1. 原始的UNet3D的CrossAttention和SparseCausalAttention
在重写的UNetPseudo3DConditionModel中,包含Attention的部分主要来自SpatioTemporalTransformerModel,而Attention主要来自其中的 SpatioTemporalTransformerBlock,其中主要包含两种CrossAttention和SparseCausalAttention(SparseCausalAttention继承自CorssAttention重写了它的forward方法)
CrossAttention
首先先介绍CrossAttention类:
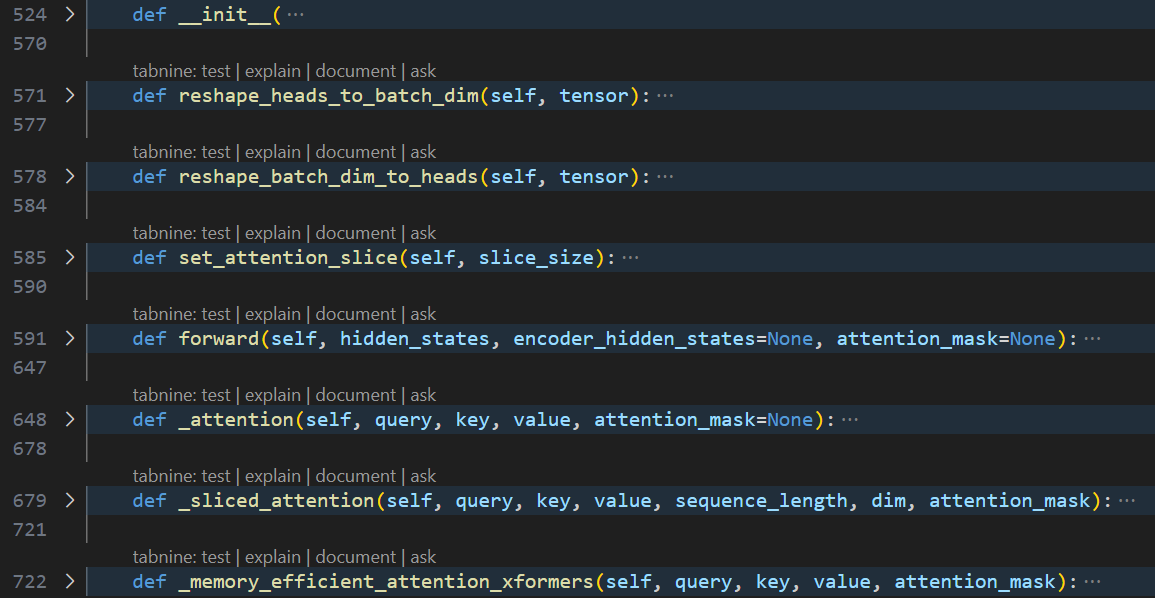
这是一个交叉注意力层的代码实现,用于模型中的注意力机制。该层接收一个查询(query)和一个编码器隐藏状态(encoder_hidden_states:key 和 value),并根据它们计算出注意力分数。具体实现如下:
- 初始化函数
__init__接收一些参数,包括查询维度(query_dim)、交叉注意力维度(cross_attention_dim)、头数(heads)、每个头的维度(dim_head)、dropout 概率(dropout)等。同时定义一些Linear layers:to_q、to_k、to_v、to_out([Linear, Dropout])、added_kv_proj_dim,以及GroupNorm layer。 - 分头与合头用于对张量进行形状变换操作,其中分头
reshape_heads_to_batch_dim把heads维度从dim维度变形到batch维度中:将(batch_size, seq_len, dim)转换为(batch_size * head_size, seq_len, dim // head_size);合头reshape_batch_dim_to_heads把heads维度从batch维度中还原到dim维度:将(batch_size * head_size, seq_len, dim // head_size)转换为(batch_size, seq_len, dim)。 - 在前向传播
forward方法中,首先对hidden_states(query)和encoder_hidden_states(key/value)进行一些形状变换和线性变换操作,将查询q、键k、值v分别通过Linear层to_q/k/v转换为内部维度(inner_dim)大小的张量,然后对张量进行分头reshape_heads_to_batch_dim。接下来,根据注意力分数的计算方式,对查询、键和值进行进一步处理。如果指定了添加的键值投影维度(added_kv_proj_dim),则将其与原始的k和v进行拼接。根据是否指定了注意力掩码(attention_mask)。进行attention(query, key, value, attention_mask)计算:计算attention_score,并进行 softmax 归一化。将attention_score与v相乘,得到最终的attention输出。可以选择普通的_attention、或者分片注意力_sliced_attention、或者xformors的_memory_efficient_attention_xformers。最后,通过to_out的线性层和 dropout 层对注意力输出进行进一步的线性变换和正则化处理,得到最终的输出结果。
def forward(self, hidden_states, encoder_hidden_states=None, attention_mask=None):
# hidden_states : q, encoder_hidden_states : k, v
batch_size, sequence_length, _ = hidden_states.shape
encoder_hidden_states = encoder_hidden_states
# 1. normalize hidden_states
if self.group_norm is not None: # normalization hidden_states
hidden_states = self.group_norm(hidden_states.transpose(1, 2)).transpose(1, 2)
# 2. linear project to q,k,v
query = self.to_q(hidden_states)
dim = query.shape[-1]
query = self.reshape_heads_to_batch_dim(query)
if self.added_kv_proj_dim is not None:
key = self.to_k(hidden_states)
value = self.to_v(hidden_states)
encoder_hidden_states_key_proj = self.add_k_proj(encoder_hidden_states)
encoder_hidden_states_value_proj = self.add_v_proj(encoder_hidden_states)
key = self.reshape_heads_to_batch_dim(key)
value = self.reshape_heads_to_batch_dim(value)
encoder_hidden_states_key_proj = self.reshape_heads_to_batch_dim(encoder_hidden_states_key_proj)
encoder_hidden_states_value_proj = self.reshape_heads_to_batch_dim(encoder_hidden_states_value_proj)
key = torch.concat([encoder_hidden_states_key_proj, key], dim=1)
value = torch.concat([encoder_hidden_states_value_proj, value], dim=1)
else:
encoder_hidden_states = encoder_hidden_states if encoder_hidden_states is not None else hidden_states
key = self.to_k(encoder_hidden_states)
value = self.to_v(encoder_hidden_states)
key = self.reshape_heads_to_batch_dim(key)
value = self.reshape_heads_to_batch_dim(value)
# 3. set attention mask
if attention_mask is not None:
if attention_mask.shape[-1] != query.shape[1]:
target_length = query.shape[1] # padding attention_mask with 0 to same_length of query
attention_mask = F.pad(attention_mask, (0, target_length), value=0.0) # (batch_size, sequence_length)
attention_mask = attention_mask.repeat_interleave(self.heads, dim=0) # repeat for heads (batch_size*heads, sequence_length)
# 4. do attention softmax(qk)/v : select _attention, _sliced_attention, _memory_efficient_attention_xformers
if self._use_memory_efficient_attention_xformers:
hidden_states = self._memory_efficient_attention_xformers(query, key, value, attention_mask)
# Some versions of xformers return output in fp32, cast it back to the dtype of the input
hidden_states = hidden_states.to(query.dtype)
else:
if self._slice_size is None or query.shape[0] // self._slice_size == 1:
hidden_states = self._attention(query, key, value, attention_mask)
else:
hidden_states = self._sliced_attention(query, key, value, sequence_length, dim, attention_mask)
# linear proj
hidden_states = self.to_out[0](hidden_states)
# dropout
hidden_states = self.to_out[1](hidden_states)
return hidden_states
- 这里我们只看一下普通的多头注意力
_attention,传入query,key,value,attention_mask。q和k计算attention_score,并进行 softmax 归一化。将attention_score与v相乘,得到最终的attention输出。其中关键的矩阵乘法操作torch.baddbmm(input, tensor1, tensor2, *, beta=1, alpha=1, out=None) → Tensor实现如下: o u t p u t = i n p u t ∗ β + α ( t e n s o r 1 @ t e n s o r 2 ) output = input*\beta + \alpha(tensor1 @ tensor2) output=input∗β+α(tensor1@tensor2)。重大疑问:这里的attention_scores = attention_scores + attention_mask是在做什么?难道不应该是乘mask吗? 因为这里的attention_mask已经【被动过手脚】,将原本为1的部分变为0,而原本为0的部分(即padding)变为一个较大的负数(-Nan),这样相加就得到了一个较大的负值,至于为什么要用【一个较大的负数】?因为这样一来经过softmax操作以后这一项就会变成接近0的小数。
def _attention(self, query, key, value, attention_mask=None):
if self.upcast_attention: # set float
query = query.float()
key = key.float()
# 1. attention_scores = scale * (q @ k)
attention_scores = torch.baddbmm(
torch.empty(query.shape[0], query.shape[1], key.shape[1], dtype=query.dtype, device=query.device),
query,
key.transpose(-1, -2),
beta=0,
alpha=self.scale,
)
# 2. use attention_mask (UnMask is 0, Mask is -Nan)
if attention_mask is not None:
attention_scores = attention_scores + attention_mask
if self.upcast_softmax:
attention_scores = attention_scores.float()
# 3. attention_map : attention_probs = Softmax(q @ k)
attention_probs = attention_scores.softmax(dim=-1)
# cast back to the original dtype
attention_probs = attention_probs.to(value.dtype)
# 4. compute attention output
hidden_states = torch.bmm(attention_probs, value)
# reshape hidden_states
hidden_states = self.reshape_batch_dim_to_heads(hidden_states)
return hidden_states
- 此外,还包含了一种分片计算注意力的方法
_sliced_attention,以节省计算资源。set_attention_slice用于设置分片大小slice_size。
SparseCausalAttention
稀疏因果自注意力SparseCausalAttention继承自CrossAttention,只重写了forward(本质上是时空自注意力机制,使用特定的帧之间的关系来计算SelfAttention,提高计算效率)
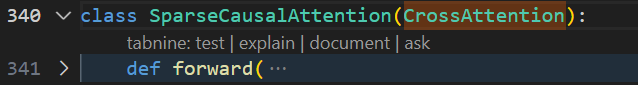
首先,如果k,v对应的encoder_hidden_states和attention_mask不为None,则抛出NotImplementedError。因为稀疏因果自注意力是Self Attention!!!,虽然复用了CrossAttention的代码,但计算不需要额外的key和value这些参数。
接下来,如果提供了group_norm,则对输入tokens hidden_states进行分组归一化(group normalization)操作。
然后,将输入张量转换为查询、键和值并重塑为多头形式。如果提供了帧数clip_length,则将key和value的frames维度从batch维度中拆分出来。
接着开始时空注意力帧选择,在计算第i帧的self-attention时,根据SparseCausalAttention_index来选择 key 和 value中对应的帧,来参与后续attention的计算(KV来自第i帧 z i z_i zi和中间帧第i帧 z [ n / / 2 ] z^{[n//2]} z[n//2]的拼接)
接下来,将key和value的frames维度还原回batch维度,并使用_attention方法,或_sliced_attention方法,或_memory_efficient_attention_xformers 计算 Spatial-temporal attention 输出:
S p a t i a l T e m p o r a l S e l f A t t e n t i o n = s o f t m a x ( W Q z i ⋅ ( W K [ z i ; z n 2 ] ) T ) ⋅ W V [ z i ; z n 2 ] SpatialTemporalSelfAttention=softmax(W^Qz^i\cdot (W^K[z^i;z^{\frac{n}{2}}])^T)\cdot W^V[z^i;z^{\frac{n}{2}}] SpatialTemporalSelfAttention=softmax(WQzi⋅(WK[zi;z2n])T)⋅WV[zi;z2n]
最后,通过线性变换和dropout层对注意力输出进行后处理,并返回结果。
class SparseCausalAttention(CrossAttention):
def forward(
self,
hidden_states,
encoder_hidden_states=None,
attention_mask=None,
clip_length: int = None,
SparseCausalAttention_index: list = [-1, 'first']
):
if (
self.added_kv_proj_dim is not None
or encoder_hidden_states is not None
or attention_mask is not None
):
raise NotImplementedError
if self.group_norm is not None:
hidden_states = self.group_norm(hidden_states.transpose(1, 2)).transpose(1, 2)
query = self.to_q(hidden_states)
dim = query.shape[-1]
query = self.reshape_heads_to_batch_dim(query)
key = self.to_k(hidden_states)
value = self.to_v(hidden_states)
if clip_length is not None:
key = rearrange(key, "(b f) d c -> b f d c", f=clip_length)
value = rearrange(value, "(b f) d c -> b f d c", f=clip_length)
# *********************** Start of Spatial-temporal attention **********
frame_index_list = []
# print(f'SparseCausalAttention_index {str(SparseCausalAttention_index)}')
if len(SparseCausalAttention_index) > 0:
for index in SparseCausalAttention_index: # select mid and last frame index
if isinstance(index, str):
if index == 'first':
frame_index = [0] * clip_length
if index == 'last':
frame_index = [clip_length-1] * clip_length
if (index == 'mid') or (index == 'middle'):
frame_index = [int(clip_length-1)//2] * clip_length
else:
assert isinstance(index, int), 'relative index must be int'
frame_index = torch.arange(clip_length) + index
frame_index = frame_index.clip(0, clip_length-1)
frame_index_list.append(frame_index)
key = torch.cat([key[:, frame_index] for frame_index in frame_index_list ], dim=2)
value = torch.cat([value[:, frame_index] for frame_index in frame_index_list ], dim=2)
# *********************** End of Spatial-temporal attention **********
key = rearrange(key, "b f d c -> (b f) d c", f=clip_length)
value = rearrange(value, "b f d c -> (b f) d c", f=clip_length)
key = self.reshape_heads_to_batch_dim(key)
value = self.reshape_heads_to_batch_dim(value)
if self._use_memory_efficient_attention_xformers:
hidden_states = self._memory_efficient_attention_xformers(query, key, value, attention_mask)
# Some versions of xformers return output in fp32, cast it back to the dtype of the input
hidden_states = hidden_states.to(query.dtype)
else:
if self._slice_size is None or query.shape[0] // self._slice_size == 1:
hidden_states = self._attention(query, key, value, attention_mask)
else:
hidden_states = self._sliced_attention(
query, key, value, hidden_states.shape[1], dim, attention_mask
)
# linear proj
hidden_states = self.to_out[0](hidden_states)
# dropout
hidden_states = self.to_out[1](hidden_states)
return hidden_states
2. register_attention_control的具体过程
register_attention_control函数传入model=UNet 和controller=AttentionStore,为UNet的交叉注意力CrossAttention 和 稀疏自注意力SparseCausalAttention关联上AttentionStore 作为 controller,用于保存和管理 attention map,用于后期P2P的注入和corss attention map构造MASK。
其中attention_controlled_forward是为CrossAttention和SparseCausalAttention重写的forward我们最后再讲。
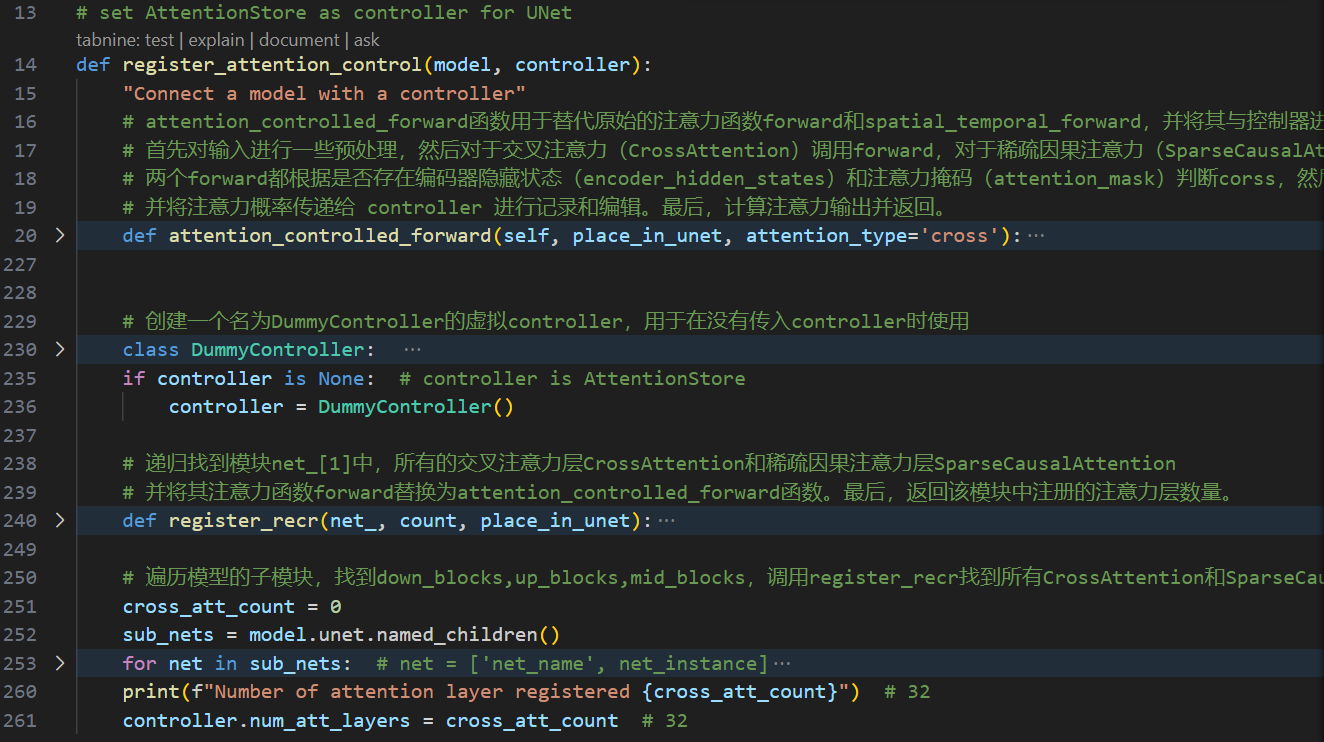
DummyController
创建一个名为DummyController的虚拟controller,用于在没有传入controller时使用,实际是用不上的。
class DummyController:
def __call__(self, *args):
return args[0]
def __init__(self):
self.num_att_layers = 0
if controller is None: # controller is AttentionStore
controller = DummyController()
register_recr
递归找到模块net_[1]中所有的CrossAttention和SparseCausalAttention。并将其前向函数forward替换为attention_controlled_forward函数。最后,返回该模块中注册的注意力层数量。
def register_recr(net_, count, place_in_unet):
if net_[1].__class__.__name__ == 'CrossAttention' or net_[1].__class__.__name__ == 'SparseCausalAttention':
net_[1].forward = attention_controlled_forward(net_[1], place_in_unet, attention_type = net_[1].__class__.__name__)
return count + 1
elif hasattr(net_[1], 'children'):
for net in net_[1].named_children():
if net[0] !='attn_temporal':
count = register_recr(net, count, place_in_unet)
return count
for model.unet.named_children()
遍历UNet模型的子模块,找到down_blocks, up_blocks, mid_blocks,调用register_recr找到所有CrossAttention和SparseCausalAttention为其修改forward
cross_att_count = 0
sub_nets = model.unet.named_children()
for net in sub_nets: # net = ['net_name', net_instance]
if "down" in net[0]:
cross_att_count += register_recr(net, 0, "down") # 12
elif "up" in net[0]:
cross_att_count += register_recr(net, 0, "up")
elif "mid" in net[0]:
cross_att_count += register_recr(net, 0, "mid")
print(f"Number of attention layer registered {
cross_att_count}") # 32
controller.num_att_layers = cross_att_count # 32
attention_controlled_forward
最后我们来看看给CrossAttention和SparseCausalAttention重写的forward函数attention_controlled_forward长什么样。
attention_controlled_forward函数用于替代CrossAttention的forward函数为新的forward,替换SparseCausalAttention的forward函数为spatial_temporal_forward,并将其与 controller 进行连接。
