Android 得到主题中对应的属性的结果或自己设置的style中的结果该文在说GetBag(uint32_t resid, std::vector<uint32_t>& child_resids)的时候,会通过FindEntry(resid, 0u /* density_override /, false / stop_at_first_match /, false / ignore_configuration */)会得到一个ResTable_map_entry结构的数据指针。该指针就是Bag资源在内存中的位置。
我们知道,查找一个资源的时候,是根据一个32位整数来查询的。这个32位整数分成3部分,前8位是包id,系统资源包id是01,应用资源包id是0x7F;接着8位是类型id,类型id是从1开始,所以查找资源的时候,在用做数组序列时,需要先减1;最后16位是对应类型中该资源收集过程中的出现序列,叫entry_idx。
查找资源的过程中,是先通过包id找到对应的包,因为包id不是从0递增,所以需要维护包id与对应数组序列的映射,从下面的代码中可以看出,然后再通过类型id,找到包中对应的类型,最后通过entry_idx找到该类型中对应的资源。
AssetManager2
前面的文章也说了,AssetManager2里面包含着应用所有的资源内容。有必要了解下该类
class AssetManager2 {
…………
// The ordered list of ApkAssets to search. These are not owned by the AssetManager, and must
// have a longer lifetime.
std::vector<const ApkAssets*> apk_assets_;
// DynamicRefTables for shared library package resolution.
// These are ordered according to apk_assets_. The mappings may change depending on what is
// in apk_assets_, therefore they must be stored in the AssetManager and not in the
// immutable ApkAssets class.
std::vector<PackageGroup> package_groups_;
// An array mapping package ID to index into package_groups. This keeps the lookup fast
// without taking too much memory.
std::array<uint8_t, std::numeric_limits<uint8_t>::max() + 1> package_ids_;
// The current configuration set for this AssetManager. When this changes, cached resources
// may need to be purged.
ResTable_config configuration_;
// Cached set of bags. These are cached because they can inherit keys from parent bags,
// which involves some calculation.
mutable std::unordered_map<uint32_t, util::unique_cptr<ResolvedBag>> cached_bags_;
// Cached set of bag resid stacks for each bag. These are cached because they might be requested
// a number of times for each view during View inspection.
mutable std::unordered_map<uint32_t, std::vector<uint32_t>> cached_bag_resid_stacks_;
// Cached set of resolved resource values.
mutable std::unordered_map<uint32_t, SelectedValue> cached_resolved_values_;
…………
}
成员apk_assets_是std::vector<const ApkAssets*>,ApkAssets对应着Apk文件。在对APK文件解析资源时,是将APK文件解析成ApkAssets对象的。
package_groups_是std::vector,它是由apk_assets_再处理得到的。
package_ids_里面存储的是包id与上面package_groups_中次序的映射。
configuration_是当前AssetManager的配置信息,它是用ResTable_config 来描述的。当它发生改变时,缓存的资源可能需要丢弃。
下面的三个成员,看名字都能看出来是用来做缓存的。
PackageGroup
针对PackageGroup,咱们还是需要好好说一下。看下它的结构
// A collection of configurations and their associated ResTable_type that match the current
// AssetManager configuration.
struct FilteredConfigGroup {
std::vector<const TypeSpec::TypeEntry*> type_entries;
};
// Represents an single package.
struct ConfiguredPackage {
// A pointer to the immutable, loaded package info.
const LoadedPackage* loaded_package_;
// A mutable AssetManager-specific list of configurations that match the AssetManager's
// current configuration. This is used as an optimization to avoid checking every single
// candidate configuration when looking up resources.
ByteBucketArray<FilteredConfigGroup> filtered_configs_;
};
// Represents a Runtime Resource Overlay that overlays resources in the logical package.
struct ConfiguredOverlay {
// The set of package groups that overlay this package group.
IdmapResMap overlay_res_maps_;
// The cookie of the overlay assets.
ApkAssetsCookie cookie;
};
// Represents a logical package, which can be made up of many individual packages. Each package
// in a PackageGroup shares the same package name and package ID.
struct PackageGroup {
// The set of packages that make-up this group.
std::vector<ConfiguredPackage> packages_;
// The cookies associated with each package in the group. They share the same order as
// packages_.
std::vector<ApkAssetsCookie> cookies_;
// Runtime Resource Overlays that overlay resources in this package group.
std::vector<ConfiguredOverlay> overlays_;
// A library reference table that contains build-package ID to runtime-package ID mappings.
std::shared_ptr<DynamicRefTable> dynamic_ref_table = std::make_shared<DynamicRefTable>();
};
每个PackageGroup 对应着一个包id。它可能包含着多个包的资源,packages_的类型是std::vector,每个ConfiguredPackage实例对应着一个包的资源。这些包的id值是相同的。
cookies_是用来描述对应的ConfiguredPackage来自哪个APK。它的次序是与packages_的次序对应的。
overlays_是与RRO相关,RRO就是运行资源遮罩。
dynamic_ref_table它是库引用表,里面包含构建包ID到运行包ID的映射。
再看ConfiguredPackage 结构,他有两个成员:loaded_package_和filtered_configs_。
loaded_package_是LoadedPackage*,它指向的是包里的资源信息。
而filtered_configs_是为了优化,根据当前的配置信息,将所有匹配的资源都放入它里面。这样就不用再去查询那些不匹配的资源信息。filtered_configs_是ByteBucketArray类型,里面的次序是(typeid -1),对应着每个类型的资源。后面为了称呼方便,这里暂且叫它优化配置资源。
FindEntry()
下面来说说FindEntry(),分段阅读:
base::expected<FindEntryResult, NullOrIOError> AssetManager2::FindEntry(
uint32_t resid, uint16_t density_override, bool stop_at_first_match,
bool ignore_configuration) const {
…………
// Might use this if density_override != 0.
ResTable_config density_override_config;
// Select our configuration or generate a density override configuration.
const ResTable_config* desired_config = &configuration_;
if (density_override != 0 && density_override != configuration_.density) {
density_override_config = configuration_;
density_override_config.density = density_override;
desired_config = &density_override_config;
}
参数 resid就是要查询的资源id;density_override是要满足的屏幕密度,如果为0,则没要求;stop_at_first_match是如果找到第一个匹配的,是否停止;ignore_configuration是否忽略配置。
这第一段代码是处理参数density_override,如果density_override不为0,并且和当前AssetManager2配置configuration_的屏幕密度不一致,则将desired_config的屏幕密度设置为 density_override。其他的配置则取configuration_的。
再看下一段代码:
…………
const uint32_t package_id = get_package_id(resid);
const uint8_t type_idx = get_type_id(resid) - 1;
const uint16_t entry_idx = get_entry_id(resid);
uint8_t package_idx = package_ids_[package_id];
if (UNLIKELY(package_idx == 0xff)) {
ANDROID_LOG(ERROR) << base::StringPrintf("No package ID %02x found for ID 0x%08x.",
package_id, resid);
return base::unexpected(std::nullopt);
}
const PackageGroup& package_group = package_groups_[package_idx];
auto result = FindEntryInternal(package_group, type_idx, entry_idx, *desired_config,
stop_at_first_match, ignore_configuration);
这块开始处理resid得到package_id ,type_idx ,entry_idx 。这个前面解释了。分别通过移位操作得到对应的值。type_idx 是移位操作之后,做了一个减1的操作。因为typeid是从1开始的。后面在通过数组的序列查找,所以需要减1。
接着就是怎么找到对应的PackageGroup,在package_ids_中存储的是对应包id的次序,然后在通过package_groups_[package_idx]就得到了对应的package_group 。
然后调用FindEntryInternal()得到FindEntryResult对象结果。这个下面再说,接着向下看代码:
…………
if (!stop_at_first_match && !ignore_configuration && !apk_assets_[result->cookie]->IsLoader()) {
for (const auto& id_map : package_group.overlays_) {
auto overlay_entry = id_map.overlay_res_maps_.Lookup(resid);
if (!overlay_entry) {
// No id map entry exists for this target resource.
continue;
}
if (overlay_entry.IsInlineValue()) {
// The target resource is overlaid by an inline value not represented by a resource.
result->entry = overlay_entry.GetInlineValue();
result->dynamic_ref_table = id_map.overlay_res_maps_.GetOverlayDynamicRefTable();
result->cookie = id_map.cookie;
…………
continue;
}
auto overlay_result = FindEntry(overlay_entry.GetResourceId(), density_override,
false /* stop_at_first_match */,
false /* ignore_configuration */);
if (UNLIKELY(IsIOError(overlay_result))) {
return base::unexpected(overlay_result.error());
}
if (!overlay_result.has_value()) {
continue;
}
if (!overlay_result->config.isBetterThan(result->config, desired_config)
&& overlay_result->config.compare(result->config) != 0) {
// The configuration of the entry for the overlay must be equal to or better than the target
// configuration to be chosen as the better value.
continue;
}
result->cookie = overlay_result->cookie;
result->entry = overlay_result->entry;
result->config = overlay_result->config;
result->dynamic_ref_table = id_map.overlay_res_maps_.GetOverlayDynamicRefTable();
…………
}
}
…………
return result;
}
这块的代码是主要处理RRO存在的情况,不准备细说,能看到,它也调用了FindEntry()来返回结果。
FindEntry()说完了。
ResTable_type
再讲FindEntryInternal()之前需要先说一下ResTable_type,查找的时候和它密切相关
/**
* Header that appears at the front of every data chunk in a resource.
*/
struct ResChunk_header
{
// Type identifier for this chunk. The meaning of this value depends
// on the containing chunk.
uint16_t type;
// Size of the chunk header (in bytes). Adding this value to
// the address of the chunk allows you to find its associated data
// (if any).
uint16_t headerSize;
// Total size of this chunk (in bytes). This is the chunkSize plus
// the size of any data associated with the chunk. Adding this value
// to the chunk allows you to completely skip its contents (including
// any child chunks). If this value is the same as chunkSize, there is
// no data associated with the chunk.
uint32_t size;
};
…………
struct ResTable_type
{
struct ResChunk_header header;
enum {
NO_ENTRY = 0xFFFFFFFF
};
// The type identifier this chunk is holding. Type IDs start
// at 1 (corresponding to the value of the type bits in a
// resource identifier). 0 is invalid.
uint8_t id;
enum {
// If set, the entry is sparse, and encodes both the entry ID and offset into each entry,
// and a binary search is used to find the key. Only available on platforms >= O.
// Mark any types that use this with a v26 qualifier to prevent runtime issues on older
// platforms.
FLAG_SPARSE = 0x01,
};
uint8_t flags;
// Must be 0.
uint16_t reserved;
// Number of uint32_t entry indices that follow.
uint32_t entryCount;
// Offset from header where ResTable_entry data starts.
uint32_t entriesStart;
// Configuration this collection of entries is designed for. This must always be last.
ResTable_config config;
};
ResTable_type数据结构对应内存中的数据内容。
header是ResChunk_header 结构。ResChunk_header 是每个数据表的开头的内容。ResChunk_header 的type代表表类型,headerSize是ResTable_type数据结构的内存大小,size是ResTable_type数据结构 + 相关数据内容 的大小。
ResTable_type 的id是type id。从1开始计数。
ResTable_type 的entryCount代表这个类型的资源的entry数量
ResTable_type 的entriesStart是数据开始的地方距离该结构开始的偏移。
ResTable_type 的config是该类型的相关配置信息。
看下图,就是该结构相关数据在内存中的布局,
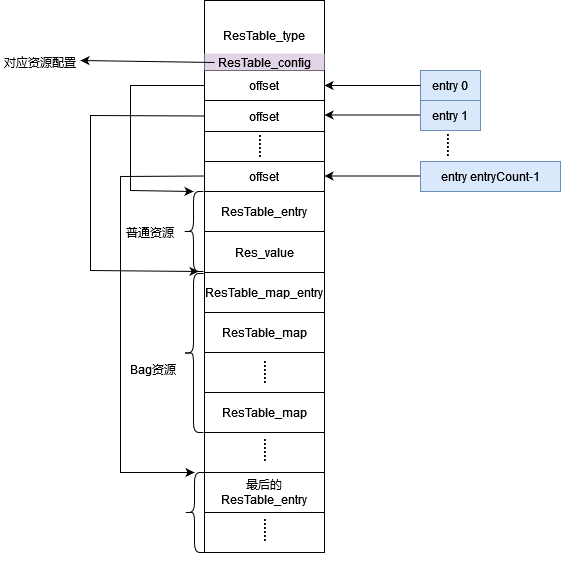
图中还能看到分为普通资源和Bag资源。普通资源就是比较简单的资源,像string类型。Bag资源是复杂一些的资源,像style类型资源,在xml文件中,包括好多条item属性内容。
ResTable_map_entry、ResTable_map数据结构在Android 得到主题中对应的属性的结果或自己设置的style中的结果说过。
ResTable_type是和资源具体的配置相关。像drawable类型的,mdpi和hdpi是两个ResTable_type来表示的。
开始说FindEntryInternal()
FindEntryInternal()
这个方法是查找资源核心的一个方法,描述了处理资源查找时比较配置,什么情况下采用优化的filtered_configs_,怎么在内存中找到对应的资源。
接着看代码,还是一段一段的看:
base::expected<FindEntryResult, NullOrIOError> AssetManager2::FindEntryInternal(
const PackageGroup& package_group, uint8_t type_idx, uint16_t entry_idx,
const ResTable_config& desired_config, bool stop_at_first_match,
bool ignore_configuration) const {
const bool logging_enabled = resource_resolution_logging_enabled_;
ApkAssetsCookie best_cookie = kInvalidCookie;
const LoadedPackage* best_package = nullptr;
incfs::verified_map_ptr<ResTable_type> best_type;
const ResTable_config* best_config = nullptr;
uint32_t best_offset = 0U;
uint32_t type_flags = 0U;
std::vector<Resolution::Step> resolution_steps;
// If `desired_config` is not the same as the set configuration or the caller will accept a value
// from any configuration, then we cannot use our filtered list of types since it only it contains
// types matched to the set configuration.
const bool use_filtered = !ignore_configuration && &desired_config == &configuration_;
参数都是从FindEntry()中传递过来的,就不说了。
定义了几个变量,best_cookie 代表资源来自哪个ApkAssets;best_package 是资源来自LoadedPackage,它对应着一个package;best_type代表它来自哪个ResTable_type;best_config 代表它来自哪中配置;best_offset 是资源的偏移值,它与前面的ResTable_type结构有关;type_flags 代表资源受影响的配置因素。
还定义了一个使用优化配置资源(上面也说了,就是用ConfiguredPackage的filtered_configs_来进行查找)的变量use_filtered 。这个变量在不忽略配置并且期望查找的配置和当前AssetManager2当前的配置信息完全一样的情况下,就会采用优化配置资源信息进行查找对应的资源。
接着下一段
const size_t package_count = package_group.packages_.size();
for (size_t pi = 0; pi < package_count; pi++) {
const ConfiguredPackage& loaded_package_impl = package_group.packages_[pi];
const LoadedPackage* loaded_package = loaded_package_impl.loaded_package_;
const ApkAssetsCookie cookie = package_group.cookies_[pi];
// If the type IDs are offset in this package, we need to take that into account when searching
// for a type.
