目录
1.StringBuilder与StringBuffer介绍
一、认识String类及学会使用
1.三种构造方式
(1)直接使用常量构造
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "I love you";
System.out.println(str);
}![]()
内存展示图:

(2)new一个String对象
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str2 = new String("love you too");
System.out.println(str2);
}

(3)使用数组进行构造
public static void main(String[] args) {
char[] arr = {'6','6','6'};
String str3 = new String(arr);
System.out.println(str3);
} 
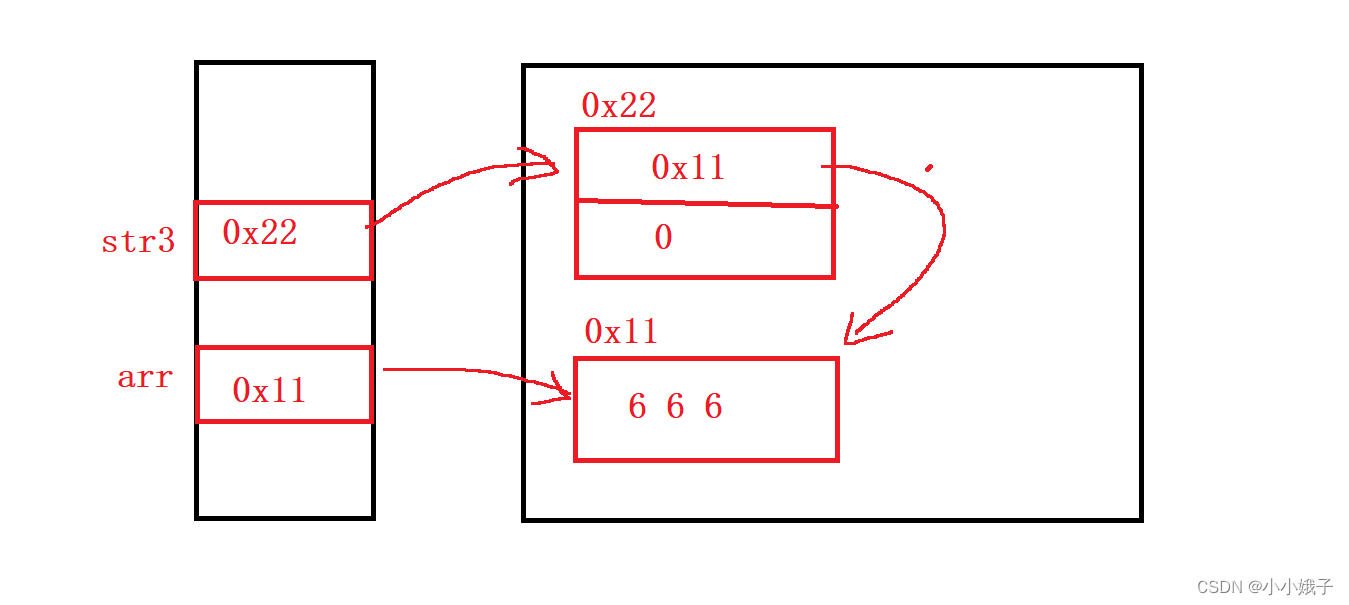
为什么String的内存布局是这样呢?就需要先往下了解String类
2.认识String类
(1)String类
- String属于一个类,可以用来实例化对象。
- String定义的变量称为引用变量,简称引用,引用中存放的是地址
- String对象中也不是直接存放字符串的
(2)String类的空间分配
- 用下面一段代码举例
String str = new String("abcd");- 调试观察其内部:

- 我们暂时只需要知道对象里面有value和hash即可,下面看内存分布图


3.String引用类型的比较
(1)比较字符串是否相等
- 先看错误的比较方法:使用等号
public static void main(String[] args) { String str1 = new String("abcd"); String str2 = new String("abcd"); System.out.println(str1==str2); if(str1==str2) { System.out.println("字符串str1==字符串str2"); }else { System.out.println("字符串str1!=字符串str2"); } }

