Intent intent = new Intent(this, MyService.class); startService(intent);
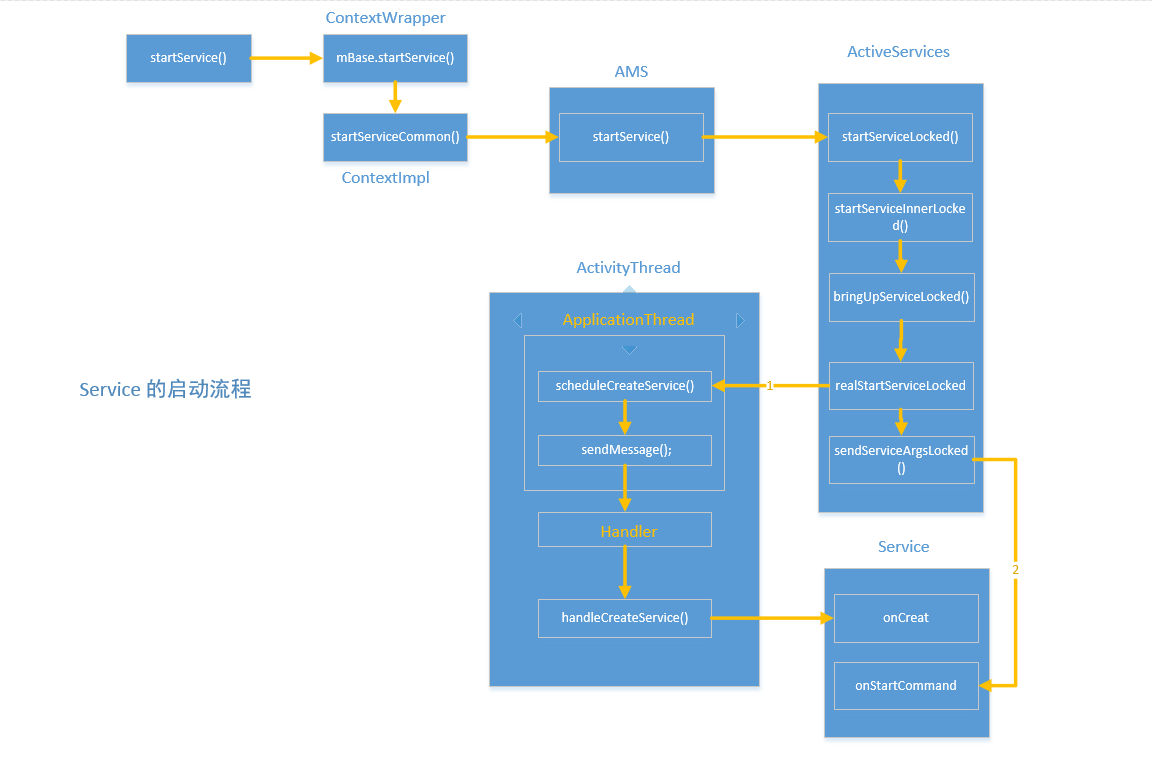
深入startService 发现调用的是ContextWrapper 的startService,如下:
public class ContextWrapper extends Context {
Context mBase;
...
@Override
public ComponentName startService(Intent service) {
return mBase.startService(service);
}
...
}
其中mBase 的类型实际上是ContextImpl,从Activity 被创建时会通过attach 方法将一个ContextImpl 对象关联起来,这个ContextImpl就是上面的 mBase,从ContextWrapper 的实现可以看出,其大部分操作都是通过mBase 来实现的,ContextImpl 的startService 方法如下:
class ContextImpl extends Context {
...
@Override
public ComponentName startService(Intent service) {
warnIfCallingFromSystemProcess();
return startServiceCommon(service, mUser);
}
private ComponentName startServiceCommon(Intent service, UserHandle user) {
try {
validateServiceIntent(service);
service.prepareToLeaveProcess();
ComponentName cn = ActivityManagerNative.getDefault().startService(
mMainThread.getApplicationThread(), service, service.resolveTypeIfNeeded(
getContentResolver()), getOpPackageName(), user.getIdentifier());
if (cn != null) {
if (cn.getPackageName().equals("!")) {
throw new SecurityException(
"Not allowed to start service " + service
+ " without permission " + cn.getClassName());
} else if (cn.getPackageName().equals("!!")) {
throw new SecurityException(
"Unable to start service " + service
+ ": " + cn.getClassName());
}
}
return cn;
} catch (RemoteException e) {
throw new RuntimeException("Failure from system", e);
}
}
...
