from __future__ import unicode_literals
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
default_encoding = 'utf-8'
import gensim
import jieba
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.font_manager import FontProperties
from sklearn.cluster import KMeans
import scipy.cluster.hierarchy as sch
class StoneStory:
def __init__(self):
self.add_to_dict(self.name_list())
self.model = self.tranning()
self.np_names, self.word_vectors = self.getVector(self.model, self.name_list())
self.font_yahei_consolas = FontProperties(fname="huawenfansong.ttf")
self.stopword = pd.read_csv("stopwords.csv", header=None, names=["Stopwords"], encoding='utf-8')
stopwords = [w[0] for w in self.stopword.values]
# 1.红楼梦正文
self.RedDream = pd.read_csv("StoneStory.txt", header=None, names=["Reddream"], encoding='utf-8')
# print '《红楼梦》全文: '
# print self.RedDream
# print("---------------------------")
# 2.提取章节名
self.indexChap = self.RedDream.Reddream.str.contains(u"^第+.+回 ")
# 4.去除章节后重建索引
RedDream_content = self.RedDream[~self.indexChap].reset_index(drop=True)
# 5.处理章节名,使用空格分割字符串
## 找出每一章节的头部索引和尾部索引
## 每一章节的名字
self.chapnames = self.RedDream.Reddream[self.indexChap].reset_index(drop=True)
self.chapnamesplit = self.chapnames.str.split(u" ").reset_index(drop=True)
# print '《红楼梦》章节名: '
# print self.chapnamesplit
# print("---------------------------")
# 6.建立保存数据的数据表
self.Red_df = pd.DataFrame(list(self.chapnamesplit), columns=["Chapter", "Leftname", "Rightname"])
# 添加章节id和完整标题
self.Red_df["Chapter_id"] = np.arange(1, 121)
self.Red_df["ChapName"] = self.Red_df.Leftname + "," + self.Red_df.Rightname
# 每章的开始行(段)索引
self.Red_df["Start_Chapter_id"] = self.indexChap[self.indexChap == True].index
## 每章的结束行数
self.Red_df["end_Chapter_id"] = self.Red_df["Start_Chapter_id"][
