项目场景:
经过推理的后处理运行时间的优化。
先来看下优化前后的时间对比:
优化前:
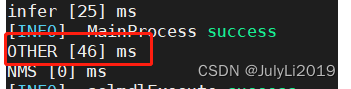
优化后:
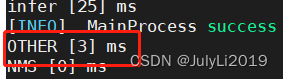
提升还是很大的。
问题描述
模型推理后得到的数据后处理操作之前时间开销很大。
auto outputsf = pRealEngine->sampleProcess->outData;
//postprogress
std::vector<float> outputvtemp;
std::vector<std::vector<BoundingBox>> preds(pRealEngine->num_class); //class-bboxes
BoundingBox temp;
auto n = pRealEngine->modelout_len*pRealEngine->nc;
// int c=0;
for(auto i=0;i<n;i++){
outputvtemp.push_back(outputsf[i]);
if((i+1)%pRealEngine->nc==0) {
if(outputvtemp[4]>pRealEngine->confidence_threshold){
auto cx = outputvtemp[0];
auto cy = outputvtemp[1];
auto w = outputvtemp[2];
auto h = outputvtemp[3];
temp.x = std::max(int((cx-w/2)),0);
temp.y = std::max(int((cy-h/2)),0);
temp.w = std::min(int(w),int(pImgInfo->i32Width-temp.x));
temp.h = std::min(int(h),int(pImgInfo->i32Height-temp.y));
temp.cx = int((cx-w/2));
temp.cy = int((cx-w/2));
temp.confidence = outputvtemp[4];
temp.classid = getfclassid(outputvtemp);
preds[temp.classid].push_back(temp);
}
outputvtemp.clear();
}
}
原因分析:
不必要的数据复制:原始代码中使用 outputvtemp.push_back(outputsf[i]) 将 outputsf[i] 添加到 outputvtemp 向量中。这将涉及内存的重新分配和数据复制。为了避免这种开销,可以直接在循环中访问 outputsf 数组,而无需使用额外的向量。
重复计算:循环中计算的值 cx - w/2 和 cy - h/2 在多个地方重复使用。可以将这些计算移动到条件判断的外部,以避免重复计算。
复杂的条件判断: 在循环中有一些条件判断,例如if (outputvtemp[4] > pRealEngine->confidence_threshold),这些条件判断可能会增加运行时间。确保这些条件判断是必要的,如果可能的话,尽量减少不必要的条件判断。
解决方案:
auto outputsf = pRealEngine->sampleProcess->outData;
std::vector<std::vector<BoundingBox>> preds(pRealEngine->num_class); //class-bboxes
BoundingBox temp;
auto n = pRealEngine->modelout_len * pRealEngine->nc;
// int elements_per_output = 5; // 每个输出元素包含 5 个值
for (auto i = 0; i < n; i +=pRealEngine->nc)// elements_per_output)
{
float confidence = outputsf[i + 4];
if (confidence > pRealEngine->confidence_threshold)
{
auto cx = outputsf[i];
auto cy = outputsf[i + 1];
auto w = outputsf[i + 2];
auto h = outputsf[i + 3];
temp.x = std::max(int((cx - w / 2)), 0);
temp.y = std::max(int((cy - h / 2)), 0);
temp.w = std::min(int(w), int(pImgInfo->i32Width - temp.x));
temp.h = std::min(int(h), int(pImgInfo->i32Height - temp.y));
temp.cx = int((cx - w / 2));
temp.cy = int((cy - h / 2));
temp.confidence = confidence;
// 将数组转换为 std::vector<float>
std::vector<float> outputvtemp(outputsf + i, outputsf + i + pRealEngine->nc);
// 调用 getfclassid 函数,并传递起始和结束索引
temp.classid = getfclassid(outputvtemp); // 传递起始和结束索引
preds[temp.classid].push_back(temp);
}
}
小结
本文是自己项目中遇到的实际问题,由于刚刚上手C++相关的项目,特此记录!!!
C++任重而道远呀,加油呀!!!
2023年9月9日15:33:36