, buf, 1) != 1)
if (settings.verbose > 0)
fprintf(stderr, "Can't read from libevent pipe\n");
switch (buf[0]) {
case 'c':
item = cq_pop(me->new_conn_queue); //从新连接队列中提取出新连接
if (NULL != item) {
conn *c = conn_new(item->sfd, item->init_state, item->event_flags,
item->read_buffer_size, item->transport, me->base); //再次调用conn_new函数
if (c == NULL) {
if (IS_UDP(item->transport)) {
fprintf(stderr, "Can't listen for events on UDP socket\n");
exit(1);
} else {
if (settings.verbose > 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "Can't listen for events on fd %d\n",
item->sfd);
}
close(item->sfd);
}
} else {
c->thread = me;
}
cqi_free(item); //释放连接到连接池
}
break;
/* we were told to pause and report in */
case 'p':
register_thread_initialized();
break;
}
}处理请求
当连接状态是conn_new_cmd时, 首先检查当前请求次数是否超标,如果没有超标则调用reset_cmd_handler函数,超标的话会调用update_event函数,这部分后面再说,先按照正常流程进行;在reset_cmd_handler函数时,新命令清空当前item,并调用conn_shrink函数对当前连接中的buf进行缩减,这时候如果读取的数据还有未解析的,设置连接状态为conn_parse_cmd,否则设置为conn_waiting;
case conn_new_cmd:
/* Only process nreqs at a time to avoid starving other
connections */
--nreqs;
if (nreqs >= 0) {
reset_cmd_handler(c);
} else {
pthread_mutex_lock(&c->thread->stats.mutex);
c->thread->stats.conn_yields++;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&c->thread->stats.mutex);
if (c->rbytes > 0) {
/* We have already read in data into the input buffer,
so libevent will most likely not signal read events
on the socket (unless more data is available. As a
hack we should just put in a request to write data,
because that should be possible ;-)
*/
if (!update_event(c, EV_WRITE | EV_PERSIST)) {
if (settings.verbose > 0)
fprintf(stderr, "Couldn't update event\n");
conn_set_state(c, conn_closing);
break;
}
}
stop = true;
}
break;static void reset_cmd_handler(conn *c) {
c->cmd = -1;
c->substate = bin_no_state;
if(c->item != NULL) {
item_remove(c->item);
c->item = NULL;
}
conn_shrink(c);
if (c->rbytes > 0) {
conn_set_state(c, conn_parse_cmd);
} else {
conn_set_state(c, conn_waiting);
}
}连接状态是conn_parse_cmd时,会调用try_read_command函数来解析读取内容,如果数据不足,会修改连接状态为conn_waiting,继续等待读取数据;
try_read_command函数中,首先根据连接使用的协议解析数据,根据使用的协议类型不同分别调用dispatch_bin_command或者process_command来处理命令,什么协议不影响本质处理,这里按照process_command来继续;
static int try_read_command(conn *c) {
assert(c != NULL);
assert(c->rcurr <= (c->rbuf + c->rsize));
assert(c->rbytes > 0);
if (c->protocol == negotiating_prot || c->transport == udp_transport) {
if ((unsigned char)c->rbuf[0] == (unsigned char)PROTOCOL_BINARY_REQ) {
c->protocol = binary_prot;
} else {
c->protocol = ascii_prot;
}
if (settings.verbose > 1) {
fprintf(stderr, "%d: Client using the %s protocol\n", c->sfd,
prot_text(c->protocol));
}
}
if (c->protocol == binary_prot) {
/* Do we have the complete packet header? */
if (c->rbytes < sizeof(c->binary_header)) {
/* need more data! */
return 0;
} else {
#ifdef NEED_ALIGN
if (((long)(c->rcurr)) % 8 != 0) {
/* must realign input buffer */
memmove(c->rbuf, c->rcurr, c->rbytes);
c->rcurr = c->rbuf;
if (settings.verbose > 1) {
fprintf(stderr, "%d: Realign input buffer\n", c->sfd);
}
}
#endif
