前言:想着用Capsules网络去跑自己的数据集,发现自己的数据集(1,64,64)和Capsules论文中用到的Mnnist数据集(1,28,28)的H,W大小不一致,所以自己魔改了一份代码,在自己的数据集上跑出来的效果不错。由于太菜再魔改的时候,踩了一些坑,现在贴出来供大家参考。
论文中使用的网络结构如下:
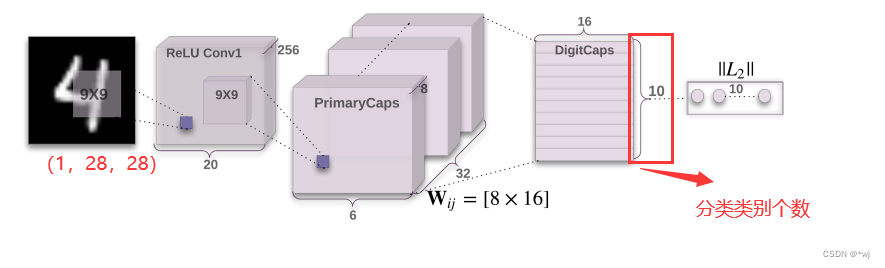
现在我的需求是输入(c, h,w)为(1,64, 64)分类类别为8类,所有需要需要以下的几个参数:
二、代码
import torch
from torch import nn
# Available device
# device = torch.device('cpu')
device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
def squash(x, dim=-1):
squared_norm = (x ** 2).sum(dim=dim, keepdim=True)
scale = squared_norm / (1 + squared_norm)
return scale * x / (squared_norm.sqrt() + 1e-8)
class PrimaryCaps(nn.Module):
"""Primary capsule layer."""
def __init__(self, num_conv_units, in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride):
super(PrimaryCaps, self).__init__()
# Each conv unit stands for a single capsule.
self.conv = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=in_channels,
out_channels=out_channels * num_conv_units,
kernel_size=kernel_size,
stride=stride)
self.out_channels = out_channels
def forward(self, x):
# Shape of x: (batch_size, in_channels, height, weight)
# Shape of out: out_capsules * (batch_size, out_channels, height, weight)
out = self.conv(x)
# Flatten out: (batch_size, out_capsules * height * weight, out_channels)
batch_size = out.shape[0]
return squash(out.contiguous().view(batch_size, -1, self.out_channels), dim=-1)
class DigitCaps(nn.Module):
"""Digit capsule layer."""
def __init__(self, in_dim, in_caps, out_caps, out_dim, num_routing):
"""
Initialize the layer.
Args:
in_dim: Dimensionality of each capsule vector.
in_caps: Number of input capsules if digits layer.
out_caps: Number of capsules in the capsule layer
out_dim: Dimensionality, of the output capsule vector.
num_routing: Number of iterations during routing algorithm
"""
super(DigitCaps, self).__init__()
self.in_dim = in_dim
self.in_caps = in_caps
self.out_caps = out_caps
self.out_dim = out_dim
self.num_routing = num_routing
self.device = device
self.W = nn.Parameter(0.01 * torch.randn(1, out_caps, in_caps, out_dim, in_dim),
requires_grad=True)
def forward(self, x):
batch_size = x.size(0)
# (batch_size, in_caps, in_dim) -> (batch_size, 1, in_caps, in_dim, 1)
x = x.unsqueeze(1).unsqueeze(4)
# W @ x =
# (1, out_caps, in_caps, out_dim, in_dim) @ (batch_size, 1, in_caps, in_dim, 1) =
# (batch_size, out_caps, in_caps, out_dims, 1)
u_hat = torch.matmul(self.W, x)
# (batch_size, out_caps, in_caps, out_dim)
u_hat = u_hat.squeeze(-1)
# detach u_hat during routing iterations to prevent gradients from flowing
temp_u_hat = u_hat.detach()
b = torch.zeros(batch_size, self.out_caps, self.in_caps, 1).to(self.device)
for route_iter in range(self.num_routing - 1):
# (batch_size, out_caps, in_caps, 1) -> Softmax along out_caps
c = b.softmax(dim=1)
# element-wise multiplication
# (batch_size, out_caps, in_caps, 1) * (batch_size, in_caps, out_caps, out_dim) ->
# (batch_size, out_caps, in_caps, out_dim) sum across in_caps ->
# (batch_size, out_caps, out_dim)
s = (c * temp_u_hat).sum(dim=2)
# apply "squashing" non-linearity along out_dim
v = squash(s)
# dot product agreement between the current output vj and the prediction uj|i
# (batch_size, out_caps, in_caps, out_dim) @ (batch_size, out_caps, out_dim, 1)
# -> (batch_size, out_caps, in_caps, 1)
uv = torch.matmul(temp_u_hat, v.unsqueeze(-1))
b += uv
# last iteration is done on the original u_hat, without the routing weights update
c = b.softmax(dim=1)
s = (c * u_hat).sum(dim=2)
# apply "squashing" non-linearity along out_dim
v = squash(s)
return v
class CapsNet(nn.Module):
"""Basic implementation of capsule network layer."""
