学习过程中,遇到的问题记录下来。
props的基本用法是父组件给子组件传输数据和验证
这里我一开始就理解错了,我总以为是要把props写到父组件里面,但是看到自动构建的helloworld中有那个props才之知道我搞错了
1、Props的大小写
查阅官方文档可知:
-
官方解释:HTML 中的 attribute 名是大小写不敏感的,所以浏览器会把所有大写字符解释为小写字符。这意味着当你使用 DOM 中的模板时,camelCase (驼峰命名法) 的 prop 名需要使用其等价的 kebab-case (短横线分隔命名) 命名
-
官方示例:
这里的postTitle就是驼峰命名法
Vue.component('blog-post', {
// 在 JavaScript 中是 camelCase 的
props: ['postTitle'],
template: '<h3>{
{ postTitle }}</h3>'
})
这里的post-title就是短横线命名法
<!-- 在 HTML 中是 kebab-case 的 -->
<blog-post post-title="hello!"></blog-post>
2、Props验证
- 官方解释:我们可以为组件的 prop 指定验证要求,例如你知道的这些类型。如果有一个需求没有被满足,则 Vue 会在浏览器控制台中警告你。这在开发一个会被别人用到的组件时尤其有帮助。
- 为了定制 prop 的验证方式,你可以为 props 中的值提供一个带有验证需求的对象,而不是一个字符串数组。例如
Vue.component('my-component', {
props: {
// 基础的类型检查 (`null` 和 `undefined` 会通过任何类型验证)
propA: Number,
// 多个可能的类型
propB: [String, Number],
// 必填的字符串
propC: {
type: String,
required: true
},
// 带有默认值的数字
propD: {
type: Number,
default: 100
},
// 带有默认值的对象
propE: {
type: Object,
// 对象或数组默认值必须从一个工厂函数获取
default: function () {
return {
message: 'hello' }
}
},
// 自定义验证函数
propF: {
validator: function (value) {
// 这个值必须匹配下列字符串中的一个
return ['success', 'warning', 'danger'].includes(value)
}
}
}
})
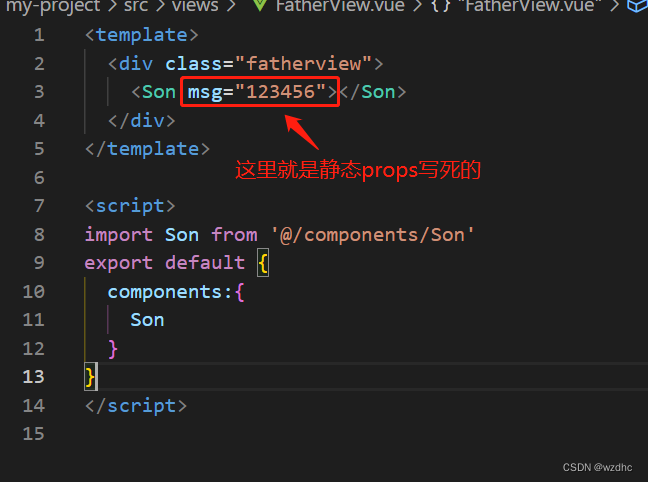
3、静态Props
例子:
FatherVIew.vue
<template>
<div class="fatherview">
<Son msg="123456"></Son>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import Son from '@/components/Son'
export default {
components:{
Son
}
}
</script>
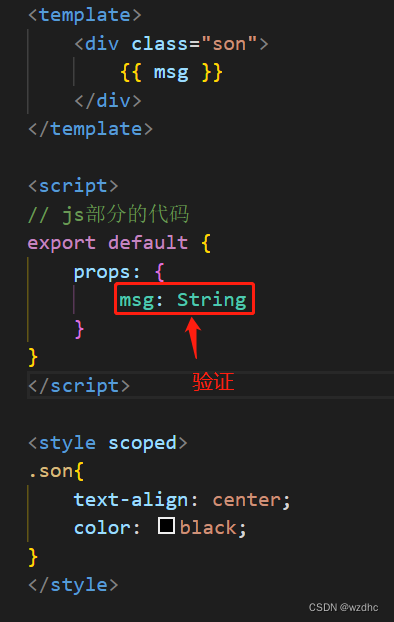
Son.vue
<template>
<div class="son">
{
{ msg }}
</div>
</template>
<script>
// js部分的代码
export default {
props: {
msg: String
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
.son{
text-align: center;
color: black;
}
</style>
4、动态Props
FatherView.vue
<template>
<div class="fatherview">
<h1>父组件</h1>
msg:<input type="text" v-model="msg"><br>
name:<input type="text" v-model="obj.name"><br>
age:<input type="text" v-model="obj.age"><br>
<p>{
{ "父组件中的数据:"}}</p>
{
{ msg }}
<p>{
{ "父组件中的对象:"}}</p>
<div v-html="obj"></div>
<Son :child-msg="msg" :child-obj="obj"></Son>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import Son from '@/components/Son'
export default {
name: "father",
components:{
Son
},
data(){
return {
msg: "嘿嘿",
obj: {
name: "lzy",
age: 18
}
}
}
}
</script>
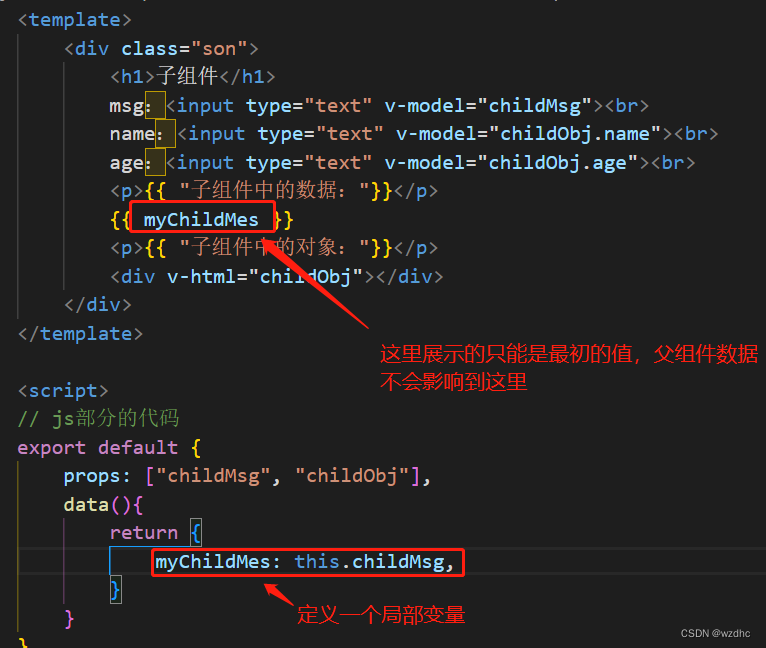
Son.vue
<template>
<div class="son">
<h1>子组件</h1>
<p>{
{ "子组件中的数据:"}}</p>
{
{ childMsg }}
<p>{
{ "子组件中的对象:"}}</p>
<div v-html="childObj"></div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
// js部分的代码
export default {
props: ["childMsg", "childObj"]
}
</script>
<style scoped>
.son{
text-align: center;
color: black;
}
</style>

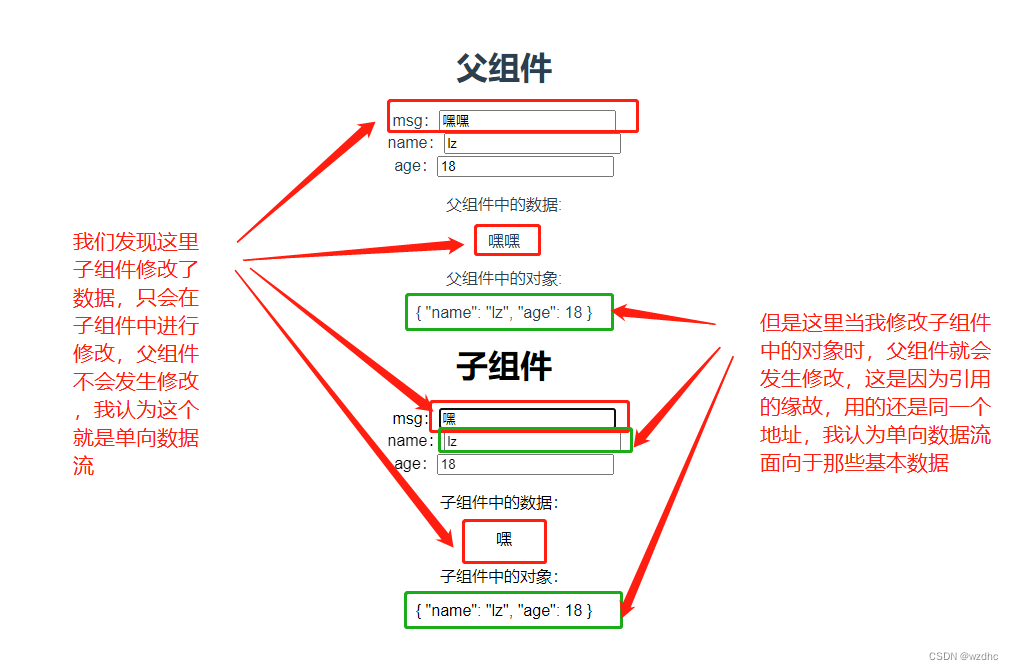
这里通过修改父组件中的数据,对应的子组件中的数据也会发生改变,我觉得这就是动态Props了