protocol_binary_request_header* req;
req = (protocol_binary_request_header*)c->rcurr;
if (settings.verbose > 1) {
/* Dump the packet before we convert it to host order */
int ii;
fprintf(stderr, "<%d Read binary protocol data:", c->sfd);
for (ii = 0; ii < sizeof(req->bytes); ++ii) {
if (ii % 4 == 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "\n<%d ", c->sfd);
}
fprintf(stderr, " 0x%02x", req->bytes[ii]);
}
fprintf(stderr, "\n");
}
c->binary_header = *req;
c->binary_header.request.keylen = ntohs(req->request.keylen);
c->binary_header.request.bodylen = ntohl(req->request.bodylen);
c->binary_header.request.cas = ntohll(req->request.cas);
if (c->binary_header.request.magic != PROTOCOL_BINARY_REQ) {
if (settings.verbose) {
fprintf(stderr, "Invalid magic: %x\n",
c->binary_header.request.magic);
}
conn_set_state(c, conn_closing);
return -1;
}
c->msgcurr = 0;
c->msgused = 0;
c->iovused = 0;
if (add_msghdr(c) != 0) {
out_of_memory(c,
"SERVER_ERROR Out of memory allocating headers");
return 0;
}
c->cmd = c->binary_header.request.opcode;
c->keylen = c->binary_header.request.keylen;
c->opaque = c->binary_header.request.opaque;
/* clear the returned cas value */
c->cas = 0;
dispatch_bin_command(c);
c->rbytes -= sizeof(c->binary_header);
c->rcurr += sizeof(c->binary_header);
}
} else {
char *el, *cont;
if (c->rbytes == 0)
return 0;
el = memchr(c->rcurr, '\n', c->rbytes);
if (!el) {
if (c->rbytes > 1024) {
/*
* We didn't have a '\n' in the first k. This _has_ to be a
* large multiget, if not we should just nuke the connection.
*/
char *ptr = c->rcurr;
while (*ptr == ' ') { /* ignore leading whitespaces */
++ptr;
}
if (ptr - c->rcurr > 100 ||
(strncmp(ptr, "get ", 4) && strncmp(ptr, "gets ", 5))) {
conn_set_state(c, conn_closing);
return 1;
}
}
return 0;
}
cont = el + 1;
if ((el - c->rcurr) > 1 && *(el - 1) == '\r') {
el--;
}
*el = '\0';
assert(cont <= (c->rcurr + c->rbytes));
c->last_cmd_time = current_time;
process_command(c, c->rcurr); //处理
c->rbytes -= (cont - c->rcurr);
c->rcurr = cont;
assert(c->rcurr <= (c->rbuf + c->rsize));
}
return 1;
}处理命令
在process_command函数中,会根据命令的不同调用不同的处理函数,对应关系如下:
get <—–> process_get_command
bget <—–> process_get_command
add <—–> process_update_command
set <—–> process_update_command
replace <—–> process_update_command
prepend <—–> process_update_command
append <—–> process_update_command
cas <—–> process_update_command
incr <—–> process_arithmetic_command
gets <—–> process_get_command
decr <—–> process_arithmetic_command
delete <—–> process_delete_command
touch <—–> process_touch_command
stats <—–> process_stat
flush_all <—->
version <—–> 返回版本信息
quit <—–> 退出,关闭连接
slabs + reassign <—–> 重新分配slabs
slabs + automove <—–> 移动内存
lru_crawler + crawl <—-> LRU操作
static void process_command(conn *c, char *command) {
token_t tokens[MAX_TOKENS];
size_t ntokens;
int comm;
assert(c != NULL);
MEMCACHED_PROCESS_COMMAND_START(c->sfd, c->rcurr, c->rbytes);
if (settings.verbose > 1)
fprintf(stderr, "<%d %s\n", c->sfd, command);
/*
* for commands set/add/replace, we build an item and read the data
* directly into it, then continue in nread_complete().
