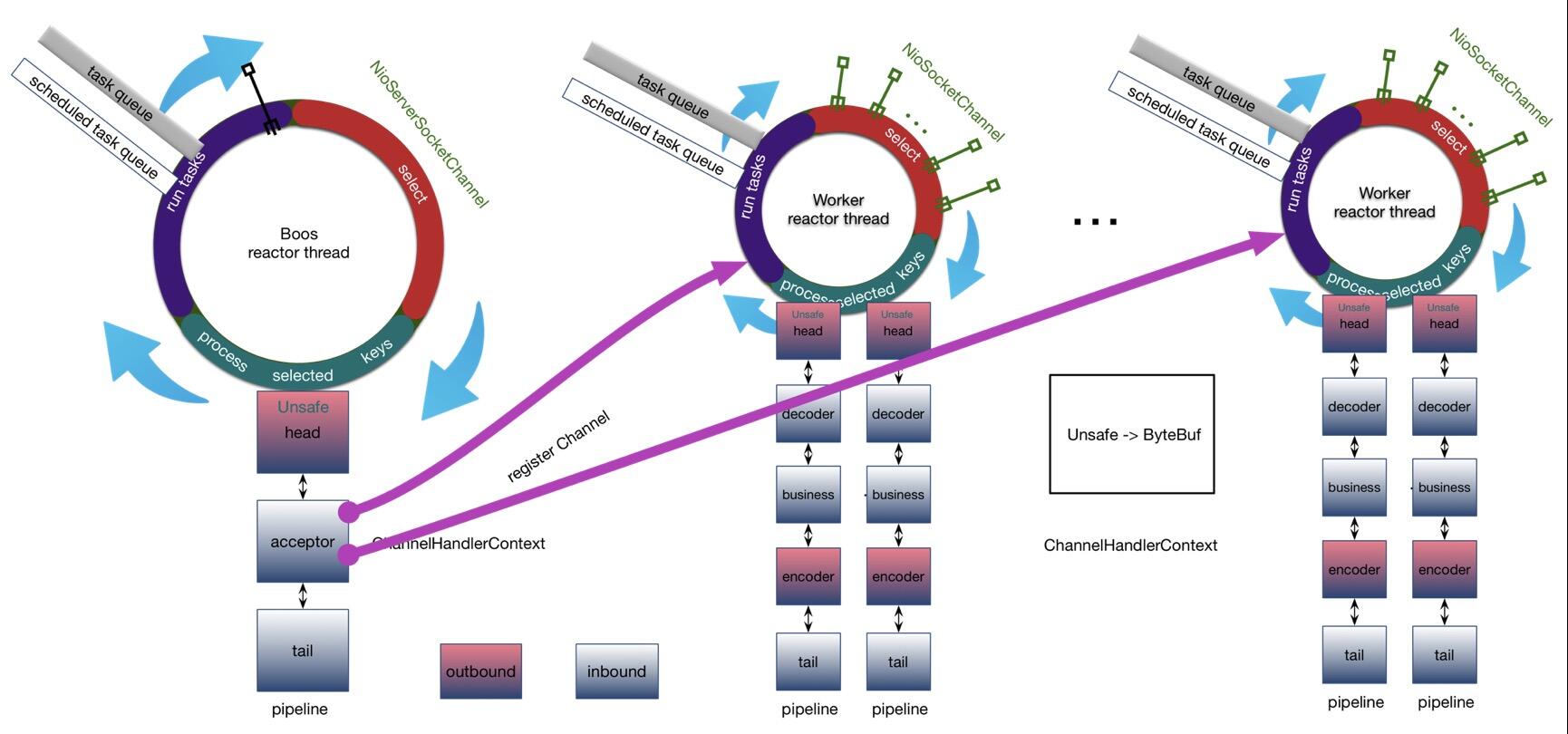
检测新连接
新连接检测从NioEventLoop的run()方法的第二阶段开始,处理io事件
processSelectedKey(SelectionKey k, AbstractNioChannel ch) 入口
->NioMessageUnsafe.read()
->doReadMessages(readBuf) while循环
->javaChannel().accept() 创建新连接对象
private void processSelectedKey(SelectionKey k, AbstractNioChannel ch) {
final AbstractNioChannel.NioUnsafe unsafe = ch.unsafe();
if (!k.isValid()) {
final EventLoop eventLoop;
try {
eventLoop = ch.eventLoop();
}
}
try {
int readyOps = k.readyOps();
// We first need to call finishConnect() before try to trigger a read(...) or write(...) as otherwise
// the NIO JDK channel implementation may throw a NotYetConnectedException.
if ((readyOps & SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT) != 0) {
// remove OP_CONNECT as otherwise Selector.select(..) will always return without blocking
// See https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/924
int ops = k.interestOps();
ops &= ~SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT;
k.interestOps(ops);
unsafe.finishConnect();
}
// Process OP_WRITE first as we may be able to write some queued buffers and so free memory.
if ((readyOps & SelectionKey.OP_WRITE) != 0) {
// Call forceFlush which will also take care of clear the OP_WRITE once there is nothing left to write
ch.unsafe().forceFlush();
}
// Also check for readOps of 0 to workaround possible JDK bug which may otherwise lead
// to a spin loop
if ((readyOps & (SelectionKey.OP_READ | SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT)) != 0 || readyOps == 0) {
//此处调用NioMessageUnsafe的read()
unsafe.read();
if (!ch.isOpen()) {
// Connection already closed - no need to handle write.
return;
}
}
} catch (CancelledKeyException ignored) {
unsafe.close(unsafe.voidPromise());
}
}
public void read() {
assert eventLoop().inEventLoop();
final ChannelConfig config = config();
final ChannelPipeline pipeline = pipeline();
final RecvByteBufAllocator.Handle allocHandle = unsafe().recvBufAllocHandle();
allocHandle.reset(config);
boolean closed = false;
Throwable exception = null;
try {
try {
do {
int localRead = doReadMessages(readBuf);
if (localRead == 0) {
break;
}
if (localRead < 0) {
closed = true;
break;
}
allocHandle.incMessagesRead(localRead);
} while (allocHandle.continueReading());
//此处的while最多accept 16条连接
} catch (Throwable t) {
exception = t;
}
int size = readBuf.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i ++) {
readPending = false;
pipeline.fireChannelRead(readBuf.get(i));
}
readBuf.clear();
allocHandle.readComplete();
pipeline.fireChannelReadComplete();
if (exception != null) {
closed = closeOnReadError(exception);
pipeline.fireExceptionCaught(exception);
}
if (closed) {
inputShutdown = true;
if (isOpen()) {
close(voidPromise());
}
}
}
}
protected int doReadMessages(List<Object> buf) throws Exception {
//ServerSocketChannel.accept() 方法监听新进来的连接。当 accept()方法返回的时候,它返回一个包含新进来的连接的 SocketChannel
//doReadMessages这个方法的名字起的有歧义,其实就是doAcceptChannel
//javaChannel()为服务端启动过程中创建的jdk的channel
SocketChannel ch = javaChannel().accept();
if (ch != null) {
/**
this 为服务端channel,即NioServerSocketChannel
ch 为jdk创建的客户端channel
NioSocketChannel 为netty包装的客户端channel
*/
buf.add(new NioSocketChannel(this, ch));
//获取到一个channel就返回
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
创建NioSocketChannel
NioSocketChannel(Channel parent, SocketChannel socket) 入口
public NioSocketChannel(Channel parent, SocketChannel socket) {
//调用父类方法
super(parent, socket);
config = new NioSocketChannelConfig(this, socket.socket());
}
protected AbstractNioChannel(Channel parent, SelectableChannel ch, int readInterestOp) {
super(parent);
this.ch = ch;
//readInterestOp为SelectionKey.OP_READ
this.readInterestOp = readInterestOp;
try {
ch.configureBlocking(false);
} catch (IOException e) {
}
}
protected AbstractChannel(Channel parent) {
//这个parent是创建此客户端channel的服务端channel
this.parent = parent;
//创建id unsafe pipeline
id = newId();
unsafe = newUnsafe();
pipeline = newChannelPipeline();
}
Channel的分类
新连接NioEventLoop分配和selector注册
服务端channel在初始化时,添加过一个特殊的handler ServerBootstrapAcceptor
for (int i = 0; i < size; i ++) {
readPending = false;
pipeline.fireChannelRead(readBuf.get(i));
}
前面的 pipeline.fireChannelRead(NioSocketChannel); 最终通过head->unsafe->ServerBootstrapAcceptor的调用链,调用到这里的 ServerBootstrapAcceptor 的channelRead方法
ServerBootstrapAcceptor中:添加childHandler,设置options和attrs,选择NioEventLoop并注册selector
private static class ServerBootstrapAcceptor extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
private final EventLoopGroup childGroup;
private final ChannelHandler childHandler;
private final Entry<ChannelOption<?>, Object>[] childOptions;
private final Entry<AttributeKey<?>, Object>[] childAttrs;
ServerBootstrapAcceptor(
EventLoopGroup childGroup, ChannelHandler childHandler,
Entry<ChannelOption<?>, Object>[] childOptions, Entry<AttributeKey<?>, Object>[] childAttrs) {
this.childGroup = childGroup;
this.childHandler = childHandler;
this.childOptions = childOptions;
this.childAttrs = childAttrs;
}
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) {
final Channel child = (Channel) msg;
child.pipeline().addLast(childHandler);
for (Entry<ChannelOption<?>, Object> e: childOptions) {
try {
if (!child.config().setOption((ChannelOption<Object>) e.getKey(), e.getValue())) {
logger.warn("Unknown channel option: " + e);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
logger.warn("Failed to set a channel option: " + child, t);
}
}
for (Entry<AttributeKey<?>, Object> e: childAttrs) {
child.attr((AttributeKey<Object>) e.getKey()).set(e.getValue());
}
try {
childGroup.register(child).addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture future) throws Exception {
if (!future.isSuccess()) {
forceClose(child, future.cause());
}
}
});
} catch (Throwable t) {
forceClose(child, t);
}
}
}
注册读事件
register0() 方法的时候,向selector注册的事件代码是0,而
readInterestOp对应的事件代码是
SelectionKey.OP_READ,参考前文中创建
NioSocketChannel 的过程,稍加推理,这里其实就是将
SelectionKey.OP_READ事件注册到selector中去,表示这条通道已经可以开始处理read事件了
@Override
protected void doBeginRead() throws Exception {
// Channel.read() or ChannelHandlerContext.read() was called
final SelectionKey selectionKey = this.selectionKey;
if (!selectionKey.isValid()) {
return;
}
readPending = true;
final int interestOps = selectionKey.interestOps();
if ((interestOps & readInterestOp) == 0) {
selectionKey.interestOps(interestOps | readInterestOp);
}
}
总结:
1、服务端创建NioServerSocketChannel后,会绑定到bossThread中,然后该channel,监听accept事件,有新的连接后创建一个新的客户端channel
2、通过封装jdk底层的channel创建 NioSocketChannel以及一系列的netty核心组件
3、将该条连接通过chooser,选择一条worker reactor线程绑定上去
4、注册读事件,开始新连接的读写
参考:
https://www.jianshu.com/p/0242b1d4dd21