数组描述栈
#pragma warning(disable:4996)
#include <iostream>
#include<iterator>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
//边长一维数组(增加或减少)
//改变一个一维数组的长度
template<class T>
void changeLength1D(T*& a, int oldLength, int newLength)
{
if (newLength < 0)
{
cout << "错误:newLength 小于 0!";
exit(-1);
}
T* temp = new T[newLength];
int number = min(oldLength, newLength);
copy(a, a + number, temp);
delete[] a;
a = temp;
}
template<class T>
class stack
{
public:
virtual ~stack() {};
virtual bool empty() const = 0;
virtual int size() const = 0;
virtual T& top() = 0;
virtual void pop() = 0;
virtual void push(const T& theElement) = 0;
};
template<class T>
class arrayStack :public stack<T>
{
public:
arrayStack(int initialCapacity = 10);
~arrayStack() { delete[] stack; }
bool empty() const { return stackTop == -1; }
int size() const { return stackTop + 1; }
T& top()
{
if (stackTop == -1)
{
cout << "栈中没有元素" << endl;
exit(-1);
}
return stack[stackTop];
}
void pop()
{
if (stackTop == -1)
{
cout << "栈中没有元素" << endl;
exit(-1);
}
stack[stackTop--].~T();
}
void push(const T& theElement);
void output(ostream& out) const;
private:
friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const arrayStack<T>& x);
//当前栈顶
int stackTop;
//栈容量
int arrayLength;
//元素数组
T *stack;
};
template<class T>
arrayStack<T>::arrayStack(int initialCapacity)
{
if (initialCapacity < 1)
{
cout << "initialCapacity must be > 0" << endl;
exit(-1);
}
arrayLength = initialCapacity;
stack = new T[arrayLength];
stackTop = -1;
}
template<class T>
void arrayStack<T>::push(const T& theElement)
{
//判断是否还有空间
if (stackTop == arrayLength - 1)
{
changeLength1D(stack, arrayLength, 2 * arrayLength);
arrayLength *= 2;
}
stack[++stackTop] = theElement;
}
template<typename T> ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const arrayStack<T>& x)
{
x.output(out);
return out;
}
template<typename T> void arrayStack<T>::output(ostream& out) const
{
//把栈插入输出流
copy(stack, stack + stackTop + 1, ostream_iterator<T>(cout, " "));
}
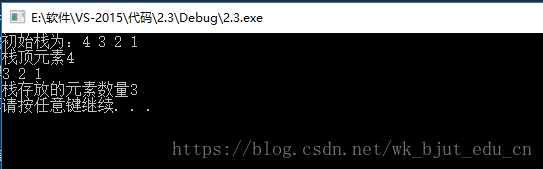
int main()
{
arrayStack<int> s;
s.push(1);
s.push(2);
s.push(3);
s.push(4);
cout << "初始栈为:";
s.output(cout);
cout << endl;
cout << "栈顶元素" <<s.top() << endl;
s.pop();
s.output(cout);
cout << endl;
cout << "栈存放的元素数量"<<s.size() << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}

链表描述栈
当用链表描述栈时,必须要确定用链表的哪段作为栈顶。若用链表的右端作为栈顶,则栈操作top、push和pop的实现需要用时O(size())。而用链表的左端作为栈顶,需要调用的链表方法是get(0)、insert(0,theElement)和erase(0),其中每一个链表方法需要用时O(1)。所以选择链表的左端作为栈顶。
#pragma warning(disable:4996)
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
//链表节点的结构定义
template<class T>
struct chainNode
{
T element;
chainNode<T> *next;
chainNode() {}
chainNode(const T& element)
{
this->element = element;
}
chainNode(const T& element, chainNode<T>* next)
{
this->element = element;
this->next = next;
}
};
template<class T>
class stack
{
public:
virtual ~stack() {};
virtual bool empty() const = 0;
virtual int size() const = 0;
virtual T& top() = 0;
virtual void pop() = 0;
virtual void push(const T& theElement) = 0;
};
template<class T>
class linkStack :public stack<T>
{
public:
linkStack()
{
stackTop = NULL;
stackSize = 0;
}
~linkStack();
bool empty() const
{
return stackSize == 0;
}
int size() const
{
return stackSize;
}
T& top()
{
if (stackSize == 0)
{
cout << "栈内无元素" << endl;
exit(-1);
}
return stackTop->element;
}
void pop();
void push(const T& theElement);
void output(ostream& out) const;
private:
friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const linkStack<T>& x);
//栈顶指针
chainNode<T>* stackTop;
//栈中元素个数
int stackSize;
};
template<class T>
void linkStack<T>::pop()
{
if (stackSize == 0)
{
cout << "栈内无元素" << endl;
exit(-1);
}
chainNode<T>* nextNode = stackTop->next;
delete stackTop;
stackTop = nextNode;
stackSize--;
}
template<class T>
void linkStack<T>::push(const T& theElement)
{
stackTop = new chainNode<T>(theElement, stackTop);
stackSize++;
}
template<class T>
linkStack<T>::~linkStack()
{
while (stackTop != NULL)
{
chainNode<T>* nextNode = stackTop->next;
delete stackTop;
stackTop = nextNode;
}
}
template<typename T> ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const linkStack<T>& x)
{
x.output(out);
return out;
}
template<class T>
void linkStack<T>::output(ostream& out) const
{
for (chainNode<T>* nextNode = stackTop; nextNode != NULL;
nextNode = nextNode->next)
out << nextNode->element << " ";
}
int main()
{
linkStack<int> s;
s.push(1);
s.push(2);
s.push(3);
s.push(4);
cout << "初始栈为:";
s.output(cout);
cout << endl;
cout << "栈顶元素" <<s.top() << endl;
s.pop();
s.output(cout);
cout << endl;
cout << "栈存放的元素数量"<<s.size() << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
用数组栈解决括号匹配问题
int main()
{
arrayStack<int> s;
string expr;
getline(cin, expr);
int length = (int)expr.size();
for (int i = 0; i < length; ++i)
{
if (expr[i] == '(')
s.push(i);
else if (expr[i] == ')')
{
if (s.empty())
cout << "没有和右括号"<<i<<"匹配的左括号" << endl;
else
{
cout << s.top() << ' ' << i << endl;
s.pop();
}
}
}
while (!s.empty())
{
cout << "没有和左括号"<<s.top()<<"匹配的右括号" << endl;
s.pop();
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}