本章从源码角度分析dubbo是如何进行服务的注册和服务的暴露,这个在dubbo整个机制中是非常重要也是比较复杂的,接下来就一步步来分析:其实dubbo使用起来还是比较简单的,比如看一个官方的demo,配置文件如下:这个是服务提供者的简单配置文件
<beans xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:dubbo="http://code.alibabatech.com/schema/dubbo" xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.5.xsd http://code.alibabatech.com/schema/dubbo http://code.alibabatech.com/schema/dubbo/dubbo.xsd"> <!-- 提供方应用信息,用于计算依赖关系 --> <dubbo:application name="demo-provider"/> <dubbo:registry protocol="zookeeper" address="127.0.0.1:2181" /> <!-- 用dubbo协议在20880端口暴露服务 --> <dubbo:protocol name="dubbo" port="20880"/> <!-- 和本地bean一样实现服务 --> <bean id="demoService" class="com.alibaba.dubbo.demo.provider.DemoServiceImpl"/> <!-- 声明需要暴露的服务接口 --> <dubbo:service interface="com.alibaba.dubbo.demo.DemoService" ref="demoService"/> </beans>
配置文件内容很简单,主要定义了服务接口和服务实现类以及协议和注册中心,但是dubbo是如何把它们有机的整合起来呢?这里面有很多的准备工作要做..,首先dubbo为了配置文件比较好维护,进行xsd扩展并和spring进行了结合,我们需要先熟悉一下这个实现过程.因为上面的配置标签都是通过这个解析之后转换成dubbo特定的配置实体类信息.一般完成一个自定义xsd的步骤如下:
& 设计配置标签属性
& 设计对应的javabean
& 编写NamespaceHandlerSupport
& 编写BeanDefinitionParser
& 编写spring.handlers和spring.schema进行串联
接下来看看dubbo是怎么进行实现的:
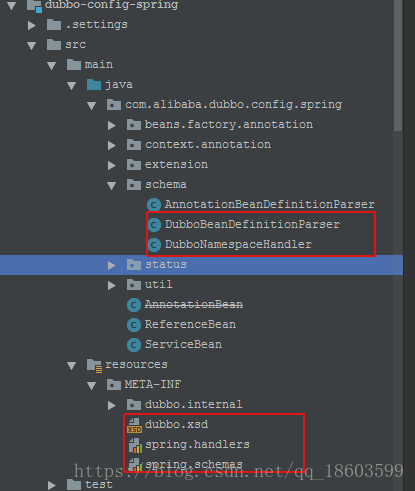
1 编写DubboNameSpaceHandlerSupport
package com.alibaba.dubbo.config.spring.schema; import com.alibaba.dubbo.common.Version; import com.alibaba.dubbo.config.*; import com.alibaba.dubbo.config.spring.ReferenceBean; import com.alibaba.dubbo.config.spring.ServiceBean; import org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.NamespaceHandlerSupport; /** * DubboNamespaceHandler * * @export */ public class DubboNamespaceHandler extends NamespaceHandlerSupport { static { Version.checkDuplicate(DubboNamespaceHandler.class); } public void init() {
//注册各种element对应的parser registerBeanDefinitionParser("application", new DubboBeanDefinitionParser(ApplicationConfig.class, true)); registerBeanDefinitionParser("module", new DubboBeanDefinitionParser(ModuleConfig.class, true)); registerBeanDefinitionParser("registry", new DubboBeanDefinitionParser(RegistryConfig.class, true)); registerBeanDefinitionParser("monitor", new DubboBeanDefinitionParser(MonitorConfig.class, true)); registerBeanDefinitionParser("provider", new DubboBeanDefinitionParser(ProviderConfig.class, true)); registerBeanDefinitionParser("consumer", new