目录
QLExpress
github: https://github.com/alibaba/QLExpress
优点:
- 线程安全,引擎运算过程中的产生的临时变量都是threadlocal类型。
- 高效执行,比较耗时的脚本编译过程可以缓存在本地机器,运行时的临时变量创建采用了缓冲池的技术,和groovy性能相当。
- 弱类型脚本语言,和groovy,javascript语法类似,虽然比强类型脚本语言要慢一些,但是使业务的灵活度大大增强。
- 安全控制,可以通过设置相关运行参数,预防死循环、高危系统api调用等情况。
- 代码精简,依赖最小,250k的jar包适合所有java的运行环境,在android系统的低端pos机也得到广泛运用。
- 支持高精度计算
————————————————
版权声明:本文为CSDN博主「包子丹」的原创文章,遵循CC 4.0 BY-SA版权协议,转载请附上原文出处链接及本声明。
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_37590206/article/details/108344988
运行架构图:
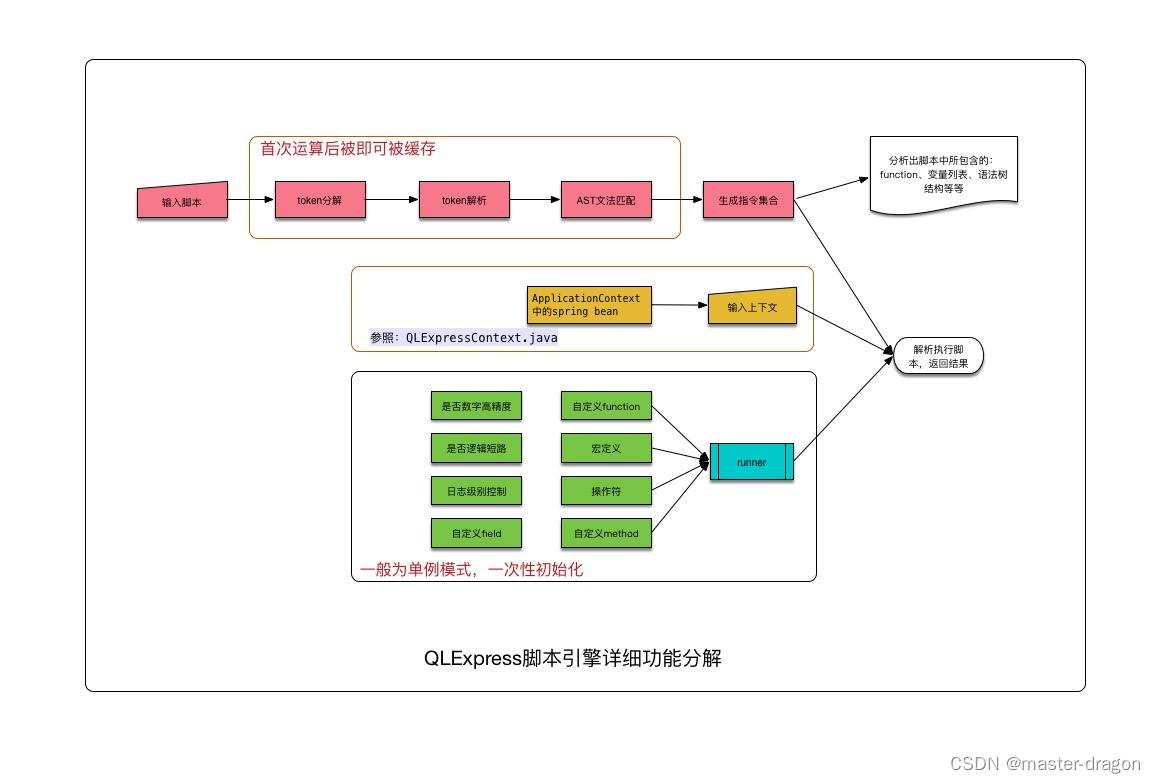
普通表达式执行
@Test
public void testDemo() throws Exception {
String express = "10 * 10 + 1 + 2 * 3 + 5 * 2";
ExpressRunner runner = new ExpressRunner();
Object r = runner.execute(express, null, null, false, false);
Assert.assertTrue("表达式计算", r.toString().equalsIgnoreCase("117"));
System.out.println("表达式计算:" + express + " = " + r);
}
debug:
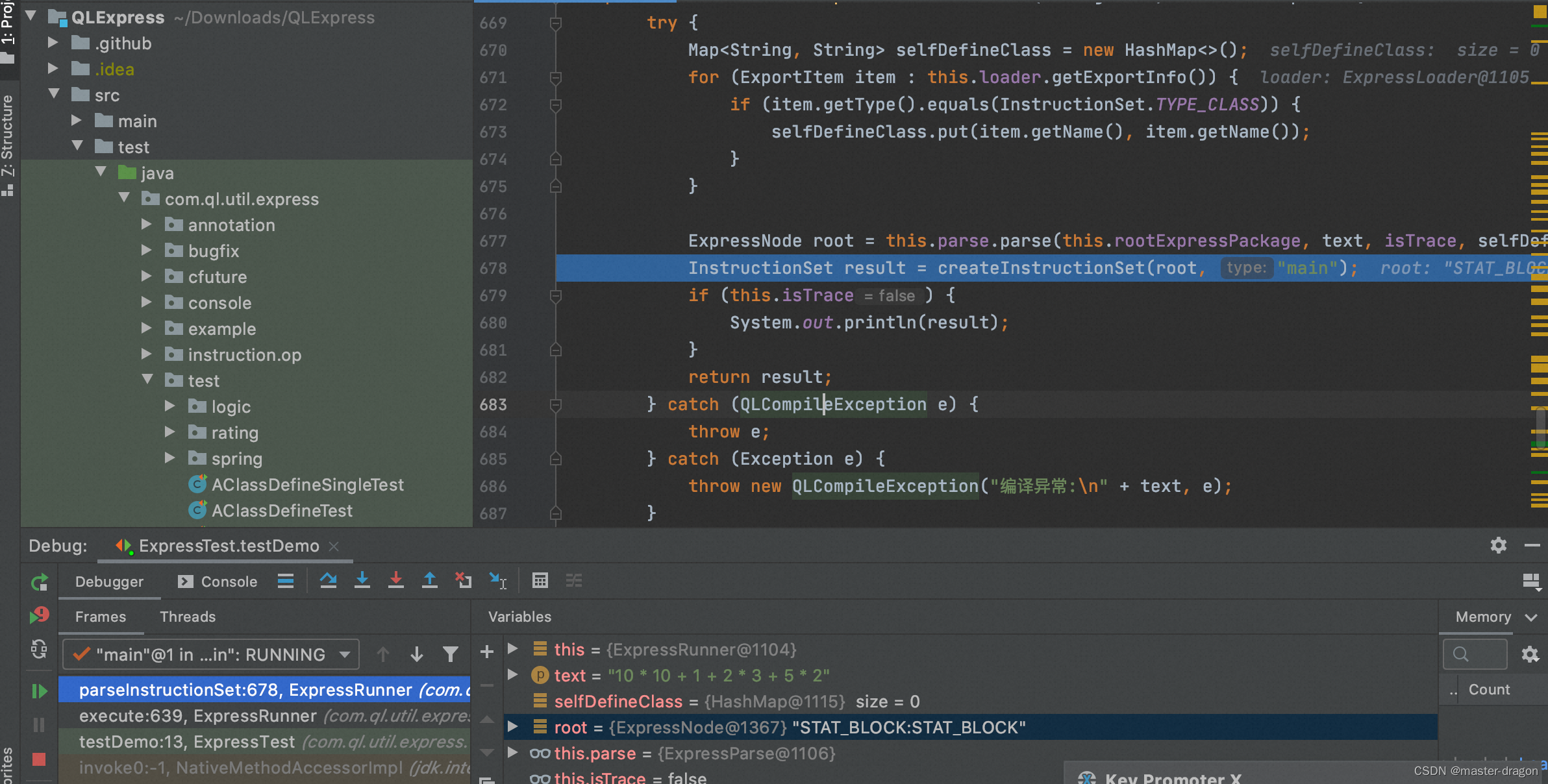
解析并转化为ExpressNode
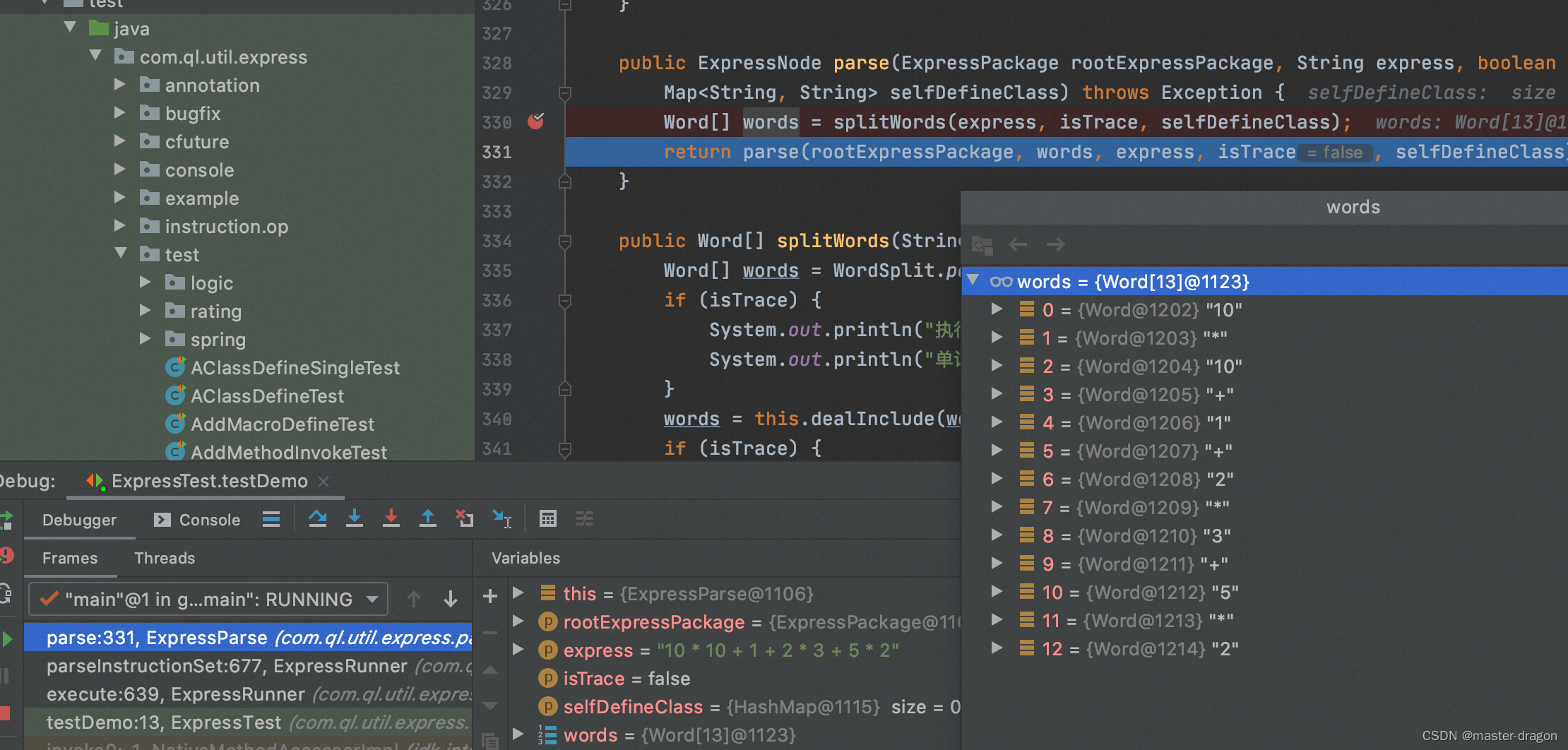
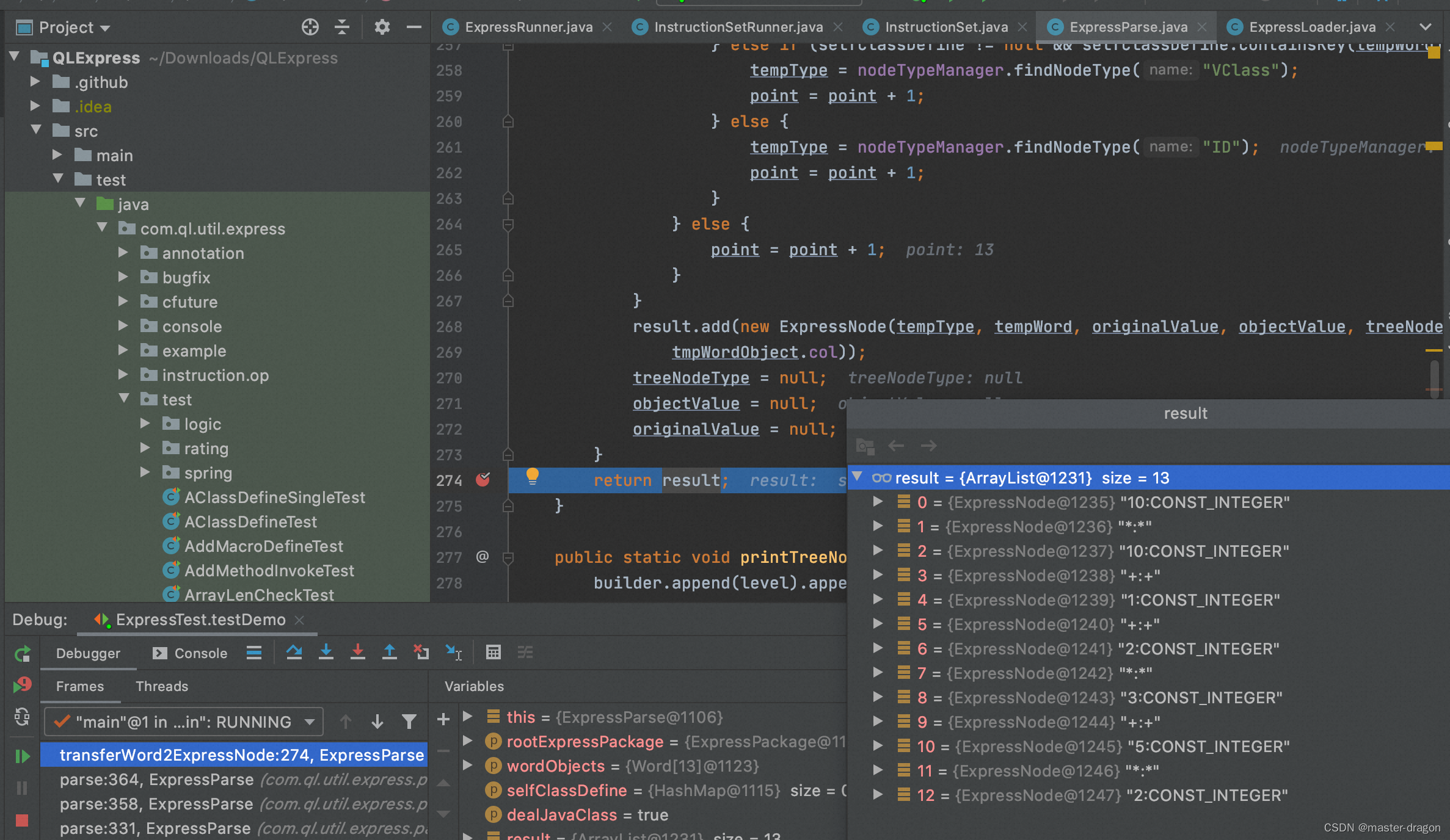
语法解析,得到如下的语法树
即10 * 10 + 1 + 2 * 3 + 5 * 2转化为类似后缀表达式(逆波兰式): 10 10 * 1 + 2 3 * + 5 2 * +
1: STAT_BLOCK:STAT_BLOCK STAT_BLOCK
2: STAT_SEMICOLON:STAT_SEMICOLON STAT_SEMICOLON
3: +:+ +
4: +:+ +
5: +:+ +
6: *:* *
7: 10:CONST_INTEGER CONST
7: 10:CONST_INTEGER CONST
6: 1:CONST_INTEGER CONST
5: *:* *
6: 2:CONST_INTEGER CONST
6: 3:CONST_INTEGER CONST
4: *:* *
5: 5:CONST_INTEGER CONST
5: 2:CONST_INTEGER CONST
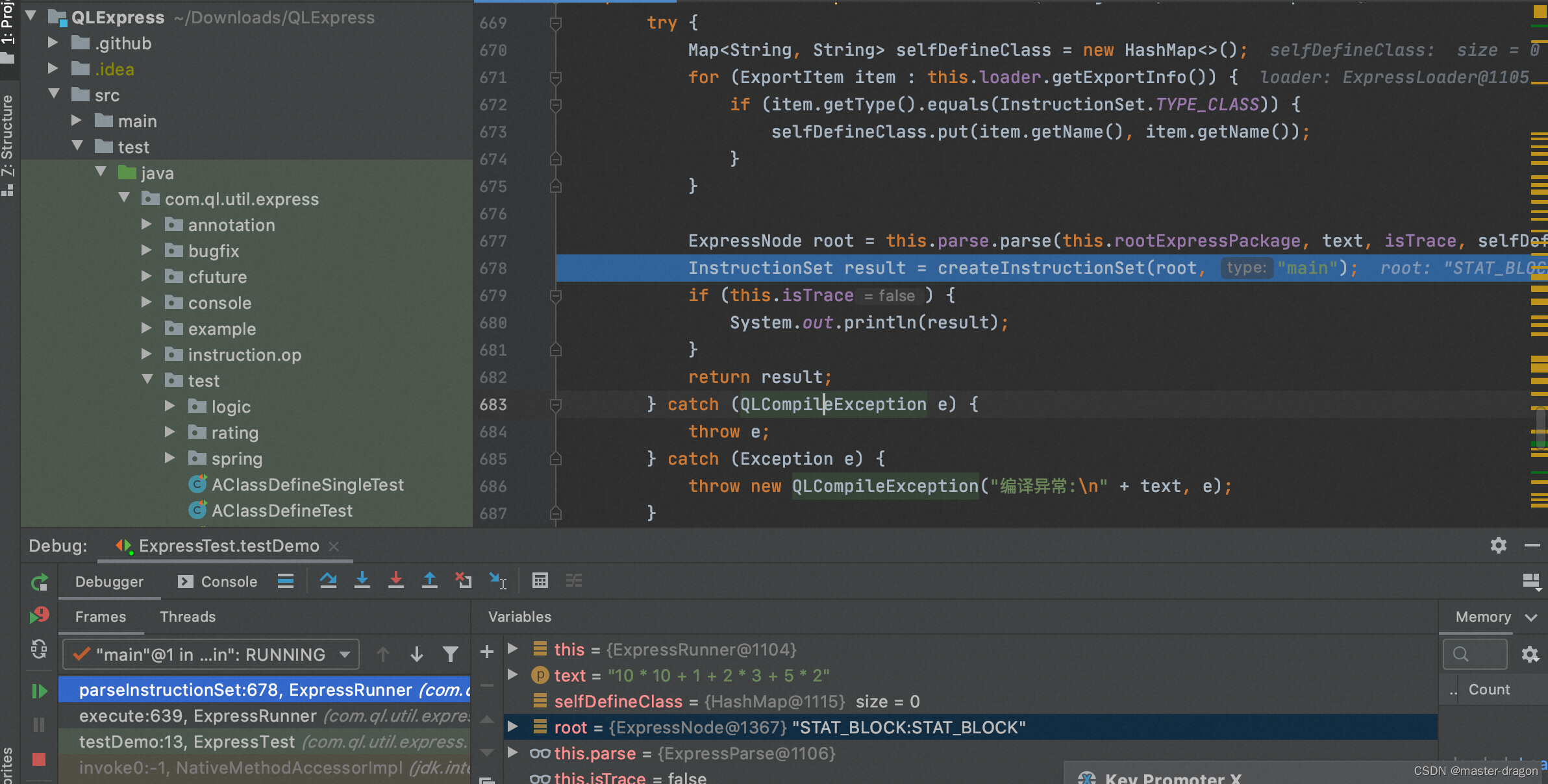
根据 ExpressNode 树生成指令树
即按照后缀表达式(逆波兰式): 10 10 * 1 + 2 3 * + 5 2 * + 执行
1:LoadData 10
2:LoadData 10
3:OP : * OPNUMBER[2]
4:LoadData 1
5:OP : + OPNUMBER[2]
6:LoadData 2
7:LoadData 3
8:OP : * OPNUMBER[2]
9:OP : + OPNUMBER[2]
10:LoadData 5
11:LoadData 2
12:OP : * OPNUMBER[2]
13:OP : + OPNUMBER[2]
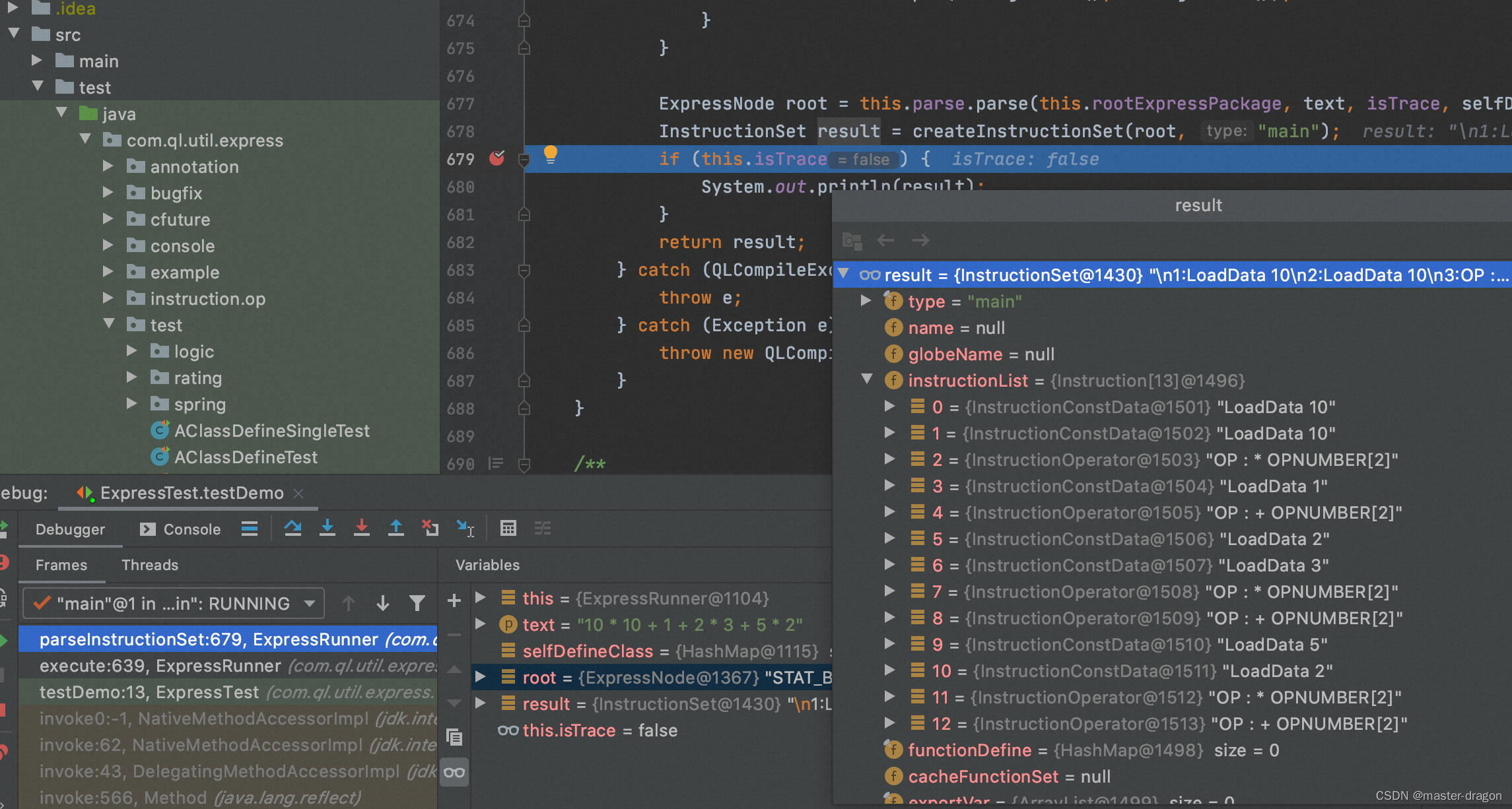
执行指令树得到结果
private Object executeReentrant(InstructionSet sets, IExpressContext<String, Object> iExpressContext,
List<String> errorList, boolean isTrace, boolean isCatchException) throws Exception {
try {
int reentrantCount = threadReentrantCount.get() + 1;
threadReentrantCount.set(reentrantCount);
return reentrantCount > 1 ?
