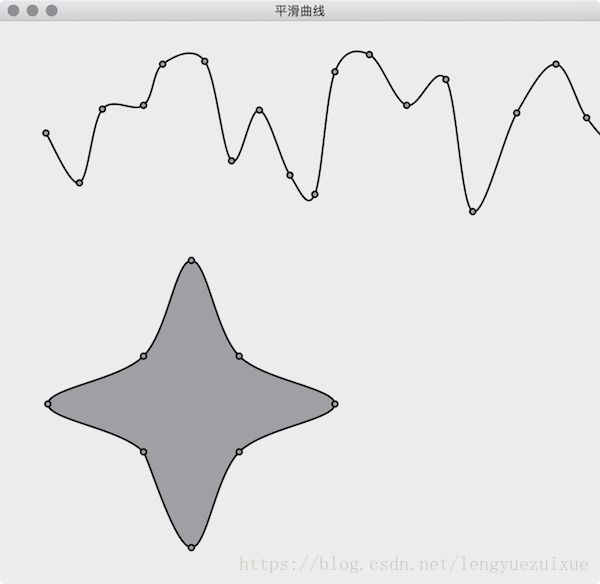
本文介绍在 Qt 中绘制平滑曲线的实现,调用下面的函数 SmoothCurveGenerator::generateSmoothCurve(points) 即可。默认曲线的 2 个顶点之间被分割为 16 个小线段来拟合曲线,下图展示了 tension 为 0.5(默认值) 的曲线效果,tension 并不是越大越好,默认的 0.5 大多数时候就不错。
SmoothCurveGenerator
// 文件名: SmoothCurveGenerator.h
#ifndef SMOOTHCURVEGENERATOR_H
#define SMOOTHCURVEGENERATOR_H
#include <QList>
#include <QPainterPath>
class SmoothCurveGenerator {
public:
/**
* @brief generateSmoothCurve 的重载函数
*/
static QPainterPath generateSmoothCurve(QList<QPointF> points, bool closed = false, double tension = 0.5, int numberOfSegments = 16);
/**
* @brief 使用传入的曲线顶点坐标创建平滑曲线。
*
* @param points 曲线顶点坐标数组,
* points[i+0] 是第 i 个点的 x 坐标,
* points[i+1] 是第 i 个点的 y 坐标
* @param closed 曲线是否封闭,默认不封闭
* @param tension 密集程度,默认为 0.5
* @param numberOfSegments 平滑曲线 2 个顶点间的线段数,默认为 16
* @return 平滑曲线的 QPainterPath
*/
static QPainterPath generateSmoothCurve(QList<double>points, bool closed = false, double tension = 0.5, int numberOfSegments = 16);
};
#endif // SMOOTHCURVEGENERATOR_H// 文件名: SmoothCurveGenerator.cpp
#include "SmoothCurveGenerator.h"
#include <QtMath>
QPainterPath SmoothCurveGenerator::generateSmoothCurve(QList<QPointF> points, bool closed, double tension, int numberOfSegments) {
QList<double> ps;
foreach (QPointF p, points) {
ps << p.x() << p.y();
}
return SmoothCurveGenerator::generateSmoothCurve(ps, closed, tension, numberOfSegments);
}
QPainterPath SmoothCurveGenerator::generateSmoothCurve(QList<double> points, bool closed, double tension, int numberOfSegments) {
QList<double> ps(points); // clone array so we don't change the original points
QList<double> result; // generated smooth curve coordinates
double x, y;
double t1x, t2x, t1y, t2y;
double c1, c2, c3, c4;
double st;
// The algorithm require a previous and next point to the actual point array.
// Check if we will draw closed or open curve.