官方解释:所有的 prop 都使得其父子 prop 之间形成了一个单向下行绑定:父级 prop 的更新会向下流动到子组件中,但是反过来则不行。这样会防止从子组件意外变更父级组件的状态,从而导致你的应用的数据流向难以理解。
注意:
- 注意Props的大小写,在father中是在template中使用的son组件,所以要用短横线,在son中是在script中接受数据,要用驼峰命名法
- 这里还有一个问题,若是子组件定义局部变量去接收,则不接受父组件数据更新,即只能接收初始值
官方解释:

并且官方建议:

也就是说当你从父组件那里拿到了数据后,还想对数据进行一些修改,最好使用计算属性
5、单向数据流
FatherView.vue
<template>
<div class="fatherview">
<h1>父组件</h1>
msg:<input type="text" v-model="msg"><br>
name:<input type="text" v-model="obj.name"><br>
age:<input type="text" v-model="obj.age"><br>
<p>{
{ "父组件中的数据:"}}</p>
{
{ msg }}
<p>{
{ "父组件中的对象:"}}</p>
<div v-html="obj"></div>
<Son :child-msg="msg" :child-obj="obj"></Son>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import Son from '@/components/Son'
export default {
name: "father",
components:{
Son
},
data(){
return {
msg: "嘿嘿",
obj: {
name: "lzy",
age: 18
}
}
}
}
</script>
Son.vue
<template>
<div class="son">
<h1>子组件</h1>
msg:<input type="text" v-model="childMsg"><br>
name:<input type="text" v-model="childObj.name"><br>
age:<input type="text" v-model="childObj.age"><br>
<p>{
{ "子组件中的数据:"}}</p>
{
{ childMsg }}
<p>{
{ "子组件中的对象:"}}</p>
<div v-html="childObj"></div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
// js部分的代码
export default {
props: ["childMsg", "childObj"],
}
</script>
<style scoped>
.son{
text-align: center;
color: black;
}
</style>
参考文章:https://blog.csdn.net/VegetableKCCCC/article/details/119410145