}
由上可知,最终会调用ActivityManagerNative.getDefault().startService 方法,实际就是AMS 的startService 方法,如下所示:
final ActiveServices mServices;
@Override
public ComponentName startService(IApplicationThread caller, Intent service,
String resolvedType, String callingPackage, int userId)
throws TransactionTooLargeException {
enforceNotIsolatedCaller("startService");
// Refuse possible leaked file descriptors
if (service != null && service.hasFileDescriptors() == true) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("File descriptors passed in Intent");
}
if (callingPackage == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("callingPackage cannot be null");
}
if (DEBUG_SERVICE) Slog.v(TAG_SERVICE,
"startService: " + service + " type=" + resolvedType);
synchronized(this) {
final int callingPid = Binder.getCallingPid();
final int callingUid = Binder.getCallingUid();
final long origId = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
ComponentName res = mServices.startServiceLocked(caller, service,
resolvedType, callingPid, callingUid, callingPackage, userId);
Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(origId);
return res;
}
}
从代码中可看出,AMS 的startService 方法会调用 ActiveServices 的startServiceLocked 方法来完成Service 的后续启动流程,ActiveServices 是一个富足AMS 进行Service 管理的类,包括Service 的启动、绑定、停止等,如下所示:
ComponentName startServiceLocked(IApplicationThread caller, Intent service, String resolvedType,
int callingPid, int callingUid, String callingPackage, int userId)
throws TransactionTooLargeException {
...
return startServiceInnerLocked(smap, service, r, callerFg, addToStarting);
}
在startServiceLocked 方法中,会继续调用startServiceInnerLocked 方法,如下所示:
ComponentName startServiceInnerLocked(ServiceMap smap, Intent service, ServiceRecord r,
boolean callerFg, boolean addToStarting) throws TransactionTooLargeException {
ProcessStats.ServiceState stracker = r.getTracker();
if (stracker != null) {
stracker.setStarted(true, mAm.mProcessStats.getMemFactorLocked(), r.lastActivity);
}
r.callStart = false;
synchronized (r.stats.getBatteryStats()) {
r.stats.startRunningLocked();
}
String error = bringUpServiceLocked(r, service.getFlags(), callerFg, false);
if (error != null) {
return new ComponentName("!!", error);
}
if (r.startRequested && addToStarting) {
boolean first = smap.mStartingBackground.size() == 0;
smap.mStartingBackground.add(r);
r.startingBgTimeout = SystemClock.uptimeMillis() + BG_START_TIMEOUT;
if (DEBUG_DELAYED_SERVICE) {
RuntimeException here = new RuntimeException("here");
here.fillInStackTrace();
Slog.v(TAG_SERVICE, "Starting background (first=" + first + "): " + r, here);
} else if (DEBUG_DELAYED_STARTS) {
Slog.v(TAG_SERVICE, "Starting background (first=" + first + "): " + r);
}
if (first) {
smap.rescheduleDelayedStarts();
}
} else if (callerFg) {
smap.ensureNotStartingBackground(r);
}
return r.name;
}
在上述代码中,ServiceRecord 描述的是一个Service 记录,ServiceRecord 一致贯穿着整个Service 的启动过程。startServiceInnerLocked 方法并没有完成具体的启动工作,而是把后续的工作交给了bringUpServiceLocked 方法来处理,bringUpServiceLocked 源码如下:
private final String bringUpServiceLocked(ServiceRecord r, int intentFlags, boolean execInFg,
boolean whileRestarting) throws TransactionTooLargeException {
...
if (app != null && app.thread != null) {
try {
app.addPackage(r.appInfo.packageName, r.appInfo.versionCode, mAm.mProcessStats);
//启动服务
realStartServiceLocked(r, app, execInFg);
return null;
} catch (TransactionTooLargeException e) {
throw e;
} catch (RemoteException e) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Exception when starting service " + r.shortName, e);
}
...
return null;
}
在bringUpServiceLocked 方法中会调用realStartServiceLocked 方法来真正的启动Service,如下所示:
private final void realStartServiceLocked(ServiceRecord r,
ProcessRecord app, boolean execInFg) throws RemoteException {
...
boolean created = false;
try {
if (LOG_SERVICE_START_STOP) {
String nameTerm;
int lastPeriod = r.shortName.lastIndexOf('.');
nameTerm = lastPeriod >= 0 ? r.shortName.substring(lastPeriod) : r.shortName;
EventLogTags.writeAmCreateService(
r.userId, System.identityHashCode(r), nameTerm, r.app.uid, r.app.pid);
}
synchronized (r.stats.getBatteryStats()) {
r.stats.startLaunchedLocked();
}
mAm.ensurePackageDexOpt(r.serviceInfo.packageName);
app.forceProcessStateUpTo(ActivityManager.PROCESS_STATE_SERVICE);
//创建Service 对象并调用其 onCreat 方法
app.thread.scheduleCreateService(r, r.serviceInfo,
mAm.compatibilityInfoForPackageLocked(r.serviceInfo.applicationInfo),
app.repProcState);
r.postNotification();
created = true;
} catch (DeadObjectException e) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Application dead when creating service " + r);
mAm.appDiedLocked(app);
throw e;
} finally {
if (!created) {
// Keep the executeNesting count accurate.
final boolean inDestroying = mDestroyingServices.contains(r);
serviceDoneExecutingLocked(r, inDestroying, inDestroying);
// Cleanup.
if (newService) {
app.services.remove(r);
r.app = null;
}
// Retry.
if (!inDestroying) {
scheduleServiceRestartLocked(r, false);
}
}
}
requestServiceBindingsLocked(r, execInFg);
updateServiceClientActivitiesLocked(app, null, true);
// If the service is in the started state, and there are no
// pending arguments, then fake up one so its onStartCommand() will
// be called.
if (r.startRequested && r.callStart && r.pendingStarts.size() == 0) {
r.pendingStarts.add(new ServiceRecord.StartItem(r, false, r.makeNextStartId(),
null, null));
}
//调用Service 的其他方法
sendServiceArgsLocked(r, execInFg, true);
...
}
public final void scheduleCreateService(IBinder token,
ServiceInfo info, CompatibilityInfo compatInfo, int processState) {
updateProcessState(processState, false);
CreateServiceData s = new CreateServiceData();
s.token = token;
s.info = info;
s.compatInfo = compatInfo;
sendMessage(H.CREATE_SERVICE, s);
}
这里和Activity 类似,都是通过发送消息给Handler H 来完成,如下所示:
case CREATE_SERVICE:
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "serviceCreate");
handleCreateService((CreateServiceData)msg.obj);
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
break;
H会接收到这个消息,并通过ActivityThread 的handleCreateService 方法来完成 Service 的最终启动,如下所示:
final ArrayMap<IBinder, Service> mServices = new ArrayMap<>();
private void handleCreateService(CreateServiceData data) {
// If we are getting ready to gc after going to the background, well
// we are back active so skip it.
unscheduleGcIdler();
LoadedApk packageInfo = getPackageInfoNoCheck(
data.info.applicationInfo, data.compatInfo);
Service service = null;
try {
//创建Service 对象
java.lang.ClassLoader cl = packageInfo.getClassLoader();
service = (Service) cl.loadClass(data.info.name).newInstance();
} catch (Exception e) {
if (!mInstrumentation.onException(service, e)) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Unable to instantiate service " + data.info.name
+ ": " + e.toString(), e);
}
}
try {
if (localLOGV) Slog.v(TAG, "Creating service " + data.info.name);
//创建ContextImpl 对象
ContextImpl context = ContextImpl.createAppContext(this, packageInfo);
context.setOuterContext(service);
//创建Application 对象
Application app = packageInfo.makeApplication(false, mInstrumentation);
//通过service.attach 方法关联ContextImpl
service.attach(context, this, data.info.name, data.token, app,
ActivityManagerNative.getDefault());
//调用service.onCreate 方法
service.onCreate();
//将Service对象存储到ActivityThread 中的一个列表中
mServices.put(data.token, service);
try {
ActivityManagerNative.getDefault().serviceDoneExecuting(
data.token, SERVICE_DONE_EXECUTING_ANON, 0, 0);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
// nothing to do.
}
} catch (Exception e) {
if (!mInstrumentation.onException(service, e)) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Unable to create service " + data.info.name
+ ": " + e.toString(), e);
}
}
}
- 首先通过类加载器创建 Service 的实例
- 然后创建Application 对象并调用其 onCreat,Application 的创建过程只会有一次
- 接着创建ContextImpl 对象并通过 Service 的 attach 方法建立二者之间的关系,这个过程和Activity 类似
- 最后调用 Service 的onCreat 方法,并将Service 对象存储到ActivityThread 的 mServices列表中。
private void handleServiceArgs(ServiceArgsData data) {
Service s = mServices.get(data.token);
if (s != null) {
try {
if (data.args != null) {
data.args.setExtrasClassLoader(s.getClassLoader());
data.args.prepareToEnterProcess();
}
int res;
if (!data.taskRemoved) {
//调用Service 的 onStartCommand 方法
res = s.onStartCommand(data.args, data.flags, data.startId);
} else {
s.onTaskRemoved(data.args);
res = Service.START_TASK_REMOVED_COMPLETE;
}
QueuedWork.waitToFinish();
try {
ActivityManagerNative.getDefault().serviceDoneExecuting(
data.token, SERVICE_DONE_EXECUTING_START, data.startId, res);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
// nothing to do.
}
ensureJitEnabled();
} catch (Exception e) {
if (!mInstrumentation.onException(s, e)) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Unable to start service " + s
+ " with " + data.args + ": " + e.toString(), e);
}
}
}
}
@Override
public boolean bindService(Intent service, ServiceConnection conn,
int flags) {
return mBase.bindService(service, conn, flags);
}
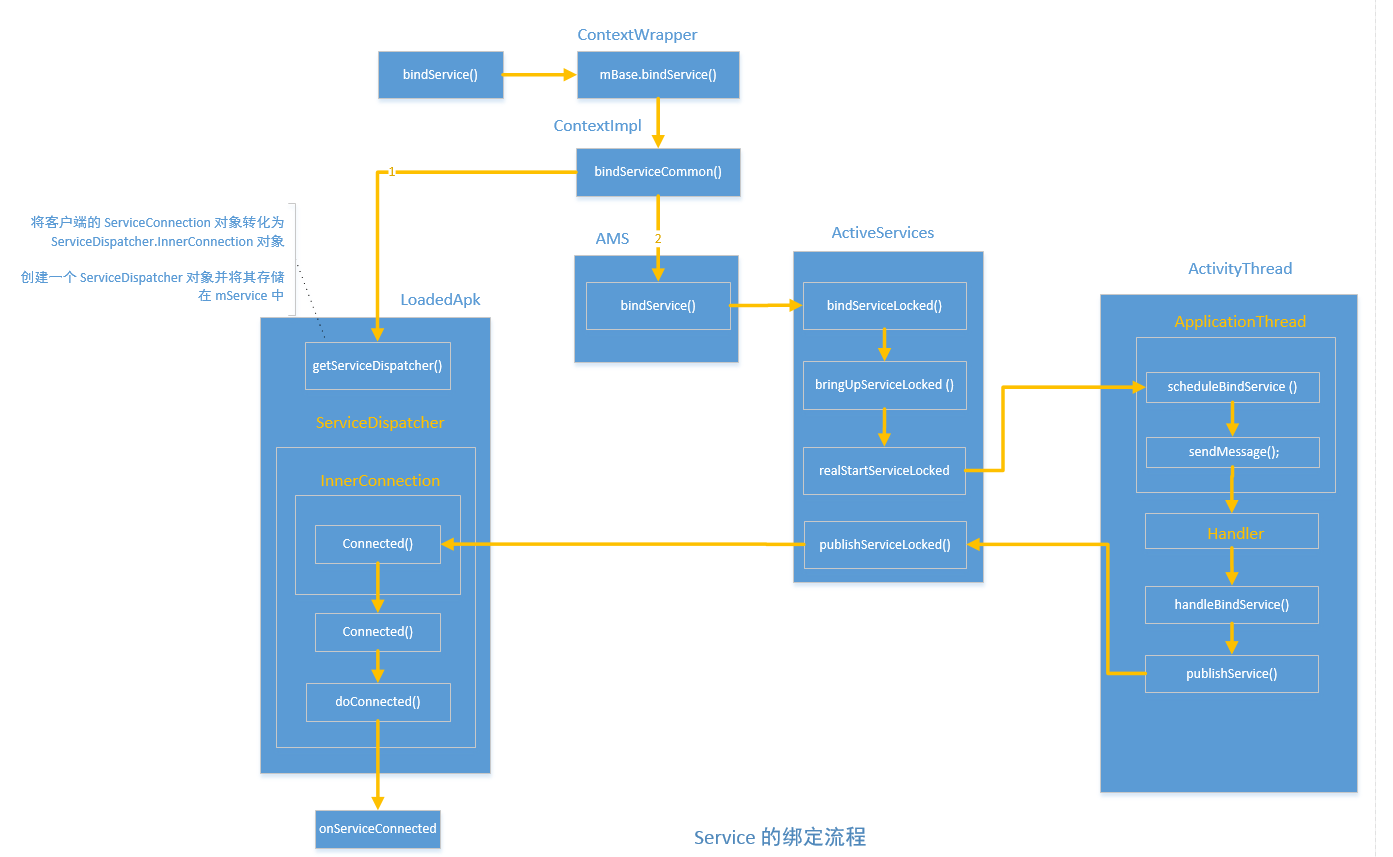
和Service 的启动过程类似,mBase 也是ContextImpl 类型对象,ContextImpl 的bindService 方法最终会调用自己的 bindServiceCommon 方法,如下所示:
@Override
public boolean bindService(Intent service, ServiceConnection conn,
int flags) {
warnIfCallingFromSystemProcess();
return bindServiceCommon(service, conn, flags, Process.myUserHandle());
}
bindServiceCommon 源码如下:
final LoadedApk mPackageInfo;
private final ArrayMap<Context, ArrayMap<ServiceConnection, LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher>> mServices
= new ArrayMap<Context, ArrayMap<ServiceConnection, LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher>>();
...