遍历model.unet.named_children()得到的 net 包含两部分 net = ['net_name', net_instance],net[0]是模块的名字,net[1]是模块对象本身。
传入的参数:(self, place_in_unet, attention_type='cross'),其中self是net[1]模块对象本身,place_in_unet是"down"、“mid”、“up”。attention_type 是 net_[1].__class__.__name__,即模块的类名。(例如区别模块名attn1和类名CrossAttention)
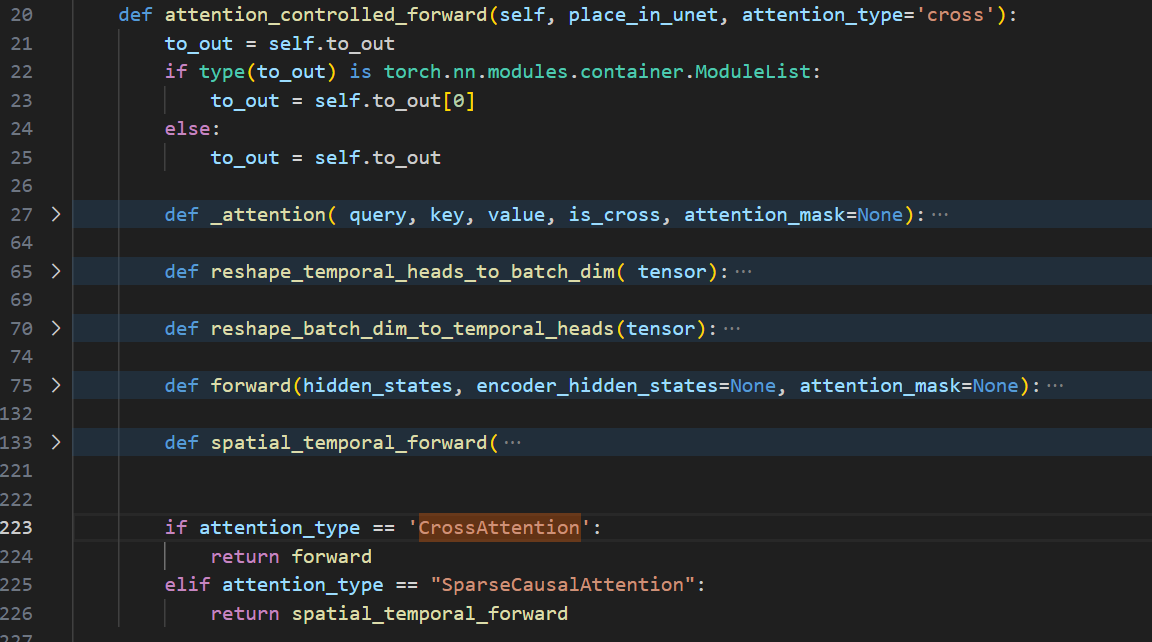
CrossAttention和SparseCausalAttention重写的两种forward思路和原始的forward基本一样,都是根据输入得到query,key,value,然后调用自定义的注意力函数_attention()进行注意力计算,计算注意力输出并返回。新加入的关键代码:在得到attention_probs后,将注意力概率张量 attention_probs的形状变换为(batch_size, num_heads, seq_length, seq_length),传递给 controller 进行记录和编辑。
# START OF CORE FUNCTION
# Record during inversion and edit the attention probs during editing
attention_probs = controller(reshape_batch_dim_to_temporal_heads(attention_probs),
is_cross, place_in_unet)
attention_probs = reshape_temporal_heads_to_batch_dim(attention_probs)
# END OF CORE FUNCTION
reshape_batch_dim_to_temporal_heads和reshape_temporal_heads_to_batch_dim对注意力矩阵进行维度转换:
-
reshape_temporal_heads_to_batch_dim函数将注意力矩阵从形状(batch_size*num_heads, seq_length, seq_length)重塑为形状(batch_size, num_heads, seq_length, seq_length)。具体操作是使用rearrange函数,将头数维度和批量大小维度分开,保持序列长度维度不变。 -
reshape_batch_dim_to_temporal_heads函数将注意力矩阵从形状(batch_size, num_heads, seq_length, seq_length)重塑为形状(batch_size*num_heads, seq_length, seq_length)。具体操作也是使用rearrange函数,将头数维度和批量大小维度合并,保持序列长度维度不变。
def reshape_temporal_heads_to_batch_dim( tensor):
head_size = self.heads
tensor = rearrange(tensor, " b h s t -> (b h) s t ", h = head_size)
return tensor
def reshape_batch_dim_to_temporal_heads(tensor):
head_size = self.heads
tensor = rearrange(tensor, "(b h) s t -> b h s t", h = head_size)
return tensor
CrossAttention和SparseCausalAttention的新的forward输出的最后去掉了Dropout,其余没有任何变化:
hidden_states = self.to_out[1](hidden_states)
3. UNet forward时controller AttentionStore如何发挥作用
前面说了每次Attention 进行 forward的时候,把attention_probs存入controller。
attention_probs = controller(reshape_batch_dim_to_temporal_heads(attention_probs), is_cross, place_in_unet)
当我们call我们的controller时,内部是怎么运行的呢?接下来分析两个类:注意力存储器 AttentionStore 是一个用于注意力编辑的基类。这个类继承了 AttentionControl 类,并且新增了一些方法和属性。
AttentionControl
AttentionControl 是一个抽象基类(ABC),定义了一堆抽象方法等着AttentionStore 去重写。
__init__方法:初始化 AttentionControl 类的实例,设置了一些默认属性。
def __init__(self,
):
self.LOW_RESOURCE = False # assume the edit have cfg
self.cur_step = 0
self.num_att_layers = -1
self.cur_att_layer = 0
step_callback方法:在每次前向传播forward之后调用,用于更新当前步数和当前注意力层。
def step_callback(self, x_t):
self.cur_att_layer = 0
self.cur_step += 1
self.between_steps()
return x_t
between_steps方法:在denoising step 之间调用,可以用于添加自定义逻辑,这里是一个空方法。
def between_steps(self):
return
num_uncond_att_layers属性:返回 uncondition 注意力层的数量,默认为0。
@property
def num_uncond_att_layers(self):
"""I guess the diffusion of google has some unconditional attention layer
No unconditional attention layer in Stable diffusion