const TypeSpec* type_spec = loaded_package->GetTypeSpecByTypeIndex(type_idx);
if (UNLIKELY(type_spec == nullptr)) {
continue;
}
// Allow custom loader packages to overlay resource values with configurations equivalent to the
// current best configuration.
const bool package_is_loader = loaded_package->IsCustomLoader();
auto entry_flags = type_spec->GetFlagsForEntryIndex(entry_idx);
if (UNLIKELY(!entry_flags.has_value())) {
return base::unexpected(entry_flags.error());
}
type_flags |= entry_flags.value();
const FilteredConfigGroup& filtered_group = loaded_package_impl.filtered_configs_[type_idx];
const size_t type_entry_count = (use_filtered) ? filtered_group.type_entries.size()
: type_spec->type_entries.size();
开始进入一个循环,这个是循环包id相同的所有包。
首先拿到LoadedPackage类型loaded_package,然后调用它的GetTypeSpecByTypeIndex(type_idx)方法得到一个TypeSpec类型type_spec。loaded_package里面包含解析APK文件的资源表(resources.arsc)中的所有资源信息。这个得到的type_spec就指向包含着该typeidx对应的类型的配置信息和资源数据信息。看一下它的结构
// TypeSpec is going to be immediately proceeded by
// an array of Type structs, all in the same block of memory.
struct TypeSpec {
struct TypeEntry {
incfs::verified_map_ptr<ResTable_type> type;
// Type configurations are accessed frequently when setting up an AssetManager and querying
// resources. Access this cached configuration to minimize page faults.
ResTable_config config;
};
// Pointer to the mmapped data where flags are kept. Flags denote whether the resource entry is
// public and under which configurations it varies.
incfs::verified_map_ptr<ResTable_typeSpec> type_spec;
std::vector<TypeEntry> type_entries;
…………
};
它的type_spec是incfs::verified_map_ptr<ResTable_typeSpec>类型,它里面包含着entry受哪些配置影响。我们通过entryidx,就能得到对应资源受影响的flags。type_entries是TypeEntry的集合,每一个TypeEntry对象又包含incfs::verified_map_ptr<ResTable_type> type,ResTable_type这个在前面解释过了。
接着看代码,调用type_spec->GetFlagsForEntryIndex(entry_idx)得到影响该资源配置flags。并且如果存在多个包的情况下,会将所有的影响flags都收集起来。
再根据前面的变量use_filtered来判断是否能用优化配置收集的资源来查找资源。
如果采用优化配置资源集合,就取filtered_group.type_entries,否则就取type_spec->type_entries,得到他们的数量type_entry_count,这个数量是对应类型的资源数量。filtered_group.type_entries里面是所有满足当前配置的类型资源,而type_spec->type_entries里面则是所有的类型资源。所以使用filtered_group.type_entries能免去许多不必要的比较开销,当然这个是得根据参数来判断的。
再接着向下看代码:
for (size_t i = 0; i < type_entry_count; i++) {
const TypeSpec::TypeEntry* type_entry = (use_filtered) ? filtered_group.type_entries[i]
: &type_spec->type_entries[i];
// We can skip calling ResTable_config::match() if the caller does not care for the
// configuration to match or if we're using the list of types that have already had their
// configuration matched.
const ResTable_config& this_config = type_entry->config;
if (!(use_filtered || ignore_configuration || this_config.match(desired_config))) {
continue;
}
…………
// The configuration matches and is better than the previous selection.
