

拷贝构造函数
概念
在现实生活中,可能存在一个与你一样的自己,我们称其为双胞胎

那在创建对象时,可否创建一个与已存在对象一某一样的新对象呢?
拷贝构造函数:只有单个形参,该形参是对本类类型对象的引用(一般常用const修饰),在用已存在的类类型对象创建新对象时由编译器自动调用
特征
拷贝构造函数也是特殊的成员函数,其特征如下:
- 拷贝构造函数是构造函数的一个重载形式
- 拷贝构造函数的参数只有一个且必须是类类型对象的引用,使用传值方式编译器直接报错,因为会引发无穷递归调用
class Date
{
public:
Date(int year = 1900, int month = 1, int day = 1)
{
_year = year;
_month = month;
_day = day;
}
// Date(const Date& d) // 正确写法
Date(const Date& d) // 错误写法:编译报错,会引发无穷递归
{
_year = d._year;
_month = d._month;
_day = d._day;
}
private:
int _year;
int _month;
int _day;
};
int main()
{
Date d1;
Date d2(d1);
return 0;
}
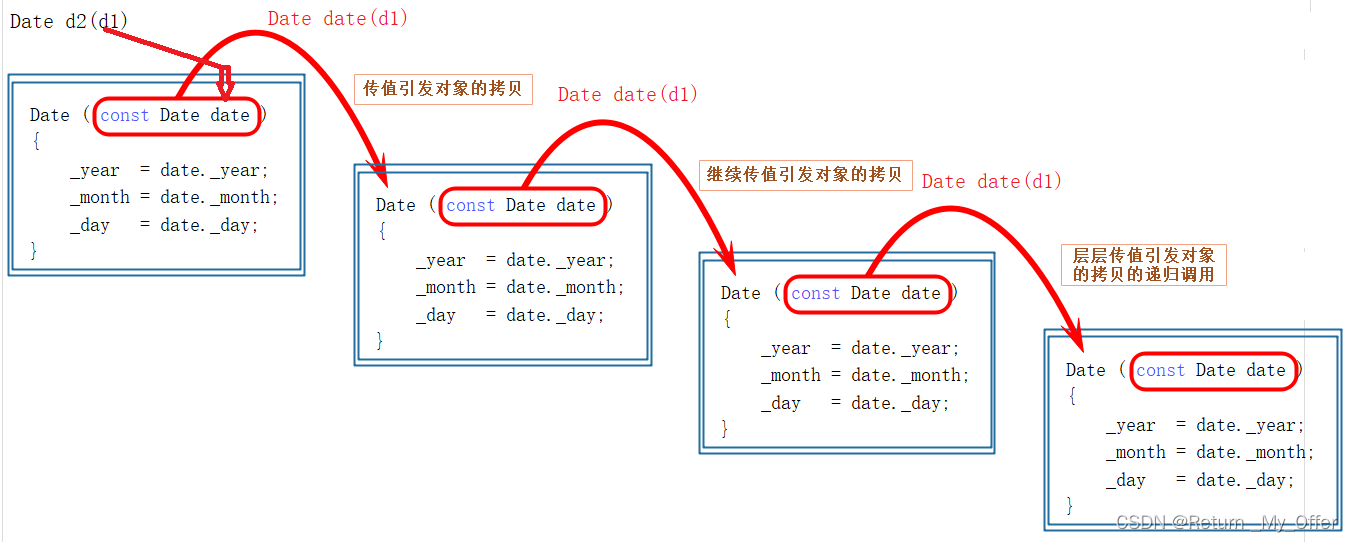
这里大家可能会很疑惑为什么会出现无穷递归的现象 下面我画一个图大家理解一下
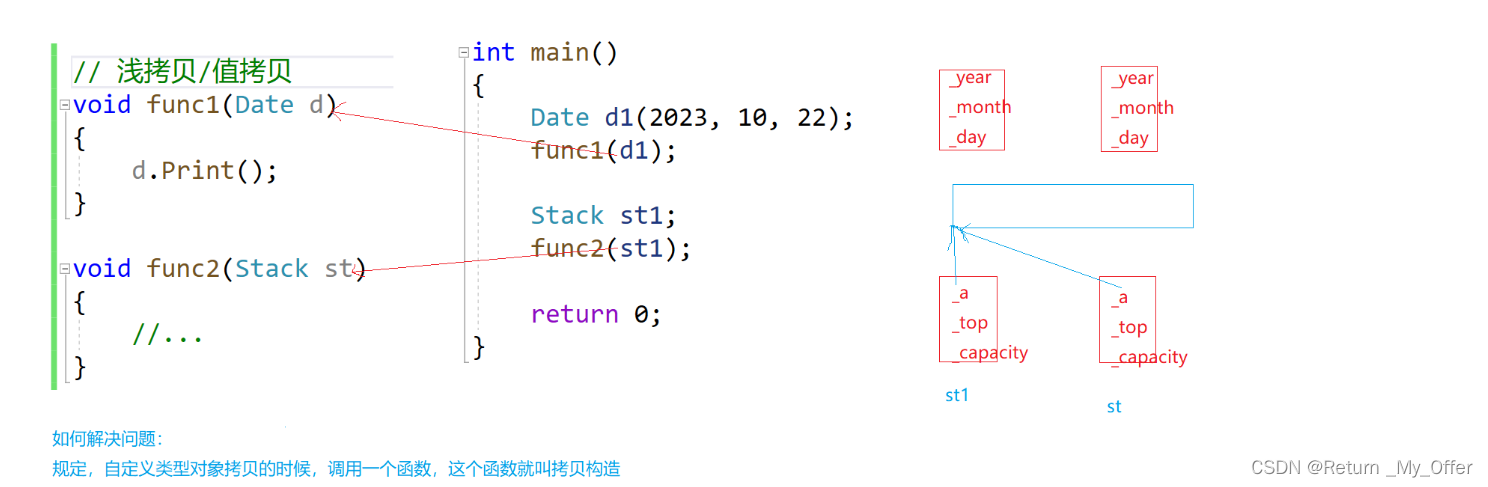
- 若未显式定义,编译器会生成默认的拷贝构造函数。 默认的拷贝构造函数对象按内存存储按字节序完成拷贝,这种拷贝叫做浅拷贝,或者值拷贝
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Date
{
public:
Date(int year = 1900, int month = 1, int day = 1)
{
_year = year;
_month = month;
_day = day;
}
Date(const Date& dd)
{
_year = dd._year;
_month = dd._month;
_day = dd._day;
}
void Print()
{
cout << _year << "/" << _month << "/" << _day << endl;
}
private:
int _year;
int _month;
int _day;
};
void func1(Date& d)
{
d.Print();
}
int main()
{
//拷贝构造函数
Date d1(2023, 10, 22);
func1(d1);
Date d2(d1);
注意:在编译器生成的默认拷贝构造函数中,内置类型是按照字节方式直接拷贝的,而自定义类型是调用其拷贝构造函数完成拷贝的
4. 编译器生成的默认拷贝构造函数已经可以完成字节序的值拷贝了,还需要自己显式实现吗?当然像日期类这样的类是没必要的。那么下面的类呢?验证一下试试?
class Stack
{
public:
Stack(size_t capacity = 3)
{
cout << "Stack(size_t capacity = 3)" << endl;
