AIO,在NIO的基础上引入了异步通道的概念,并提供了异步文件和异步套接字通道的实现,从而在真正意义上实现了异步非阻塞,这是在jdk1.7及以后才有的。
AIO不需要通过类似NIO的多路复用器对注册的通道进行轮训操作,即可实现异步读写,从而简化了NIO的编程模型。也可以称为NIO2.0.这种模式才是真正的异步非阻塞模型。
AsynchonousServerSocketChannel
AsynchonousSocketChannel
代码:
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.channels.AsynchronousChannelGroup;
import java.nio.channels.AsynchronousServerSocketChannel;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
public class Server {
//线程池
private ExecutorService executorService;
//线程组
private AsynchronousChannelGroup threadGroup;
//服务器通道
public AsynchronousServerSocketChannel assc;
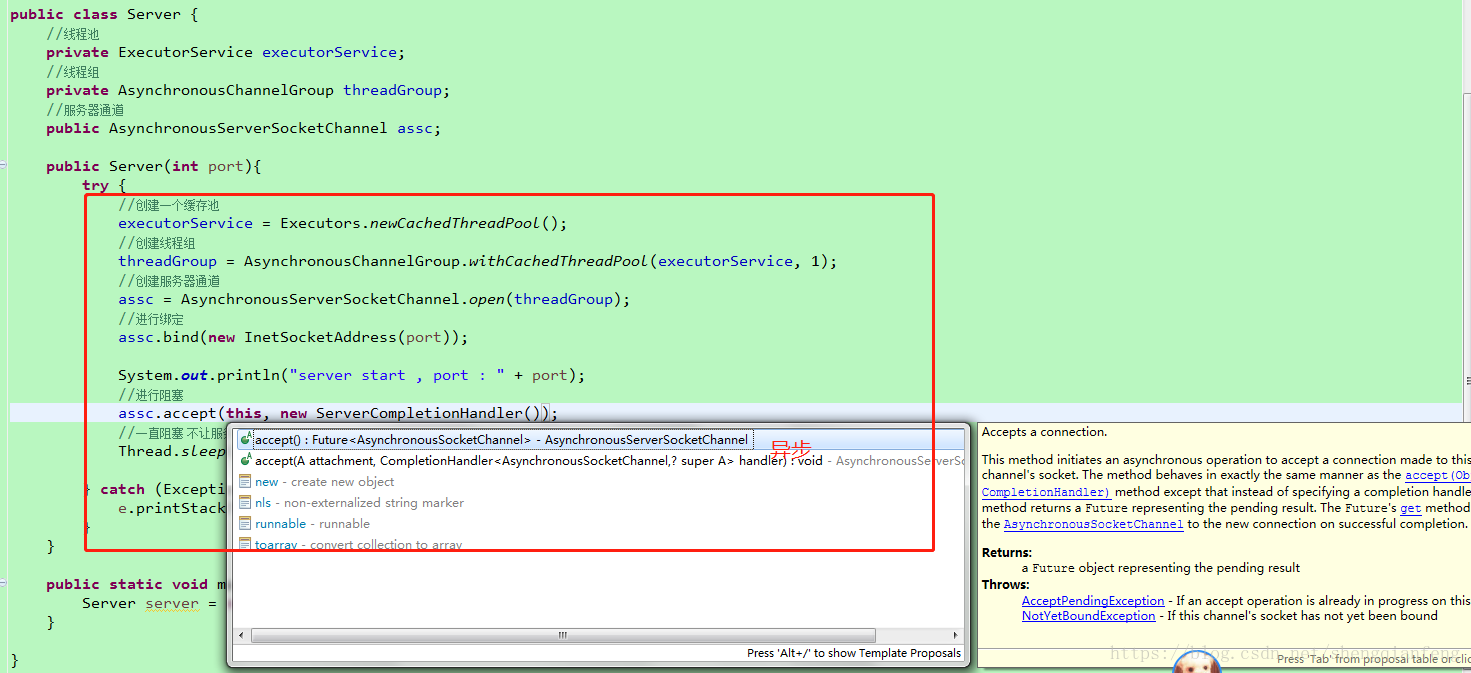
public Server(int port){
try {
//创建一个缓存池
executorService = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
//创建线程组
threadGroup = AsynchronousChannelGroup.withCachedThreadPool(executorService, 1);
//创建服务器通道
assc = AsynchronousServerSocketChannel.open(threadGroup);
//进行绑定
assc.bind(new InetSocketAddress(port));
System.out.println("server start , port : " + port);
//进行阻塞
assc.accept(this, new ServerCompletionHandler());
//一直阻塞 不让服务器停止
Thread.sleep(Integer.MAX_VALUE);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Server server = new Server(8765);
}
}
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.AsynchronousSocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.CompletionHandler;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
public class ServerCompletionHandler implements CompletionHandler<AsynchronousSocketChannel, Server> {
@Override
public void completed(AsynchronousSocketChannel asc, Server attachment) {
//当有下一个客户端接入的时候 直接调用Server的accept方法,这样反复执行下去,保证多个客户端都可以阻塞
attachment.assc.accept(attachment, this);
read(asc);
}
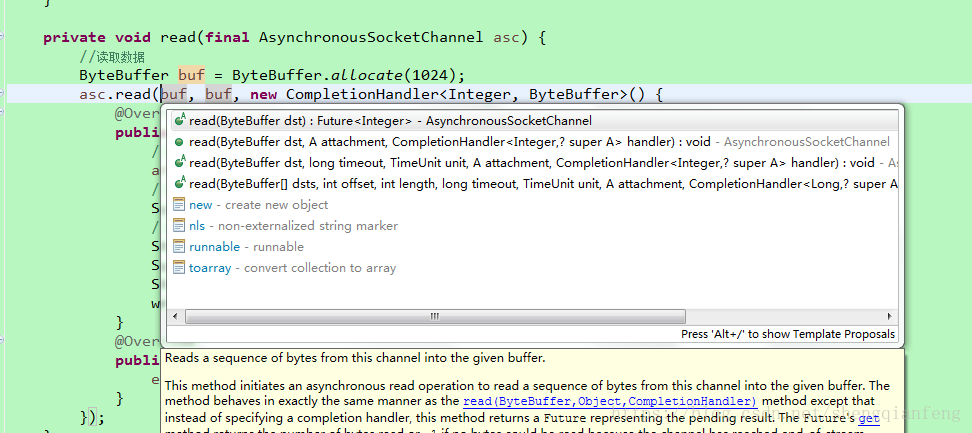
private void read(final AsynchronousSocketChannel asc) {
//读取数据
ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
asc.read(buf, buf, new CompletionHandler<Integer, ByteBuffer>() {
@Override
public void completed(Integer resultSize, ByteBuffer attachment) {
//进行读取之后,重置标识位
attachment.flip();
//获得读取的字节数
System.out.println("Server -> " + "收到客户端的数据长度为:" + resultSize);
//获取读取的数据
String resultData = new String(attachment.array()).trim();
System.out.println("Server -> " + "收到客户端的数据信息为:" + resultData);
String response = "服务器响应, 收到了客户端发来的数据: " + resultData;
write(asc, response);
}
@Override
public void failed(Throwable exc, ByteBuffer attachment) {