1:len(self.Red_df["Start_Chapter_id"])].reset_index(
drop=True) - 1
self.Red_df["end_Chapter_id"][[len(self.Red_df["end_Chapter_id"]) - 1]] = self.RedDream.index[-1]
## 每章的段落长度
self.Red_df["Lengthchaps"] = self.Red_df.end_Chapter_id - self.Red_df.Start_Chapter_id
self.Red_df["Article"] = " "
## 每章节的内容
for ii in self.Red_df.index:
## 将内容使用句号连接
chapid = np.arange(self.Red_df.Start_Chapter_id[ii] + 1, int(self.Red_df.end_Chapter_id[ii]))
## 每章节的内容,
self.Red_df["Article"][ii] = "".join(list(self.RedDream.Reddream[chapid]))
##每章的字数
self.Red_df["len_char"] = self.Red_df.Article.apply(len)
# print self.Red_df
# 7.获取某一章的段落索引
def Chapter_index(self, chap_numb):
return np.arange(self.Red_df.Start_Chapter_id[chap_numb - 1] + 1,
int(self.Red_df.end_Chapter_id[chap_numb - 1]) + 1)
# 8.获取某一章的内容
def Chapter_Content(self, chap_numb):
index = np.arange(self.Red_df.Start_Chapter_id[chap_numb - 1] + 1,
int(self.Red_df.end_Chapter_id[chap_numb - 1]) + 1)
return self.RedDream.Reddream[index]
# 9.字长和段落长的散点图
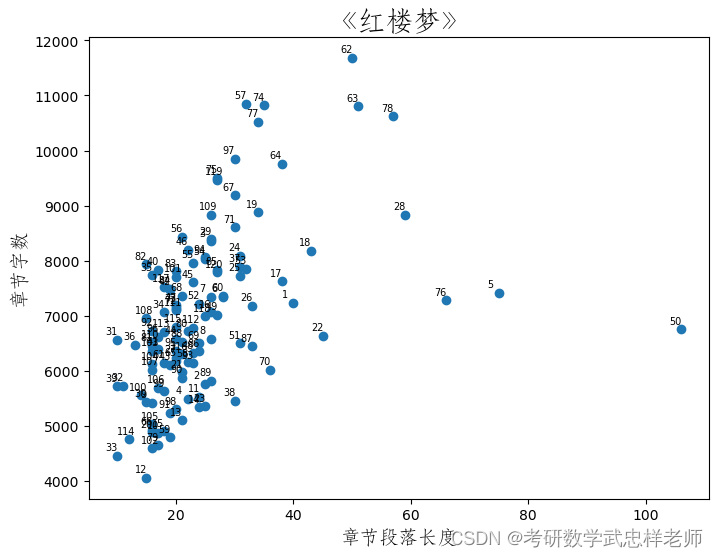
def char_len_para_len_distribute1(self):
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 6))
plt.scatter(self.Red_df.Lengthchaps, self.Red_df.len_char)
for ii in self.Red_df.index:
# plt.text(Red_df.Lengthchaps[ii]+1,Red_df.len_char[ii],Red_df.Chapter[ii])
plt.text(self.Red_df.Lengthchaps[ii] - 2, self.Red_df.len_char[ii] + 100, self.Red_df.Chapter_id[ii],
size=7)
plt.xlabel('章节段落长度', fontproperties=self.font_yahei_consolas,
fontsize=14)
plt.ylabel('章节字数', fontproperties=self.font_yahei_consolas,
fontsize=14)
plt.title('《红楼梦》', fontproperties=self.font_yahei_consolas,
fontsize=20)
plt.show()
# 10.折线图
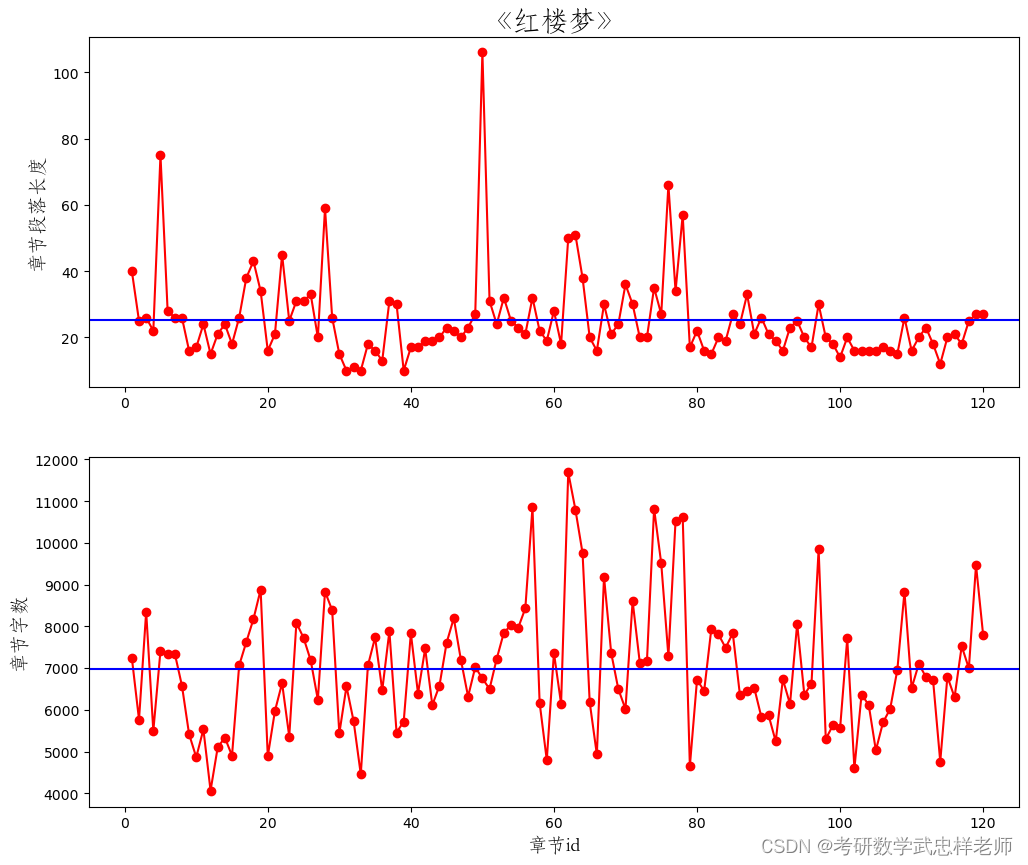
def char_len_para_len_distribute2(self):