*/
c->msgcurr = 0;
c->msgused = 0;
c->iovused = 0;
if (add_msghdr(c) != 0) {
out_of_memory(c, "SERVER_ERROR out of memory preparing response");
return;
}
ntokens = tokenize_command(command, tokens, MAX_TOKENS);
if (ntokens >= 3 &&
((strcmp(tokens[COMMAND_TOKEN].value, "get") == 0) ||
(strcmp(tokens[COMMAND_TOKEN].value, "bget") == 0))) {
process_get_command(c, tokens, ntokens, false);
} else if ((ntokens == 6 || ntokens == 7) &&
((strcmp(tokens[COMMAND_TOKEN].value, "add") == 0 && (comm = NREAD_ADD)) ||
(strcmp(tokens[COMMAND_TOKEN].value, "set") == 0 && (comm = NREAD_SET)) ||
(strcmp(tokens[COMMAND_TOKEN].value, "replace") == 0 && (comm = NREAD_REPLACE)) ||
(strcmp(tokens[COMMAND_TOKEN].value, "prepend") == 0 && (comm = NREAD_PREPEND)) ||
(strcmp(tokens[COMMAND_TOKEN].value, "append") == 0 && (comm = NREAD_APPEND)) )) {
process_update_command(c, tokens, ntokens, comm, false);
} else if ((ntokens == 7 || ntokens == 8) && (strcmp(tokens[COMMAND_TOKEN].value, "cas") == 0 && (comm = NREAD_CAS))) {
process_update_command(c, tokens, ntokens, comm, true);
} else if ((ntokens == 4 || ntokens == 5) && (strcmp(tokens[COMMAND_TOKEN].value, "incr") == 0)) {
process_arithmetic_command(c, tokens, ntokens, 1);
} else if (ntokens >= 3 && (strcmp(tokens[COMMAND_TOKEN].value, "gets") == 0)) {
process_get_command(c, tokens, ntokens, true);
} else if ((ntokens == 4 || ntokens == 5) && (strcmp(tokens[COMMAND_TOKEN].value, "decr") == 0)) {
process_arithmetic_command(c, tokens, ntokens, 0);
} else if (ntokens >= 3 && ntokens <= 5 && (strcmp(tokens[COMMAND_TOKEN].value, "delete") == 0)) {
process_delete_command(c, tokens, ntokens);
} else if ((ntokens == 4 || ntokens == 5) && (strcmp(tokens[COMMAND_TOKEN].value, "touch") == 0)) {
process_touch_command(c, tokens, ntokens);
} else if (ntokens >= 2 && (strcmp(tokens[COMMAND_TOKEN].value, "stats") == 0)) {
process_stat(c, tokens, ntokens);
} else if (ntokens >= 2 && ntokens <= 4 && (strcmp(tokens[COMMAND_TOKEN].value, "flush_all") == 0)) {
time_t exptime = 0;
rel_time_t new_oldest = 0;
set_noreply_maybe(c, tokens, ntokens);
pthread_mutex_lock(&c->thread->stats.mutex);
c->thread->stats.flush_cmds++;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&c->thread->stats.mutex);
if (!settings.flush_enabled) {
// flush_all is not allowed but we log it on stats
out_string(c, "CLIENT_ERROR flush_all not allowed");
return;
}
if (ntokens != (c->noreply ? 3 : 2)) {
exptime = strtol(tokens[1].value, NULL, 10);
if(errno == ERANGE) {
out_string(c, "CLIENT_ERROR bad command line format");
return;
}
}
/*
If exptime is zero realtime() would return zero too, and
realtime(exptime) - 1 would overflow to the max unsigned
value. So we process exptime == 0 the same way we do when
no delay is given at all.