_a = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * capacity);
if (_a == nullptr)
{
perror("malloc fail");
/*exit(-1)*/return;
}
_capacity = capacity;
_top = 0;
}
~Stack()
{
cout << "~Stack()" << endl;
free(_a);
_capacity = _top = 0;
_a = nullptr;
}
Stack(const Stack& stt)
{
//深拷贝
_a = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * stt._capacity);
if (_a == nullptr)
{
perror("malloc fail");
exit(-1);//return;
}
memcpy(_a, stt._a, sizeof(int) * stt._top);
_top = stt._top;
_capacity = stt._capacity;
}
private:
int* _a;
int _capacity;
int _top;
};
int main()
{
//拷贝构造函数
Date d1(2023, 10, 22);
func1(d1);
Date d2(d1);
Stack st1;
func2(st1);
Stack st2(st1);
注意:类中如果没有涉及资源申请时,拷贝构造函数是否写都可以;一旦涉及到资源申请时,则拷贝构造函数是一定要写的,否则就是浅拷贝

5. 拷贝构造函数典型调用场景:
使用已存在对象创建新对象
函数参数类型为类类型对象
函数返回值类型为类类型对象
class Date
{
public:
Date(int year, int minute, int day)
{
cout << "Date(int,int,int):" << this << endl;
}
Date(const Date& d)
{
cout << "Date(const Date& d):" << this << endl;
}
~Date()
{
cout << "~Date():" << this << endl;
}
private:
int _year;
int _month;
int _day;
};
Date Test(Date d)
{
Date temp(d);
return temp;
}
int main()
{
Date d1(2022,1,13);
Test(d1);
return 0;
}
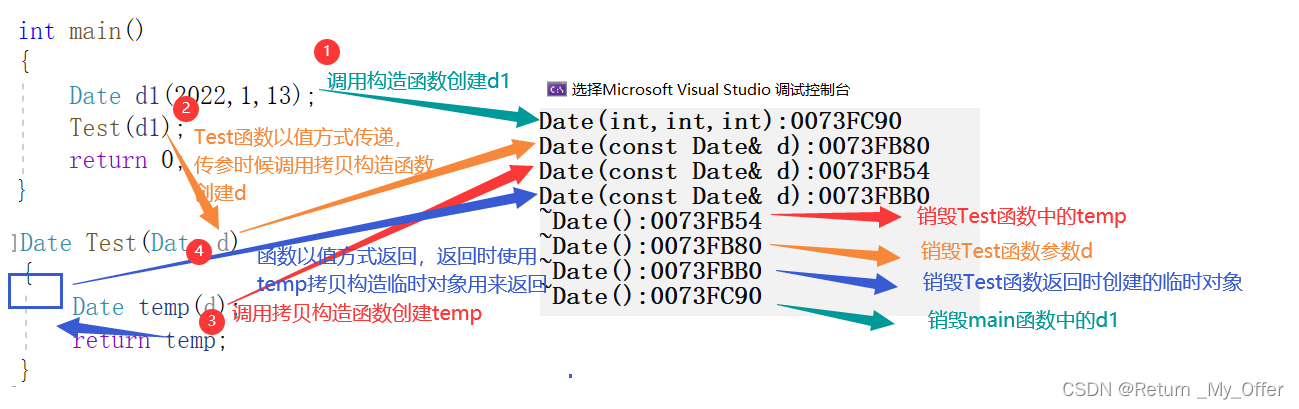
为了提高程序效率,一般对象传参时,尽量使用引用类型,返回时根据实际场景,能用引用尽量使用引用
赋值运算符重载
运算符重载
C++为了增强代码的可读性引入了运算符重载,运算符重载是具有特殊函数名的函数,也具有其
返回值类型,函数名字以及参数列表,其返回值类型与参数列表与普通的函数类似。
函数名字为:关键字operator后面接需要重载的运算符符号
函数原型:返回值类型 operator操作符(参数列表)
注意:
不能通过连接其他符号来创建新的操作符:比如operator
重载操作符必须有一个类类型参数
用于内置类型的运算符,其含义不能改变,例如:内置的整型+,不能改变其含义
作为类成员函数重载时,其形参看起来比操作数数目少1,因为成员函数的第一个参数为隐
藏的this
.* :: sizeof ?: . 注意以上5个运算符不能重载。这个经常在笔试选择题中出现
// 全局的operator==
class Date
{
public:
Date(int year = 1900, int month = 1, int day = 1)
{
_year = year;
_month = month;
_day = day;
}
//private:
int _year;
int _month;
int _day;
};
// 这里会发现运算符重载成全局的就需要成员变量是公有的,那么问题来了,封装性如何保证?
// 这里其实可以用我们后面学习的友元解决,或者干脆重载成成员函数。
bool operator==(const Date& d1, const Date& d2)
{
return d1._year == d2._year
&& d1._month == d2._month
&& d1._day == d2._day;
}
void Test ()
{
Date d1(2018, 9, 26);
Date d2(2018, 9, 27);
cout<<(d1 == d2)<<endl;
}
class Date
{
public:
Date(int year = 1900, int month = 1, int day = 1)
{
_year = year;
_month = month;
_day = day;
}
// bool operator==(Date* this, const Date& d2)
// 这里需要注意的是,左操作数是this,指向调用函数的对象
bool operator==(const Date& d2)
{
return _year == d2._year;
&& _month == d2._month
&& _day == d2._day;
}
private:
int _year;
int _month;
int _day;
};
以下是我们关于赋值运算符重载的总代码
class Date
{
public:
Date(int year = 1, int month = 1, int day = 1)
{
_year = year;
_month = month;
_day = day;
}
void Print()
{
cout << _year << "/" << _month << "/" << _day << endl;
}
//int GetYear();
bool operator==(const Date& y)
{
return _year == y._year
&& _month == y._month
&& _day == y._day;
}
bool operator>(const Date& y)
{
if (_year > y._year)
{
return true;
}
else if (_year == y._year && _month > y._month)
{
return true;
}
else if (_year == y._year && _month == y._month && _day > y._day)
{
return true;
}
return false;
}
// d1 - d2
int operator-(const Date& d)
{
// ...
return 0;
}
int GetMonthDay(int year, int month)
{
assert(year >= 1 && month >= 1 && month <= 12);
int monthArray[13] = {
0, 31, 28, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30,31 };
if (month == 2 && ((year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0) || (year % 400 == 0)))
return 29;
return monthArray[month];
}
// d1 += 100
Date& operator+=(int day)
{
_day += day;
while (_day > GetMonthDay(_year, _month))
{
_day -= GetMonthDay(_year, _month);
++_month;
if (_month == 13)
{
_year++;
_month = 1;
}
}
return *this;
}
// d1 + 50
/*Date operator+(int day)
{
Date tmp(*this);
tmp._day += day;
while (tmp._day > GetMonthDay(tmp._year, tmp._month))
{
tmp._day -= GetMonthDay(tmp._year, tmp._month);
++tmp._month;
if (tmp._month == 13)
{
tmp._year++;
tmp._month = 1;
}
}
return tmp;
}*/
Date operator+(int day)
{
Date tmp(*this);
tmp += day;
return tmp;
}
private:
int _year;
int _month;
int _day;
};
int main()
{
Date d1;
Date d2(2023, 10, 22);
bool ret1 = d1 > d2; // d1.operator>(d2) -> d1.operator>(&d1, d2)
bool ret2 = d1 == d2; // d1.operator==(d2) -> d1.operator==(&d1, d2)
// d1.operator>(d2);
// 一个重载哪些运算符呢?主要这个运算符有没有意义
// 有意义就可以实现,没有意义就不要实现
//d1 + d2;
d1 - d2;
//d1 * d2;
//d1 / d2;
d2 += 50;
d2.Print();
Date ret3 = d1 + 50;
d1.Print();
ret3.Print();
int i = 0, j = 0;
//i += 50;
int ret = j += i += 50;
return 0;
}
赋值运算符重载
- 赋值运算符重载格式
参数类型:const T&,传递引用可以提高传参效率
返回值类型:T&,返回引用可以提高返回的效率,有返回值目的是为了支持连续赋值检测是否自己给自己赋值
返回*this :要复合连续赋值的含义
class Date
{
public :
Date(int year = 1900, int month = 1, int day = 1)
{
_year = year;
_month = month;
_day = day;
}
Date (const Date& d)
{
_year = d._year;
_month = d._month;
_day = d._day;
}
Date& operator=(const Date& d)
{
if(this != &d)
{
_year = d._year;
_month = d._month;
_day = d._day;
}
return *this;
}
private:
int _year ;
int _month ;
int _day ;
};
- 赋值运算符只能重载成类的成员函数不能重载成全局函数
class Date
{
public:
Date(int year = 1900, int month = 1, int day = 1)
{
_year = year;
_month = month;
_day = day;
}
int _year;
int _month;
int _day;
};
// 赋值运算符重载成全局函数,注意重载成全局函数时没有this指针了,需要给两个参数
Date& operator=(Date& left, const Date& right)
{
if (&left != &right)
{
left._year = right._year;
left._month = right._month;
left._day = right._day;
}
return left;
}
// 编译失败:
// error C2801: “operator =”必须是非静态成员
原因:赋值运算符如果不显式实现,编译器会生成一个默认的。此时用户再在类外自己实现一个全局的赋值运算符重载,就和编译器在类中生成的默认赋值运算符重载冲突了,故赋值运算符重载只能是类的成员函数

3. 用户没有显式实现时,编译器会生成一个默认赋值运算符重载,以值的方式逐字节拷贝。注意:内置类型成员变量是直接赋值的,而自定义类型成员变量需要调用对应类的赋值运算符重载完成赋值
class Time
{
public:
Time()
{
_hour = 1;
_minute = 1;
_second = 1;
}
Time& operator=(const Time& t)
{
if (this != &t)
{
_hour = t._hour;
_minute = t._minute;
_second = t._second;
}
return *this;
}
private:
int _hour;
int _minute;
int _second;
};
class Date
{
private:
// 基本类型(内置类型)
int _year = 1970;
int _month = 1;
int _day = 1;
// 自定义类型
Time _t;
};
int main()
{
Date d1;
Date d2;
d1 = d2;
return 0;
}
前置++和后置++重载
class Date
{
public:
Date(int year = 1900, int month = 1, int day = 1)
{
_year = year;
_month = month;
_day = day;
}
// 前置++:返回+1之后的结果
// 注意:this指向的对象函数结束后不会销毁,故以引用方式返回提高效率
Date& operator++()
{
_day += 1;
return *this;
}
// 后置++:
// 前置++和后置++都是一元运算符,为了让前置++与后置++形成能正确重载
// C++规定:后置++重载时多增加一个int类型的参数,但调用函数时该参数不用传递,编译器
自动传递
// 注意:后置++是先使用后+1,因此需要返回+1之前的旧值,故需在实现时需要先将this保存
一份,然后给this+1
// 而temp是临时对象,因此只能以值的方式返回,不能返回引用
Date operator++(int)
{
Date temp(*this);
_day += 1;
return temp;
}
private:
int _year;
int _month;
int _day;
};
int main()
{
Date d;
Date d1(2022, 1, 13);
d = d1++; // d: 2022,1,13 d1:2022,1,14
d = ++d1; // d: 2022,1,15 d1:2022,1,15
return 0;
}