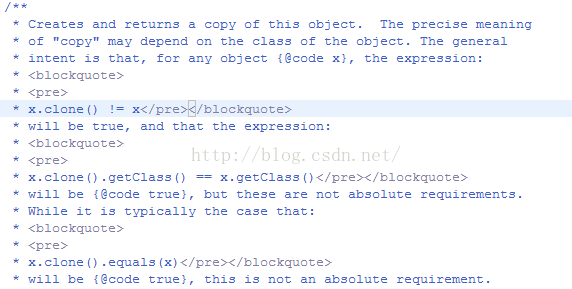
大概意思是说:返回一个要克隆对象的副本,克隆的类型依赖被克隆对象,换句话说:克隆后的对象类型与被克隆对象的类型相同。
一、简单用法
只需要在需要clone的对象上实现(implements)Cloneable接口,然后再在类中加上clone方法,在方法中只需要调用super.clone(),根据自己的需要实现即可。
- public class Student implements Cloneable {
- private String name;
- private int age;
- public String getName() {
- return name;
- }
- public void setName(String name) {
- this.name = name;
- }
- public int getAge() {
- return age;
- }
- public void setAge(int age) {
- this.age = age;
- }
- @Override
- protected Student clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
- return (Student)super.clone();
- }
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- Student stu = new Student();
- stu.setAge(1);
- stu.setName("aa");
- System.out.println(stu + " age: " + stu.getAge() + " name: " + stu.getName());
- try {
- Student sC = stu.clone();
- System.out.println(sC + " sC.age: " + sC.getAge() + " sC.name: " + sC.getName());
- sC.setAge(12);
- sC.setName("bb");
- System.out.println(stu + " age: " + stu.getAge() + " name: " + stu.getName());
- System.out.println(sC + " sC.age: " + sC.getAge() + " sC.name: " + sC.getName());
- } catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
- // TODO Auto-generated catch block
- e.printStackTrace();
- }
- }
- }
public class Student implements Cloneable {
private String name;
private int age;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
protected Student clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
return (Student)super.clone();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student stu = new Student();
stu.setAge(1);
stu.setName("aa");
System.out.println(stu + " age: " + stu.getAge() + " name: " + stu.getName());
try {
Student sC = stu.clone();
System.out.println(sC + " sC.age: " + sC.getAge() + " sC.name: " + sC.getName());
sC.setAge(12);
sC.setName("bb");
System.out.println(stu + " age: " + stu.getAge() + " name: " + stu.getName());
System.out.println(sC + " sC.age: " + sC.getAge() + " sC.name: " + sC.getName());
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
输出结果:
testClone.Student@15db9742 age: 1 name: aa
testClone.Student@6d06d69c sC.age: 1 sC.name: aa
testClone.Student@15db9742 age: 1 name: aa
testClone.Student@6d06d69c sC.age: 12 sC.name: bb
分析结果:1、根据输出结果中前边的类名,可以得出被克隆对象的与原来的对象是同一种类型。2、根据内存地址(hashcode)知道,被克隆对象的与原来的对象是存在于内存中的不同的两个对象。所以后边有一个赋值,对原来对象没有任何影响。
二、“影子”克隆与深度克隆
首先看一个例子:
- class Bag{//学生的书包
- private int width;
- private String logo;
- public int getWidth() {
- return width;
- }
- public void setWidth(int width) {
- this.width = width;
- }
- public String getLogo() {
- return logo;
- }
- public void setLogo(String logo) {
- this.logo = logo;
- }
- }
- public class Student2 implements Cloneable {
- private String name;
- private int age;
- private Bag bag;
- public Bag getBag() {
- return bag;
- }
- public void setBag(Bag bag) {
- this.bag = bag;
- }
- public String getName() {
- return name;
- }
- public void setName(String name) {
- this.name = name;
- }
- public int getAge() {
- return age;
- }
- public void setAge(int age) {
- this.age = age;
- }
- @Override
- protected Student2 clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
- return (Student2)super.clone();
- }
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- Student2 stu = new Student2();
- stu.setAge(1);
- stu.setName("aa");
- Bag b = new Bag();
- b.setWidth(10);
- b.setLogo("Nike");
- stu.setBag(b);
- printStudent(stu);
- try {
- Student2 sC = stu.clone();
- printStudent(sC);
- sC.setAge(12);
- sC.setName("bb");
- sC.getBag().setWidth(100);//改变书包的属性
- sC.getBag().setLogo("JNike");
- printStudent(stu);
- printStudent(sC);
- } catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
- // TODO Auto-generated catch block
- e.printStackTrace();
- }
- }
- /**
- * 输出
- * @param stu
- */
- private static void printStudent(Student2 stu) {
- System.out.println(stu + " age: " + stu.getAge() + " name: " + stu.getName() +
- " bag: " + stu.getBag() + "(" + stu.getBag().getLogo() + " width: " +
- stu.getBag().getWidth() + ")");
- }
- }
class Bag{//学生的书包
private int width;
private String logo;
public int getWidth() {
return width;
}
public void setWidth(int width) {
this.width = width;
}
public String getLogo() {
return logo;
}
public void setLogo(String logo) {
this.logo = logo;
}
}
public class Student2 implements Cloneable {
private String name;
private int age;
private Bag bag;
public Bag getBag() {
return bag;
}
public void setBag(Bag bag) {
this.bag = bag;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
protected Student2 clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
return (Student2)super.clone();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student2 stu = new Student2();
stu.setAge(1);
stu.setName("aa");
Bag b = new Bag();
b.setWidth(10);
b.setLogo("Nike");
stu.setBag(b);
printStudent(stu);
try {
Student2 sC = stu.clone();
printStudent(sC);
sC.setAge(12);
sC.setName("bb");
sC.getBag().setWidth(100);//改变书包的属性
sC.getBag().setLogo("JNike");
printStudent(stu);
printStudent(sC);
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 输出
* @param stu
*/
private static void printStudent(Student2 stu) {
System.out.println(stu + " age: " + stu.getAge() + " name: " + stu.getName() +
" bag: " + stu.getBag() + "(" + stu.getBag().getLogo() + " width: " +
stu.getBag().getWidth() + ")");
}
}
输出结果:
testClone.Student2@15db9742 age: 1 name: aa bag: testClone.Bag@6d06d69c(Nike width: 10)
testClone.Student2@7852e922 age: 1 name: aa bag: testClone.Bag@6d06d69c(Nike width: 10)
testClone.Student2@15db9742 age: 1 name: aa bag: testClone.Bag@6d06d69c(JNike width: 100)
testClone.Student2@7852e922 age: 12 name: bb bag: testClone.Bag@6d06d69c(JNike width: 100)
分析:发现是不是跟预期的不太一样,通过第二个同学改变书包,但是第一个同学的书包也被改变了。并且通过内存地址可知,他们是同一对象(书包)。原因:调用Object类中clone()方法产生的效果是:先在内存中开辟一块和原始对象一样的空间,然后原样拷贝原始对象中的内 容。对基本数据类型,这样的操作是没有问题的,但对非基本类型变量,我们知道它们保存的仅仅是对象的引用,这也导致clone后的非基本类型变量和原始对 象中相应的变量指向的是同一个对象。 这就是所谓的“影子”克隆。
解决方案:深度克隆,既是对里边的引用也要克隆。以下是实现:
- class Bag implements Cloneable{//学生的书包
- private int width;//宽
- private String logo;//品牌
- public int getWidth() {
- return width;
- }
- public void setWidth(int width) {
- this.width = width;
- }
- public String getLogo() {
- return logo;
- }
- public void setLogo(String logo) {
- this.logo = logo;
- }
- @Override
- protected Bag clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
- return (Bag)super.clone();
- }
- }
- public class Student3 implements Cloneable {
- private String name;
- private int age;
- private Bag bag;
- public Bag getBag() {
- return bag;
- }
- public void setBag(Bag bag) {
- this.bag = bag;
- }
- public String getName() {
- return name;
- }
- public void setName(String name) {
- this.name = name;
- }
- public int getAge() {
- return age;
- }
- public void setAge(int age) {
- this.age = age;
- }
- @Override
- protected Student3 clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
- Student3 stu = (Student3)super.clone();
- stu.bag = bag.clone();
- return stu;
- }
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- Student3 stu = new Student3();
- stu.setAge(1);
- stu.setName("aa");
- Bag b = new Bag();
- b.setWidth(10);
- b.setLogo("Nike");
- stu.setBag(b);
- printStudent(stu);
- try {
- Student3 sC = stu.clone();
- printStudent(sC);
- sC.setAge(12);
- sC.setName("bb");
- sC.getBag().setWidth(100);//改变书包的属性
- sC.getBag().setLogo("JNike");
- printStudent(stu);
- printStudent(sC);
- } catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
- // TODO Auto-generated catch block
- e.printStackTrace();
- }
- }
- /**
- * 输出
- * @param stu
- */
- private static void printStudent(Student3 stu) {
- System.out.println(stu + " age: " + stu.getAge() + " name: " + stu.getName() +
- " bag: " + stu.getBag() + "(" + stu.getBag().getLogo() + " width: " +
- stu.getBag().getWidth() + ")");
- }
- }
class Bag implements Cloneable{//学生的书包
private int width;//宽
private String logo;//品牌
public int getWidth() {
return width;
}
public void setWidth(int width) {
this.width = width;
}
public String getLogo() {
return logo;
}
public void setLogo(String logo) {
this.logo = logo;
}
@Override
protected Bag clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
return (Bag)super.clone();
}
}
public class Student3 implements Cloneable {
private String name;
private int age;
private Bag bag;
public Bag getBag() {
return bag;
}
public void setBag(Bag bag) {
this.bag = bag;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
protected Student3 clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
Student3 stu = (Student3)super.clone();
stu.bag = bag.clone();
return stu;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student3 stu = new Student3();
stu.setAge(1);
stu.setName("aa");
Bag b = new Bag();
b.setWidth(10);
b.setLogo("Nike");
stu.setBag(b);
printStudent(stu);
try {
Student3 sC = stu.clone();
printStudent(sC);
sC.setAge(12);
sC.setName("bb");
sC.getBag().setWidth(100);//改变书包的属性
sC.getBag().setLogo("JNike");
printStudent(stu);
printStudent(sC);
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 输出
* @param stu
*/
private static void printStudent(Student3 stu) {
System.out.println(stu + " age: " + stu.getAge() + " name: " + stu.getName() +
" bag: " + stu.getBag() + "(" + stu.getBag().getLogo() + " width: " +
stu.getBag().getWidth() + ")");
}
}
输出:
testClone.Student3@15db9742 age: 1 name: aa bag: testClone.Bag@6d06d69c(Nike width: 10)
testClone.Student3@7852e922 age: 1 name: aa bag: testClone.Bag@4e25154f(Nike width: 10)
testClone.Student3@15db9742 age: 1 name: aa bag: testClone.Bag@6d06d69c(Nike width: 10)
testClone.Student3@7852e922 age: 12 name: bb bag: testClone.Bag@4e25154f(JNike width: 100)
与我们期望的相同了。
三、是不是万事大吉了?