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 10))
plt.subplot(2, 1, 1)
plt.plot(self.Red_df.Chapter_id, self.Red_df.Lengthchaps, "ro-", label="paragraph")
plt.ylabel("章节段落长度", fontproperties=self.font_yahei_consolas,
fontsize=14)
plt.title("《红楼梦》", fontproperties=self.font_yahei_consolas,
fontsize=20)
## 添加平均值
plt.hlines(np.mean(self.Red_df.Lengthchaps), -5, 125, "b")
plt.xlim((-5, 125))
plt.subplot(2, 1, 2)
plt.plot(self.Red_df.Chapter_id, self.Red_df.len_char, "ro-", label="paragraph")
plt.xlabel("章节id", fontproperties=self.font_yahei_consolas,
fontsize=14)
plt.ylabel("章节字数", fontproperties=self.font_yahei_consolas,
fontsize=14)
## 添加平均值
plt.hlines(np.mean(self.Red_df.len_char), -5, 125, "b")
plt.xlim((-5, 125))
plt.show()
# 读取人物词典
def name_list(self):
with open('names.txt', encoding='utf-8') as f:
characters_names = [line.strip('\n') for line in f.readlines()]
return characters_names
# 添加人物词典
def add_to_dict(self, characters_names):
for name in characters_names:
jieba.add_word(name) # 保证添加的词不会被cut掉
# 训练词向量
def tranning(self):
with open('StoneStory.txt', encoding='utf-8') as f:
data = [line.strip()
for line in f.readlines()
if line.strip()]
sentences = []
for line in data:
words = list(jieba.cut(line))
sentences.append(words)
model = gensim.models.Word2Vec(sentences, vector_size=100, window=5, min_count=5, workers=4) # 100维词向量
return model
# 训练人物的词向量
def getVector(self, model, characters_names):
all_names = []
word_vectors = None
np_names = None
for name in characters_names:
if name in model.wv:
all_names.append(name)
for name in all_names:
if word_vectors is None:
word_vectors = model.wv[name]
else:
# 存储各名字对应的词向量
word_vectors = np.vstack((word_vectors, model.wv[name]))
np_names = np.array(all_names)