错误原因:它们都属于引用类型,不能直接用等号(==)比较;而用等号比较则比较的是它们对象的地址
- 使用euqls方法比较
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str1 = new String("abcd");
String str2 = new String("abcd");
System.out.println(str1.equals(str2));
}
- 简单学习一下String类重写的equals方法
这是String类重写equals的原码:需要使用String类型的变量去调用才会使用该方法

Object(父类)的equals方法:

画图解析:
String类的equals方法

Object类的方法:如果没有去使用String变量去调用equals方法,而直接使用==号比较,本质会默认调用Object的equals方法

- 忽视大小写比较的方法:equalsIgnoreCase
代码举例:
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str1 = new String("abcd");
String str2 = new String("ABCD");
System.out.println(str1.equalsIgnoreCase(str2));
}
(2)比较字符串大小
- compareTo方法
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str1 = new String("abcd");
String str2 = new String("abce");
String str3 = new String("abc");
System.out.println(str1.compareTo(str2));
System.out.println(str1.compareTo(str3));
}
比较方式:
(1)一一对比它们的ASCII值,如a的ASCII值<b的ASCII值,则返回小于0的数字
(2)字符串长度不一,但是前面有的部分都相同时,长的字符串大;如:abc<abcd
返回值:
返回值的数字=它们之间的ASCII的差值;如:a<b。则返回-1,b>a,则返回1
- 忽略大小写比较:compareToIgnoreCase
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str1 = new String("abcd");
String str2 = new String("ABCC");
System.out.println(str1.compareToIgnoreCase(str2));
}
二、字符/串查找方法
前言:都需要使用String类型来调用
1.charAt(int index)方法
- 用于查看指定位置的字符
(1)方法认识

功能:返回index位置上字符,如果index为负数或者越界,抛出IndexOutOfBoundsException异常
(2)举例
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = new String("abcdefg");
int index = str.charAt(3);
System.out.println(index);
System.out.println(str.charAt(0));
}

2indexOf() 方法
(1)int indexOf(int ch)方法
- 用来查找指定字符在字符串中第一次出现的位置

功能:返回ch第一次出现的位置,没有返回-1
举例:
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = new String("aabbccdd");
int index = str.indexOf('b');//查找b
System.out.println(index);
System.out.println(str.indexOf('d'));//查找d
}

(2)int indexOf(int ch, int fromIndex)方法
- 从fromIndex位置开始找ch第一次出现的位置(该位置是从起始位置开始数),没有返回-1
- 认识方法

- 举例:
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = new String("aabbccdd");
System.out.println(str.indexOf('c',2));
}直接从2位置(第一个b的位置)开始找;如果从d的位置,则会找不到

(3)int indexOf(String str) 方法
- 用于查找指定字符串第一次出现的位置
功能:返回str第一次出现的位置,没有返回-1
- 举例:
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = new String("aabbccdd");
System.out.println(str.indexOf("ab"));
}
(4)int indexOf(String str, int fromIndex)方法
- 从指定位置查找指定字符串
功能:从fromIndex位置开始找str第一次出现的位置,没有返回-1

- 举例
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = new String("aabbccdd");
System.out.println(str.indexOf("ab",2));
}
3.lastIndexOf() 方法
(1)int lastIndexOf(int ch) 方法
- 从后往前找,返回ch第一次出现的位置,没有返回-1

- 举例
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = new String("abcdef");
System.out.println(str.lastIndexOf('b'));
}
(2)int lastIndexOf(int ch, int fromIndex)方法
- 从fromIndex位置开始找,从后往前找ch第一次出现的位置,没有返回-1

- 举例
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = new String("abcdef");
System.out.println(str.lastIndexOf('b',5));
}
(3)int lastIndexOf(String str) 方法
- 从后往前找,返回str第一次出现的位置,没有返回-1

- 举例
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = new String("abcdef");
System.out.println(str.lastIndexOf("abc"));
}
(4)int lastIndexOf(String str, int fromIndex)方法
- 从fromIndex位置开始找,从后往前找str第一次出现的位置,没有返
回-1

