C++ 文件操作之配置文件读取
- 在项目应用时常常会涉及一些调参工作,如果项目封装成了.exe或者.dll,那么频繁调参多次编译是一件十分低效的事情,如果代码算法或者逻辑是一定的,那么参数完全可以通过读入配置文件来获取
- 之前在用C++ - opencv的yaml文件配置参数,但是后边参数导入时会出现异常情况,因此更换成 .txt \ .ini \ .config \ .info等格式,这些均为文本文件读取。
1. yaml的使用
1.1 yaml写入
#include "opencv2/core.hpp"
#include <time.h>
using namespace cv;
int main(int, char** argv)
{
FileStorage fs("test.yml", FileStorage::WRITE);
fs << "frameCount" << 5;
time_t rawtime; time(&rawtime);
fs << "calibrationDate" << asctime(localtime(&rawtime));
Mat cameraMatrix = (Mat_<double>(3,3) << 1000, 0, 320, 0, 1000, 240, 0, 0, 1);
Mat distCoeffs = (Mat_<double>(5,1) << 0.1, 0.01, -0.001, 0, 0);
fs << "cameraMatrix" << cameraMatrix << "distCoeffs" << distCoeffs;
fs << "features" << "[";
for( int i = 0; i < 3; i++ )
{
int x = rand() % 640;
int y = rand() % 480;
uchar lbp = rand() % 256;
fs << "{:" << "x" << x << "y" << y << "lbp" << "[:";
for( int j = 0; j < 8; j++ )
fs << ((lbp >> j) & 1);
fs << "]" << "}";
}
fs << "]";
fs.release();
return 0;
}
%YAML:1.0
frameCount: 5
calibrationDate: "Fri Jun 17 14:09:29 2011\n"
cameraMatrix: !!opencv-matrix
rows: 3
cols: 3
dt: d
data: [ 1000., 0., 320., 0., 1000., 240., 0., 0., 1. ]
distCoeffs: !!opencv-matrix
rows: 5
cols: 1
dt: d
data: [ 1.0000000000000001e-01, 1.0000000000000000e-02,
-1.0000000000000000e-03, 0., 0. ]
features:
- {
x:167, y:49, lbp:[ 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1 ] }
- {
x:298, y:130, lbp:[ 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1 ] }
- {
x:344, y:158, lbp:[ 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0 ] }
1.2 yaml读取
#include "opencv2/core.hpp"
#include <time.h>
using namespace cv;
int main(int, char** argv)
{
FileStorage fs2("test.yml", FileStorage::READ);
int frameCount = (int)fs2["frameCount"];
String date;
fs2["calibrationDate"] >> date;
Mat cameraMatrix2, distCoeffs2;
fs2["cameraMatrix"] >> cameraMatrix2;
fs2["distCoeffs"] >> distCoeffs2;
cout << "frameCount: " << frameCount << endl
<< "calibration date: " << date << endl
<< "camera matrix: " << cameraMatrix2 << endl
<< "distortion coeffs: " << distCoeffs2 << endl;
FileNode features = fs2["features"];
FileNodeIterator it = features.begin(), it_end = features.end();
int idx = 0;
std::vector<uchar> lbpval;
for( ; it != it_end; ++it, idx++ )
{
cout << "feature #" << idx << ": ";
cout << "x=" << (int)(*it)["x"] << ", y=" << (int)(*it)["y"] << ", lbp: (";
(*it)["lbp"] >> lbpval;
for( int i = 0; i < (int)lbpval.size(); i++ )
cout << " " << (int)lbpval[i];
cout << ")" << endl;
}
fs2.release();
return 0;
}
2. ini文件读取
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
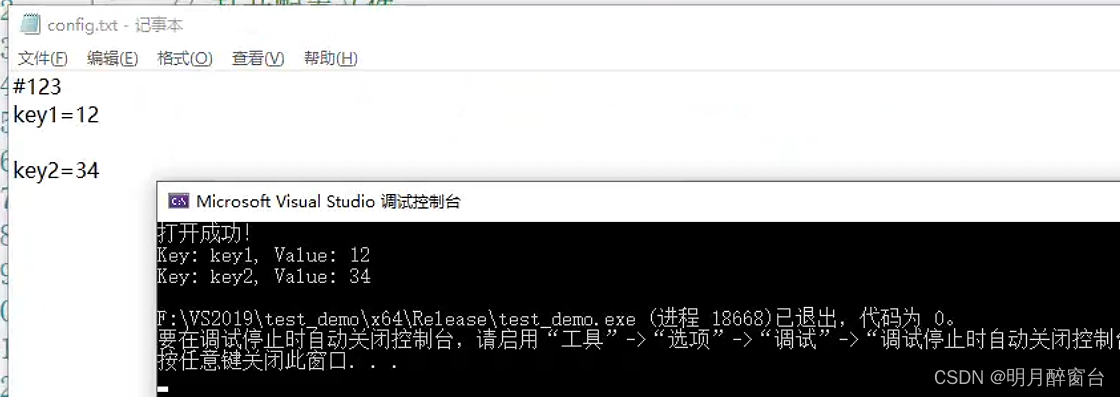
ifstream config_file("config.txt");
if (!config_file.is_open())
{
cerr << "Failed to open config file." << endl;
return -1;
}
string line;
while (getline(config_file, line))
{
if (line.empty() || line[0] == '#')
continue;
size_t pos = line.find('=');
if (pos != string::npos)
{
string key = line.substr(0, pos);
string value = line.substr(pos + 1);
cout << "Key: " << key << ", Value: " << value << endl;
}
}
config_file.close();
return 0;
}