return np_names, word_vectors
# 查找人物关系
def find_relationship(self, a, b, c):
"""
返回 d
a与b的关系,跟c与d的关系一样
"""
d, _ = self.model.wv.most_similar(positive=[c, b], negative=[a])[0]
print("“{}”与“{}”的关系,跟“{}”与“{}”有类似的关系".format(a, b, c, d))
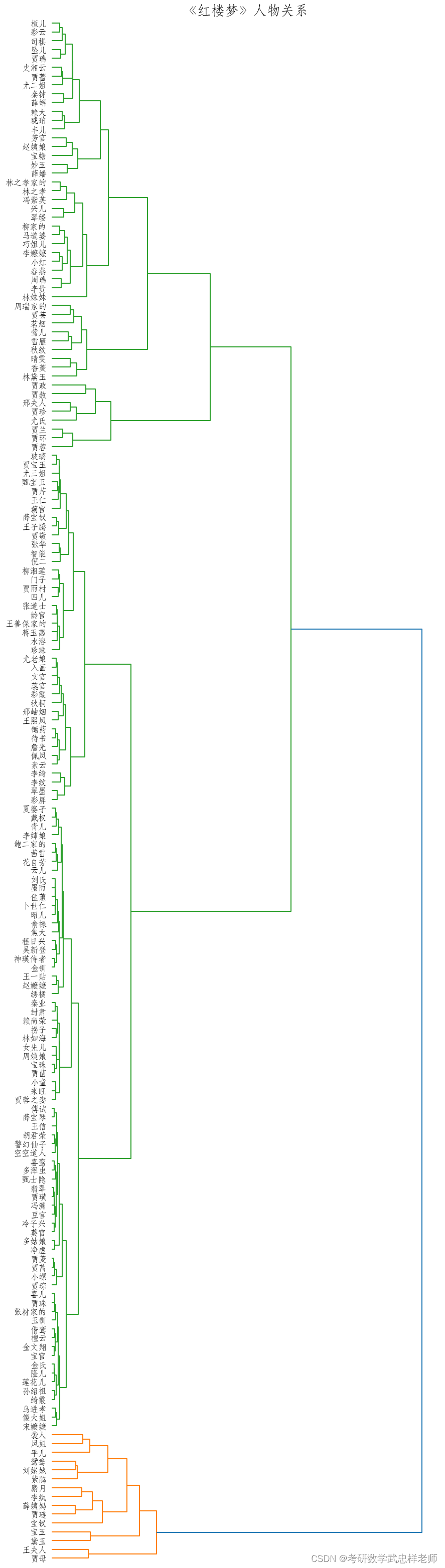
# 层次聚类查看人物关系
def hierarchy(self):
Y = sch.linkage(self.word_vectors, method="ward")
_, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(10, 40))
Z = sch.dendrogram(Y, orientation='right')
idx = Z['leaves']
ax.set_xticks([])
ax.set_title('《红楼梦》人物关系', fontproperties=self.font_yahei_consolas,
fontsize=20)
ax.set_yticklabels(self.np_names[idx], fontproperties=self.font_yahei_consolas,
fontsize=12)
ax.set_frame_on(False)
plt.show()
# 按词频找出主要人物
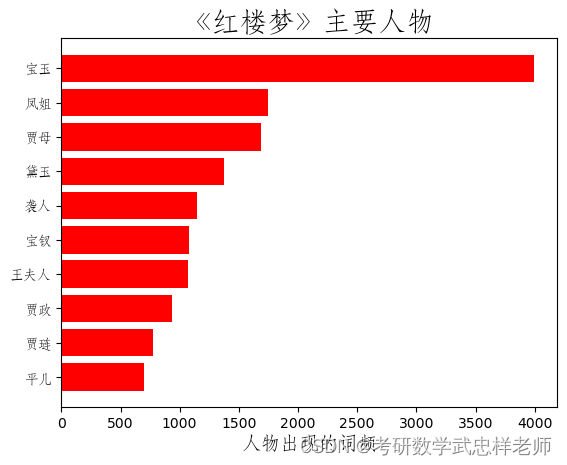
def find_main_charecters(self, num=10):
with open('StoneStory.txt', encoding='utf-8') as f:
data = f.read()
with open('names.txt', encoding='utf-8') as f:
characters_names = [line.strip('\n') for line in f.readlines()]
count = []
for name in characters_names:
count.append([name, data.count(name)])
count.sort(key=lambda x: x[1])
_, ax = plt.subplots()
numbers = [x[1] for x in count[-num:]]
names = [x[0] for x in count[-num:]]
ax.barh(range(num), numbers, color='red', align='center')
ax.set_title('《红楼梦》主要人物', fontproperties=self.font_yahei_consolas,
fontsize=20)
ax.set_yticks(range(num))
ax.set_yticklabels(names, fontproperties=self.font_yahei_consolas, )
plt.xlabel('人物出现的词频', fontproperties=self.font_yahei_consolas,
fontsize=14)
plt.show()
# kmeans聚类人物关系
def kmeans(self):
N = 3
label = KMeans(N).fit(self.word_vectors).labels_
for c in range(N):
print("类别{}:".format(c + 1))
for idx, name in enumerate(self.np_names[label == c]):
print(name),
if idx % 10 == 9:
print('')
print(' ')