DubboBeanDefinitionParser(ConsumerConfig.class, true)); registerBeanDefinitionParser("protocol", new DubboBeanDefinitionParser(ProtocolConfig.class, true)); registerBeanDefinitionParser("service", new DubboBeanDefinitionParser(ServiceBean.class, true)); registerBeanDefinitionParser("reference", new DubboBeanDefinitionParser(ReferenceBean.class, false)); registerBeanDefinitionParser("annotation", new AnnotationBeanDefinitionParser()); } }
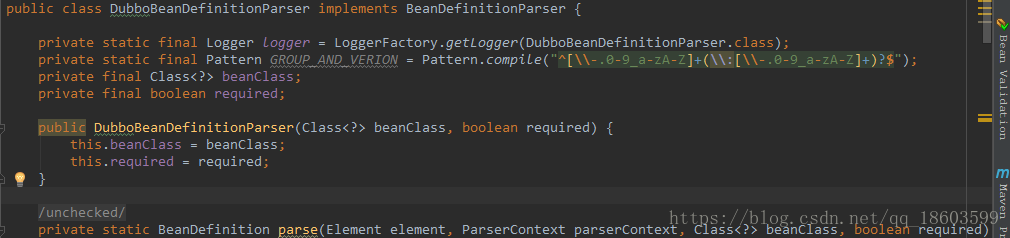
2 编写DubboBeanDefinitionParser进行element标签解析:主要就是parse方法
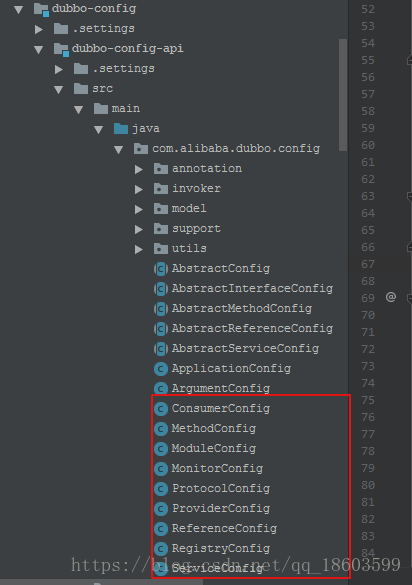
这些配置是有专门的javabean与之对应的:主要config模块:
ConsumerConfig:消费者的配置信息
MethodConfig:方法的配置信息
ProtocolConfig:协议的配置信息
ReferenceConfig:服务引用的配置信息
RegistryConfig:注册中心的配置信息
ServiceConfig:服务暴露的配置信息
而最后一个ServiceConfig这个类非常重要因为其实它本质是一个ServiceBean,看一下源码
public class ServiceBean<T> extends ServiceConfig<T> implements InitializingBean, DisposableBean, ApplicationContextAware, ApplicationListener<ContextRefreshedEvent>, BeanNameAware
这个类因为实现了spring里面的很多的接口,其中有一个很重要的方法是afterPropertiesSet():看一下这个方法源代码
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception { if (getProvider() == null) { Map<String, ProviderConfig> providerConfigMap = applicationContext == null ? null : BeanFactoryUtils.beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors(applicationContext, ProviderConfig.class, false, false); if (providerConfigMap != null && providerConfigMap.size() > 0) { Map<String, ProtocolConfig> protocolConfigMap = applicationContext == null ? null : BeanFactoryUtils.beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors(applicationContext, ProtocolConfig.class, false, false); if ((protocolConfigMap == null || protocolConfigMap.size() == 0) && providerConfigMap.size() > 1) { // backward compatibility List<ProviderConfig> providerConfigs = new ArrayList<ProviderConfig>(); for (ProviderConfig config : providerConfigMap.values()) { if (config.isDefault() != null && config.isDefault().booleanValue()) { providerConfigs.add(config); } } if (providerConfigs.size() > 0) { setProviders(providerConfigs); } } else { ProviderConfig providerConfig = null; for (ProviderConfig config : providerConfigMap.values()) { if (config.isDefault() == null || config.isDefault().booleanValue()) { if (providerConfig != null) { throw new IllegalStateException("Duplicate provider configs: " + providerConfig + " and " + config); } providerConfig = config; } } if (providerConfig != null) { setProvider(providerConfig); } } } } if (getApplication() == null && (getProvider() == null || getProvider().getApplication() == null)) { Map<String, ApplicationConfig> applicationConfigMap = applicationContext == null ? null : BeanFactoryUtils.beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors(applicationContext, ApplicationConfig.class, false, false); if (applicationConfigMap != null && applicationConfigMap.size() > 0) { ApplicationConfig applicationConfig = null; for (ApplicationConfig config : applicationConfigMap.values()) { if (config.isDefault() == null || config.isDefault().booleanValue()) { if (applicationConfig != null) { throw new IllegalStateException("Duplicate application configs: " + applicationConfig + " and " + config); } applicationConfig = config; } } if (applicationConfig != null) { setApplication(applicationConfig); } } } if (getModule() == null && (getProvider() == null || getProvider().getModule() == null)) { Map<String, ModuleConfig> moduleConfigMap = applicationContext == null ? null : BeanFactoryUtils.beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors(applicationContext, ModuleConfig.class, false, false); if (moduleConfigMap != null && moduleConfigMap.size() > 0) { ModuleConfig moduleConfig = null; for (ModuleConfig config : moduleConfigMap.values()) { if (config.isDefault() == null || config.isDefault().booleanValue()) { if (moduleConfig != null) { throw new IllegalStateException("Duplicate module configs: " + moduleConfig + " and " + config); } moduleConfig = config; } } if (moduleConfig != null) { setModule(moduleConfig); } } } if ((getRegistries() == null || getRegistries().size() == 0) && (getProvider() == null || getProvider().getRegistries() == null || getProvider().getRegistries().size() == 0) && (getApplication() == null || getApplication().getRegistries() == null || getApplication().getRegistries().size() == 0)) { Map<String, RegistryConfig> registryConfigMap = applicationContext == null ? null : BeanFactoryUtils.beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors(applicationContext, RegistryConfig.class, false, false); if (registryConfigMap != null && registryConfigMap.size() > 0) { List<RegistryConfig> registryConfigs = new ArrayList<RegistryConfig>(); for (RegistryConfig config : registryConfigMap.values()) { if (config.isDefault() == null || config.isDefault().booleanValue()) { registryConfigs.add(config); } } if (registryConfigs != null && registryConfigs.size() > 0) { super.setRegistries(registryConfigs); } } } if (getMonitor() == null && (getProvider() == null || getProvider().getMonitor() == null) && (getApplication() == null || getApplication().getMonitor() == null)) { Map<String, MonitorConfig> monitorConfigMap = applicationContext == null ? null : BeanFactoryUtils.beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors(applicationContext, MonitorConfig.class, false, false); if (monitorConfigMap != null && monitorConfigMap.size() > 0) { MonitorConfig monitorConfig = null; for (MonitorConfig config : monitorConfigMap.values()) { if (config.isDefault() == null || config.isDefault().booleanValue()) { if (monitorConfig != null) { throw new IllegalStateException("Duplicate monitor configs: " + monitorConfig + " and " + config); } monitorConfig = config; } } if (monitorConfig != null) { setMonitor(monitorConfig); } } } if ((getProtocols() == null || getProtocols().size() == 0) && (getProvider() == null || getProvider().getProtocols() == null || getProvider().getProtocols().size() == 0)) { Map<String, ProtocolConfig> protocolConfigMap = applicationContext == null ? null : BeanFactoryUtils.beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors(applicationContext, ProtocolConfig.class, false, false); if (protocolConfigMap != null && protocolConfigMap.size() > 0) { List<ProtocolConfig> protocolConfigs = new ArrayList<ProtocolConfig>(); for (ProtocolConfig config : protocolConfigMap.values()) { if (config.isDefault() == null || config.isDefault().booleanValue()) { protocolConfigs.add(config); } } if (protocolConfigs != null && protocolConfigs.size() > 0) { super.setProtocols(protocolConfigs); } } } if (getPath() == null || getPath().length() == 0) { if (beanName != null && beanName.length() > 0 && getInterface() != null && getInterface().length() > 0 && beanName.startsWith(getInterface())) { setPath(beanName); } } if (!isDelay()) { export(); } }
红色标注的方法基本上都是准备前的工作要做,而蓝色的export方法是最核心,它是暴露服务的方法,而它其实是调用ServiceConfig的export方法:
/** * 暴露服务 */ public synchronized void export() { if (provider != null) { if (export == null) { export = provider.getExport(); } if (delay == null) { delay = provider.getDelay(); } } if (export != null && !export) { return; } //根据参数配置 决定是否延迟服务的暴露 if (delay != null && delay > 0) { delayExportExecutor.schedule(new Runnable() { public void run() { doExport(); } }, delay, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS); } else { doExport(); } }
而它继续调用doExport方法:做一些列的检查工作和暴露服务的URL
if (unexported) { throw new IllegalStateException("Already unexported!"); } if (exported) { return; } exported = true; if (interfaceName == null || interfaceName.length() == 0) { throw new IllegalStateException("<dubbo:service interface=\"\" /> interface not allow null!"); } checkDefault(); if (provider != null) { if (application == null) { application = provider.getApplication(); } if (module == null) { module = provider.getModule(); } if (registries == null) { registries = provider.getRegistries(); } if (monitor == null) { monitor = provider.getMonitor(); } if (protocols == null) { protocols = provider.getProtocols(); } } if (module != null) { if (registries == null) { registries = module.getRegistries(); } if (monitor == null) { monitor = module.getMonitor(); } } if (application != null) { if (registries == null) { registries = application.getRegistries(); } if (monitor == null) { monitor = application.getMonitor(); } } if (ref instanceof GenericService) { interfaceClass = GenericService.class; if (StringUtils.isEmpty(generic)) { generic = Boolean.TRUE.toString(); } } else { try { interfaceClass = Class.forName(interfaceName, true, Thread.currentThread() .getContextClassLoader()); } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { throw new IllegalStateException(e.getMessage(), e); } checkInterfaceAndMethods(interfaceClass, methods); checkRef(); generic = Boolean.FALSE.toString(); } if (local != null) { if ("true".equals(local)) { local = interfaceName + "Local"; } Class<?> localClass; try { localClass = ClassHelper.forNameWithThreadContextClassLoader(local); } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { throw new IllegalStateException(e.getMessage(), e); } if (!interfaceClass.isAssignableFrom(localClass)) { throw new IllegalStateException("The local implementation class " + localClass.getName() + " not implement interface " + interfaceName); } } if (stub != null) { if ("true".equals(stub)) { stub = interfaceName + "Stub"; } Class<?