- 举例
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = new String("abcdef");
System.out.println(str.lastIndexOf("abc",2));
}三、字符串转换方法
1.数字转字符串方法
(1)认识valueOf()
- 调用格式:String.valueOf()
- 参数:数字
(2)举例
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = String.valueOf(1234);
System.out.println(str);
}
从数字1234变成字符串1234
2.字符串转数字方法
一般用于转化数字字符串
(1)认识Integer.parseInt()
- 格式:Integer.parseInt()
- 参数:字符串/字符
(2)举例
-
public static void main(String[] args) { int tmp = Integer.parseInt("1234"); System.out.println(tmp); }

字符串1234变成了数字1234
3.大小写转换方法
(1)小写转大写
- 方法名:toUpperCase()
- 使用String类型调用
- 举例:
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = new String("abcd");
String tmp = str.toUpperCase();
System.out.println(tmp);
}
(2)大写转小写
- 方法名:toLowerCase()
- 使用String类型来调用
- 举例:
public static void main(String[] args) { String str = new String("ABCD"); String tmp = str.toLowerCase(); System.out.println(tmp); }
4.字符串转数组
(1)字符串转数字
- 方法名:toCharArray()
- 使用String类型来调用
- 举例:
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = new String("abcde");
char[] arr = str.toCharArray();
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
System.out.print(arr[i]+" ");
}
}
(2)数字转字符串
- 这就是字符串的构造方法之一
- 举例
public static void main(String[] args) {
char[] ch = {'a','b','c'};
String s = new String(ch);
System.out.println(s);
}
5.字符串格式化
- 方法名:format()
- 使用String类型来调用
- 举例
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = String.format("%d--%d--%d",1999,5,1);
System.out.println(str);
}
四、字符串的替换、拆分与截取方法
1.字符串替换
(1)替换所有的指定内容
- 方法名:replaceAll

- 使用String类型来调用
- 举例:
public static void main(String[] args) { String str = new String("aabbccdd"); String tmp= str.replaceAll("ab","xx"); System.out.println(tmp); }
(2)只替换第一个指定内容
- 方法名:repalceFirst()

- 使用String类型来调用
- 举例:
public static void main(String[] args) { String str = new String("aabbccdd"); String tmp= str.replaceFirst("a","xx"); System.out.println(tmp); }
2.字符串拆分
(1)全部按指定拆分
- 方法:split(String regex)

- 使用String类型来调用
- 拆分会形成多个字符串,需要拿String类型的数组接收
- 举例:
public static void main(String[] args) { String str = new String("abc def ghi"); String[] tmp = str.split(" ");//以空格作为拆分依据 for (String s:tmp) { System.out.println(s); } }
(2)指定拆分n组
- 方法:split(String regex, int limit)

- 使用String类型来调用
- 拆分会形成多个字符串,需要拿String类型的数组接收
- 举例:
public static void main(String[] args) { String str = new String("abc def ghi"); String[] tmp = str.split(" ",2);//拆成两组 for (String s:tmp) { System.out.println(s); } }
(3)需要转义的拆分标志
- 以这些标志来拆分的话需要转义:点号(.),竖线(|),加号(+),反斜杠(/),星号(*)
- 点号(.):两个\\转义成一个\再与.转义
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = new String("aa.bb.cc");
String[] tmp = str.split("\\.");
for(String s:tmp) {
System.out.println(s);
}
}
- 反斜杠(/):
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = new String("aa\\bb\\cc");//两个\\表示一个\
String[] tmp = str.split("\\\\");//四个\表示一个\
for(String s:tmp) {
System.out.println(s);
}
}- 加号(+):
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = new String("aa+bb+cc");
String[] tmp = str.split("\\+");//2个\表示一个\
for(String s:tmp) {
System.out.println(s);
}
}
- 竖线(|):
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = new String("aa|bb|cc");
String[] tmp = str.split("\\|");//2个\表示一个\
for(String s:tmp) {
System.out.println(s);
}
}
- 星号(*):
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = new String("aa*bb*cc");
String[] tmp = str.split("\\*");//2个\表示一个\
for(String s:tmp) {
System.out.println(s);
}
}
(4)拆分多标志
- 如果一个字符串中有多个分隔符,可以用"|"作为连字符
- 举例:
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = new String("aa-bb cc");
String[] tmp = str.split("-| ");//以-和空格拆分
for(String s:tmp) {
System.out.println(s);
}
}
3.字符串截取
(1)从指定位置截取到末尾
- 方法:substring(int beginIndex)

- 使用String类型来调用
- 举例:
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = new String("0123456");
String tmp = str.substring(2);//从2下标开始截取
System.out.println(tmp);
}
(2)截取指定区间
- 方法:substring(int beginIndex, int endIndex)
- 指定区间为前闭后开,如[3,5)
- 举例:
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = new String("0123456");
String tmp = str.substring(2,5);//截取[2,5)
System.out.println(tmp);
}
4.其他方法
- 功能:去掉字符串中的左右空格,保留中间空格
- 方法:String trim()
- 举例:
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = new String(" I love you ");
System.out.println(str);//未去空格
System.out.println(str.trim());//去掉空格
}
五、String类的总结
1.字符串不可改变
(1)String类就是用来定义字符串的,而字符串中的内容不可修改
(2) 所有涉及到可能修改字符串内容的操作都是创建一个新对象,改变的是新对象

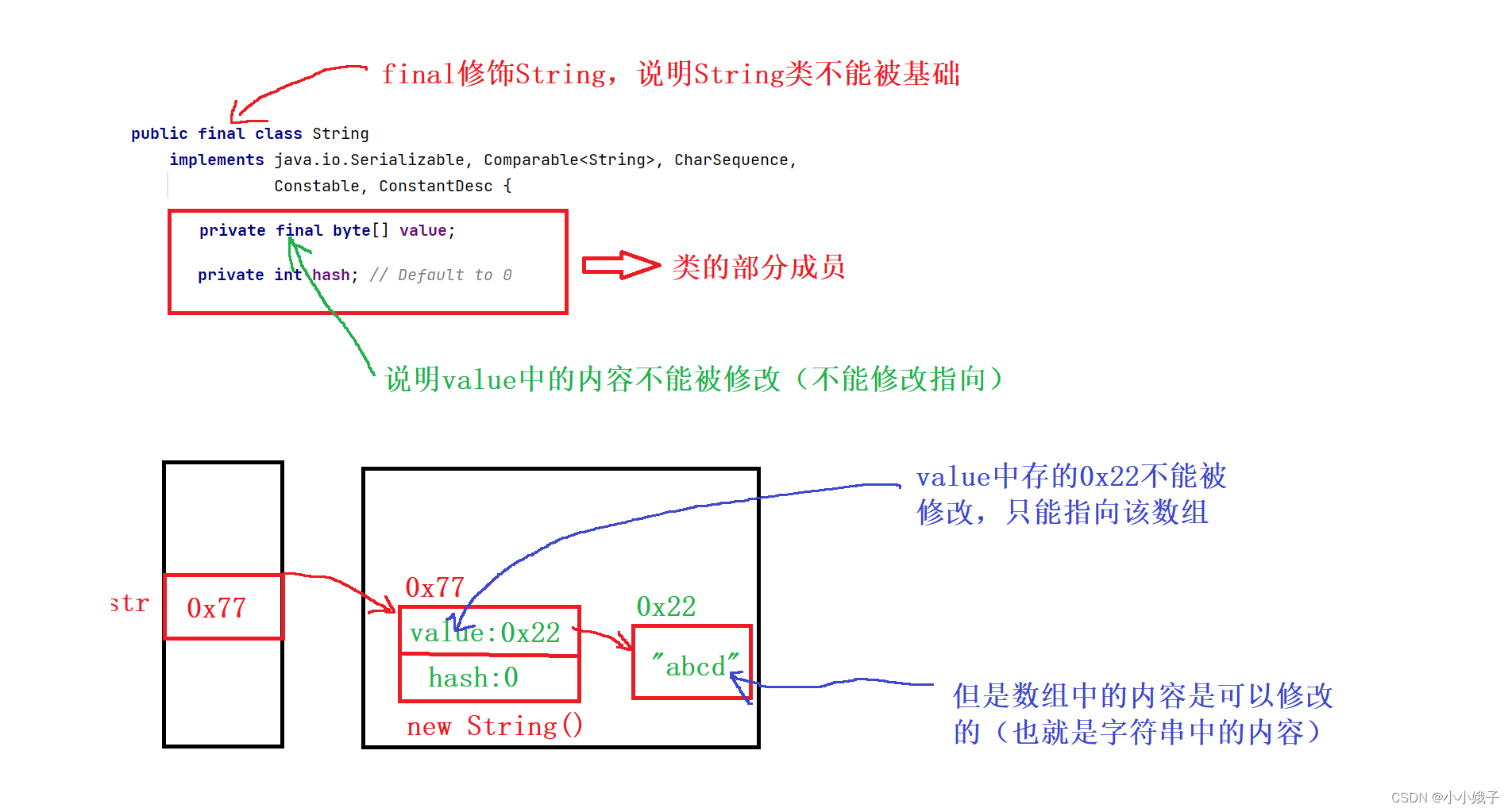
(3)简单认识String类
- 这两个final都不是字符串不能被修改的原因
2.不可修改的原因
(1)原因1
- 常量字符串不可被修改,如:
String str = "abcd";(2)原因2
- 想要修改字符串,就是拿要value指向的数组
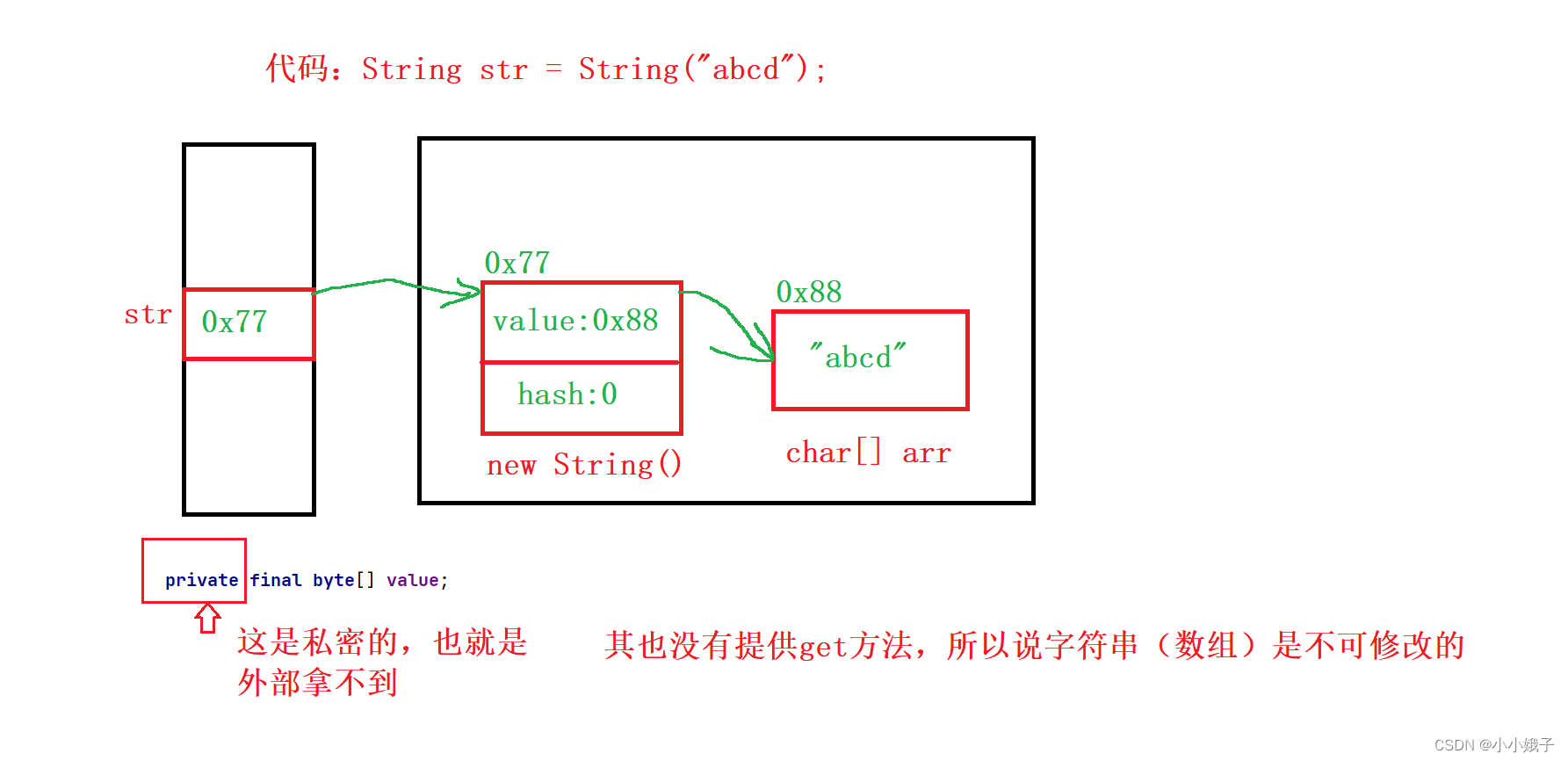
如:
public static void main(String[] args) {
char[] value = {'a','b','c','d'};
value[1] = 'x';//修改数组内容
value = new char[10];//指向新的对象
}加final前:

加了final后

- 可以修改数组但不是字符串
public static void main(String[] args) {
char[] arr = {'a','b','c','d'};
arr[0] = 'x';
arr[1] = 'q';
String str = new String(arr);
System.out.println(str);
} 
六、StringBuilder和StringBuffer
前言:SrtingBuilder和StringBuffer都是两个特殊的类,与String类似,都是字符串类型。
1.StringBuilder与StringBuffer介绍
(1)StringBuilder
- 用来实例化对象
public static void main(String[] args) {
StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder("abcd");
System.out.println(stringBuilder);
}
- 不能直接赋值常量字符串

- StringBuilder中操作字符串的方法:和String类差不多,但是方法比String类少一些
- append方法:拼接字符串
public static void main(String[] args) {
StringBuilder stirngBuilder = new StringBuilder("abcd");
stirngBuilder.append("1234");//在字符串后面拼接1234
stirngBuilder.append("xxx").append("ppp");//可以多次拼接
System.out.println(stirngBuilder);//操作的都是同一个对象
}

- reverse() 方法:逆置字符串
public static void main(String[] args) {
StringBuilder stirngBuilder = new StringBuilder("abcd");
stirngBuilder.reverse();
System.out.println(stirngBuilder);
}

- StringBuilder对字符串操作不会产生新对象
(2)StringBuffer
- 实例化对象
public static void main(String[] args) {
StringBuffer stringBuffer =new StringBuffer("abcd");
System.out.println(stringBuffer);
}
- 同样不能直接赋值常量字符串

- StringBuffer中同样有很多的方法
- StringBuffer与StringBuilder内部很相似,后面不介绍
2.三者关系与区别
(1)StringBuffer与StringBuilder的区别
- StringBuffer用于多线程部分,每次只能有一个对象调用该方法(一个马桶一个人)
(2)StringBuilder与String的相互转化
- StringBuilder变为String: 调用toString()方法
public static void main(String[] args) {
StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder("abcd");
String str = stringBuilder.toString();
System.out.println(str);
}
- String变为StringBuilder:第一种,直接调用构造方法
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = new String("abcd");
StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder(str);//调用构造方法
System.out.println(stringBuilder);
}
- String变为StringBuilder:第二种,调用append()方法
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = new String("abcd");
StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();
stringBuilder.append(str);
System.out.println(stringBuilder);
}
(3)StringBuffer、StringBuilder和String的区别
- String对象中的内容无法修改(每次操作都会产生新对象)
- StringBuffer与StringBuilder可以修改(操作的都是同一个对象)