Returns:
_type_: _description_
"""
# return self.num_att_layers if config_dict['LOW_RESOURCE'] else 0
return 0
forward方法:抽象方法,子类必须实现该方法以执行注意力修改的逻辑。
@abc.abstractmethod
def forward (self, attn, is_cross: bool, place_in_unet: str):
raise NotImplementedError
__call__方法:调用实例对象时会执行该方法。根据当前注意力层和条件,选择是否调用forward方法来修改注意力图。
def __call__(self, attn, is_cross: bool, place_in_unet: str):
if self.cur_att_layer >= self.num_uncond_att_layers:
if self.LOW_RESOURCE:
# For inversion without null text file
attn = self.forward(attn, is_cross, place_in_unet)
else:
# For classifier-free guidance scale!=1
h = attn.shape[0]
attn[h // 2:] = self.forward(attn[h // 2:], is_cross, place_in_unet)
self.cur_att_layer += 1
return attn
reset方法:重置所有状态,包括当前步数、当前注意力层等。
def reset(self):
self.cur_step = 0
self.cur_att_layer = 0
AttentionStore
AttentionStore继承自AttentionControl类。AttentionStore类的主要功能是在训练过程中存储和处理注意力矩阵,以便后续使用。
__init__方法:初始化AttentionStore对象。它设置了一些初始变量,包括是否保存自注意力矩阵save_self_attention、是否将注意力矩阵存储到磁盘上disk_store,磁盘存储路径store_dir,当前denoising step中的注意力图存储器step_store(通过调用get_empty_store()方法创建的空存储器初始化),注意力图的存储字典attention_store(用于存储每个denoising step中的注意力图),注意力图的latents的列表latents_store,存储所有denoising step中的注意力图的路径列表attention_store_all_step。
def __init__(self, save_self_attention:bool=True, disk_store=False):
super(AttentionStore, self).__init__()
self.disk_store = disk_store
if self.disk_store:
time_string = get_time_string()
path = f'./trash/attention_cache_{
time_string}'
os.makedirs(path, exist_ok=True)
self.store_dir = path
else:
self.store_dir =None
self.step_store = self.get_empty_store() # for one step attn_map
self.attention_store = {
} # for all step attn_map
self.save_self_attention = save_self_attention # bool
self.latents_store = [] # for all step latents
self.attention_store_all_step = [] # for all step attn_map path
step_callback方法:在每个时间步骤中被调用,用于将注意力矩阵x_t添加到latents_store列表中,并返回x_t。
def step_callback(self, x_t):
x_t = super().step_callback(x_t)
self.latents_store.append(x_t.cpu().detach())
return x_t
get_empty_store方法:返回一个空的存储字典,包含不同类型的注意力矩阵。
@staticmethod
def get_empty_store():
return {
"down_cross": [], "mid_cross": [], "up_cross": [],
"down_self": [], "mid_self": [], "up_self": []}
get_empty_cross_store方法:返回一个空的存储字典,只包含跨注意力矩阵。
@staticmethod
def get_empty_cross_store():
return {
"down_cross": [], "mid_cross": [], "up_cross": [],
}
forward方法:接收注意力矩阵attn、一个布尔值is_cross和一个字符串place_in_unet作为输入。根据is_cross和save_self_attention的取值,将注意力矩阵添加到step_store字典的相应位置。
def forward(self, attn, is_cross: bool, place_in_unet: str):
key = f"{
place_in_unet}_{
'cross' if is_cross else 'self'}"
if attn.shape[-2] <= 32 ** 2: # avoid memory overhead
# print(f"Store attention map {key} of shape {attn.shape}")
if is_cross or self.save_self_attention:
if attn.shape[-2] == 32**2:
append_tensor = attn.cpu().detach()
else:
append_tensor = attn
self.step_store[key].append(copy.deepcopy(append_tensor))