exc.printStackTrace();
}
});
}
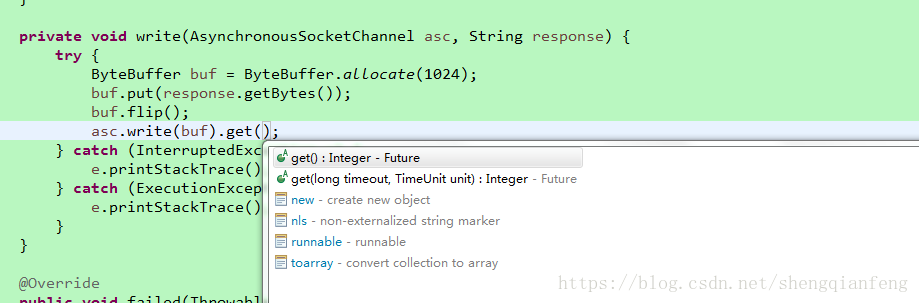
private void write(AsynchronousSocketChannel asc, String response) {
try {
ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
buf.put(response.getBytes());
buf.flip();
asc.write(buf).get();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
public void failed(Throwable exc, Server attachment) {
exc.printStackTrace();
}
}
import java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.AsynchronousSocketChannel;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
public class Client implements Runnable{
private AsynchronousSocketChannel asc ;
public Client() throws Exception {
asc = AsynchronousSocketChannel.open();
}
public void connect(){
asc.connect(new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1", 8765));
}
public void write(String request){
try {
asc.write(ByteBuffer.wrap(request.getBytes())).get();
read();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private void read() {
ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
try {
asc.read(buf).get();
buf.flip();
byte[] respByte = new byte[buf.remaining()];
buf.get(respByte);
System.out.println(new String(respByte,"utf-8").trim());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
public void run() {
while(true){
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Client c1 = new Client();
c1.connect();
Client c2 = new Client();
c2.connect();
Client c3 = new Client();
c3.connect();
new Thread(c1, "c1").start();
new Thread(c2, "c2").start();
new Thread(c3, "c3").start();
Thread.sleep(1000);
c1.write("c1 aaa");
c2.write("c2 bbbb");
c3.write("c3 ccccc");
}
}
打印:
server端:
server start , port : 8765 Server -> 收到客户端的数据长度为:6 Server -> 收到客户端的数据信息为:c1 aaa Server -> 收到客户端的数据长度为:7 Server -> 收到客户端的数据信息为:c2 bbbb Server -> 收到客户端的数据长度为:8 Server -> 收到客户端的数据信息为:c3 ccccc
client端:
服务器响应, 收到了客户端发来的数据: c1 aaa 服务器响应, 收到了客户端发来的数据: c2 bbbb 服务器响应, 收到了客户端发来的数据: c3 ccccc
简单解读:
对于ServerCompletionHandler的Complent和fail方法的场景分别是,当服务器端接入了客户端channel后,就会调用complete方法,参数为(AsynchronousSocketChannel asc, Server attachment),就是一个客户端的channel和服务器端实例。
需要注意:
@Override
public void completed(AsynchronousSocketChannel asc, Server attachment) {
//当有下一个客户端接入的时候 直接调用Server的accept方法,这样反复执行下去,保证多个客户端都可以阻塞
attachment.assc.accept(attachment, this);
read(asc);
}
一定要先调用attachment.assc.accept(attachment, this);这个异步方法,保证后来的客户端可以正常接入。
异步方法: