for n = 200, m = 500
import numpy as np from scipy import linalg n = 200 m = 500 A = np.random.normal(size = (n,m) ) B = linalg.toeplitz(np.random.normal(size = (1,m)), np.random.normal(size = (1,m)))
9.1
Calculate A + A, AAT; ATA and AB. Write a function that computes A(B - λI) for any λ
print("A+A=",A+A)
print("AAT=",np.dot(A,A.T))
print("ATA=",np.dot(A.T,A))
print("AB=",np.dot(A,B))
def func(x):
return np.dot(A,B - x * np.eye(m))
9.2
Generate a vector b with m entries and solve Bx = b
b = np.random.random(m)
x = np.linalg.solve(B,b)
print("Bx = ",np.dot(B,x))
print("b = ",b)
9.3
Compute the Frobenius norm of A: kAkF and the infinity norm of B: kBk1. Also find the largest and
smallest singular values of B
print("the fro norm of A = ",linalg.norm(A))
print("the infinity norm of B = ",linalg.norm(B, np.inf))
u,sigma,vt = linalg.svd(B)
print("the largest singular values of B = ",np.max(sigma))
print("the smallest singular values of B = ",np.min(sigma))
9.4
Generate a matrix Z, n × n, with Gaussian entries, and use the power iteration to find the largest
eigenvalue and corresponding eigenvector of Z. How many iterations are needed till convergence?
Optional: use the time.clock() method to compare computation time when varying n
import numpy as np from scipy import linalg import time def eig(n): Z = np.random.normal(size = (n,n)) v = np.ones(n) a = linalg.norm(v, np.inf) temp = 0 x = 0 t = time.clock() while True: temp = a y = np.dot(Z, v) a = linalg.norm(y, np.inf) v = y / a x = x + 1 if abs(temp - a) < 0.00000100: break t = time.clock() - t print("times:",x) print("time:",t) print("eigenvector:",v) print("eigenvalue:",a)
9.5
Generate an n × n matrix, denoted by C, where each entry is 1 with probability p and 0 otherwise. Use
the linear algebra library of Scipy to compute the singular values of C. What can you say about the
relationship between n, p and the largest singular value?
import numpy as np
from scipy import linalg
def Singular(n,p):
C = np.random.binomial(1,p,[n,n])
u,sigma,vt = linalg.svd(C)
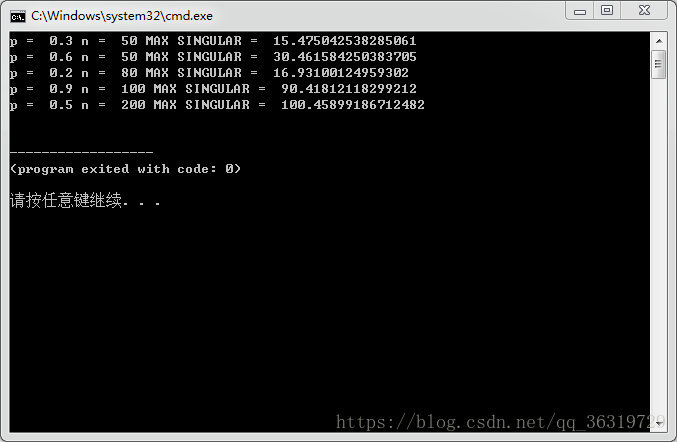
print("p = ", p, "n = ",n, "MAX SINGULAR = ",np.max(sigma))
Singular(50,0.3)
Singular(50,0.6)
Singular(80,0.2)
Singular(100,0.9)
Singular(200,0.5)
执行效果如下:
结论是:N足够大时,此时最大的奇异值收敛于np
9.6
Write a function that takes a value z and an array A and finds the element in A that is closest to z. The
function should return the closest value, not index
import numpy as np def find(A,z): a = np.abs(A - z) return A[np.argmin(a)]