新建测试文件
from flask import Flask,current_app
app = Flask(__name__)
a = current_app
b = current_app.config['DEBUG']
if __name__=='__main__':
app.run(debug=True)当运行文件时会报错:
RuntimeError: Working outside of application context.
查看current_app源码
# context locals
_request_ctx_stack = LocalStack()
_app_ctx_stack = LocalStack()
current_app = LocalProxy(_find_app)
request = LocalProxy(partial(_lookup_req_object, 'request'))
session = LocalProxy(partial(_lookup_req_object, 'session'))
g = LocalProxy(partial(_lookup_app_object, 'g'))
'''
current_app,request,session三者都是localProxy对象
'''查看localProxy源码
@implements_bool
class LocalProxy(object):
__slots__ = ('__local', '__dict__', '__name__', '__wrapped__')
def __init__(self, local, name=None):
object.__setattr__(self, '_LocalProxy__local', local)
object.__setattr__(self, '__name__', name)
if callable(local) and not hasattr(local, '__release_local__'):
# "local" is a callable that is not an instance of Local or
# LocalManager: mark it as a wrapped function.
object.__setattr__(self, '__wrapped__', local)
def _get_current_object(self):
if not hasattr(self.__local, '__release_local__'):
return self.__local()
try:
return getattr(self.__local, self.__name__)
except AttributeError:
raise RuntimeError('no object bound to %s' % self.__name__)
@property
def __dict__(self):
try:
return self._get_current_object().__dict__
except RuntimeError:
raise AttributeError('__dict__')
def __repr__(self):
try:
obj = self._get_current_object()
except RuntimeError:
return '<%s unbound>' % self.__class__.__name__
return repr(obj)
def __bool__(self):
try:
return bool(self._get_current_object())
except RuntimeError:
return False
def __unicode__(self):
try:
return unicode(self._get_current_object()) # noqa
except RuntimeError:
return repr(self)
def __dir__(self):
try:
return dir(self._get_current_object())
except RuntimeError:
return []
def __getattr__(self, name):
if name == '__members__':
return dir(self._get_current_object())
return getattr(self._get_current_object(), name)
def __setitem__(self, key, value):
self._get_current_object()[key] = value
def __delitem__(self, key):
del self._get_current_object()[key]
if PY2:
__getslice__ = lambda x, i, j: x._get_current_object()[i:j]
def __setslice__(self, i, j, seq):
self._get_current_object()[i:j] = seq
def __delslice__(self, i, j):
del self._get_current_object()[i:j]
__setattr__ = lambda x, n, v: setattr(x._get_current_object(), n, v)
__delattr__ = lambda x, n: delattr(x._get_current_object(), n)
__str__ = lambda x: str(x._get_current_object())
__lt__ = lambda x, o: x._get_current_object() < o
__le__ = lambda x, o: x._get_current_object() <= o
__eq__ = lambda x, o: x._get_current_object() == o
__ne__ = lambda x, o: x._get_current_object() != o
__gt__ = lambda x, o: x._get_current_object() > o
__ge__ = lambda x, o: x._get_current_object() >= o
__cmp__ = lambda x, o: cmp(x._get_current_object(), o) # noqa
__hash__ = lambda x: hash(x._get_current_object())
__call__ = lambda x, *a, **kw: x._get_current_object()(*a, **kw)
__len__ = lambda x: len(x._get_current_object())
__getitem__ = lambda x, i: x._get_current_object()[i]
__iter__ = lambda x: iter(x._get_current_object())
__contains__ = lambda x, i: i in x._get_current_object()
__add__ = lambda x, o: x._get_current_object() + o
__sub__ = lambda x, o: x._get_current_object() - o
__mul__ = lambda x, o: x._get_current_object() * o
__floordiv__ = lambda x, o: x._get_current_object() // o
__mod__ = lambda x, o: x._get_current_object() % o
__divmod__ = lambda x, o: x._get_current_object().__divmod__(o)
__pow__ = lambda x, o: x._get_current_object() ** o
__lshift__ = lambda x, o: x._get_current_object() << o
__rshift__ = lambda x, o: x._get_current_object() >> o
__and__ = lambda x, o: x._get_current_object() & o
__xor__ = lambda x, o: x._get_current_object() ^ o
__or__ = lambda x, o: x._get_current_object() | o
__div__ = lambda x, o: x._get_current_object().__div__(o)
__truediv__ = lambda x, o: x._get_current_object().__truediv__(o)
__neg__ = lambda x: -(x._get_current_object())
__pos__ = lambda x: +(x._get_current_object())
__abs__ = lambda x: abs(x._get_current_object())
__invert__ = lambda x: ~(x._get_current_object())
__complex__ = lambda x: complex(x._get_current_object())
__int__ = lambda x: int(x._get_current_object())
__long__ = lambda x: long(x._get_current_object()) # noqa
__float__ = lambda x: float(x._get_current_object())
__oct__ = lambda x: oct(x._get_current_object())
__hex__ = lambda x: hex(x._get_current_object())
__index__ = lambda x: x._get_current_object().__index__()
__coerce__ = lambda x, o: x._get_current_object().__coerce__(x, o)
__enter__ = lambda x: x._get_current_object().__enter__()
__exit__ = lambda x, *a, **kw: x._get_current_object().__exit__(*a, **kw)
__radd__ = lambda x, o: o + x._get_current_object()
__rsub__ = lambda x, o: o - x._get_current_object()
__rmul__ = lambda x, o: o * x._get_current_object()
__rdiv__ = lambda x, o: o / x._get_current_object()
if PY2:
__rtruediv__ = lambda x, o: x._get_current_object().__rtruediv__(o)
else:
__rtruediv__ = __rdiv__
__rfloordiv__ = lambda x, o: o // x._get_current_object()
__rmod__ = lambda x, o: o % x._get_current_object()
__rdivmod__ = lambda x, o: x._get_current_object().__rdivmod__(o)
__copy__ = lambda x: copy.copy(x._get_current_object())
__deepcopy__ = lambda x, memo: copy.deepcopy(x._get_current_object(), memo)探究以下问题
AppContext、RequestContext、Flask与Request之间的关系
- flask中上下文机制:
flask中上下文是一种对象
'''
*应用上下文: 对象 Flask*
*请求上下文: 对象 Request*
Flask --> Appcontext
Request --> RequestContext
'''
#Appcontext是对Flask的封装,将Flask的外部操作封装到Appcontext对象中
#Request同上通过
from flask import current_app,request
实际是通过LocalProxy方法找到flask核心对象和Request类
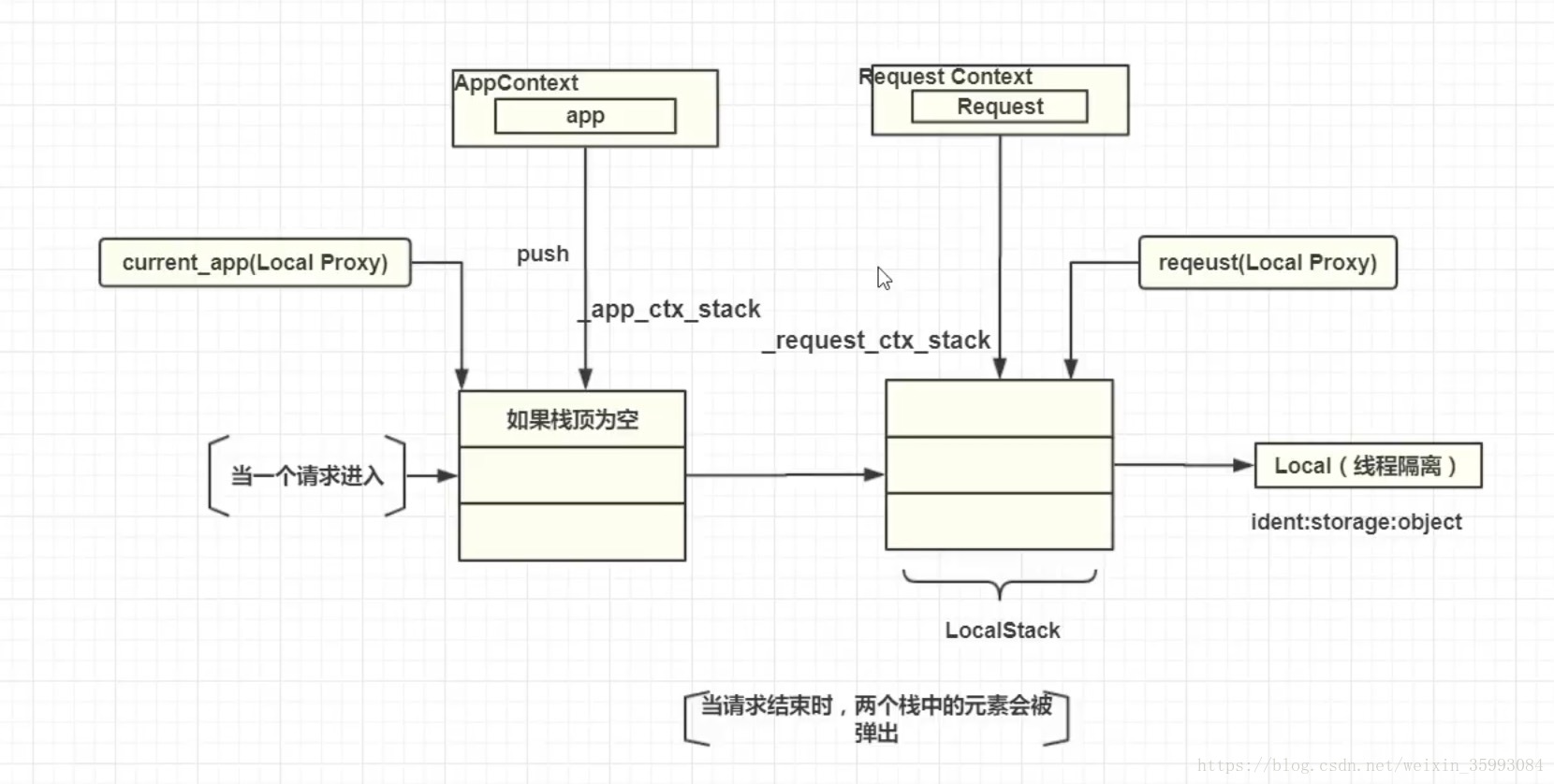
flask核心机制图解
flask实现栈的对象是LocalStack
falsk实例化两个栈:
_app_ctx_stack = LocalStack()
_request_ctx_stack = LocalStack()
当请求进入时,RequestContext先被实例化,实例化后推入_reuqest_ctx_stack栈中,此时flask会检测_app_ctx_stack栈顶是否为空,如果为空flask会将当前应用对象AppContext实例化后推入_app_ctx_stack栈顶
current_app=LoaclProxy(find_app)中find_app源码如下:
def _find_app():
#取栈顶对象
top = _app_ctx_stack.top
if top is None:
raise RuntimeError(_app_ctx_err_msg)
#返回栈顶AppContext中的app对象
return top.app此时current_app返回应用上下文AppContext中app对象
request=LocalProxy(partial(_lookup_req_object,’request’))
中_lookup_req_objext源码如下:
def _lookup_req_object(name):
#获取request栈顶对象
top = _request_ctx_stack.top
if top is None:
raise RuntimeError(_request_ctx_err_msg)
#返回栈顶对象的name
return getattr(top, name)
current_app和request永远指向两个栈的栈顶对象
以上可看出,当请求通过flask访问时,会先生成Request请求上下文对象的实例化,并通过request代理指向request对象。然后由flask来实例化AppContext 对象,并推入栈中,从而让current_app有指向对象
当进行离线应用、单元测试时,因为没有触发request请求,需要自行将应用上下文推入栈中。再手动弹出
from flask import current_app,request
app = Flask(__name__)
ctx = app.app_context()
ctx.push()
a = current_app
curent_app.config['DEBUG']
ctx.pop()
python中优化写法,使用with语句
* 使用了上下文协议的对象使用with
* 上下文管理器
* __enter__ __exit__
* 上下文表达式必须要返回一个上下文管理器
例如:文件读写
with open('/2.txt') as f:
f.read()
#f是__enter__方法的返回值flask优化改写:
from flask import Flask,current_app
app = Flask(__name__)
with app.app_context():
a = current_app
b = current_app.config['DEBUG']
'''
app_context()方法返回一个AppContext应用上下文管理器
在AppContext中定义了__enter__和__exit__方法
'''Appcontext中上下文管理器部分源码:
def __enter__(self):
self.push()
return self
def __exit__(self, exc_type, exc_value, tb):
self.pop(exc_value)因此在with语句中,AppContext中定义了__exit__方法,所以当current_app离开with语句中时,_app_ctx_stack栈顶的AppContext已被弹出,current_app没有任何指向对象。