private boolean bindServiceCommon(Intent service, ServiceConnection conn, int flags,
UserHandle user) {
IServiceConnection sd;
if (conn == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("connection is null");
}
if (mPackageInfo != null) {
//将客户端的 ServiceConnection 对象转化为 ServiceDispatcher.InnerConnection 对象
sd = mPackageInfo.getServiceDispatcher(conn, getOuterContext(),
mMainThread.getHandler(), flags);
} else {
throw new RuntimeException("Not supported in system context");
}
validateServiceIntent(service);
try {
IBinder token = getActivityToken();
if (token == null && (flags&BIND_AUTO_CREATE) == 0 && mPackageInfo != null
&& mPackageInfo.getApplicationInfo().targetSdkVersion
< android.os.Build.VERSION_CODES.ICE_CREAM_SANDWICH) {
flags |= BIND_WAIVE_PRIORITY;
}
service.prepareToLeaveProcess();
//通过 AMS 的bindService 来完成具体的绑定过程
int res = ActivityManagerNative.getDefault().bindService(
mMainThread.getApplicationThread(), getActivityToken(), service,
service.resolveTypeIfNeeded(getContentResolver()),
sd, flags, getOpPackageName(), user.getIdentifier());
if (res < 0) {
throw new SecurityException(
"Not allowed to bind to service " + service);
}
return res != 0;
} catch (RemoteException e) {
throw new RuntimeException("Failure from system", e);
}
}
- 首先将客户端的 ServiceConnection 对象转化为 ServiceDispatcher.InnerConnection 对象。
private final ArrayMap<Context, ArrayMap<ServiceConnection, LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher>> mServices
= new ArrayMap<Context, ArrayMap<ServiceConnection, LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher>>();
public final IServiceConnection getServiceDispatcher(ServiceConnection c,
Context context, Handler handler, int flags) {
synchronized (mServices) {
LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher sd = null;
ArrayMap<ServiceConnection, LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher> map = mServices.get(context);
if (map != null) {
sd = map.get(c);
}
if (sd == null) {
sd = new ServiceDispatcher(c, context, handler, flags);
if (map == null) {
map = new ArrayMap<ServiceConnection, LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher>();
mServices.put(context, map);
}
map.put(c, sd);
} else {
sd.validate(context, handler);
}
return sd.getIServiceConnection();
}
}
static final class ServiceDispatcher {
private final ServiceDispatcher.InnerConnection mIServiceConnection;
private final ServiceConnection mConnection;
private final Context mContext;
private final Handler mActivityThread;
private final ServiceConnectionLeaked mLocation;
private final int mFlags;
private RuntimeException mUnbindLocation;
private boolean mDied;
private boolean mForgotten;
private static class ConnectionInfo {
IBinder binder;
IBinder.DeathRecipient deathMonitor;
}
private static class InnerConnection extends IServiceConnection.Stub {
final WeakReference<LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher> mDispatcher;
InnerConnection(LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher sd) {
mDispatcher = new WeakReference<LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher>(sd);
}
public void connected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) throws RemoteException {
LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher sd = mDispatcher.get();
if (sd != null) {
sd.connected(name, service);
}
}
}
private final ArrayMap<ComponentName, ServiceDispatcher.ConnectionInfo> mActiveConnections
= new ArrayMap<ComponentName, ServiceDispatcher.ConnectionInfo>();
ServiceDispatcher(ServiceConnection conn,
Context context, Handler activityThread, int flags) {
mIServiceConnection = new InnerConnection(this);
mConnection = conn;
mContext = context;
mActivityThread = activityThread;
mLocation = new ServiceConnectionLeaked(null);
mLocation.fillInStackTrace();
mFlags = flags;
}
void validate(Context context, Handler activityThread) {
if (mContext != context) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"ServiceConnection " + mConnection +
" registered with differing Context (was " +
mContext + " now " + context + ")");
}
if (mActivityThread != activityThread) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"ServiceConnection " + mConnection +
" registered with differing handler (was " +
mActivityThread + " now " + activityThread + ")");
}
}
void doForget() {
synchronized(this) {
for (int i=0; i<mActiveConnections.size(); i++) {
ServiceDispatcher.ConnectionInfo ci = mActiveConnections.valueAt(i);
ci.binder.unlinkToDeath(ci.deathMonitor, 0);
}
mActiveConnections.clear();
mForgotten = true;
}
}
ServiceConnectionLeaked getLocation() {
return mLocation;
}
ServiceConnection getServiceConnection() {
return mConnection;
}
IServiceConnection getIServiceConnection() {
return mIServiceConnection;
}
int getFlags() {
return mFlags;
}
void setUnbindLocation(RuntimeException ex) {
mUnbindLocation = ex;
}
RuntimeException getUnbindLocation() {
return mUnbindLocation;
}
public void connected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {
if (mActivityThread != null) {
mActivityThread.post(new RunConnection(name, service, 0));
} else {
doConnected(name, service);
}
}
public void death(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {
ServiceDispatcher.ConnectionInfo old;
synchronized (this) {
mDied = true;
old = mActiveConnections.remove(name);
if (old == null || old.binder != service) {
// Death for someone different than who we last
// reported... just ignore it.
return;
}
old.binder.unlinkToDeath(old.deathMonitor, 0);
}
if (mActivityThread != null) {
mActivityThread.post(new RunConnection(name, service, 1));
} else {
doDeath(name, service);
}
}
public void doConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {
ServiceDispatcher.ConnectionInfo old;
ServiceDispatcher.ConnectionInfo info;
synchronized (this) {
if (mForgotten) {
// We unbound before receiving the connection; ignore
// any connection received.
return;
}
old = mActiveConnections.get(name);
if (old != null && old.binder == service) {
// Huh, already have this one. Oh well!
return;
}
if (service != null) {
// A new service is being connected... set it all up.
mDied = false;
info = new ConnectionInfo();
info.binder = service;
info.deathMonitor = new DeathMonitor(name, service);
try {
service.linkToDeath(info.deathMonitor, 0);
mActiveConnections.put(name, info);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
// This service was dead before we got it... just
// don't do anything with it.
mActiveConnections.remove(name);
return;
}
} else {
// The named service is being disconnected... clean up.
mActiveConnections.remove(name);
}
if (old != null) {
old.binder.unlinkToDeath(old.deathMonitor, 0);
}
}
// If there was an old service, it is not disconnected.
if (old != null) {
mConnection.onServiceDisconnected(name);
}
// If there is a new service, it is now connected.
if (service != null) {
mConnection.onServiceConnected(name, service);
}
}
public void doDeath(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {
mConnection.onServiceDisconnected(name);
}
private final class RunConnection implements Runnable {
RunConnection(ComponentName name, IBinder service, int command) {
mName = name;
mService = service;
mCommand = command;
}
public void run() {
if (mCommand == 0) {
doConnected(mName, mService);
} else if (mCommand == 1) {
doDeath(mName, mService);
}
}
final ComponentName mName;
final IBinder mService;
final int mCommand;
}
....
}
- 接着会通过 AMS 的bindService 来完成具体的绑定过程。源码如下所示:
final ActiveServices mServices;
public int bindService(IApplicationThread caller, IBinder token, Intent service,
String resolvedType, IServiceConnection connection, int flags, String callingPackage,
int userId) throws TransactionTooLargeException {
enforceNotIsolatedCaller("bindService");
// Refuse possible leaked file descriptors
if (service != null && service.hasFileDescriptors() == true) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("File descriptors passed in Intent");
}
if (callingPackage == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("callingPackage cannot be null");
}
synchronized(this) {
return mServices.bindServiceLocked(caller, token, service,
resolvedType, connection, flags, callingPackage, userId);
}
}
接着会通过 AMS 的bindService 来完成具体的绑定过程。源码如下所示:
接下来AMS 会调用 ActiveServices 的 bindServiceLocked 方法,在bindServiceLocked 方法中会调用 bringUpServiceLocked 方法,bringUpServiceLocked 又会调用 realStartServiceLocked 方法,其执行逻辑和startService 过程中 realStartServiceLocked 类似,最终都是通过 ApplicationThread 来完成 Service 实例的创建并执行其 onCreat 方法的,和启动Service 不同的是,Service 的绑定过程会调用 app.thread 的scheduleBindService 方法, 这个过程是在 ActivityServices 的 requestServiceBindingLocked 方法中实现的,如下所示:
private final boolean requestServiceBindingLocked(ServiceRecord r, IntentBindRecord i,
boolean execInFg, boolean rebind) throws TransactionTooLargeException {
if (r.app == null || r.app.thread == null) {
// If service is not currently running, can't yet bind.
return false;
}
if ((!i.requested || rebind) && i.apps.size() > 0) {
try {
bumpServiceExecutingLocked(r, execInFg, "bind");
r.app.forceProcessStateUpTo(ActivityManager.PROCESS_STATE_SERVICE);
r.app.thread.scheduleBindService(r, i.intent.getIntent(), rebind,
r.app.repProcState);
if (!rebind) {
i.requested = true;
}
i.hasBound = true;
i.doRebind = false;
} catch (TransactionTooLargeException e) {
// Keep the executeNesting count accurate.
if (DEBUG_SERVICE) Slog.v(TAG_SERVICE, "Crashed while binding " + r, e);
final boolean inDestroying = mDestroyingServices.contains(r);
serviceDoneExecutingLocked(r, inDestroying, inDestroying);
throw e;
} catch (RemoteException e) {
if (DEBUG_SERVICE) Slog.v(TAG_SERVICE, "Crashed while binding " + r);
// Keep the executeNesting count accurate.
final boolean inDestroying = mDestroyingServices.contains(r);
serviceDoneExecutingLocked(r, inDestroying, inDestroying);
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
AMS 的scheduleBindService 方法如下所示:
public final void scheduleBindService(IBinder token, Intent intent,
boolean rebind, int processState) {
updateProcessState(processState, false);
BindServiceData s = new BindServiceData();
s.token = token;
s.intent = intent;
s.rebind = rebind;
if (DEBUG_SERVICE)
Slog.v(TAG, "scheduleBindService token=" + token + " intent=" + intent + " uid="
+ Binder.getCallingUid() + " pid=" + Binder.getCallingPid());
sendMessage(H.BIND_SERVICE, s);
}
ActivityThread 的Handler H 对BIND_SERVICE 消息的处理方式如下:
case BIND_SERVICE:
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "serviceBind");
handleBindService((BindServiceData)msg.obj);
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
break;
private void handleBindService(BindServiceData data) {
//根据Service 的token 取出 Service 对象
Service s = mServices.get(data.token);
if (DEBUG_SERVICE)
Slog.v(TAG, "handleBindService s=" + s + " rebind=" + data.rebind);
if (s != null) {
try {
data.intent.setExtrasClassLoader(s.getClassLoader());
data.intent.prepareToEnterProcess();
try {
if (!data.rebind) {
//调用service 的onBind 方法
IBinder binder = s.onBind(data.intent);
ActivityManagerNative.getDefault().publishService(
data.token, data.intent, binder);
} else {
s.onRebind(data.intent);
ActivityManagerNative.getDefault().serviceDoneExecuting(
data.token, SERVICE_DONE_EXECUTING_ANON, 0, 0);
}
ensureJitEnabled();
} catch (RemoteException ex) {
}
} catch (Exception e) {
if (!mInstrumentation.onException(s, e)) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Unable to bind to service " + s
+ " with " + data.intent + ": " + e.toString(), e);
}
}
}
}
public void publishService(IBinder token, Intent intent, IBinder service) {
// Refuse possible leaked file descriptors
if (intent != null && intent.hasFileDescriptors() == true) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("File descriptors passed in Intent");
}
synchronized(this) {
if (!(token instanceof ServiceRecord)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Invalid service token");
}
mServices.publishServiceLocked((ServiceRecord)token, intent, service);
}
}
void publishServiceLocked(ServiceRecord r, Intent intent, IBinder service) {
final long origId = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
try {
if (DEBUG_SERVICE) Slog.v(TAG_SERVICE, "PUBLISHING " + r
+ " " + intent + ": " + service);
if (r != null) {
Intent.FilterComparison filter
= new Intent.FilterComparison(intent);
IntentBindRecord b = r.bindings.get(filter);
if (b != null && !b.received) {
b.binder = service;
b.requested = true;
b.received = true;
for (int conni=r.connections.size()-1; conni>=0; conni--) {
ArrayList<ConnectionRecord> clist = r.connections.valueAt(conni);
for (int i=0; i<clist.size(); i++) {
ConnectionRecord c = clist.get(i);
if (!filter.equals(c.binding.intent.intent)) {
if (DEBUG_SERVICE) Slog.v(
TAG_SERVICE, "Not publishing to: " + c);
if (DEBUG_SERVICE) Slog.v(
TAG_SERVICE, "Bound intent: " + c.binding.intent.intent);
if (DEBUG_SERVICE) Slog.v(
TAG_SERVICE, "Published intent: " + intent);
continue;
}
if (DEBUG_SERVICE) Slog.v(TAG_SERVICE, "Publishing to: " + c);
try {
c.conn.connected(r.name, service);
} catch (Exception e) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Failure sending service " + r.name +
" to connection " + c.conn.asBinder() +
" (in " + c.binding.client.processName + ")", e);
}
}
}
}
serviceDoneExecutingLocked(r, mDestroyingServices.contains(r), false);
}
} finally {
Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(origId);
}
}
ServicesDispatcher.InnerConnection 的定义如下:
private static class InnerConnection extends IServiceConnection.Stub {
final WeakReference<LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher> mDispatcher;
InnerConnection(LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher sd) {
mDispatcher = new WeakReference<LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher>(sd);
}
public void connected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) throws RemoteException {
LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher sd = mDispatcher.get();
if (sd != null) {
sd.connected(name, service);
}
}
}
ServiceDispatcher(ServiceConnection conn,
Context context, Handler activityThread, int flags) {
mIServiceConnection = new InnerConnection(this);
mConnection = conn;
mContext = context;
mActivityThread = activityThread;
...
public void connected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {
if (mActivityThread != null) {
mActivityThread.post(new RunConnection(name, service, 0));
} else {
doConnected(name, service);
}
}
...
}
对于Service 的绑定过程来说,ServiceDispatcher 的 mActivityThread 是一个Handler,其实它就是 ActivityThread 中的 H,从前面ServiceDispatcher 的创建过程来说, mActivityThread 不会为null ,这样一来,RunConnection 就可以经由 H的 post 方法从而运行在主线程中,因此客户端ServiceConnection 中的方法是在主线程被回调的。RunConnection 的定义如下所示:
private final class RunConnection implements Runnable {
RunConnection(ComponentName name, IBinder service, int command) {
mName = name;
mService = service;
mCommand = command;
}
public void run() {
if (mCommand == 0) {
doConnected(mName, mService);
} else if (mCommand == 1) {
doDeath(mName, mService);
}
}
final ComponentName mName;
final IBinder mService;
final int mCommand;
}
public void doConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {
ServiceDispatcher.ConnectionInfo old;
ServiceDispatcher.ConnectionInfo info;
synchronized (this) {
if (mForgotten) {
// We unbound before receiving the connection; ignore
// any connection received.
return;
}
old = mActiveConnections.get(name);
if (old != null && old.binder == service) {
// Huh, already have this one. Oh well!
return;
}
if (service != null) {
// A new service is being connected... set it all up.
mDied = false;
info = new ConnectionInfo();
info.binder = service;
info.deathMonitor = new DeathMonitor(name, service);
try {
service.linkToDeath(info.deathMonitor, 0);
mActiveConnections.put(name, info);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
// This service was dead before we got it... just
// don't do anything with it.
mActiveConnections.remove(name);
return;
}
} else {
// The named service is being disconnected... clean up.
mActiveConnections.remove(name);
}
if (old != null) {
old.binder.unlinkToDeath(old.deathMonitor, 0);
}
}
// If there was an old service, it is not disconnected.
if (old != null) {
mConnection.onServiceDisconnected(name);
}
// If there is a new service, it is now connected.
if (service != null) {
mConnection.onServiceConnected(name, service);
}
}