def __init__(self):
super(CapsNet, self).__init__()
# Conv2d layer
#==================这里的卷积层的个数根据自己输入数据的尺寸修改=============
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(1, 256, 9, stride=2) # 如果输入数据是彩色图片,那么把通道1改为3
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(256, 256, 9)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
# Primary capsule
self.primary_caps = PrimaryCaps(num_conv_units=32,
in_channels=256,
out_channels=8,
kernel_size=9,
stride=2)
# Digit capsule
self.digit_caps = DigitCaps(in_dim=8,
in_caps=32 * 6 * 6,
#==================表示输出的类别=============
out_caps=8,
out_dim=16,
num_routing=3)
# Reconstruction layer
self.decoder = nn.Sequential(
#==================表示输出的类别数*16=========================================
nn.Linear(16 * 8, 512),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Linear(512, 1024),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
#==================这里的64*64需要根据自己的输入数据的h,w尺寸需改=============
nn.Linear(1024, 64*64),
nn.Sigmoid())
def forward(self, x):
out = self.relu(self.conv1(x)) #(1, 256, 56, 56)
out = self.relu(self.conv2(out))#(1, 256, 48, 48)
out = self.primary_caps(out)
out = self.digit_caps(out) #(128, 8, 16)
# Shape of logits: (batch_size, out_capsules)
logits = torch.norm(out, dim=-1)
# (128, 8)
#==================eye(表示输出的类别数)=========================================
pred = torch.eye(8).to(device).index_select(dim=0, index=torch.argmax(logits, dim=1))
# Reconstruction
batch_size = out.shape[0] # 128
# (128, 8)->(128,8,1)*(128, 8, 16)->(128,128)
out = (out * pred.unsqueeze(2)).contiguous().view(batch_size, -1) # (128, 128)
reconstruction = self.decoder(out) # (128,4096)
return logits, reconstruction
class CapsuleLoss(nn.Module):
"""Combine margin loss & reconstruction loss of capsule network."""
def __init__(self, upper_bound=0.9, lower_bound=0.1, lmda=0.5):
super(CapsuleLoss, self).__init__()
self.upper = upper_bound
self.lower = lower_bound
self.lmda = lmda
self.reconstruction_loss_scalar = 5e-4
self.mse = nn.MSELoss(reduction='sum')
def forward(self, images, labels, logits, reconstructions):
# Shape of left / right / labels: (batch_size, num_classes)
left = (self.upper - logits).relu() ** 2 # True negative #(128,8)
right = (logits - self.lower).relu() ** 2 # False positive #(128,8)
margin_loss = torch.sum(labels * left) + self.lmda * torch.sum((1 - labels) * right)
# Reconstruction loss
reconstruction_loss = self.mse(reconstructions.contiguous().view(images.shape), images) # 一个数值
# Combine two losses
return margin_loss + self.reconstruction_loss_scalar * reconstruction_loss
def test():
x = torch.rand(128, 1, 64, 64)
net = CapsNet()
logits, reconstruction = net(x)
print(logits.size())
print(logits.argmax())
print(reconstruction.size())
if __name__ == '__main__':
test()
在训练自己网络的时候需要使用到如下损失函数
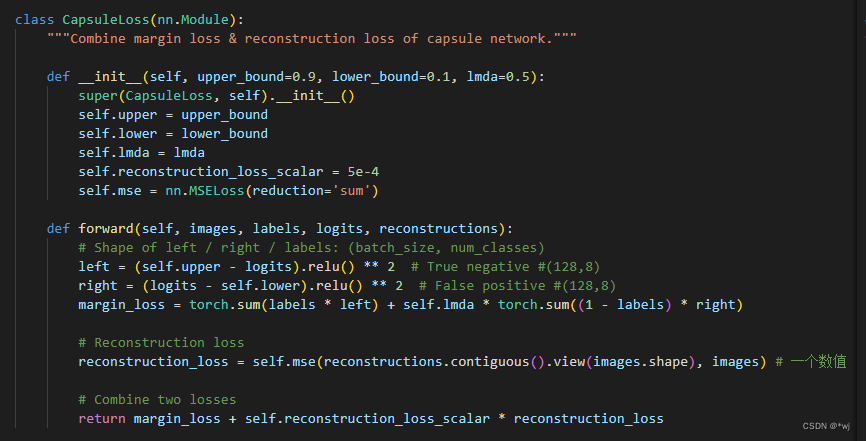
训练网络如下:**说明:训练的主干网络中的一些超参数,自己根据自己的设置,比如lr=1e-3,epochs=50,batch_size=128,数据集 **
import argparse
import random
import sys
import numpy as np
import torch
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
from torch import nn
from tqdm import tqdm
device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
# 数据集,形状(b,c,h,w)
train_loader = '自己的'
test_loader = '自己的'
# 选择梯度下降优化函数
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(params=net.parameters(), lr=lr) #weight_decay=0.001)
# 定义余弦退火学习率衰减
scheduler = torch.optim.lr_scheduler.StepLR(optimizer, step_size=10, gamma=0.5, last_epoch=-1)
# 选择损失函数 用于多分类的问题
criterion = capsnet.CapsuleLoss()
# 训练函数
def train(epoch, dataloader, model, optimizer):
# 调用train函数之后,网络就会自动加载其中的batchNormal和dropout俩个函数
model.train()
# 定义一个损失值初始化数据
loss_all, correct = 0., 0
with tqdm(dataloader, unit="batch", file=sys.stdout) as tepoch:
for (data, label) in tepoch:
# tepoch.set_description(f"Epoch {epoch}")
# 送入到搭建好的网络中进行前向传播训练
data = data.to(device)
label = torch.eye(8).index_select(dim=0, index=label).to(device)
logits, reconstruction = model(data)
# torch.Size([128, 8])
loss = criterion(data, label, logits, reconstruction)
# 累计epochs的次数之后的总的准确率是多少
correct += torch.sum(torch.argmax(logits, dim=1) == torch.argmax(label, dim=1)).item()
# 累计所有的损失值
loss_all += loss.item()
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
tepoch.desc="epoch[{}/{}] train Loss:{:.3f} Accuracy: {:.2f}%".format(epoch + 1,
opt.epochs,
loss_all/len(dataloader),
100 * correct/len(dataloader.dataset))
# scheduler.step()
# 计算平均loss
loss_all /= len(dataloader)# 获取数据的长度
correct /= len(dataloader.dataset)
return loss_all, correct
# 测试函数
def test(dataloader, model):
model.eval()
test_loss, correct = 0, 0
with torch.no_grad(): #在该模块下,所有计算得出的tensor的requires_grad都自动设置为False。
for data, label in dataloader:
data = data.to(device)
label = torch.eye(8).index_select(dim=0, index=label).to(device)
logits, reconstruction = model(data)
# 通过损失函数记录pred 和标签对不上的值
test_loss += criterion(data, label, logits, reconstruction).item()
# 累计epochs的次数之后的总的准确率是多少
correct += torch.sum(torch.argmax(logits, dim=1) == torch.argmax(label, dim=1)).item()
test_loss /= len(dataloader)
correct /= len(dataloader.dataset)
# 提前停止训练
early_stopping(test_loss, model)
print("------------>test Loss: {:.3f}, Accuracy: {:.2f}%\n".format(test_loss, (100 * correct)))
return test_loss, correct
for epoch in range(opt.epochs):
# 传入训练的参数
train_loss, train_acc = train(epoch, train_loader, net, optimizer)
# 传入测试的参数
test_loss, test_acc = test(test_loader, net)
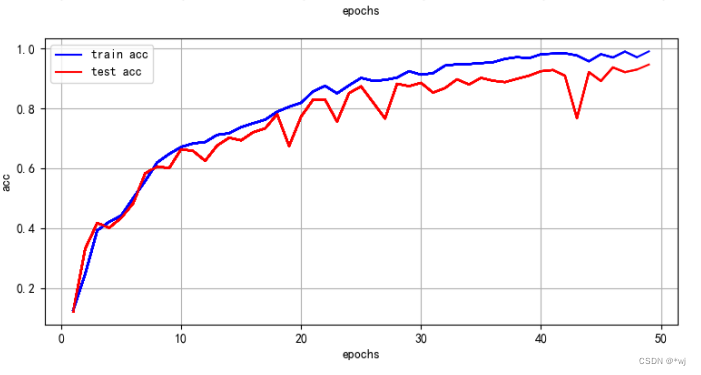
自己数据集训练的效果如下: