目录
1. 组件的基本使用
简单的组件示例
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<!-- 3.使用组件 -->
<my-cpn></my-cpn>
<my-cpn></my-cpn>
<my-cpn></my-cpn>
<cpnc></cpnc>
</div>
<script src="../js/vue.js"></script>
<script>
// 1.创建组件构造器对象
const cpnc = Vue.extend({
template:`
<div>
<h2>标题</h2>
<p>内容1...<p>
<p>内容2...<p>
</div>`
})
// 2.全局注册组件
Vue.component('my-cpn', cpnc)
const app = new Vue({
el:"#app",
data:{
},
components:{
//局部组件创建
cpnc:cpnc
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html> 组件是可复用的 Vue 实例,且带有一个名字:在这个例子中是 my-cpn。我们可以在一个通过 new Vue 创建的 Vue 根实例中,把这个组件作为自定义元素来使用: <my-cpn></my-cpn>。
1.1 创建组件构造器对象
template中是组件的DOM元素内容。
1.2 注册组件
- 全局注册,通过
Vue.component。 - 局部注册,通过
components:{cpnc:cpnc}。
1.3 使用组件
像使用html标签一样使用。
<div id="app">
<!-- 3.使用组件 -->
<my-cpn></my-cpn>
<my-cpn></my-cpn>
<my-cpn></my-cpn>
<cpnc></cpnc>
</div>
2. 全局组件和局部组件
组件的注册方式有两种,一种是全局组件一种是局部组件。
<div id="app">
<h2>全局组件</h2>
<my-cpn></my-cpn>
<h2>局部组件</h2>
<cpnc></cpnc>
</div>
<script src="../js/vue.js"></script>
<script>
// 1.创建组件构造器对象
const cpnc = Vue.extend({
template:`
<div>
<h2>标题</h2>
<p>内容1</p>
<p>内容2</p>
</div>`
})
// 2.注册组件(全局组件,可以在多个vue实例中使用)
Vue.component('my-cpn', cpnc)
const app = new Vue({
el:"#app",
components:{//局部组件创建
cpnc:cpnc
}
})
</script>2.1 全局组件
全局组件,可以在多个vue实例中使用,类似于全局变量。
使用Vue.component('my-cpn', cpnc)方式注册,直接使用<my-cpn></my-cpn>调用。my-cpn是全局组件的名字,cpnc是定义的组件对象。
2.2 局部组件
局部组件,只能在当前vue实例挂载的对象中使用,类似于局部变量,有块级作用域。
注册方式
const app = new Vue({
el:"#app",
components:{//局部组件创建
cpnc:cpnc
}
}) 使用方式与全局变量一样,直接使用<cpnc></cpnc>调用。cpnc:cpnc第一个cpnc是给组件命名的名字,第二个是定义的组件对象。如果俩个同名也可以直接使用es6语法:
components:{//局部组件创建
cpnc
}3. 父组件和子组件的区别
<div id="app">
<cpn2></cpn2>
</div>
<script src="../js/vue.js"></script>
<script>
// 1.创建组件构造器对象
const cpn1 = Vue.extend({
template:`
<div>
<h2>标题1</h2>
<p>组件1</p>
</div>`
})
// 组件2中使用组件1
const cpn2 = Vue.extend({
template:`
<div>
<h2>标题2</h2>
<p>组件2</p>
<cpn1></cpn1>
</div>`,
components:{
cpn1:cpn1
}
})
const app = new Vue({
el:"#app",
components:{//局部组件创建
cpn2:cpn2
}
})
</script> 上述代码中定义了两个组件对象cpn1和cpn2,在组件cpn2中使用局部组件注册了cpn1,并在template中使用了注册的cpn1,然后在vue实例中使用注册了局部组件cpn2,在vue实例挂载的div中调用了cpn2,cpn2与cpn1形成父子组件关系。
注意:组件就是一个vue实例,vue实例的属性,组件也可以有,例如data、methods、computed等。
4. 注册组件的语法糖
<div id="app">
<cpn1></cpn1>
<cpn2></cpn2>
</div>
<script src="../js/vue.js"></script>
<script>
// 1.注册全局组件语法糖
Vue.component('cpn1', {
template:`
<div>
<h2>全局组件语法糖</h2>
<p>全局组件语法糖</p>
</div>`
})
const app = new Vue({
el:"#app",
components:{//局部组件创建
cpn2:{
template:`
<div>
<h2>局部组件语法糖</h2>
<p>局部组件语法糖</p>
</div>`
}
}
})
</script>注册组件时候可以不实例化组件对象,直接在注册的时候实例化。{}就是一个组件对象。
5. 组件模板的分离写法
5.1 script标签
使用script标签定义组件的模板,script标签注意类型是text/x-template。
<!-- 1.script标签注意类型是text/x-template -->