// Find the entry value if it exists for this configuration.
const auto& type = type_entry->type;
const auto offset = LoadedPackage::GetEntryOffset(type, entry_idx);
…………
best_cookie = cookie;
best_package = loaded_package;
best_type = type;
best_config = &this_config;
best_offset = offset.value();
…………
// Any configuration will suffice, so break.
if (stop_at_first_match) {
break;
}
}
}
得到类型资源的数量,就开始循环。首先得到type_entry ,它是TypeSpec::TypeEntry*,这个上面说过了。然后得到它的配置this_config 。
接着就是一个判断,必须三个条件都为false的情况下,会直接进入下次循环比较。use_filtered是使用优化配置资源,ignore_configuration是忽略配置,第三个是this_config.match(desired_config),这个是当前这个资源的配置符合期望的配置。这三个条件均不满足的情况,舍弃当前类型资源,会直接进行下个类型资源比较。如果有一个满足,就向下执行。
接着得到type,它是上面说的ResTable_type指针,再通过LoadedPackage::GetEntryOffset(type, entry_idx)得到offset,这个就是上面讲述ResTable_type时,所说的entry的偏移量。
再向下,就是认为找到了合适的结果了,就把best_cookie,best_package,best_type,best_config,best_offset均赋值。
判断参数stop_at_first_match是否设置为true了,如果设置了,就会跳出第一层循环。如果没有设置,继续进行循环,直到两层循环结束。
两层循环的内容就说完了,继续向下看代码:
…………
auto best_entry_result = LoadedPackage::GetEntryFromOffset(best_type, best_offset);
…………
const incfs::map_ptr<ResTable_entry> best_entry = *best_entry_result;
…………
const auto entry = GetEntryValue(best_entry.verified());
…………
return FindEntryResult{
.cookie = best_cookie,
.entry = *entry,
.config = *best_config,
.type_flags = type_flags,
.package_name = &best_package->GetPackageName(),
.type_string_ref = StringPoolRef(best_package->GetTypeStringPool(), best_type->id - 1),
.entry_string_ref = StringPoolRef(best_package->GetKeyStringPool(),
best_entry->key.index),
.dynamic_ref_table = package_group.dynamic_ref_table.get(),
};
}
这最后的这段代码就是处理结果了。
LoadedPackage::GetEntryFromOffset(best_type, best_offset)这块得到ResTable_entry指针best_entry_result ,这块就是咱们上面说的ResTable_type数据结构,通过相对于entriesStart的偏移量,就找到ResTable_entry的位置了。
然后通过GetEntryValue(best_entry.verified())得到EntryValue类型entry 。看下相关代码:
using EntryValue = std::variant<Res_value, incfs::verified_map_ptr<ResTable_map_entry>>;
base::expected<EntryValue, IOError> GetEntryValue(
incfs::verified_map_ptr<ResTable_entry> table_entry) {
const uint16_t entry_size = dtohs(table_entry->size);
// Check if the entry represents a bag value.
if (entry_size >= sizeof(ResTable_map_entry) &&
(dtohs(table_entry->flags) & ResTable_entry::FLAG_COMPLEX)) {
const auto map_entry = table_entry.convert<ResTable_map_entry>();
if (!map_entry) {
return base::unexpected(IOError::PAGES_MISSING);
}
return map_entry.verified();
}
// The entry represents a non-bag value.
const auto entry_value = table_entry.offset(entry_size).convert<Res_value>();
if (!entry_value) {
return base::unexpected(IOError::PAGES_MISSING);
}
Res_value value;
value.copyFrom_dtoh(entry_value.value());
return value;
}
可以看到EntryValue 可能的值类型是Res_value或incfs::verified_map_ptr<ResTable_map_entry>,在该资源是Bag资源的时候,会是incfs::verified_map_ptr<ResTable_map_entry>;如果是普通资源的情况下,则是Res_value。还可以看到,在ResTable_entry类成员变量flags有ResTable_entry::FLAG_COMPLEX时,会是Bag资源。
再看上面最后一段代码,最后拼成一个FindEntryResult结构作为结果返回。看下其成员type_string_ref和entry_string_ref。type_string_ref是取的对应LoadedPackage的类型Type 的ResStringPool,entry_string_ref取的对应LoadedPackage的Key的ResStringPool。并且成员dynamic_ref_table取的是对应package_group.dynamic_ref_table。
这样,FindEntry()函数就说完了。