# FIXME: Are these deepcopy all necessary?
# self.step_store[key].append(append_tensor)
return attn
between_steps方法:在每个时间步之间被调用,用于将step_store字典的内容累加到attention_store字典中,并将step_store重置为空。
def between_steps(self):
# 1. add step_store to attention_store
if len(self.attention_store) == 0:
self.attention_store = self.step_store
else:
for key in self.attention_store:
for i in range(len(self.attention_store[key])):
self.attention_store[key][i] += self.step_store[key][i]
# 2. save this step attn_map, save path to attention_store_all_step
if self.disk_store:
path = self.store_dir + f'/{
self.cur_step:03d}.pt'
torch.save(copy.deepcopy(self.step_store), path)
self.attention_store_all_step.append(path)
else:
self.attention_store_all_step.append(copy.deepcopy(self.step_store))
# 3. empty step_store
self.step_store = self.get_empty_store()
get_average_attention方法:计算attention_store字典中注意力矩阵所有step的平均值,并返回结果。
def get_average_attention(self):
"divide the attention map value in attention store by denoising steps"
average_attention = {
key: [item / self.cur_step for item in self.attention_store[key]] for key in self.attention_store}
return average_attention
reset方法:重置AttentionStore对象的状态。
def reset(self):
super(AttentionStore, self).reset()
self.step_store = self.get_empty_store()
self.attention_store_all_step = []
self.attention_store = {
}
4. show_cross_attention 可视化AttentionStore的cs_map
回顾 self/corss attention map存储过程
前面说了每个step的Unet的Attention前向forward过程,都会自动调用AttentionStore父类AttentionControl的__call__方法,保存当前step的每层Attention Layer的attention map到controller:
attention_probs = controller(reshape_batch_dim_to_temporal_heads(attention_probs), is_cross, place_in_unet)
从AttentionControl的__call__方法,我们可以看到,我们只存储大于num_uncond_att_layers的Attention Layer的attention map。其中有两种存储方式:(一般在Inversion时,设置为LOW_RESOURCE=False,关闭classifier-free guidance;在Sample时,设置为LOW_RESOURCE=True,开启classifier-free guidance)
-
低资源存储 LOW_RESOURCE:针对不使用classifier-free guidance的inversion 来说,只用text prompt作为condition,而没有使用null text prompt。此时的attn_map就是text_prompt的attn_map,可以直接存储。 -
非低资源存储classifier-free guidance:因为此时的attn_map中即包含了text_prompt的,也包含了null text prompt的。但是我们存储的目标是text_prompt的attn_map(因为空文本的corss_attn map不能反映语义layout,没有什么用)。因此,我们对attn_map的形状进行划分,取attn_map的后半部分,即text_prompt的attn_map,调用forward方法进行处理。
def __call__(self, attn, is_cross: bool, place_in_unet: str):
if self.cur_att_layer >= self.num_uncond_att_layers:
if self.LOW_RESOURCE:
# For inversion without null text file
attn = self.forward(attn, is_cross, place_in_unet)
else:
# For classifier-free guidance scale!=1
h = attn.shape[0]
attn[h // 2:] = self.forward(attn[h // 2:], is_cross, place_in_unet)
self.cur_att_layer += 1
return attn
AttentionStore重写了其中的forward方法:接收注意力矩阵attn、一个布尔值is_cross、一个表示Attention Layer位置的字符串place_in_unet作为输入。根据is_cross和save_self_attention的取值,将注意力矩阵添加到step_store字典的相应位置{key: value},key表示attn_map的位置(down,mid,up)和类型(cross,self),value表示attn_map张量对象。
def forward(self, attn, is_cross: bool, place_in_unet: str):
key = f"{
place_in_unet}_{
'cross' if is_cross else 'self'}"
if attn.shape[-2] <= 32 ** 2: # avoid memory overhead
# print(f"Store attention map {key} of shape {attn.shape}")
if is_cross or self.save_self_attention:
if attn.shape[-2] == 32**2:
append_tensor = attn.cpu().detach()
else:
append_tensor = attn
self.step_store[key].append(copy.deepcopy(append_tensor))