<script type="text/x-template" id="cpn1">
<div>
<h2>组件模板的分离写法</h2>
<p>script标签注意类型是text/x-template</p>
</div>
</script>5.2 template标签
使用template标签,将内容写在标签内。
<!-- 2.template标签 -->
<template id="cpn2">
<div>
<h2>组件模板的分离写法</h2>
<p>template标签</p>
</div>
</template>调用分离的模板,使用
template:'#cpn1'
<script src="../js/vue.js"></script>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el: "#app",
components: { //局部组件创建
cpn1:{
template:'#cpn1'
},
cpn2: {
template: '#cpn2'
}
}
})
</script>6. 组件的数据
6.1 存放问题
前面说过vue组件就是一个vue实例,相应的vue组件也有data属性来存放数据。
<div id="app">
<cpn1></cpn1>
</div>
<script src="../js/vue.js"></script>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el: "#app",
components: { //局部组件创建
cpn1:{
template:'<div>{
{msg}}</div>',
data(){
return {
msg:"组件的数据存放必须要是一个函数"
}
}
}
}
})
</script>在template中使用组件内部的数据msg。

6.2 组件的data为什么必须要是函数
组件的思想是复用,定义组件当然是把通用的公共的东西抽出来复用。
<div id="app">
<h2>data不使用函数</h2>
<cpn1></cpn1>
<cpn1></cpn1>
<hr>
<h2>data使用函数</h2>
<cpn2></cpn2>
<cpn2></cpn2>
<hr>
</div>
<script src="../js/vue.js"></script>
<template id="cpn1">
<div>
<button @click="count--">-</button>
当前计数:{
{count}}
<button @click="count++">+</button>
</div>
</template>
<template id="cpn2">
<div>
<button @click="count--">-</button>
当前计数:{
{count}}
<button @click="count++">+</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
const obj = {
count:0
};
const app = new Vue({
el: "#app",
components: { //局部组件创建
cpn1: {
template: '#cpn1',
data() {
return obj;
}
},
cpn2: {
template: '#cpn2',
data() {
return {
count: 0
}
}
}
}
})
</script>上述代码中定义了两个组件cpn1和cpn2,都是定义了两个计数器,con1的data虽然使用了函数,但是为了模拟data:{count:0},使用了常量obj来返回count。
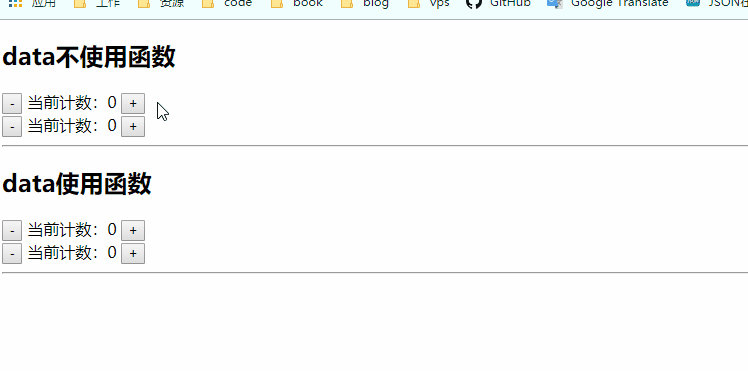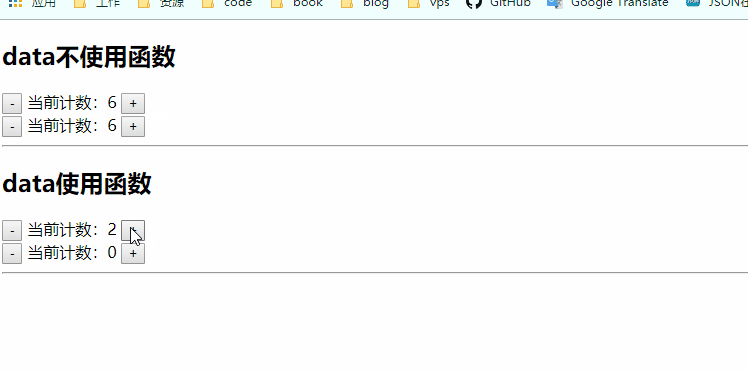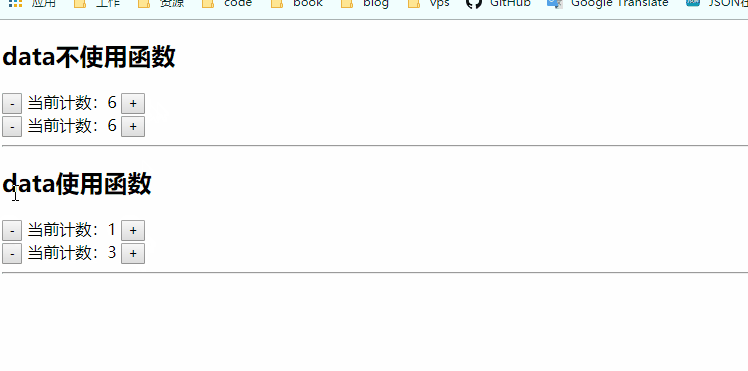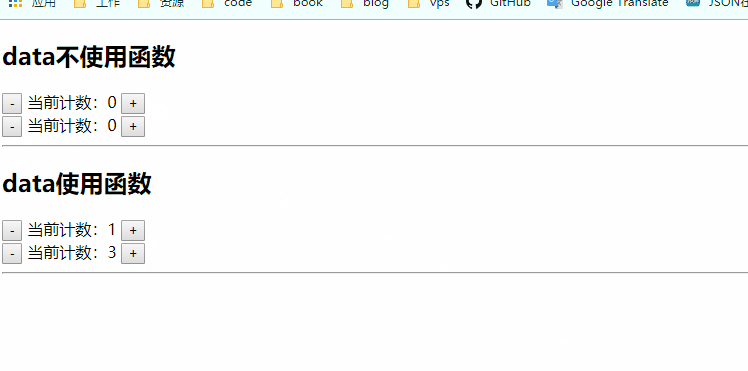
图中可以看到,不使用函数data的好像共用一个count属性,而使用函数的data的count是各自用各自的,像局部变量一样有块级作用域,这个块级就是vue组件的作用域。
我们在复用组件的时候肯定希望,各自组件用各自的变量,如果确实需要都用一样的,可以全局组件注册,也可以是用vuex来进行状态管理。
7. 父组件给子组件传递数据
7.1 使用props属性,父组件向子组件传递数据
使用组件的
props属性
const cpn = {
template: "#cpn",
props: {
cmessage: {
type: String,
default: 'zzzzz',
required: true //在使用组件必传值
}
}
}向cmessage对象传值
<div id="app">
<cpn :cMessage="message"></cpn>
</div>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el: "#app",
data: {
message: "你好",
movies: ["复仇者联盟", "钢铁侠", "星际穿越", "哪吒传奇"]
},
components: {
cpn
}
})
</script>7.2 props属性使用
数组写法
props: ['cmovies', 'cmessage']对象写法
props: {
cmessage: {
type: String,
default: 'zzzzz',
required: true //在使用组件必传值
}
}props属性的类型限制
//1.类型限制(多个类使用数组)
cmovies:Array,//限制为数组类型
cmessage:String,//限制为Strin类型
cmessage:['String','Number']//限制为String或Number类型props属性的默认值
// 2.提供一些默认值,以及必传值
cmessage: {
type: String,
default: 'zzzzz',//默认值
}props属性的必传值
cmessage: {
type: String,
default: 'zzzzz',
required: true //在使用组件必传值
}类型是Object/Array,默认值必须是一个函数
//类型是Object/Array,默认值必须是一个函数
cmovies: {
type: Array,
default () {
return [1, 2, 3, 4]
}
},自定义验证函数
vaildator: function (value) {
//这个传递的值必须匹配下列字符串中的一个
return ['zzzzz', 'ttttt', 'yyy'].indexOf(value) !== -1
}自定义类型
function Person(firstName,lastName) {
this.firstName = firstName
this.lastName = lastName
}
cmessage:Person//限定了cmeessage必须是Person类型综合使用
<div id="app">
<cpn :cMovies="movies" :cMessage="message"></cpn>
</div>
<template id="cpn">
<div>
<ul>
<li v-for="(item, index) in cmovies" :key="index">{
{item}}</li>
</ul>
<h2>{
{cmessage}}</h2>
</div>
</template>
<script src="../js/vue.js"></script>
<script>
function Person(firstName,lastName) {
this.firstName = firstName
this.lastName = lastName
}
// 父传子:props
const cpn = {
template: "#cpn",
// props: ['cmovies', 'cmessage'],//数组写法
props: { //对象写法
// 1.类型限制(多个类使用数组)
// cmovies:Array,
// cmessage:String,
// cmessage:['String','Number'],
// 2.提供一些默认值,以及必传值
cmessage: {
type: String,
default: 'zzzzz',
required: true //在使用组件必传值
},
//类型是Object/Array,默认值必须是一个函数
cmovies: {
type: Array,
default () {
return [1, 2, 3, 4]
}
},
// 3.自定义验证函数
// vaildator: function (value) {
// //这个传递的值必须匹配下列字符串中的一个
// return ['zzzzz', 'ttttt', 'yyy'].indexOf(value) !== -1
// }
// 4.自定义类型
// cmessage:Person,
},
data() {
return {
}
},
methods: {
},
};
const app = new Vue({
el: "#app",
data: {
message: "你好",
movies: ["复仇者联盟", "钢铁侠", "星际穿越", "哪吒传奇"]
},
components: {
cpn
}
})
</script>8. 组件通信
8.1 父传子(props的驼峰标识)
v-bind是 不支持使用驼峰标识的,例如cUser要改成c-User。
<div id="app">
<!-- v-bind不支持驼峰 :cUser改成 :c-User-->
<!-- <cpn :cUser="user"></cpn> -->
<cpn :c-User="user"></cpn>
<cpn :cuser="user" ></cpn>
</div>
<template id="cpn">
<div>
<!-- 使用驼峰 -->
<h2>{
{cUser}}</h2>
<!-- 不使用 -->
<h2>{
{cuser}}</h2>
</div>
</template>
<script src="../js/vue.js"></script>
<script>
// 父传子:props
const cpn = {
template: "#cpn",
props: { //对象写法
//驼峰
cUser:Object,
//未使用驼峰
cuser:Object
},
data() {return {}},
methods: {},
};
const app = new Vue({
el: "#app",
data: {
user:{
name:'zzz',
age:18,
height:175
}
},
components: {
cpn
}
})
</script>props接收引用类型
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title></title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<!-- <cpn1 :msg="message"></cpn1> -->
<!-- <cpn1 :msg="message2"></cpn1> -->
<cpn1 :msgab="add"></cpn1>
<h2>{
{count}}</h2>
</div>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/[email protected]/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el: "#app",
data: {
/* message: ['蔡英文', '吴钊燮'] */
/* message2:{
name:'蔡英文',
age:56,
sex:'女'
} */
count:0
},
methods: {
add:function(){
return this.count++
}
},
computed: {
},
components: {
cpn1: {
/* template: `
<div>我是中国人{
{msg.name}}{
{msg.sex}}</div>
`, */
template: `
<div>
<div @click="sum">+</div>
</div>
`,
props: {
/* msg:{
type: Array
} */
/* msg:{
type: Object
} */
msgab:{
type:Function
},
},
methods:{
sum(){
this.msgab()
}
}
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>8.2 子传父$emit
子组件向父组件传值,使用自定义事件$emit。
<!-- 父组件 -->
<div id="app">
<!-- 不写参数默认传递btnClick的item -->
<cpn @itemclick="cpnClcik"></cpn>
</div>
<!-- 子组件 -->
<template id="cpn">
<div>
<button v-for="(item, index) in categoties" :key="index" @click="btnClick(item)">{
{item.name}}</button>
</div>
</template>
<script src="../js/vue.js"></script>
<script>
const cpn = {
template: "#cpn",
data() {
return {
categoties: [{
id: 'aaa',
name: '热门推荐'
},
{
id: 'bbb',
name: '手机数码'
},
{
id: 'ccc',
name: '家用家电'
},
{
id: 'ddd',
name: '电脑办公'
},
]
}
},
methods: {
btnClick(item) {
this.$emit('itemclick', item)
}
},
};
const app = new Vue({
el: "#app",
data() {
return {
}
},
methods: {
cpnClcik(item) {
console.log('cpnClick'+item.name);
}
},
components: {
cpn
},
})
</script>1.在子组件中定义一个方法btnClick(item),使用$emit,'itemclick'是事件名,item是传过去的值。
methods: {
btnClick(item) {
this.$emit('itemclick', item)
}
},2.在子组件中监听点击事件并回调此方法
<div>
<button v-for="(item, index) in categoties" :key="index" @click="btnClick(item)">{
{item.name}}</button>
</div>3.在父组件中定义一个方法cpnClcik(item)
methods: {
cpnClcik(item) {
console.log('cpnClick'+item.name);
}
},4.并在父组件(vue实例)中调用<cpn @itemclick="cpnClcik"></cpn>(不写参数默认传递btnClick的item ),父组件监听事件名为itemclick的子组件传过来的事件。
<cpn @itemclick="cpnClcik"></cpn>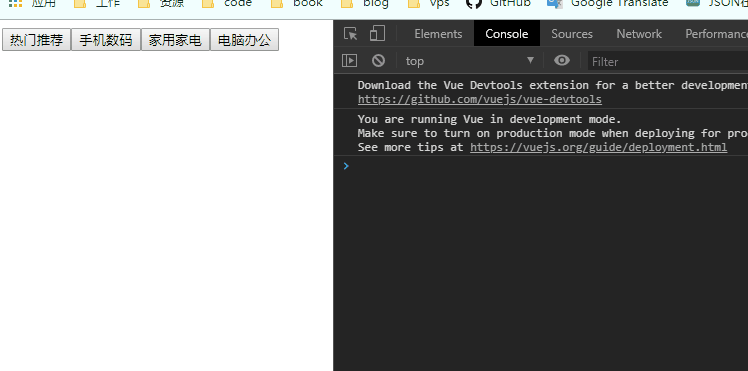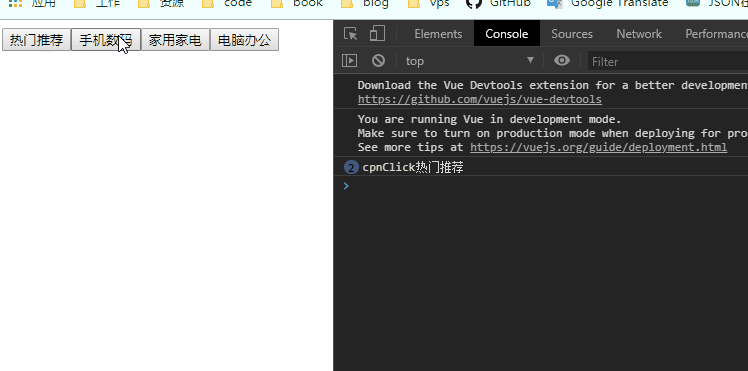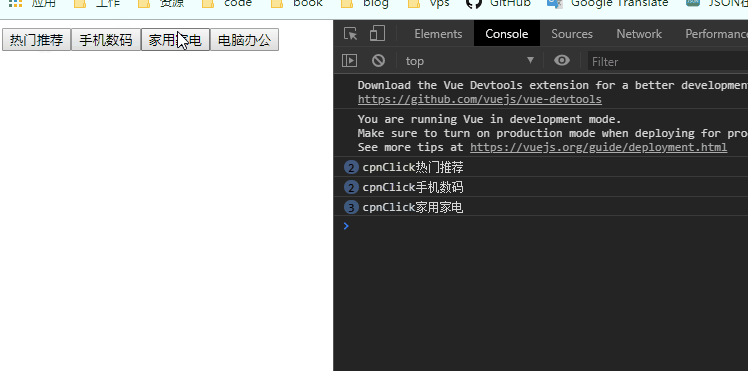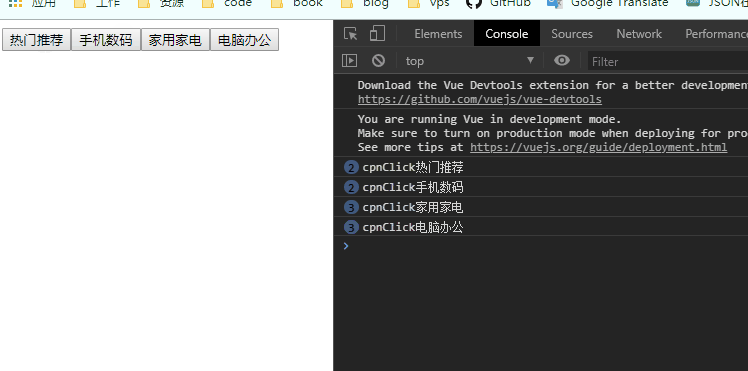
监听原生点击事件
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Document</title>
<script type="text/javascript" src="./vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<cpn @click.native="btnClick">点击</cpn>
</div>
<!-- 子组件 -->
<template id="cpn">
<div>
我是子组件
</div>
</template>
</body>
<script type="text/javascript">
// 父传子:props
const cpn = {
template: "#cpn",
data() {
return {
name:"我是子组件的name"
}
}
};
const app = new Vue({
el: "#app",
data() {
return {
message:"hello"
}
},
methods: {
btnClick(){
console.log('click')
}
},
components: {
cpn
},
})
</script>
</html>8.3 父子组件通信案例
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>组件通信-父子通信案例</title>
</head>
<body>
<!-- 父组件 -->
<div id="app">
<cpn :number1='num1' :number2='num2'></cpn>
</div>
<!-- 子组件 -->
<template id="cpn">
<div>
<h2>number1:{
{number1}}</h2>
<input type="text" v-model="number1">
<h2>number2:{
{number2}}</h2>
<input type="text" v-model="number2">
</div>
</template>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script>
// 父传子:props
const cpn = {
template: "#cpn",
data() {
return {
}
},
props:{
number1:[Number,String],
number2:[Number,String],
},
};
const app = new Vue({
el: "#app",
data: {
num1:1,
num2:2
},
components: {
cpn
},
})
</script>
</body>
</html>以上报错 不能直接改变props里面的值,可以改成下面这样
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>组件通信-父子通信案例</title>
</head>
<body>
<!-- 父组件 -->
<div id="app">
<cpn :number1='num1' :number2='num2'></cpn>
</div>
<!-- 子组件 -->
<template id="cpn">
<div>
<h2>number1:{
{number1}}</h2>
<h2>number1:{
{dnumber1}}</h2>
<input type="text" v-model="dnumber1">
<h2>number2:{
{number2}}</h2>
<h2>number2:{
{dnumber2}}</h2>
<input type="text" v-model="dnumber2">
</div>
</template>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script>
// 父传子:props
const cpn = {
template: "#cpn",
data() {
return {
dnumber1:this.number1,
dnumber2:this.number2
}
},
props:{
number1:[Number,String],
number2:[Number,String],
},
};
const app = new Vue({
el: "#app",
data: {
num1:1,
num2:2
},
components: {
cpn
},
})
</script>
</body>
</html> 实现父子组件的值双向绑定。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>组件通信-父子通信案例</title>
</head>
<body>
<!-- 父组件 -->
<div id="app">
<h2>子组件</h2>
<cpn :number1='num1' :number2='num2'
@num1change="num1Change"
@num2change="num2Change"></cpn>
<h2>--------------</h2>
<h2>父组件{
{num1}}</h2>
<input type="text" v-model="num1" >
<h2>父组件{
{num2}}</h2>
<input type="text" v-model="num2">
</div>
<!-- 子组件 -->
<template id="cpn">
<div>
<h2>number1:{
{number1}}</h2>
<h2>dnumber1:{
{dnumber1}}</h2>
<input type="text" :value="dnumber1" @input="num1input">
<h2>number2:{
{number2}}</h2>
<h2>dnumber2:{
{dnumber2}}</h2>
<input type="text" :value="dnumber2" @input="num2input">
</div>
</template>
<script src="../js/vue.js"></script>
<script>
// 父传子:props
const cpn = {
template: "#cpn",
data() {
return {
dnumber1:this.number1,
dnumber2:this.number2
}
},
props:{
number1:[Number,String],
number2:[Number,String],
},
methods: {
num1input(event){
this.dnumber1 = event.target.value
this.$emit('num1change',this.dnumber1)
},
num2input(event){
this.dnumber2 = event.target.value
this.$emit('num2change',this.dnumber2)
}
},
};
const app = new Vue({
el: "#app",
data: {
num1:1,
num2:2
},
methods: {
num1Change(value){
this.num1=value
},
num2Change(value){
this.num1=value
}
},
components: {
cpn
},
})
</script>
</body>
</html>使用watch实现。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>组件通信-父子通信案例(watch实现)</title>
</head>
<body>
<!-- 父组件 -->
<div id="app">
<cpn :number1='num1' :number2='num2' @num1change="num1Change" @num2change="num2Change"></cpn>
<h2>父组件{
{num1}}</h2>
<input type="text" v-model="num1" >
<h2>父组件{
{num2}}</h2>
<input type="text" v-model="num2">
</div>
<!-- 子组件 -->
<template id="cpn">
<div>
<h2>{
{number1}}</h2>
<input type="text" v-model="dnumber1">
<h2>{
{number2}}</h2>
<input type="text" v-model="dnumber2">
</div>
</template>
<script src="../js/vue.js"></script>
<script>
// 父传子:props
const cpn = {
template: "#cpn",
data() {
return {
dnumber1:this.number1,
dnumber2:this.number2
}
},
props:{
number1:[Number,String],
number2:[Number,String],
},
watch: {
dnumber1(newValue){
this.dnumber1 = newValue
this.$emit('num1change',newValue)
},
dnumber2(newValue){
this.dnumber1 = newValue
this.$emit('num2change',newValue)
}
},
};
const app = new Vue({
el: "#app",
data() {
return {
num1:1,
num2:2,
}
},
methods: {
num1Change(value){
this.num1=value*10
},
num2Change(value){
this.num1=value*100
}
},
components: {
cpn
},
})
</script>
</body>
</html>最终实现
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title></title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<h2>子组件</h2>
<cpn :number1="num1" :number2="num2" @num1change="Num1change" @num2change="Num2change"></cpn>
<h2>--------------</h2>
<h2>父组件{
{num1}}</h2>
<input type="text" v-model="num1">
<h2>父组件{
{num2}}</h2>
<input type="text" v-model="num2">
</div>
<template id="cpn">
<div>
<h2>dnumber1:{
{dnumber1}}</h2>
<h2>number1:{
{number1}}</h2>
<input type="text" v-model="dnumber1"/>
<br />
<h2>dnumber2:{
{dnumber2}}</h2>
<h2>number2:{
{number2}}</h2>
<input type="text" v-model="dnumber2"/>
</div>
</template>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/[email protected]/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script>
/* 子组件 */
const cpn = {
template: '#cpn',
data() {
return {
dnumber1: this.number1,
dnumber2: this.number2
}
},
props: {
number1: {
type: [Number,String]
},
number2: {
type:[Number,String]
}
},
watch:{
dnumber1(n){
this.$emit('num1change', n/100)
},
dnumber2(n){
this.$emit('num2change', n*100)
},
number1(n){
this.dnumber1 = n*100
},
number2(n){
this.dnumber2 = n/100
}
}
}
/* 父组件 */
const app = new Vue({
el: "#app",
data() {
return {
num1: 1,
num2: 2
}
},
methods: {
Num1change(value) {
this.num1 = value
},
Num2change(value) {
this.num2 = value
}
},
computed: {
},
components: {
cpn
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>9. 父访问子(children-ref)
父组件访问子组件,有时候需要直接操作子组件的方法,或是属性,此时需要用到$children和$ref。
<!-- 父组件 -->
<div id="app">
<cpn></cpn>
<cpn></cpn>
<cpn ref="aaa"></cpn>
<button @click="btnClick" >按钮</button>
</div>
<!-- 子组件 -->
<template id="cpn">
<div>
我是子组件
</div>
</template>
<script src="../js/vue.js"></script>
<script>
// 父传子:props
const cpn = {
template: "#cpn",
data() {
return {
name:"我是子组件的name"
}
},
methods: {
showMessage(){
console.log("showMessage");
}
},
};
const app = new Vue({
el: "#app",
data() {
return {
message:"hello"
}
},
methods: {
btnClick(){
// 1.children
// console.log(this.$children[0].showMessage)
// for (let cpn of this.$children) {
// console.log(cpn.showMessage)
// }
// 2.$ref
console.log(this.$refs.aaa.name)
}
},
components: {
cpn
},
})
</script>
$children方式
// 1.children
console.log(this.$children[0].showMessage)
for (let cpn of this.$children) {
console.log(cpn.showMessage)
}使用this.$children直接获取**当前实例的直接子组件,需要注意 $children 并不保证顺序,也不是响应式的。**如果你发现自己正在尝试使用 $children 来进行数据绑定,考虑使用一个数组配合 v-for 来生成子组件,并且使用 Array 作为真正的来源。
$refs方式:ref 被用来给元素或子组件注册引用信息。引用信息将会注册在父组件的 $refs 对象上。如果在普通的 DOM 元素上使用,引用指向的就是 DOM 元素;如果用在子组件上,引用就指向组件实例:
ref的基本使用 用在元素上
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title></title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<p ref="p" @click="handelClick" id="ppp">hello</p>
</div>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/[email protected]/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el: "#app",
data: {
},
methods: {
handelClick(){
console.log(this.$refs.p);
const ppp = document.querySelector('#ppp')
console.log(ppp);
}
},
computed:{
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>先定义子组件
<cpn ref="aaa"></cpn>直接调用
ref在子组件上的使用
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title></title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<counter ref="one" @change="handelChange"></counter>
<counter ref="two" @change="handelChange"></counter>
<div>total:{
{total}}</div>
</div>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/[email protected]/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script>
Vue.component('counter',{
template:'<div @click="handelclick">{
{number}}</div>',
data(){
return {
number:0
}
},
methods:{
handelclick(){
this.number++;
this.$emit('change');
}
}
})
const app = new Vue({
el: "#app",
data: {
total:0
},
methods: {
handelChange(){
this.total = this.$refs.one.number + this.$refs.two.number
}
},
computed:{
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
<!-- ref可以调用组件中的数据 --><!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title></title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<helloworld ref="hello"></helloworld>
<button @click="getHello">获取helloworld组件中的值</button>
</div>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/[email protected]/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script>
Vue.component('helloworld',{
template:'<div></div>',
data(){
return {
number:0
}
},
methods:{
handelclick(){
console.log('被调用了');
}
}
})
const app = new Vue({
el: "#app",
data: {
},
methods: {
getHello(){
this.$refs.hello.handelclick();
console.log(this.$refs.hello.number);
console.log(this.$refs.hello.$el.innerHTML);
}
},
computed:{
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
<!-- ref可以调用组件中的方法 -->is用于动态组件且基于 DOM 内模板的限制来工作。
基于 DOM 内模板的限制来工作
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title></title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<table>
<tr is="row">
</tr>
</table>
</div>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/[email protected]/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script>
Vue.component('row',{
template:'<tr><td>111</td></tr>'
})
const app = new Vue({
el: "#app",
data() {
return {}
},
methods: {
},
computed:{
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>动态组件component
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title></title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<!-- <child-one></child-one>
<child-two></child-two> -->
<component :is="type"></component>
<button @click="handerClick">点击</button>
</div>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script>
Vue.component('child-one',{
template:'<div>child-one</div>'
})
Vue.component('child-two',{
template:'<div>child-two</div>'
})
const app = new Vue({
el:'#app',
data(){
return {
type:'child-one'
}
},
methods:{
handerClick(){
console.log('111');
this.type=this.type==='child-one'?'child-two':'child-one';
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>这是动态组件官网案例
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title></title>
<style>
.tab-button {
padding: 6px 10px;
border-top-left-radius: 3px;
border-top-right-radius: 3px;
border: 1px solid #ccc;
cursor: pointer;
background: #f0f0f0;
margin-bottom: -1px;
margin-right: -1px;
}
.tab-button:hover {
background: #e0e0e0;
}
.tab-button.active {
background: #e0e0e0;
}
.tab {
border: 1px solid #ccc;
padding: 10px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<button v-for="(tab,index) in tabs":key="index" @click="handelclick(tab)" :class="getStyle(tab)">{
{tab}}</button>
<component :is="currentTabComponent"></component>
</div>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script>
Vue.component('tab-home',{
template:'<div>child-one</div>'
})
Vue.component('tab-posts',{
template:'<div>child-two</div>'
})
Vue.component('tab-archive',{
template:'<div>child-three</div>'
})
const app = new Vue({
el:'#app',
data(){
return {
currentTab: "Home",
tabs: ["Home", "Posts", "Archive"]
}
},
methods:{
handelclick(tab){
this.currentTab = tab
},
getStyle(tab){
return ['tab-button',{active:this.currentTab===tab}]
}
},
computed:{
currentTabComponent(){
/* return `tab-${this.currentTab}`.toLowerCase() */
return "tab-"+this.currentTab.toLowerCase()
},
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>