// If closed, copy end points to beginning and first points to end
// If open, duplicate first points to befinning, end points to end
if (closed) {
ps.prepend(points[points.length() - 1]);
ps.prepend(points[points.length() - 2]);
ps.prepend(points[points.length() - 1]);
ps.prepend(points[points.length() - 2]);
ps.append(points[0]);
ps.append(points[1]);
} else {
ps.prepend(points[1]); // copy 1st point and insert at beginning
ps.prepend(points[0]);
ps.append(points[points.length() - 2]); // copy last point and append
ps.append(points[points.length() - 1]);
}
// 1. loop goes through point array
// 2. loop goes through each segment between the 2 points + 1e point before and after
for (int i = 2; i < (ps.length() - 4); i += 2) {
// calculate tension vectors
t1x = (ps[i + 2] - ps[i - 2]) * tension;
t2x = (ps[i + 4] - ps[i - 0]) * tension;
t1y = (ps[i + 3] - ps[i - 1]) * tension;
t2y = (ps[i + 5] - ps[i + 1]) * tension;
for (int t = 0; t <= numberOfSegments; t++) {
// calculate step
st = (double)t / (double)numberOfSegments;
// calculate cardinals
c1 = 2 * qPow(st, 3) - 3 * qPow(st, 2) + 1;
c2 = -2 * qPow(st, 3) + 3 * qPow(st, 2);
c3 = qPow(st, 3) - 2 * qPow(st, 2) + st;
c4 = qPow(st, 3) - qPow(st, 2);
// calculate x and y cords with common control vectors
x = c1 * ps[i] + c2 * ps[i + 2] + c3 * t1x + c4 * t2x;
y = c1 * ps[i + 1] + c2 * ps[i + 3] + c3 * t1y + c4 * t2y;
//store points in array
result << x << y;
}
}
// 使用的平滑曲线的坐标创建 QPainterPath
QPainterPath path;
path.moveTo(result[0], result[1]);
for (int i = 2; i < result.length() - 2; i += 2) {
path.lineTo(result[i+0], result[i+1]);
}
if (closed) {
path.closeSubpath();
}
return path;
}Form
// 文件名: Form.h
#ifndef FORM_H
#define FORM_H
#include <QWidget>
#include <QList>
#include <QPainterPath>
class Form : public QWidget {
Q_OBJECT
public:
explicit Form(QWidget *parent = 0);
~Form();
protected:
void paintEvent(QPaintEvent *event) Q_DECL_OVERRIDE;
private:
QList<QPointF> points1; // 曲线一的顶点数组
QList<QPointF> points2; // 曲线二的顶点数组
QPainterPath smoothCurvePath1; // 平滑曲线一
QPainterPath smoothCurvePath2; // 平滑曲线二
};
#endif // FORM_H/ 文件名: Form.cpp
#include "Form.h"
#include "SmoothCurveGenerator.h"
#include <QDebug>
#include <QPainter>
#include <QDateTime>
Form::Form(QWidget *parent) : QWidget(parent) {
qsrand(QDateTime::currentDateTime().toTime_t());
// 随机生成曲线第一条曲线的坐标
int x = 0, y = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 100; ++i) {
x += qrand() % 30 + 20;
y = qrand() % 180 + 30;
points1 << QPointF(x, y);
}
// 第二条星行曲线的坐标
points2 << QPointF(0, 150) << QPointF(50, 50) << QPointF(150, 0) << QPointF(50, -50)
<< QPointF(0, -150) << QPointF(-50, -50) << QPointF(-150, 0) << QPointF(-50, 50);
// 使用曲线的坐标生成平滑曲线
smoothCurvePath1 = SmoothCurveGenerator::generateSmoothCurve(points1); // 第一条曲线不封闭
smoothCurvePath2 = SmoothCurveGenerator::generateSmoothCurve(points2, true); // 第二条曲线是封闭的
}
Form::~Form() {
}
void Form::paintEvent(QPaintEvent *) {
QPainter painter(this);
painter.setRenderHint(QPainter::Antialiasing);
painter.setPen(QPen(Qt::black, 2));
// 绘制第一条平滑曲线和曲线上的顶点
painter.drawPath(smoothCurvePath1);
painter.setBrush(Qt::gray);
for (int i = 0; i < points1.length() ; i += 1) {
painter.drawEllipse(points1[i].x()-3, points1[i].y()-3, 6, 6);
}
// 绘制第二条平滑曲线和曲线上的顶点
painter.translate(200, 400);
painter.drawPath(smoothCurvePath2);
for (int i = 0; i < points2.length() ; i += 1) {
painter.drawEllipse(points2[i].x()-3, points2[i].y()-3, 6, 6);
}
}