注意:要知道不是所有的类都能实现深度clone的。例如,StringBuffer,看一下 JDK API中关于StringBuffer的说明,StringBuffer没有重载clone()方法,更为严重的是StringBuffer还是一个 final类,这也是说我们也不能用继承的办法间接实现StringBuffer的clone。如果一个类中包含有StringBuffer类型对象或和 StringBuffer相似类的对象,我们有两种选择:要么只能实现影子clone,要么自己重新生成对象: new StringBuffer(oldValue.toString()); 进行赋值。
你是不是想问上边例子中的String呢,难道实现了clone?(查询String.java源码,发现并没有)通过以下的例子为你解答疑惑:
- class StrCloneDemo implements Cloneable {
- public String str;
- public StringBuffer strBuff;
- public Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
- return (StrCloneDemo) super.clone();
- }
- }
- public class StrCloneDemoTest {
- public static void main(String[] a) {
- StrCloneDemo scd1 = new StrCloneDemo();
- scd1.str = new String("abcdefghijk");
- scd1.strBuff = new StringBuffer("rstuvwxyz");
- System.out.println("before clone,scd1.str = " + scd1.str);
- System.out.println("before clone,scd1.strBuff = " + scd1.strBuff);
- StrCloneDemo scd2 = null;
- try {
- scd2 = (StrCloneDemo) scd1.clone();
- } catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
- e.printStackTrace();
- }
- scd2.str = scd2.str.substring(0, 3);
- scd2.strBuff = scd2.strBuff.append("RSTUVWXYZ");
- System.out.println("******************************************");
- System.out.println("after clone,scd1.str = " + scd1.str);
- System.out.println("after clone,scd1.strBuff = " + scd1.strBuff);
- System.out.println("******************************************");
- System.out.println("after clone,scd2.str = " + scd2.str);
- System.out.println("after clone,scd2.strBuff = " + scd2.strBuff);
- }
- }
class StrCloneDemo implements Cloneable {
public String str;
public StringBuffer strBuff;
public Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
return (StrCloneDemo) super.clone();
}
}
public class StrCloneDemoTest {
public static void main(String[] a) {
StrCloneDemo scd1 = new StrCloneDemo();
scd1.str = new String("abcdefghijk");
scd1.strBuff = new StringBuffer("rstuvwxyz");
System.out.println("before clone,scd1.str = " + scd1.str);
System.out.println("before clone,scd1.strBuff = " + scd1.strBuff);
StrCloneDemo scd2 = null;
try {
scd2 = (StrCloneDemo) scd1.clone();
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
scd2.str = scd2.str.substring(0, 3);
scd2.strBuff = scd2.strBuff.append("RSTUVWXYZ");
System.out.println("******************************************");
System.out.println("after clone,scd1.str = " + scd1.str);
System.out.println("after clone,scd1.strBuff = " + scd1.strBuff);
System.out.println("******************************************");
System.out.println("after clone,scd2.str = " + scd2.str);
System.out.println("after clone,scd2.strBuff = " + scd2.strBuff);
}
}
输出:
before clone,scd1.str = abcdefghijk
before clone,scd1.strBuff = rstuvwxyz
******************************************
after clone,scd1.str = abcdefghijk
after clone,scd1.strBuff = rstuvwxyzRSTUVWXYZ
******************************************
after clone,scd2.str = abc
after clone,scd2.strBuff = rstuvwxyzRSTUVWXYZ
分析:String类型的变量好象已经实现了深度clone,因为对scd2.str的改动并没有影响到scd1.str!实质上,在clone的时候scd1.str与scd2.str仍然是引用,而且都指向了同一个 String对象。但在执行c2.str = c2.str.substring(0,5)的时候,生成了一个新的String类型,然后又赋回给scd2.str。这是因为String被 Sun公司的工程师写成了一个不可更改的类(immutable class),在所有String类中的函数都不能更改自身的值。类似的,String类中的其它方法也是如此,都是生成一个新的对象返回。当然StringBuffer还是原来的对象。