> stubClass; try { stubClass = ClassHelper.forNameWithThreadContextClassLoader(stub); } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { throw new IllegalStateException(e.getMessage(), e); } if (!interfaceClass.isAssignableFrom(stubClass)) { throw new IllegalStateException("The stub implementation class " + stubClass.getName() + " not implement interface " + interfaceName); } } checkApplication(); checkRegistry(); checkProtocol(); appendProperties(this); checkStubAndMock(interfaceClass); if (path == null || path.length() == 0) { path = interfaceName; } doExportUrls();//暴露服务的URL:经过参数的组装 ProviderModel providerModel = new ProviderModel(getUniqueServiceName(), this, ref); ApplicationModel.initProviderModel(getUniqueServiceName(), providerModel); }
而它继续调用
private void doExportUrls() { List<URL> registryURLs = loadRegistries(true); for (ProtocolConfig protocolConfig : protocols) { //协议 和 注册 doExportUrlsFor1Protocol(protocolConfig, registryURLs); } }
doExportUrlsFor1Protocol 这个方法比较冗长,接下来只分析核心的代码,它主要提供了本地暴露和远程暴露,
// export to local if the config is not remote (export to remote only when config is remote) if (!Constants.SCOPE_REMOTE.toString().equalsIgnoreCase(scope)) { exportLocal(url);//解决本地服务暴露 }
如果不是本地服务暴露:
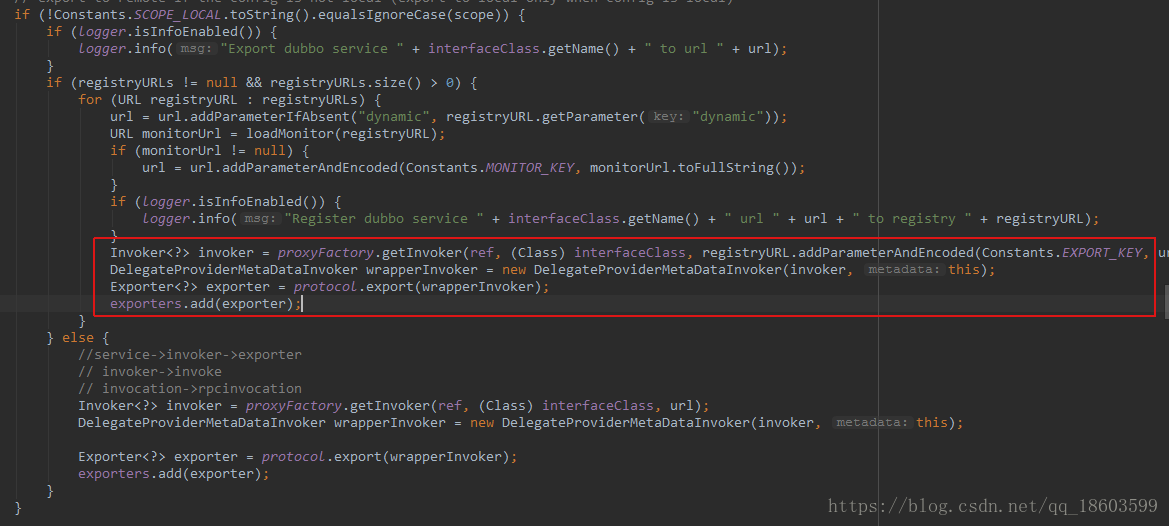
红色标注的是最关键的代码:
proxyFactory:这里最终实现是使用JavassitProxyFactory来通过代理获取到Invoker
wrapperInvoker:对Invoker进行了包装成服务提供方
protocol:这里最终使用的是RegisterProtocol来实现服务的注册,
OK 接下来在看
RegistryProtocol 这给类里面的重点方法分析export
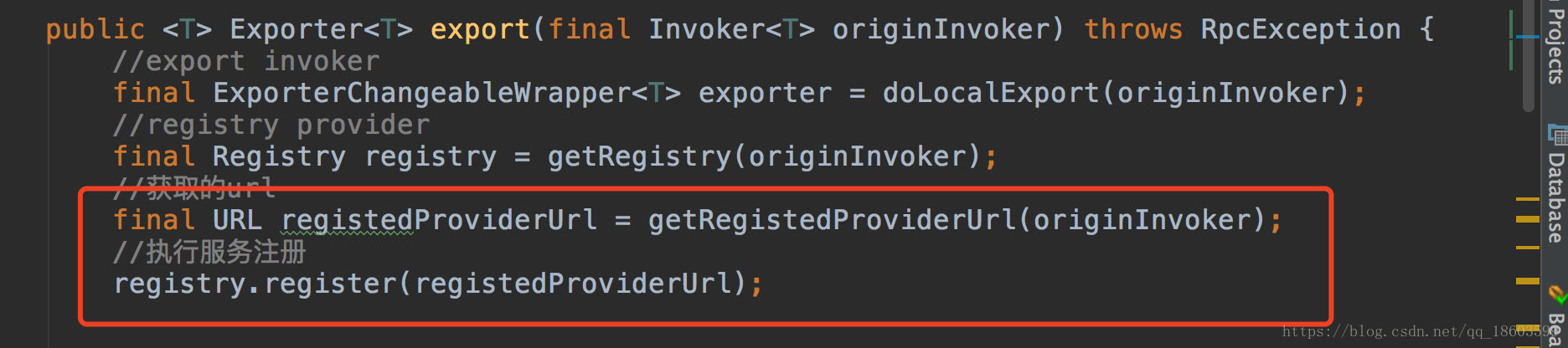
public <T> Exporter<T> export(final Invoker<T> originInvoker) throws RpcException { //暴露exporter final ExporterChangeableWrapper<T> exporter = doLocalExport(originInvoker); URL registryUrl = getRegistryUrl(originInvoker); //注册provider final Registry registry = getRegistry(originInvoker); final URL registedProviderUrl = getRegistedProviderUrl(originInvoker); //to judge to delay publish whether or not boolean register = registedProviderUrl.getParameter("register", true); ProviderConsumerRegTable.registerProvider(originInvoker, registryUrl, registedProviderUrl); if (register) { register(registryUrl, registedProviderUrl); ProviderConsumerRegTable.getProviderWrapper(originInvoker).setReg(true); } // 订阅 final URL overrideSubscribeUrl = getSubscribedOverrideUrl(registedProviderUrl); final