# FIXME: Are these deepcopy all necessary?
# self.step_store[key].append(append_tensor)
return attn
一个空的step_store字典如下:
{
"down_cross": [], "mid_cross": [], "up_cross": [], "down_self": [], "mid_self": [], "up_self": []}
DDIM Inversion所有的step结束后(50个),attention_store_all_step 列表就存储了50个 step_store字典:
[
{
"down_cross": [], "mid_cross": [], "up_cross": [], "down_self": [], "mid_self": [], "up_self": []},
{
"down_cross": [], "mid_cross": [], "up_cross": [], "down_self": [], "mid_self": [], "up_self": []},
...,
{
"down_cross": [], "mid_cross": [], "up_cross": [], "down_self": [], "mid_self": [], "up_self": []}
]
而attention_store字典则是每个step对step_store字典的累加,用于最后计算聚合平均attention_map:
{
"down_cross": [], "mid_cross": [], "up_cross": [], "down_self": [], "mid_self": [], "up_self": []}
可视化cross_attn map
在完成Inversion后,attention map已经存储在store_controller中,我们用show_cross_attention进行可视化
然后用register_attention_control将UNet的controller替换为空的EmptyControl,从而将存储好的AttentionStore分离出来,防止后续Sample的时候修改其中的内容:
attention_output = attention_util.show_cross_attention(self.tokenizer, prompt, self.store_controller,
res=16, from_where=["up", "down"], save_path = save_path+'/cross_attention')
# Detach the controller for safety (attention_store -> empty_controller)
attention_util.register_attention_control(self, self.empty_controller)
对于show_cross_attention用于展示交叉注意力的可视化结果。
函数接受多个参数:
- tokenizer:用于将文本转换为标记序列的分词器。
- prompts:包含一个或多个提示文本的列表list。
- attention_store:存储注意力计算结果的AttentionStore对象。
- res:指定的分辨率 16。
- from_where:指定注意力来自哪个位置,可以是"up"和"down"。
- select:选择要展示交叉注意力的提示文本在prompts列表中的索引,默认为0,即选择第一句prompt。
- save_path:保存结果的路径。
函数首先判断prompts是否为字符串类型,如果是则将其转换为包含单个元素的列表。然后使用tokenizer对选定的prompt进行编码,得到标记序列。
接下来调用aggregate_attention函数,从attention_store中聚合所需的注意力计算结果。
然后创建一个存储注意力可视化结果的列表attention_list。接着循环遍历attention_maps的frames维度,生成每个token位置的注意力可视化图像,并将其添加到images列表中(注意: 尽管attention_maps的token_dim 维度是77,但我们并不需要遍历所有的token,只需要根据遍历text_prompt对应的有效token,后面的tokens都是0 padding)。最后,将images列表中的图像拼接成一张大图,并将其添加到attention_list中。如果指定了save_path,则会根据当前时间生成一个唯一的文件名,并将attention_list保存为gif格式的动画文件。最后返回attention_list列表。
def show_cross_attention(tokenizer, prompts, attention_store: AttentionStore,
res: int, from_where: List[str], select: int = 0, save_path = None):
"""
attention_store (AttentionStore):
["down", "mid", "up"] X ["self", "cross"]
4, 1, 6
head*res*text_token_len = 8*res*77
res=1024 -> 64 -> 1024
res (int): res
from_where (List[str]): "up", "down'
"""
if isinstance(prompts, str):
prompts = [prompts,]
tokens = tokenizer.encode(prompts[select]) # select prompt in all_prompts to show cross-attn map
decoder = tokenizer.decode
# torch.Size([15, 16, 16, 77])
attention_maps = aggregate_attention(prompts, attention_store, res, from_where, True, select)
attention_list = []
if attention_maps.dim()==3: attention_maps=attention_maps[None, ...]
for j in range(attention_maps.shape[0]): # visualize for every frame (all 15)
images = []
for i in range(len(tokens)): # visualize for every token in j frame (all 11, last 66 tokens is 0 padding)
image = attention_maps[j, :, :, i] # torch.Size([15, 16, 16, 77]) -> torch.Size([16, 16])
image = 255 * image / image.max()
image = image.unsqueeze(-1).expand(*image.shape, 3)
image = image.numpy().astype(np.uint8)
image = np.array(Image.fromarray(image).resize((256, 256)))
image = ptp_utils.text_under_image(image, decoder(int(tokens[i])))
images.append(image)
ptp_utils.view_images(np.stack(images, axis=0), save_path=save_path)
atten_j = np.concatenate(images, axis=1)
attention_list.append(atten_j)
if save_path is not None:
now = datetime.datetime.now().strftime("%Y-%m-%dT%H-%M-%S")
video_save_path = f'{
save_path}/{
now}.gif'
save_gif_mp4_folder_type(attention_list, video_save_path)
return attention_list
对于aggregate_attention用于聚合分辨率为res=16*16的**位置为from_where={down,up}**的cross_attn map。
def aggregate_attention(prompts, attention_store: AttentionStore, res: int, from_where: List[str], is_cross: bool, select: int):
out = []
attention_maps = attention_store.get_average_attention()
num_pixels = res ** 2 # 256 = 16*16
# get reslution = 16*16, place = {up_cross, down_cross} avg_cross_attn_maps
for location in from_where:
for item in attention_maps[f"{
location}_{
'cross' if is_cross else 'self'}"]:
if item.dim() == 3:
if item.shape[1] == num_pixels:
cross_maps = item.reshape(len(prompts), -1, res, res, item.shape[-1])[select]
out.append(cross_maps)
elif item.dim() == 4: # eg.torch.Size([time=15, heads=8, res_sq=256, token_dim=77])
t, h, res_sq, token = item.shape
if item.shape[2] == num_pixels:
cross_maps = item.reshape(len(prompts), t, -1, res, res, item.shape[-1])[select]
out.append(cross_maps) # 5 * [torch.Size([15, 8, 16, 16, 77])]
out = torch.cat(out, dim=-4) # concat heads: torch.Size([15, 40, 16, 16, 77])
out = out.sum(-4) / out.shape[-4] # torch.Size([15, 16, 16, 77])
return out.cpu()
其中调用AttentionStore的get_average_attention:对attention_store(attention_store是累加每个step的attention_map)的每个位置的attention_map值除以self.cur_step(就是总的step数),得到每个位置平均的attention_map:
def get_average_attention(self):
"divide the attention map value in attention store by denoising steps"
average_attention = {
key: [item / self.cur_step for item in self.attention_store[key]] for key in self.attention_store}
return average_attention