*/
if (exptime > 0) {
new_oldest = realtime(exptime);
} else { /* exptime == 0 */
new_oldest = current_time;
}
if (settings.use_cas) {
settings.oldest_live = new_oldest - 1;
if (settings.oldest_live <= current_time)
settings.oldest_cas = get_cas_id();
} else {
settings.oldest_live = new_oldest;
}
out_string(c, "OK");
return;
} else if (ntokens == 2 && (strcmp(tokens[COMMAND_TOKEN].value, "version") == 0)) {
out_string(c, "VERSION " VERSION);
} else if (ntokens == 2 && (strcmp(tokens[COMMAND_TOKEN].value, "quit") == 0)) {
conn_set_state(c, conn_closing);
} else if (ntokens == 2 && (strcmp(tokens[COMMAND_TOKEN].value, "shutdown") == 0)) {
if (settings.shutdown_command) {
conn_set_state(c, conn_closing);
raise(SIGINT);
} else {
out_string(c, "ERROR: shutdown not enabled");
}
} else if (ntokens > 1 && strcmp(tokens[COMMAND_TOKEN].value, "slabs") == 0) {
if (ntokens == 5 && strcmp(tokens[COMMAND_TOKEN + 1].value, "reassign") == 0) {
int src, dst, rv;
if (settings.slab_reassign == false) {
out_string(c, "CLIENT_ERROR slab reassignment disabled");
return;
}
src = strtol(tokens[2].value, NULL, 10);
dst = strtol(tokens[3].value, NULL, 10);
if (errno == ERANGE) {
out_string(c, "CLIENT_ERROR bad command line format");
return;
}
rv = slabs_reassign(src, dst);
switch (rv) {
case REASSIGN_OK:
out_string(c, "OK");
break;
case REASSIGN_RUNNING:
out_string(c, "BUSY currently processing reassign request");
break;
case REASSIGN_BADCLASS:
out_string(c, "BADCLASS invalid src or dst class id");
break;
case REASSIGN_NOSPARE:
out_string(c, "NOSPARE source class has no spare pages");
break;
case REASSIGN_SRC_DST_SAME:
out_string(c, "SAME src and dst class are identical");
break;
}
return;
} else if (ntokens == 4 &&
(strcmp(tokens[COMMAND_TOKEN + 1].value, "automove") == 0)) {
process_slabs_automove_command(c, tokens, ntokens);
} else {
out_string(c, "ERROR");
}
} else if (ntokens > 1 && strcmp(tokens[COMMAND_TOKEN].value, "lru_crawler") == 0) {
if (ntokens == 4 && strcmp(tokens[COMMAND_TOKEN + 1].value, "crawl") == 0) {
int rv;
if (settings.lru_crawler == false) {
out_string(c, "CLIENT_ERROR lru crawler disabled");
return;
}
rv = lru_crawler_crawl(tokens[2].value);
switch(rv) {
case CRAWLER_OK:
out_string(c, "OK");
break;
case CRAWLER_RUNNING:
out_string(c, "BUSY currently processing crawler request");
break;
case CRAWLER_BADCLASS:
out_string(c, "BADCLASS invalid class id");
break;
case CRAWLER_NOTSTARTED:
out_string(c, "NOTSTARTED no items to crawl");
break;
}
return;
} else if (ntokens == 4 && strcmp(tokens[COMMAND_TOKEN + 1].value, "tocrawl") == 0) {
uint32_t tocrawl;
if (!safe_strtoul(tokens[2].value, &tocrawl)) {
out_string(c, "CLIENT_ERROR bad command line format");
return;
}
settings.lru_crawler_tocrawl = tocrawl;
out_string(c, "OK");
return;
} else if (ntokens == 4 && strcmp(tokens[COMMAND_TOKEN + 1].value, "sleep") == 0) {
uint32_t tosleep;
if (!safe_strtoul(tokens[2].value, &tosleep)) {
out_string(c, "CLIENT_ERROR bad command line format");
return;
}
if (tosleep > 1000000) {
out_string(c, "CLIENT_ERROR sleep must be one second or less");
return;
}
settings.lru_crawler_sleep = tosleep;
out_string(c, "OK");
return;
} else if (ntokens == 3) {
if ((strcmp(tokens[COMMAND_TOKEN + 1].value, "enable") == 0)) {
if (start_item_crawler_thread() == 0) {
out_string(c, "OK");
} else {
out_string(c, "ERROR failed to start lru crawler thread");
}
} else if ((strcmp(tokens[COMMAND_TOKEN + 1].value, "disable") == 0)) {
if (stop_item_crawler_thread() == 0) {
out_string(c, "OK");
} else {
out_string(c, "ERROR failed to stop lru crawler thread");
}
} else {
out_string(c, "ERROR");
}
return;
} else {
out_string(c, "ERROR");
}
} else if ((ntokens == 3 || ntokens == 4) && (strcmp(tokens[COMMAND_TOKEN].value, "verbosity") == 0)) {
process_verbosity_command(c, tokens, ntokens);
} else {
out_string(c, "ERROR");
}
return;
}