OverrideListener overrideSubscribeListener = new OverrideListener(overrideSubscribeUrl, originInvoker); overrideListeners.put(overrideSubscribeUrl, overrideSubscribeListener); registry.subscribe(overrideSubscribeUrl, overrideSubscribeListener);//订阅 // 确保每一次返回的都是一个新的实例 return new DestroyableExporter<T>(exporter, originInvoker, overrideSubscribeUrl, registedProviderUrl); }
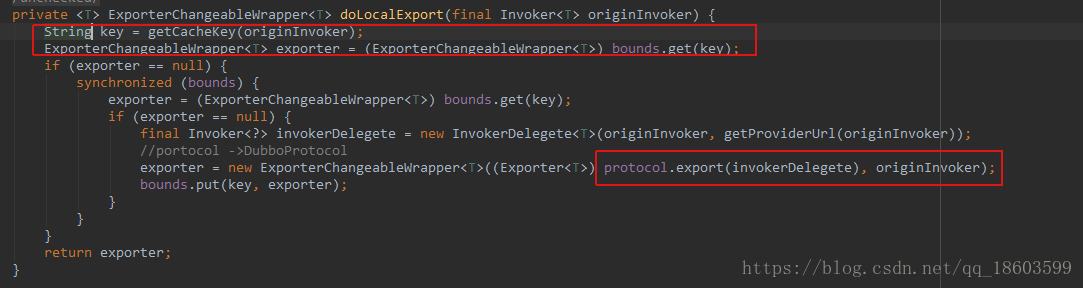
红色标注的代码,一个一个来分析:,首先看第一个dolocalExport方法
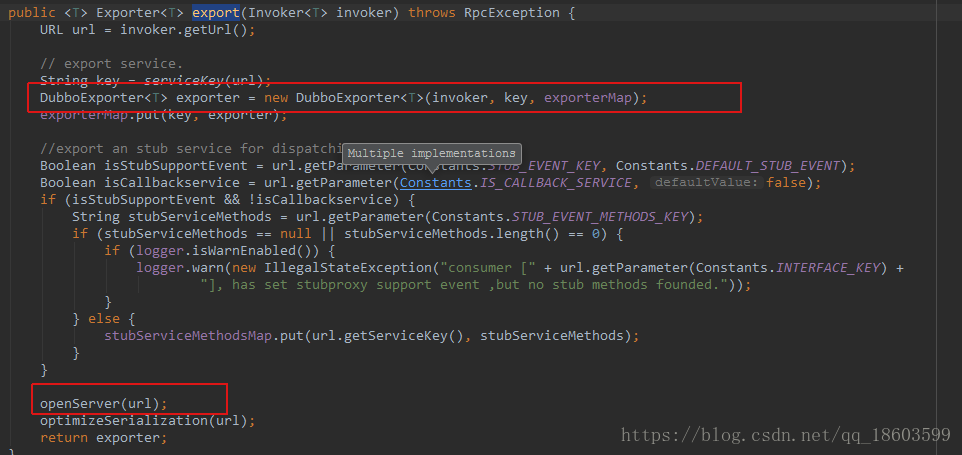
它返回的是一个要注册的exporter,但是是先从缓存中获取,没有再通过protocol来获取,这个protocol得协议实现是DubboProtocol,那就看一下这个类的相关方法:
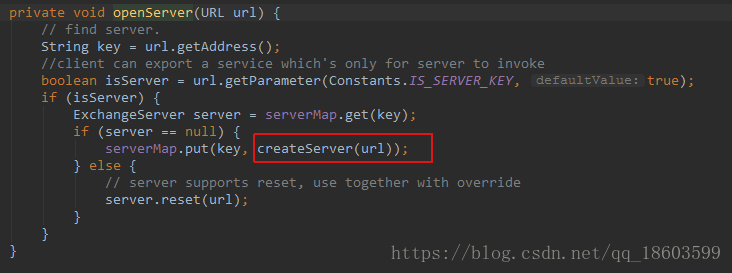
首先从缓存中获取,如果没有再使用openServer获取一个:
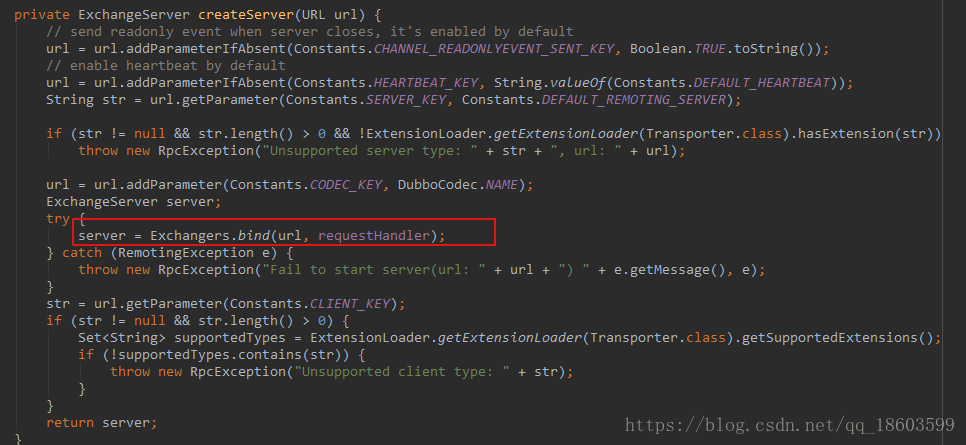
createServer核心实现:
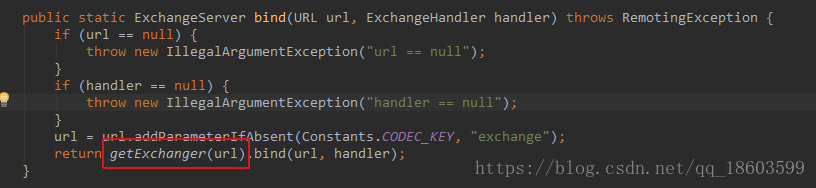
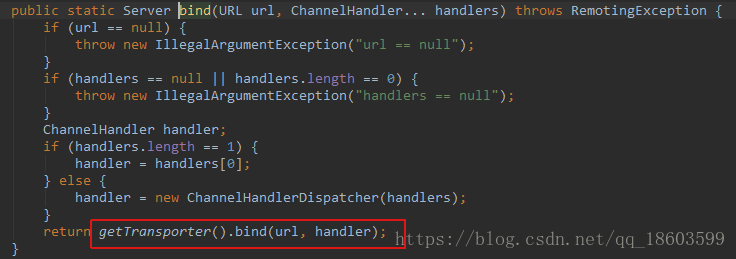
bind方法
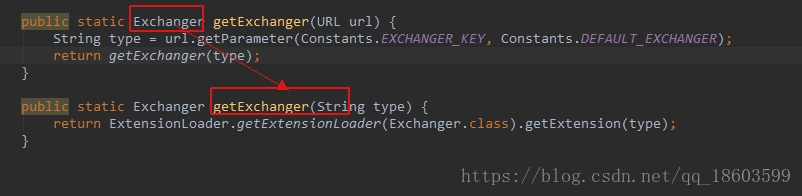
而这个方法实际调用的是
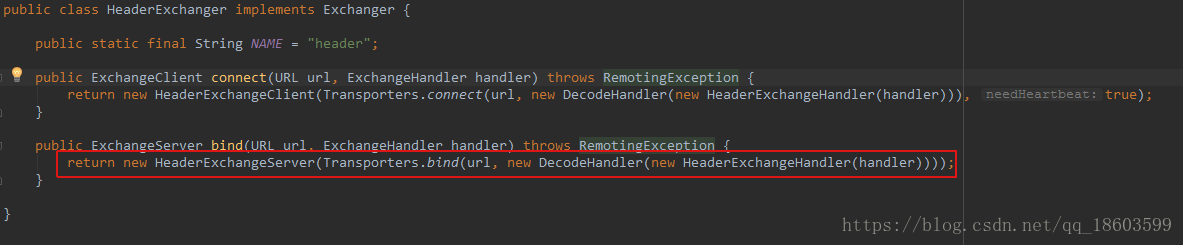
根据SPI实现机制这个Exchanger的实现是HeaderExchanger,继续看这个类的实现:
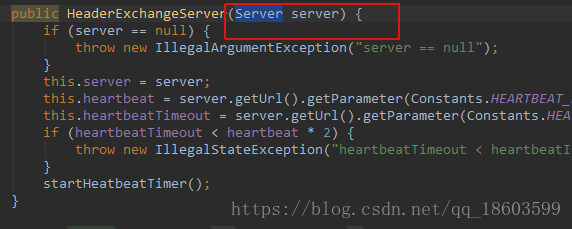
继续看HeaderExchangerServer这个实现:
它需要一个Server,这个Server是通过
获取的,继续看这个bind方法,
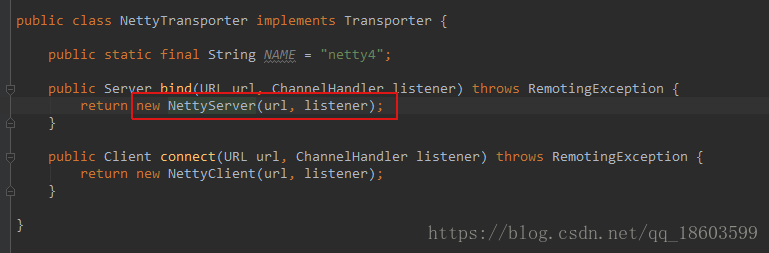
而getTransporter方法,是通过SPI实现的:
这个实现是在运行期适配的,最终实现是使用NettyTransporter,如下图所示
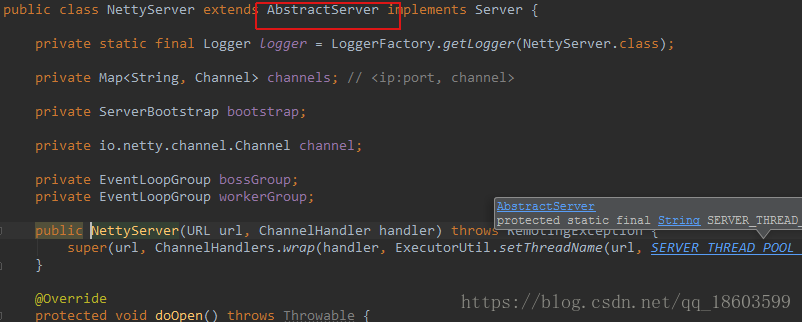
到这里才发现终于使用NettyServer,继续往下走:会发现它继承与父类
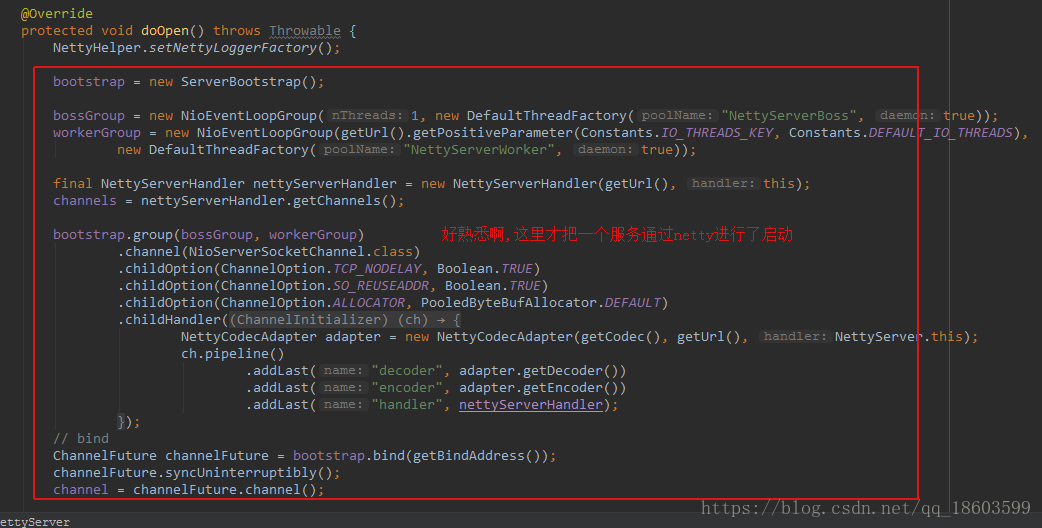
在看一下AbstractServer类,会发现调用了doOpen这个方法:
OK,再回过头来看一下doOpen这个方法:
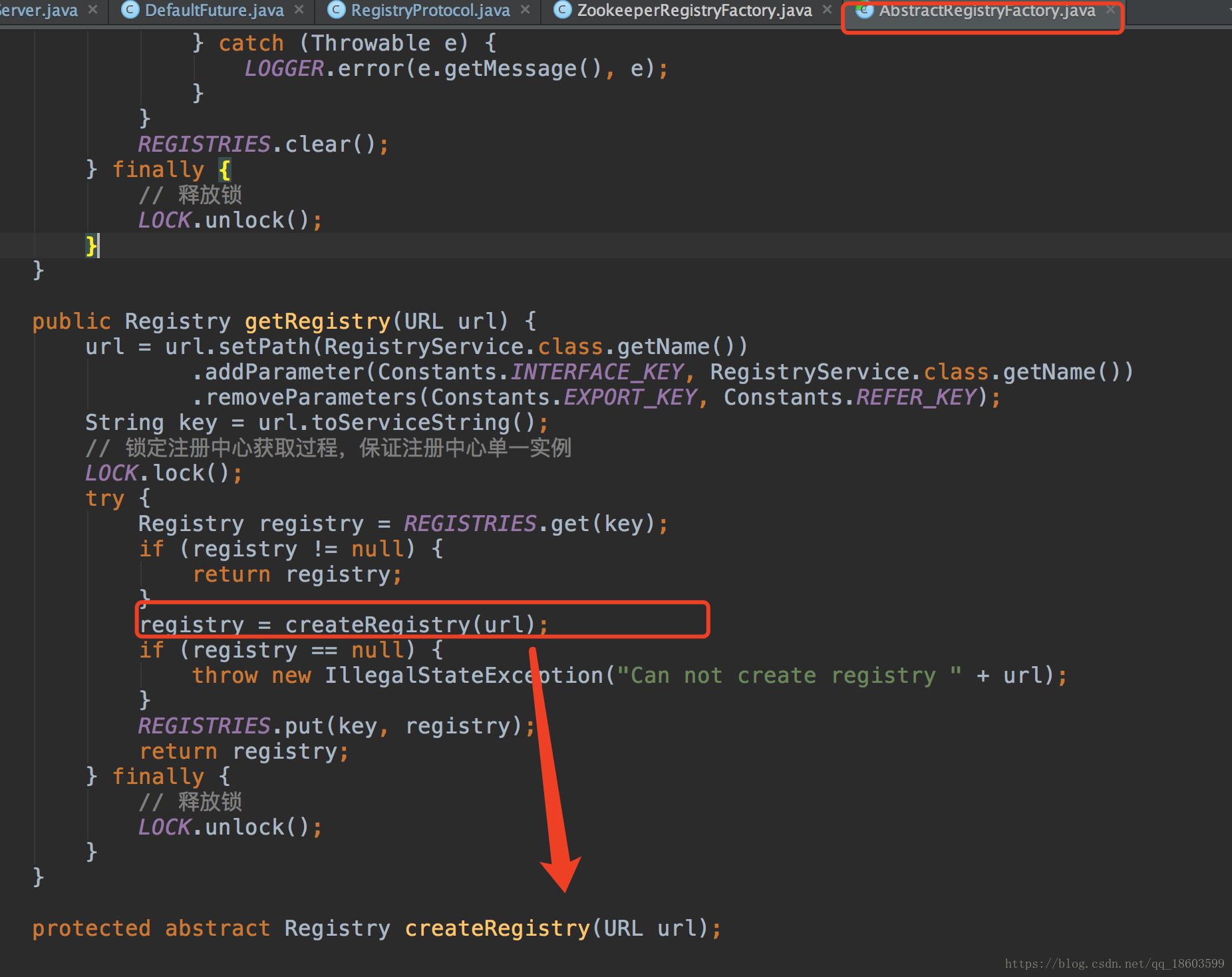
到此为止一个服务真正诞生了,接下来就可以把这个服务真正注册到注册中心了,接下回到RegistryProtocol,开始进行注册
进入getRegistry方法,
根据spi动态适配机制,这个工程最终实现是
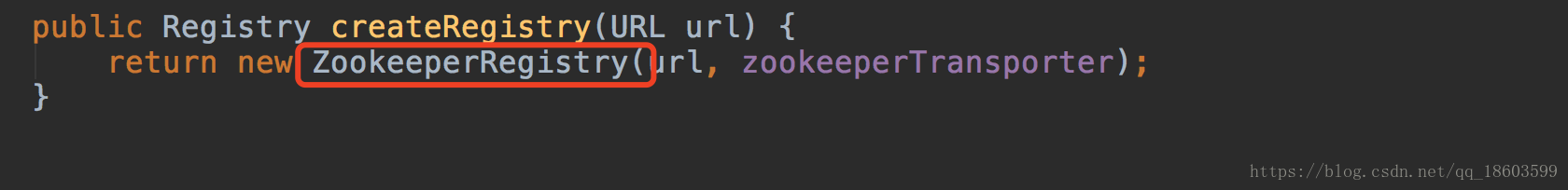
而它实现了自己的方法,用来返回的是一个基于zookeeperregistry实例
这个方法是被抽象的父类调用了,主要使用了模版设计模式.看一下代码截图:
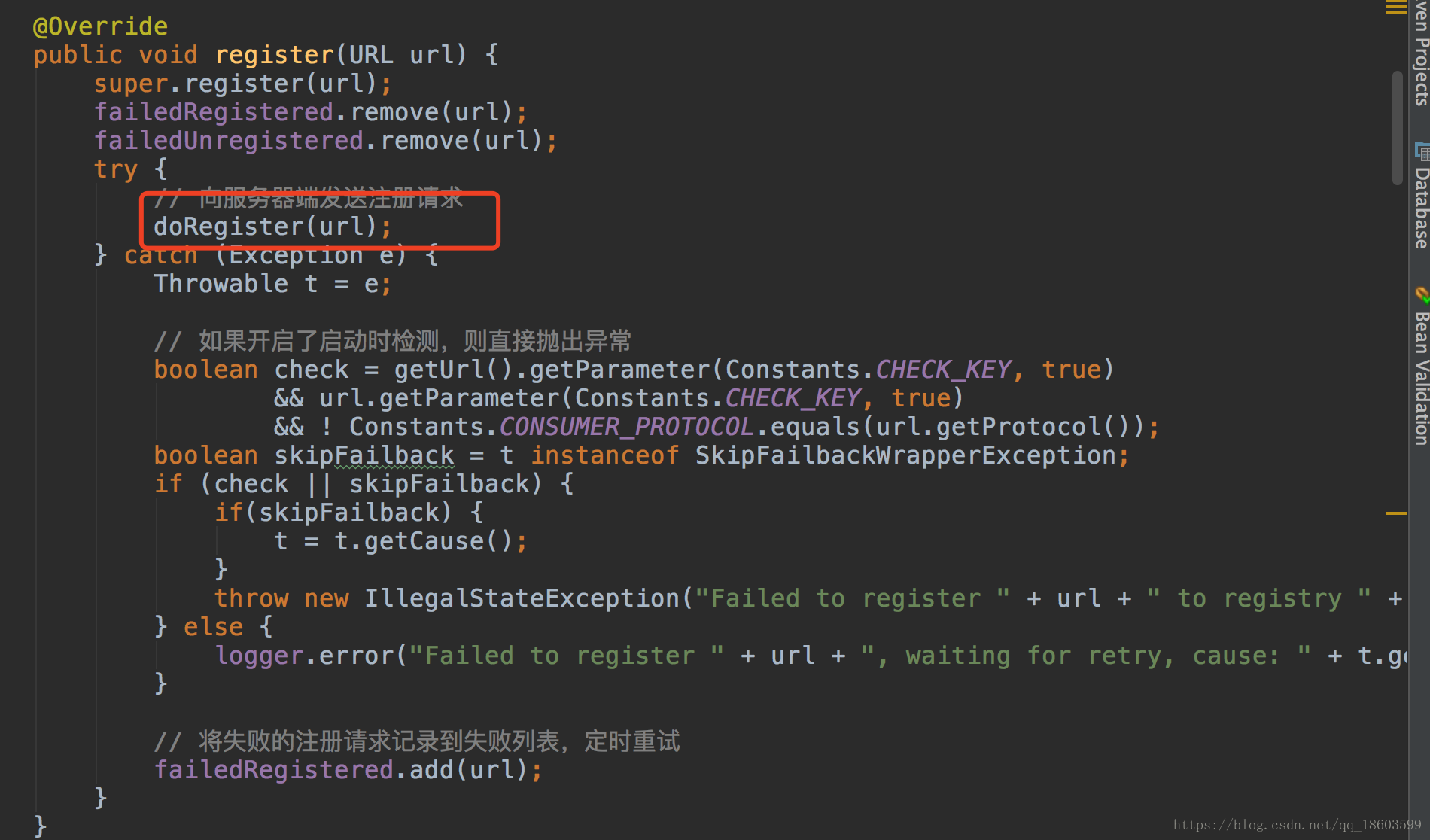
在获取到注册实例之后就开始调用registry方法进行真正服务的注册:
OK 那么按照刚才上面分析,使用的注册实例是
里面有这个方法
而它调用的是子类自己实现的是doregistry方法,所以还是要返回到子类看这个方法:
那么到这里服务注册就完成了,紧急着还要实现服务的订阅,真正的实现方法和注册是一致的,都是调用的父类的方法,然后子类实现真正的方法.看代码截图:还是在
FailbackRegistry.java这个类里面
对应的
ZookeeperRegistry类里面的dosubcribed方法的实现
protected void doSubscribe(final URL url, final NotifyListener listener) { try { if (Constants.ANY_VALUE.equals(url.getServiceInterface())) { String root = toRootPath(); ConcurrentMap<NotifyListener, ChildListener> listeners = zkListeners.get(url); if (listeners == null) { zkListeners.putIfAbsent(url, new ConcurrentHashMap<NotifyListener, ChildListener>()); listeners = zkListeners.get(url); } ChildListener zkListener = listeners.get(listener); if (zkListener == null) { listeners.putIfAbsent(listener, new ChildListener() { public void childChanged(String parentPath, List<String> currentChilds) { for (String child : currentChilds) { child = URL.decode(child); if (! anyServices.contains(child)) { anyServices.add(child); subscribe(url.setPath(child).addParameters(Constants.INTERFACE_KEY, child, Constants.CHECK_KEY, String.valueOf(false)), listener); } } } }); zkListener = listeners.get(listener); } zkClient.create(root, false); List<String> services = zkClient.addChildListener(root, zkListener); if (services != null && services.size() > 0) { for (String service : services) { service = URL.decode(service); anyServices.add(service); subscribe(url.setPath(service).addParameters(Constants.INTERFACE_KEY, service, Constants.CHECK_KEY, String.valueOf(false)), listener); } } } else { List<URL> urls = new ArrayList<URL>(); for (String path : toCategoriesPath(url)) { ConcurrentMap<NotifyListener, ChildListener> listeners = zkListeners.get(url); if (listeners == null) { zkListeners.putIfAbsent(url, new ConcurrentHashMap<NotifyListener, ChildListener>()); listeners = zkListeners.get(url); } ChildListener zkListener = listeners.get(listener); if (zkListener == null) { listeners.putIfAbsent(listener, new ChildListener() { public void childChanged(String parentPath, List<String> currentChilds) { ZookeeperRegistry.this.notify(url, listener, toUrlsWithEmpty(url, parentPath, currentChilds)); } }); zkListener = listeners.get(listener); } zkClient.create(path, false); List<String> children = zkClient.addChildListener(path, zkListener); if (children != null) { urls.addAll(toUrlsWithEmpty(url, path, children)); } } notify(url, listener, urls);//提醒消费者 } } catch (Throwable e) { throw new RpcException("Failed to subscribe " + url + " to zookeeper " + getUrl() + ", cause: " + e.getMessage(), e); } }
补充一下:DubboProtocol这个类在分析的时候还缺少了几点没有讲,就是它并不是立马返回一个invoker而是经过一些列的wrapper和一些列的filter,主要是下面这几个类
- ProtocolFilterWrapper负责初始化invoker所有的Filter。
- ProtocolListenerWrapper负责初始化暴露或引用服务的监听器。还有一个地方要注意就是serviceconfig中的protocol是一个复合类型的protocol,它实际上是由DubboProtocol+RegistryProtocol+ProtocolListenerWrapper+ProtocolFilterWrapper几个组成的:OK 到此为止关于provider server的注册和暴露源码分析就差不多了。。最后简单的做个总结:上面的过程存在一定的转化关系
- 远端service转化成invoker,invoker再转化成exporter(客户端需要的接口)