1 Zygote简介
Zygote是Android中最重要的一个进程,Zygote进程和Init进程、SystemServer进程是Android最重要的三大进程。Zygote是Android系统创建新进程的核心进程,负责启动Dalvik虚拟机,加载一些必要的系统资源和系统类,启动system_server进程,随后进入等待处理app应用请求。
在Android系统中,应用程序进程都是由Zygote进程孵化出来的,而Zygote进程是由Init进程启动的。Zygote进程在启动时会创建一个Dalvik虚拟机实例,每当它孵化一个新的应用程序进程时,都会将这个Dalvik虚拟机实例复制到新的应用程序进程里面去,从而使得每一个应用程序进程都有一个独立的Dalvik虚拟机实例。
Zygote涉及的类:
frameworks/base/cmds/app_process/app_main.cpp
frameworks/base/core/jni/AndroidRuntime.cpp
frameworks/base/core/java/com/android/internal/os/
- Zygote.java
- ZygoteInit.java
- ZygoteServer.java
- ZygoteConnection.java
2 Zygote启动
本文基于Android10(Q)的源码做分析
2.1 init进程解析init.rc脚本
Zygote由init进程解析init.rc脚本启动的。脚本传入app_process的main方法做分割,根据字符串命令做相应逻辑。
现在机器分为32位和64位,Zygote的启动脚本init.rc也各有区别:
- init.zygote32.rc:zygote进程对应的执行程序是app_process(纯32bit模式)
- init.zygote64.rc:zygote进程对应的执行程序是app_process64(纯64bit模式)
- init.zygote32_64.rc:启动两个zygote进程,对应的执行程序分别是app_process32(主模式)、app_process64
- init.zygote64_32.rc:启动两个zygote进程,对应的执行程序分别是app_process64(主模式)、app_process32
zygote要执行的程序便是system/bin/app_process,它的源代码在app_main.cpp。我们先来看看app_main是如何处理脚本命令:
frameworks/base/cmds/app_process/app_main.cpp
165 #if defined(__LP64__)
166 static const char ABI_LIST_PROPERTY[] = "ro.product.cpu.abilist64";
167 static const char ZYGOTE_NICE_NAME[] = "zygote64";
168 #else
169 static const char ABI_LIST_PROPERTY[] = "ro.product.cpu.abilist32";
170 static const char ZYGOTE_NICE_NAME[] = "zygote";
171 #endif
172
173 int main(int argc, char* const argv[])
174 {
......
256 // Parse runtime arguments. Stop at first unrecognized option.
257 bool zygote = false;
258 bool startSystemServer = false;
259 bool application = false;
260 String8 niceName;
261 String8 className;
262
263 ++i; // Skip unused "parent dir" argument.
264 while (i < argc) {
265 const char* arg = argv[i++];
266 if (strcmp(arg, "--zygote") == 0) {
267 zygote = true;
268 niceName = ZYGOTE_NICE_NAME;
269 } else if (strcmp(arg, "--start-system-server") == 0) {
270 startSystemServer = true;
271 } else if (strcmp(arg, "--application") == 0) {
272 application = true;
273 } else if (strncmp(arg, "--nice-name=", 12) == 0) {
274 niceName.setTo(arg + 12);
275 } else if (strncmp(arg, "--", 2) != 0) {
276 className.setTo(arg);
277 break;
278 } else {
279 --i;
280 break;
281 }
282 }
......
309 if (startSystemServer) {
310 args.add(String8("start-system-server"));
311 }
......
331 if (!niceName.isEmpty()) {
332 runtime.setArgv0(niceName.string(), true /* setProcName */);
333 }
334
335 if (zygote) {
336 runtime.start("com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit", args, zygote);
337 } else if (className) {
338 runtime.start("com.android.internal.os.RuntimeInit", args, zygote);
339 } else {
340 fprintf(stderr, "Error: no class name or --zygote supplied.\n");
341 app_usage();
342 LOG_ALWAYS_FATAL("app_process: no class name or --zygote supplied.");
343 }
344 }
我们拿init.zygote64.rc为例:
1 service zygote /system/bin/app_process64 -Xzygote /system/bin --zygote --start-system-server
2 class main
3 priority -20
4 user root
5 group root readproc reserved_disk
6 socket zygote stream 660 root system
7 socket usap_pool_primary stream 660 root system
8 onrestart write /sys/android_power/request_state wake
9 onrestart write /sys/power/state on
10 onrestart restart audioserver
11 onrestart restart cameraserver
12 onrestart restart media
13 onrestart restart netd
14 onrestart restart wificond
15 writepid /dev/cpuset/foreground/tasks
主要是这个脚本命令:service zygote /system/bin/app_process64 -Xzygote /system/bin --zygote --start-system-server
实际上会被分割成:
service:服务标识
zygote:表示要开启的服务名字
/system/bin/app_process64:服务对应的路径
-Xzygote:作为虚拟机启动时所需要的参数,在AndroidRuntime.cpp中的 startVm() 中调用JNI_CreateJavaVM 使用到
/system/bin:代表虚拟机程序所在目录,因为 app_process 可以不和虚拟机在一个目录,所以 app_process 需要知道虚拟机所在的目录
–zygote :指明以 ZygoteInit 类作为入口,否则需要指定需要执行的类名
–start-system-server:仅在有 --zygote 参数时可用,告知 ZygoteInit 启动完毕后孵化出的第一个进程是 SystemServer
- 第一个if中
"--zygote"命中,zygote变量置为true表示要启动zygote进程,并将进程名改成了zygote或zygote64 - 第二个if中
"--start-system-server"命中,startSystemServer变量置为true表示要启动SystemServer进程
app_main.cpp的main方法执行后,ZygoteInit已经通过runtime.start("com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit", args, zygote);被启动了
2.2 AndroidRuntime启动ZygoteInit
其中runtime就是AndroidRuntime类,我们来看看AndroidRuntime的start方法:
/frameworks/base/core/jni/AndroidRuntime.cpp
1112 /*
1113 * Start the Android runtime. This involves starting the virtual machine
1114 * and calling the "static void main(String[] args)" method in the class
1115 * named by "className".
1116 *
1117 * Passes the main function two arguments, the class name and the specified
1118 * options string.
1119 */
1120 void AndroidRuntime::start(const char* className, const Vector<String8>& options, bool zygote)
1121 {
......
1164 /* start the virtual machine */
1165 JniInvocation jni_invocation;
1166 jni_invocation.Init(NULL);
1167 JNIEnv* env;
1168 if (startVm(&mJavaVM, &env, zygote) != 0) {
1169 return;
1170 }
1171 onVmCreated(env);
1172
1173 /*
1174 * Register android functions.
1175 */
1176 if (startReg(env) < 0) {
1177 ALOGE("Unable to register all android natives\n");
1178 return;
1179 }
......
1203
1204 /*
1205 * Start VM. This thread becomes the main thread of the VM, and will
1206 * not return until the VM exits.
1207 */
1208 char* slashClassName = toSlashClassName(className != NULL ? className : "");
1209 jclass startClass = env->FindClass(slashClassName);
1210 if (startClass == NULL) {
1211 ALOGE("JavaVM unable to locate class '%s'\n", slashClassName);
1212 /* keep going */
1213 } else {
1214 jmethodID startMeth = env->GetStaticMethodID(startClass, "main",
1215 "([Ljava/lang/String;)V");
1216 if (startMeth == NULL) {
1217 ALOGE("JavaVM unable to find main() in '%s'\n", className);
1218 /* keep going */
1219 } else {
1220 env->CallStaticVoidMethod(startClass, startMeth, strArray);
1226 }
1227 }
......
1235 }
对虚拟机和JNI方法的一些注册后,通过CallStaticVoidMethod来调用传过来的类名的main函数,我们传递过来的类名是com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit
AndroidRuntime中主要做了这三件事:
- startVm() 创建虚拟机
- startReg() 动态注册 java 调用 native 的 jni
- 反射调用 ZygoteInit 的 main()
2.3 ZygoteInit初始化
AndroidRuntime在Native层创建了Zygote,并且通过AndroidRuntime.start()从Native层转到Java层ZygoteInit的main()入口,ZygoteInit的main()方法是Android启动的第一个Java进程主方法
/frameworks/base/core/java/com/android/internal/os/ZygoteInit.java
818 @UnsupportedAppUsage
819 public static void main(String argv[]) {
820 ZygoteServer zygoteServer = null;
......
833 Runnable caller;
834 try {
......
847 boolean startSystemServer = false;
848 String zygoteSocketName = "zygote";
849 String abiList = null;
850 boolean enableLazyPreload = false;
851 for (int i = 1; i < argv.length; i++) {
852 if ("start-system-server".equals(argv[i])) {
853 startSystemServer = true;
854 } else if ("--enable-lazy-preload".equals(argv[i])) {
855 enableLazyPreload = true;
856 } else if (argv[i].startsWith(ABI_LIST_ARG)) {
857 abiList = argv[i].substring(ABI_LIST_ARG.length());
858 } else if (argv[i].startsWith(SOCKET_NAME_ARG)) {
859 zygoteSocketName = argv[i].substring(SOCKET_NAME_ARG.length());
860 } else {
861 throw new RuntimeException("Unknown command line argument: " + argv[i]);
862 }
863 }
864
865 final boolean isPrimaryZygote = zygoteSocketName.equals(Zygote.PRIMARY_SOCKET_NAME);
866
867 if (abiList == null) {
868 throw new RuntimeException("No ABI list supplied.");
869 }
870
871 // In some configurations, we avoid preloading resources and classes eagerly.
872 // In such cases, we will preload things prior to our first fork.
873 if (!enableLazyPreload) {
......
877 preload(bootTimingsTraceLog);
......
881 } else {
882 Zygote.resetNicePriority();
883 }
......
896 Zygote.initNativeState(isPrimaryZygote);
897
898 ZygoteHooks.stopZygoteNoThreadCreation();
899
900 zygoteServer = new ZygoteServer(isPrimaryZygote);
901
902 if (startSystemServer) {
903 Runnable r = forkSystemServer(abiList, zygoteSocketName, zygoteServer);
904
905 // {@code r == null} in the parent (zygote) process, and {@code r != null} in the
906 // child (system_server) process.
907 if (r != null) {
908 r.run();
909 return;
910 }
911 }
912
913 Log.i(TAG, "Accepting command socket connections");
914
915 // The select loop returns early in the child process after a fork and
916 // loops forever in the zygote.
917 caller = zygoteServer.runSelectLoop(abiList);
918 } catch (Throwable ex) {
919 Log.e(TAG, "System zygote died with exception", ex);
920 throw ex;
921 } finally {
922 if (zygoteServer != null) {
923 zygoteServer.closeServerSocket();
924 }
925 }
926
927 // We're in the child process and have exited the select loop. Proceed to execute the
928 // command.
929 if (caller != null) {
930 caller.run();
931 }
932 }
主要做了3件事:
preload()预先加载系统资源,如系统类、资源、系统共享库等创建 ZygoteServer,其实就是 ServerSocket 循环等待通知 fork 子进程创建 SystemServer进程
2.3.1 preload()
preload():资源准备,包括类加载,资源加载等
135 static void preload(TimingsTraceLog bootTimingsTraceLog) {
138 beginPreload();
141 preloadClasses();
144 cacheNonBootClasspathClassLoaders();
147 preloadResources();
150 nativePreloadAppProcessHALs();
153 maybePreloadGraphicsDriver();
155 preloadSharedLibraries();
156 preloadTextResources();
157 // Ask the WebViewFactory to do any initialization that must run in the zygote process,
158 // for memory sharing purposes.
159 WebViewFactory.prepareWebViewInZygote();
160 endPreload();
161 warmUpJcaProviders();
164 sPreloadComplete = true;
165 }
......
244 /**
245 * Performs Zygote process initialization. Loads and initializes commonly used classes.
246 *
247 * Most classes only cause a few hundred bytes to be allocated, but a few will allocate a dozen
248 * Kbytes (in one case, 500+K).
249 */
250 private static void preloadClasses() {
251 final VMRuntime runtime = VMRuntime.getRuntime();
252
253 InputStream is;
254 try {
255 is = new FileInputStream(PRELOADED_CLASSES);
256 } catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
257 Log.e(TAG, "Couldn't find " + PRELOADED_CLASSES + ".");
258 return;
259 }
260
261 Log.i(TAG, "Preloading classes...");
262 long startTime = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
263
264 // Drop root perms while running static initializers.
265 final int reuid = Os.getuid();
266 final int regid = Os.getgid();
267
268 // We need to drop root perms only if we're already root. In the case of "wrapped"
269 // processes (see WrapperInit), this function is called from an unprivileged uid
270 // and gid.
271 boolean droppedPriviliges = false;
272 if (reuid == ROOT_UID && regid == ROOT_GID) {
273 try {
274 Os.setregid(ROOT_GID, UNPRIVILEGED_GID);
275 Os.setreuid(ROOT_UID, UNPRIVILEGED_UID);
276 } catch (ErrnoException ex) {
277 throw new RuntimeException("Failed to drop root", ex);
278 }
279
280 droppedPriviliges = true;
281 }
282
283 // Alter the target heap utilization. With explicit GCs this
284 // is not likely to have any effect.
285 float defaultUtilization = runtime.getTargetHeapUtilization();
286 runtime.setTargetHeapUtilization(0.8f);
287
288 try {
289 BufferedReader br =
290 new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(is), Zygote.SOCKET_BUFFER_SIZE);
291
292 int count = 0;
293 String line;
294 while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) {
295 // Skip comments and blank lines.
296 line = line.trim();
297 if (line.startsWith("#") || line.equals("")) {
298 continue;
299 }
300
301 Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_DALVIK, line);
302 try {
303 if (false) {
304 Log.v(TAG, "Preloading " + line + "...");
305 }
306 // Load and explicitly initialize the given class. Use
307 // Class.forName(String, boolean, ClassLoader) to avoid repeated stack lookups
308 // (to derive the caller's class-loader). Use true to force initialization, and
309 // null for the boot classpath class-loader (could as well cache the
310 // class-loader of this class in a variable).
311 Class.forName(line, true, null);
312 count++;
313 } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
314 Log.w(TAG, "Class not found for preloading: " + line);
315 } catch (UnsatisfiedLinkError e) {
316 Log.w(TAG, "Problem preloading " + line + ": " + e);
317 } catch (Throwable t) {
318 Log.e(TAG, "Error preloading " + line + ".", t);
319 if (t instanceof Error) {
320 throw (Error) t;
321 }
322 if (t instanceof RuntimeException) {
323 throw (RuntimeException) t;
324 }
325 throw new RuntimeException(t);
326 }
327 Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_DALVIK);
328 }
329
330 Log.i(TAG, "...preloaded " + count + " classes in "
331 + (SystemClock.uptimeMillis() - startTime) + "ms.");
332 } catch (IOException e) {
333 Log.e(TAG, "Error reading " + PRELOADED_CLASSES + ".", e);
334 } finally {
335 IoUtils.closeQuietly(is);
336 // Restore default.
337 runtime.setTargetHeapUtilization(defaultUtilization);
338
339 // Fill in dex caches with classes, fields, and methods brought in by preloading.
340 Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_DALVIK, "PreloadDexCaches");
341 runtime.preloadDexCaches();
342 Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_DALVIK);
343
344 // Bring back root. We'll need it later if we're in the zygote.
345 if (droppedPriviliges) {
346 try {
347 Os.setreuid(ROOT_UID, ROOT_UID);
348 Os.setregid(ROOT_GID, ROOT_GID);
349 } catch (ErrnoException ex) {
350 throw new RuntimeException("Failed to restore root", ex);
351 }
352 }
353 }
354 }
......
382 /**
383 * Load in commonly used resources, so they can be shared across processes.
384 *
385 * These tend to be a few Kbytes, but are frequently in the 20-40K range, and occasionally even
386 * larger.
387 */
388 private static void preloadResources() {
389 final VMRuntime runtime = VMRuntime.getRuntime();
390
391 try {
392 mResources = Resources.getSystem();
393 mResources.startPreloading();
394 if (PRELOAD_RESOURCES) {
395 Log.i(TAG, "Preloading resources...");
396
397 long startTime = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
398 TypedArray ar = mResources.obtainTypedArray(
399 com.android.internal.R.array.preloaded_drawables);
400 int N = preloadDrawables(ar);
401 ar.recycle();
402 Log.i(TAG, "...preloaded " + N + " resources in "
403 + (SystemClock.uptimeMillis() - startTime) + "ms.");
404
405 startTime = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
406 ar = mResources.obtainTypedArray(
407 com.android.internal.R.array.preloaded_color_state_lists);
408 N = preloadColorStateLists(ar);
409 ar.recycle();
410 Log.i(TAG, "...preloaded " + N + " resources in "
411 + (SystemClock.uptimeMillis() - startTime) + "ms.");
412
413 if (mResources.getBoolean(
414 com.android.internal.R.bool.config_freeformWindowManagement)) {
415 startTime = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
416 ar = mResources.obtainTypedArray(
417 com.android.internal.R.array.preloaded_freeform_multi_window_drawables);
418 N = preloadDrawables(ar);
419 ar.recycle();
420 Log.i(TAG, "...preloaded " + N + " resource in "
421 + (SystemClock.uptimeMillis() - startTime) + "ms.");
422 }
423 }
424 mResources.finishPreloading();
425 } catch (RuntimeException e) {
426 Log.w(TAG, "Failure preloading resources", e);
427 }
428 }
preloadClasses()方法主要是从/system/etc/preloaded-classes文件中读取需要预加载的类名,然后通过Class.forname将该类加载到内存中,并会执行其中的一些静态方法(Java的类加载机制)。这里的重点是preloaded-classes文件,这个文件一般使用Android原生的文件,其路径在frameworks/base/config/preloaded-classes。
preloadResources()方法主要是做了以下几件事:
1.在Resources.startPreloading()方法中,调用updateConfiguration()方法为系统创建Configuration,这是后面应用和系统的一些配置来源。
2.从preloaded_drawables中获取预加载的drawables资源,并将其加载到内存中。preloaded_drawables字段在frameworks/base/core/res/res/values/arrays.xml中定义。
3.从preloaded_color_state_lists中获取预加载的color资源,并将其加载到内存中,preloaded_color_state_lists字段也是定义在frameworks/base/core/res/res/values/arrays.xml中。
4.如果支持自由窗口模式,则将preloaded_freeform_multi_window_drawables字段中定义的预加载的freeform drawables也加载进来。
2.3.2 ZygoteServer
ZygoteInit的main方法内实例化了ZygoteServer对象,并调用了其中runSelectLoop()、closeServerSocket()方法。
/frameworks/base/core/java/com/android/internal/os/ZygoteServer.java
48 class ZygoteServer {
.......
88 /**
89 * Listening socket that accepts new server connections.
90 */
91 private LocalServerSocket mZygoteSocket;
......
142 /**
143 * Initialize the Zygote server with the Zygote server socket, USAP pool server socket, and USAP
144 * pool event FD.
145 *
146 * @param isPrimaryZygote If this is the primary Zygote or not.
147 */
148 ZygoteServer(boolean isPrimaryZygote) {
151 if (isPrimaryZygote) {
152 mZygoteSocket = Zygote.createManagedSocketFromInitSocket(Zygote.PRIMARY_SOCKET_NAME);
153 mUsapPoolSocket =
154 Zygote.createManagedSocketFromInitSocket(
155 Zygote.USAP_POOL_PRIMARY_SOCKET_NAME);
156 } else {
157 mZygoteSocket = Zygote.createManagedSocketFromInitSocket(Zygote.SECONDARY_SOCKET_NAME);
158 mUsapPoolSocket =
159 Zygote.createManagedSocketFromInitSocket(
160 Zygote.USAP_POOL_SECONDARY_SOCKET_NAME);
161 }
166 }
......
176 /**
177 * Registers a server socket for zygote command connections. This opens the server socket
178 * at the specified name in the abstract socket namespace.
179 */
180 void registerServerSocketAtAbstractName(String socketName) {
181 if (mZygoteSocket == null) {
182 try {
183 mZygoteSocket = new LocalServerSocket(socketName);
184 mCloseSocketFd = false;
185 } catch (IOException ex) {
186 throw new RuntimeException(
187 "Error binding to abstract socket '" + socketName + "'", ex);
188 }
189 }
190 }
......
210 /**
211 * Close and clean up zygote sockets. Called on shutdown and on the
212 * child's exit path.
213 */
214 void closeServerSocket() {
215 try {
216 if (mZygoteSocket != null) {
217 FileDescriptor fd = mZygoteSocket.getFileDescriptor();
218 mZygoteSocket.close();
219 if (fd != null && mCloseSocketFd) {
220 Os.close(fd);
221 }
222 }
223 } catch (IOException ex) {
224 Log.e(TAG, "Zygote: error closing sockets", ex);
225 } catch (ErrnoException ex) {
226 Log.e(TAG, "Zygote: error closing descriptor", ex);
227 }
228
229 mZygoteSocket = null;
230 }
......
368 /**
369 * Runs the zygote process's select loop. Accepts new connections as
370 * they happen, and reads commands from connections one spawn-request's
371 * worth at a time.
372 */
373 Runnable runSelectLoop(String abiList) {
374 ArrayList<FileDescriptor> socketFDs = new ArrayList<FileDescriptor>();
375 ArrayList<ZygoteConnection> peers = new ArrayList<ZygoteConnection>();
376
377 socketFDs.add(mZygoteSocket.getFileDescriptor());
378 peers.add(null);
379
380 while (true) {
381 fetchUsapPoolPolicyPropsWithMinInterval();
382
383 int[] usapPipeFDs = null;
384 StructPollfd[] pollFDs = null;
385
386 // Allocate enough space for the poll structs, taking into account
387 // the state of the USAP pool for this Zygote (could be a
388 // regular Zygote, a WebView Zygote, or an AppZygote).
389 if (mUsapPoolEnabled) {
390 usapPipeFDs = Zygote.getUsapPipeFDs();
391 pollFDs = new StructPollfd[socketFDs.size() + 1 + usapPipeFDs.length];
392 } else {
393 pollFDs = new StructPollfd[socketFDs.size()];
394 }
395
396 /*
397 * For reasons of correctness the USAP pool pipe and event FDs
398 * must be processed before the session and server sockets. This
399 * is to ensure that the USAP pool accounting information is
400 * accurate when handling other requests like API blacklist
401 * exemptions.
402 */
403
404 int pollIndex = 0;
405 for (FileDescriptor socketFD : socketFDs) {
406 pollFDs[pollIndex] = new StructPollfd();
407 pollFDs[pollIndex].fd = socketFD;
408 pollFDs[pollIndex].events = (short) POLLIN;
409 ++pollIndex;
410 }
411
412 final int usapPoolEventFDIndex = pollIndex;
413
414 if (mUsapPoolEnabled) {
415 pollFDs[pollIndex] = new StructPollfd();
416 pollFDs[pollIndex].fd = mUsapPoolEventFD;
417 pollFDs[pollIndex].events = (short) POLLIN;
418 ++pollIndex;
419
420 for (int usapPipeFD : usapPipeFDs) {
421 FileDescriptor managedFd = new FileDescriptor();
422 managedFd.setInt$(usapPipeFD);
423
424 pollFDs[pollIndex] = new StructPollfd();
425 pollFDs[pollIndex].fd = managedFd;
426 pollFDs[pollIndex].events = (short) POLLIN;
427 ++pollIndex;
428 }
429 }
430
431 try {
432 Os.poll(pollFDs, -1);
433 } catch (ErrnoException ex) {
434 throw new RuntimeException("poll failed", ex);
435 }
436
437 boolean usapPoolFDRead = false;
438
439 while (--pollIndex >= 0) {
440 if ((pollFDs[pollIndex].revents & POLLIN) == 0) {
441 continue;
442 }
443
444 if (pollIndex == 0) {
445 // Zygote server socket
446
447 ZygoteConnection newPeer = acceptCommandPeer(abiList);
448 peers.add(newPeer);
449 socketFDs.add(newPeer.getFileDescriptor());
450
451 } else if (pollIndex < usapPoolEventFDIndex) {
452 // Session socket accepted from the Zygote server socket
453
454 try {
455 ZygoteConnection connection = peers.get(pollIndex);
456 final Runnable command = connection.processOneCommand(this);
457
458 // TODO (chriswailes): Is this extra check necessary?
459 if (mIsForkChild) {
460 // We're in the child. We should always have a command to run at this
461 // stage if processOneCommand hasn't called "exec".
462 if (command == null) {
463 throw new IllegalStateException("command == null");
464 }
465
466 return command;
467 } else {
468 // We're in the server - we should never have any commands to run.
469 if (command != null) {
470 throw new IllegalStateException("command != null");
471 }
472
473 // We don't know whether the remote side of the socket was closed or
474 // not until we attempt to read from it from processOneCommand. This
475 // shows up as a regular POLLIN event in our regular processing loop.
476 if (connection.isClosedByPeer()) {
477 connection.closeSocket();
478 peers.remove(pollIndex);
479 socketFDs.remove(pollIndex);
480 }
481 }
482 } catch (Exception e) {
483 if (!mIsForkChild) {
484 // We're in the server so any exception here is one that has taken place
485 // pre-fork while processing commands or reading / writing from the
486 // control socket. Make a loud noise about any such exceptions so that
487 // we know exactly what failed and why.
488
489 Slog.e(TAG, "Exception executing zygote command: ", e);
490
491 // Make sure the socket is closed so that the other end knows
492 // immediately that something has gone wrong and doesn't time out
493 // waiting for a response.
494 ZygoteConnection conn = peers.remove(pollIndex);
495 conn.closeSocket();
496
497 socketFDs.remove(pollIndex);
498 } else {
499 // We're in the child so any exception caught here has happened post
500 // fork and before we execute ActivityThread.main (or any other main()
501 // method). Log the details of the exception and bring down the process.
502 Log.e(TAG, "Caught post-fork exception in child process.", e);
503 throw e;
504 }
505 } finally {
506 // Reset the child flag, in the event that the child process is a child-
507 // zygote. The flag will not be consulted this loop pass after the Runnable
508 // is returned.
509 mIsForkChild = false;
510 }
511 } else {
512 // Either the USAP pool event FD or a USAP reporting pipe.
513
514 // If this is the event FD the payload will be the number of USAPs removed.
515 // If this is a reporting pipe FD the payload will be the PID of the USAP
516 // that was just specialized.
517 long messagePayload = -1;
518
519 try {
520 byte[] buffer = new byte[Zygote.USAP_MANAGEMENT_MESSAGE_BYTES];
521 int readBytes = Os.read(pollFDs[pollIndex].fd, buffer, 0, buffer.length);
522
523 if (readBytes == Zygote.USAP_MANAGEMENT_MESSAGE_BYTES) {
524 DataInputStream inputStream =
525 new DataInputStream(new ByteArrayInputStream(buffer));
526
527 messagePayload = inputStream.readLong();
528 } else {
529 Log.e(TAG, "Incomplete read from USAP management FD of size "
530 + readBytes);
531 continue;
532 }
533 } catch (Exception ex) {
534 if (pollIndex == usapPoolEventFDIndex) {
535 Log.e(TAG, "Failed to read from USAP pool event FD: "
536 + ex.getMessage());
537 } else {
538 Log.e(TAG, "Failed to read from USAP reporting pipe: "
539 + ex.getMessage());
540 }
541
542 continue;
543 }
544
545 if (pollIndex > usapPoolEventFDIndex) {
546 Zygote.removeUsapTableEntry((int) messagePayload);
547 }
548
549 usapPoolFDRead = true;
550 }
551 }
552
553 // Check to see if the USAP pool needs to be refilled.
554 if (usapPoolFDRead) {
555 int[] sessionSocketRawFDs =
556 socketFDs.subList(1, socketFDs.size())
557 .stream()
558 .mapToInt(fd -> fd.getInt$())
559 .toArray();
560
561 final Runnable command = fillUsapPool(sessionSocketRawFDs);
562
563 if (command != null) {
564 return command;
565 }
566 }
567 }
568 }
569 }
主要做3件事:
创建ZygoteServer:ZygoteServer初始化,内部对ServerSocket进行了初始化,为Zygote提供了通信的能力。zygoteServer.runSelectLoop():当zygote进程返回到main()方法后执行,从名字上和注释来看,这个方法应该是一个死循环,是不断进行循环执行命令的方法,主要做了两件事:
1.每次循环都重新构建监听文件列表,主要是ZygoteServer的socket文件(ZygoteServer的socket和其他应用进程连接过来的socket)和usap文件节点(目前看来,zygote默认是没有使用,作用未明,不做分析)。
2.监听文件列表,并从中获取命令执行。zygoteServer.closeServerSocket():在循环后,关闭ServerSocket
2.3.3 创建SystemServer进程
718 /**
719 * Prepare the arguments and forks for the system server process.
720 *
721 * @return A {@code Runnable} that provides an entrypoint into system_server code in the child
722 * process; {@code null} in the parent.
723 */
724 private static Runnable forkSystemServer(String abiList, String socketName,
725 ZygoteServer zygoteServer) {
726 long capabilities = posixCapabilitiesAsBits(
727 OsConstants.CAP_IPC_LOCK,
728 OsConstants.CAP_KILL,
729 OsConstants.CAP_NET_ADMIN,
730 OsConstants.CAP_NET_BIND_SERVICE,
731 OsConstants.CAP_NET_BROADCAST,
732 OsConstants.CAP_NET_RAW,
733 OsConstants.CAP_SYS_MODULE,
734 OsConstants.CAP_SYS_NICE,
735 OsConstants.CAP_SYS_PTRACE,
736 OsConstants.CAP_SYS_TIME,
737 OsConstants.CAP_SYS_TTY_CONFIG,
738 OsConstants.CAP_WAKE_ALARM,
739 OsConstants.CAP_BLOCK_SUSPEND
740 );
741 /* Containers run without some capabilities, so drop any caps that are not available. */
742 StructCapUserHeader header = new StructCapUserHeader(
743 OsConstants._LINUX_CAPABILITY_VERSION_3, 0);
744 StructCapUserData[] data;
745 try {
746 data = Os.capget(header);
747 } catch (ErrnoException ex) {
748 throw new RuntimeException("Failed to capget()", ex);
749 }
750 capabilities &= ((long) data[0].effective) | (((long) data[1].effective) << 32);
751
752 /* Hardcoded command line to start the system server */
753 String args[] = {
754 "--setuid=1000",
755 "--setgid=1000",
756 "--setgroups=1001,1002,1003,1004,1005,1006,1007,1008,1009,1010,1018,1021,1023,"
757 + "1024,1032,1065,3001,3002,3003,3006,3007,3009,3010",
758 "--capabilities=" + capabilities + "," + capabilities,
759 "--nice-name=system_server",
760 "--runtime-args",
761 "--target-sdk-version=" + VMRuntime.SDK_VERSION_CUR_DEVELOPMENT,
762 "com.android.server.SystemServer",
763 };
764 ZygoteArguments parsedArgs = null;
765
766 int pid;
767
768 try {
769 parsedArgs = new ZygoteArguments(args);
770 Zygote.applyDebuggerSystemProperty(parsedArgs);
771 Zygote.applyInvokeWithSystemProperty(parsedArgs);
772
773 boolean profileSystemServer = SystemProperties.getBoolean(
774 "dalvik.vm.profilesystemserver", false);
775 if (profileSystemServer) {
776 parsedArgs.mRuntimeFlags |= Zygote.PROFILE_SYSTEM_SERVER;
777 }
778
779 /* Request to fork the system server process */
780 pid = Zygote.forkSystemServer(
781 parsedArgs.mUid, parsedArgs.mGid,
782 parsedArgs.mGids,
783 parsedArgs.mRuntimeFlags,
784 null,
785 parsedArgs.mPermittedCapabilities,
786 parsedArgs.mEffectiveCapabilities);
787 } catch (IllegalArgumentException ex) {
788 throw new RuntimeException(ex);
789 }
790
791 /* For child process */
792 if (pid == 0) {
793 if (hasSecondZygote(abiList)) {
794 waitForSecondaryZygote(socketName);
795 }
796
797 zygoteServer.closeServerSocket();
798 return handleSystemServerProcess(parsedArgs);
799 }
800
801 return null;
802 }
forkSystemServer():
①调用Zygote.forkSystemServer()方法去fork一个新的进程出来。
②fork()后的子进程是SystemServer进程,则等待zygote的启动完成,并执行真正的SystemServer代码。
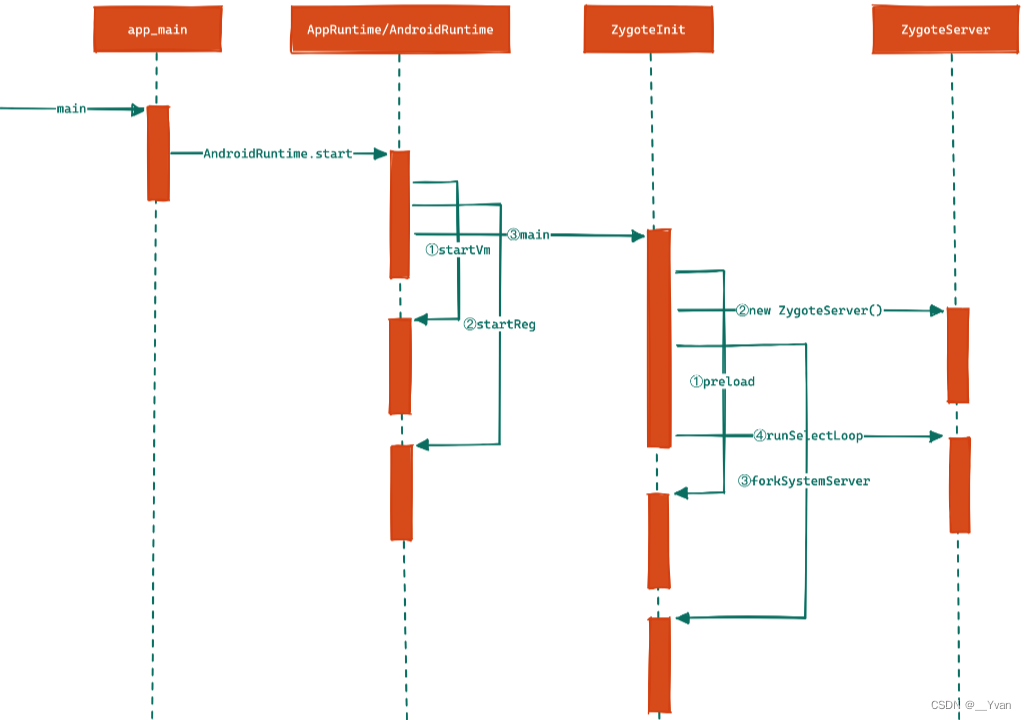
2.4 Zygote启动流程图
3 总结
所有的进程都由Zygote创建,zygote主要用来孵化system_server进程和应用程序进程。在孵化出第一个进程system_server后通过runSelectLoop等待并处理消息,分裂应用程序进程仍由system_server控制,等待 AMS 给他发消息(告诉 zygote 创建进程),如app启动时创建子进程。
从AndroidRuntime到ZygoteInit,主要分为3大过程:
1、
创建虚拟机——startVm():调用JNI虚拟机创建函数
2、注册JNI函数——startReg():前面已经创建虚拟机,这里给这个虚拟机注册一些JNI函数(后续java世界用到的函数是native实现,这里需要提前注册注册这些函数)
3、此时就要执行CallStaticViodMethod,通过这个函数将进入android精心打造的java世界,这个函数将调用com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit的main函数
在 ZygoteInit.main函数中进入Java世界,主要有4个关键步骤:
1、
预加载类和资源——preload()
主要是preloadClasses和preloadResources,其中preloadClasses一般是加载时间超过1250ms的类,因而需要在zygote预加载
2、建立IPC通信服务——初始化ZygoteServer,内部初始化了ZygoteSocket
zygote及系统中其他程序的通信并没有使用Binder,而是采用基于AF_UNIX类型的Socket,作用正是建立这个Socket
3、启动system_server——forkSystemServer()
这个函数会创建Java世界中系统Service所驻留的进程system_server,该进程是framework的核心,也是zygote孵化出的第一个进程。如果它死了,就会导致zygote自杀。
4、等待请求——runSelectLoop()
zygote从startSystemServer返回后,将进入第四个关键函数runSelectLoop,在第一个函数ZygoteServer中注册了一个用于IPC的Socket将在这里使用,这里Zygote采用高效的I/O多路复用机制,保证在没有客户端请求时或者数据处理时休眠,否则响应客户端的请求。等待 AMS 给他发消息(告诉 zygote 创建进程)。此时zygote完成了java世界的初创工作,调用runSelectLoop便开始休眠了,当收到请求或者数据处理便会随时醒来,继续工作。
4 面试题
1 init进程作用是什么
init进程起着承上启下的作用,Android本身是基于Linux而来的,init进程是Linux系统中用户空间的第一个进程。init进程属于一个守护进程,准确的说,它是Linux系统中用户控制的第一个进程,它的进程号为1(进程号为0的为内核进程),它的生命周期贯穿整个Linux内核运行的始终。Android中所有其它的进程共同的鼻祖均为init进程。
Android Q(10.0) 的init入口函数由原先的init.cpp 调整到了main.cpp,把各个阶段的操作分离开来,使代码更加简洁命令。
作为天子第1号进程,init被赋予了很多重要的职责,主要分为三个阶段:
- init进程第一阶段做的主要工作是
挂载分区,创建设备节点和一些关键目录,初始化日志输出系统,启用SELinux安全策略。- init进程第二阶段主要工作是
初始化属性系统,解析SELinux的匹配规则,处理子进程终止信号,启动系统属性服务,可以说每一项都很关键,如果说第一阶段是为属性系统,SELinux做准备,那么第二阶段就是真正去把这些功能落实。- init进行第三阶段主要是
解析init.rc来启动其他进程,进入无限循环,进行子进程实时监控(守护)。
其中第三阶段通过initrc启动其他进程,我们常见的比如启动Zygote进程、启动SeviceManager进程等。
2 Zygote进程最原始的进程是什么进程(或者Zygote进程由来)
Zygote最开始是app_process,它是在 init 进程启动时被启动的,在app_main.cpp才被修改为 Zygote。
3 Zygote 是在内核空间还是在用户空间?
因为 init 进程的创建在用户空间,而 Zygote 是由 init 进程创建启动的,所以Zygote是在用户空间。
4 Zygote为什么需要用到Socket通信而不是Binder
Zygote是Android中的一个重要进程,它是启动应用程序进程的父进程。Zygote使用Socket来与应用程序进程进行通信,而不是使用Android中的IPC机制Binder,这是因为Socket和Binder有不同的优缺点,而在Zygote进程中使用Socket可以更好地满足Zygote进程的需求。
Zygote 用 binder 通信会导致死锁
假设 Zygote 使用 Binder 通信,因为 Binder 是支持多线程的,存在并发问题,而并发问题的解决方案就是加锁,如果进程 fork 是在多线程情况下运行,Binder 等待锁在锁机制下就可能会出现死锁。Zygote 用 binder 通信会导致读写错误
根本原因在于要 new 一个 ProcessState 用于 Binder 通信时,需要 mmap 申请一片内存用以提供给内核进行数据交换使用。而如果直接 fork 了的话,子进程在进行 binder 通信时,内核还是会继续使用父进程申请的地址写数据,而此时会触发子进程 COW(Copy on Write),从而导致地址空间已经重新映射,而子进程还尝试访问之前父进程 mmap 的地址,会导致 SIGSEGV、SEGV_MAPERR段错误。Zygote初始化时,Binder还没开始初始化。Socket具有良好的跨平台性,能够在不同的操作系统和语言之间进行通信。这对于Zygote进程来说非常重要,因为它需要在不同的设备和架构上运行,并且需要与不同的应用程序进程进行通信。使用Socket可以让Zygote进程更加灵活和可扩展,因为它不需要考虑Binder所带来的特定限制和要求。Socket具有简单的API和易于使用的特点。Zygote进程需要快速启动并与应用程序进程建立通信,Socket提供了快速、可靠的通信方式,并且使用Socket API也很容易实现。相比之下,Binder需要更多的配置和维护工作,这对于Zygote进程来说可能会增加不必要的复杂性和开销。Socket在数据传输时具有更低的延迟和更高的吞吐量,这对于Zygote进程来说非常重要。Zygote进程需要在较短的时间内启动应用程序进程,并且需要传输大量的数据和代码,Socket的高性能和低延迟使其成为更好的选择。
总之,Zygote进程使用Socket而不是Binder是基于其优点和需求而做出的选择。虽然Binder在Android中扮演着重要的角色,但在某些情况下,使用Socket可以提供更好的性能和更大的灵活性。再者,Binder当初并不成熟,团队成员对于进程间通讯更倾向于用Socket,后面为了做了很多优化,才使得Binder通讯变得成熟稳定。
5 每个App都会将系统的资源,系统的类都加载一遍吗
zygote进程的作用:
1.创建一个Service端的Socket,开启一个ServerSocket实现和别的进程通信。
2.加载系统类,系统资源。
3.启动System Server进程
Zygote进程预加载系统资源后,然后通过它孵化出其他的虚拟机进程,进而共享虚拟机内存和框架层资源(共享内存),这样大幅度提高应用程序的启动和运行速度。
6 PMS 是干什么的,你是怎么理解PMS
包管理,包解析,结果缓存,提供查询接口。
- 遍历
/data/app的文件夹 - 解压
apk文件 - dom解析
AndroidManifest.xml文件。
7 为什么会有AMS AMS的作用
- 查询PMS
- 反射生成对象
- 管理Activity生命周期
AMS缓存中心:ActivityThread
8 AMS如何管理Activity,探探AMS的执行原理
Activity在应用端由ActivityClientRecord负责描述其生命周期的过程与状态,但最终这些过程与状态是由ActivityManagerService(以下简称AMS)来管理和控制的
BroadcastRecord:描述了应用进程的BroadcastReceiver,由BroadcastQueue负责管理。ServiceRecord:描述了Service服务组件,由ActiveServices负责管理。ContentProviderRecord:描述ContentProvider内容提供者,由ProviderMap管理。ActivityRecord:用于描述Activity,由ActivityStackSupervisor进行管理。