// 线程重入
InstructionSetRunner.execute(this, sets, this.loader, iExpressContext, errorList, isTrace,
isCatchException, true, false) :
InstructionSetRunner.executeOuter(this, sets, this.loader, iExpressContext, errorList, isTrace,
isCatchException, false);
} finally {
threadReentrantCount.set(threadReentrantCount.get() - 1);
}
}
得到结果,具体执行过程是
InstructionConstData 的指令执行
@Override
public void execute(RunEnvironment environment, List<String> errorList) throws Exception {
environment.push(this.operateData);
environment.programPointAddOne();
}
com.ql.util.express.RunEnvironment#push
public void push(OperateData data) {
this.point++;
if (this.point >= this.dataContainer.length) {
ensureCapacity(this.point + 1);
}
this.dataContainer[point] = data;
}
添加操作数
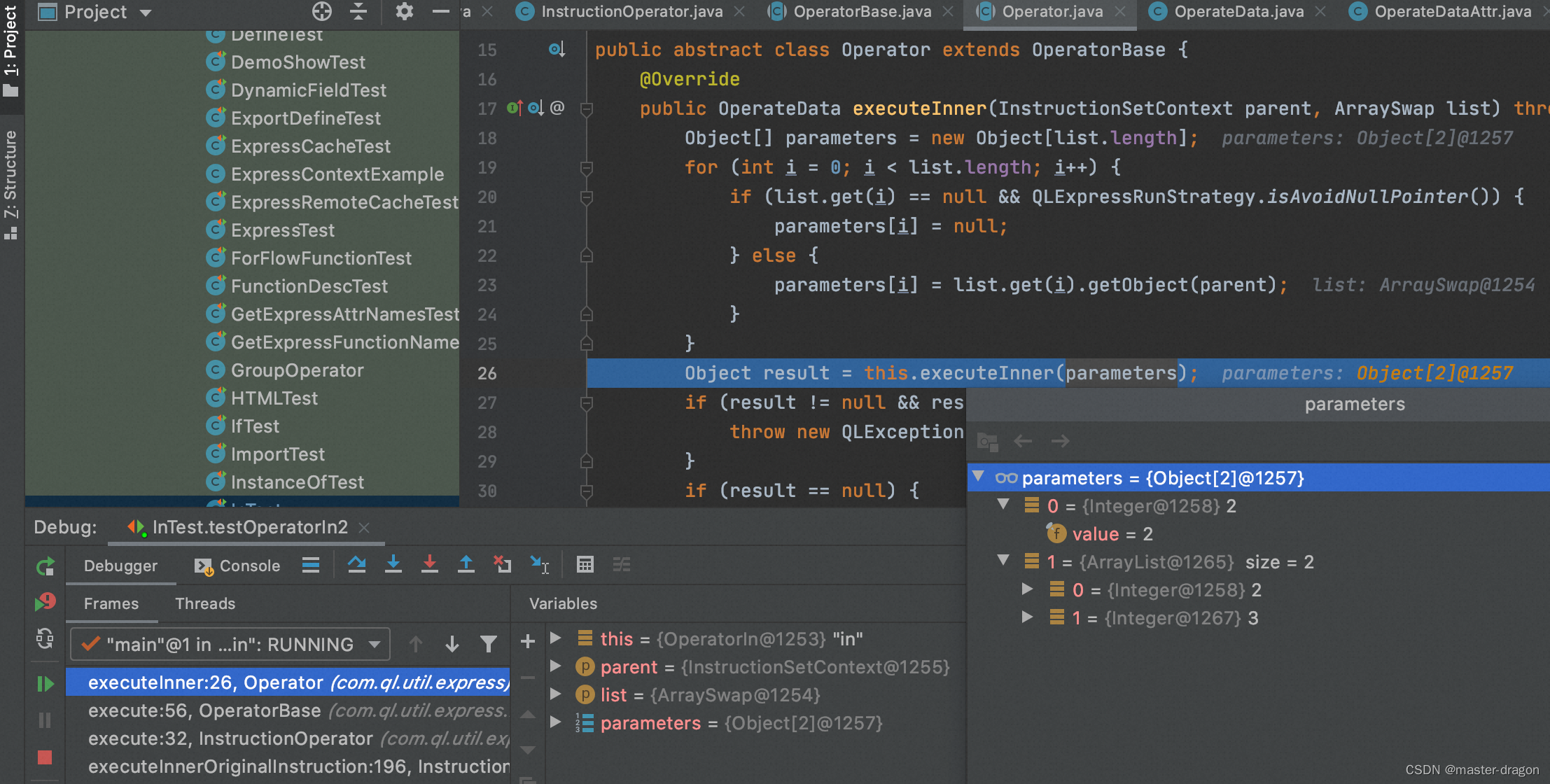
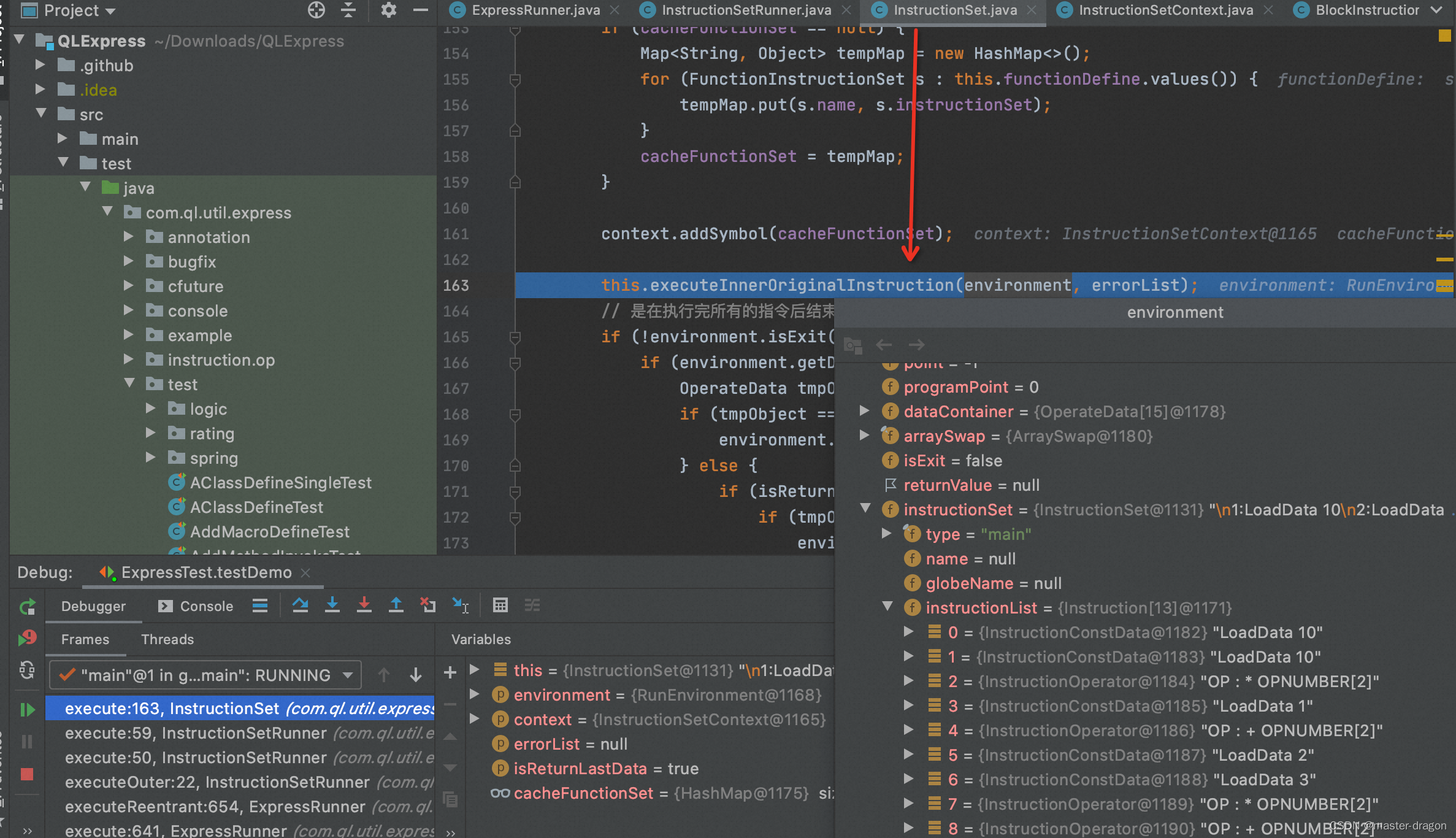
InstructionOperator的指令执行
com.ql.util.express.instruction.detail.InstructionOperator#execute
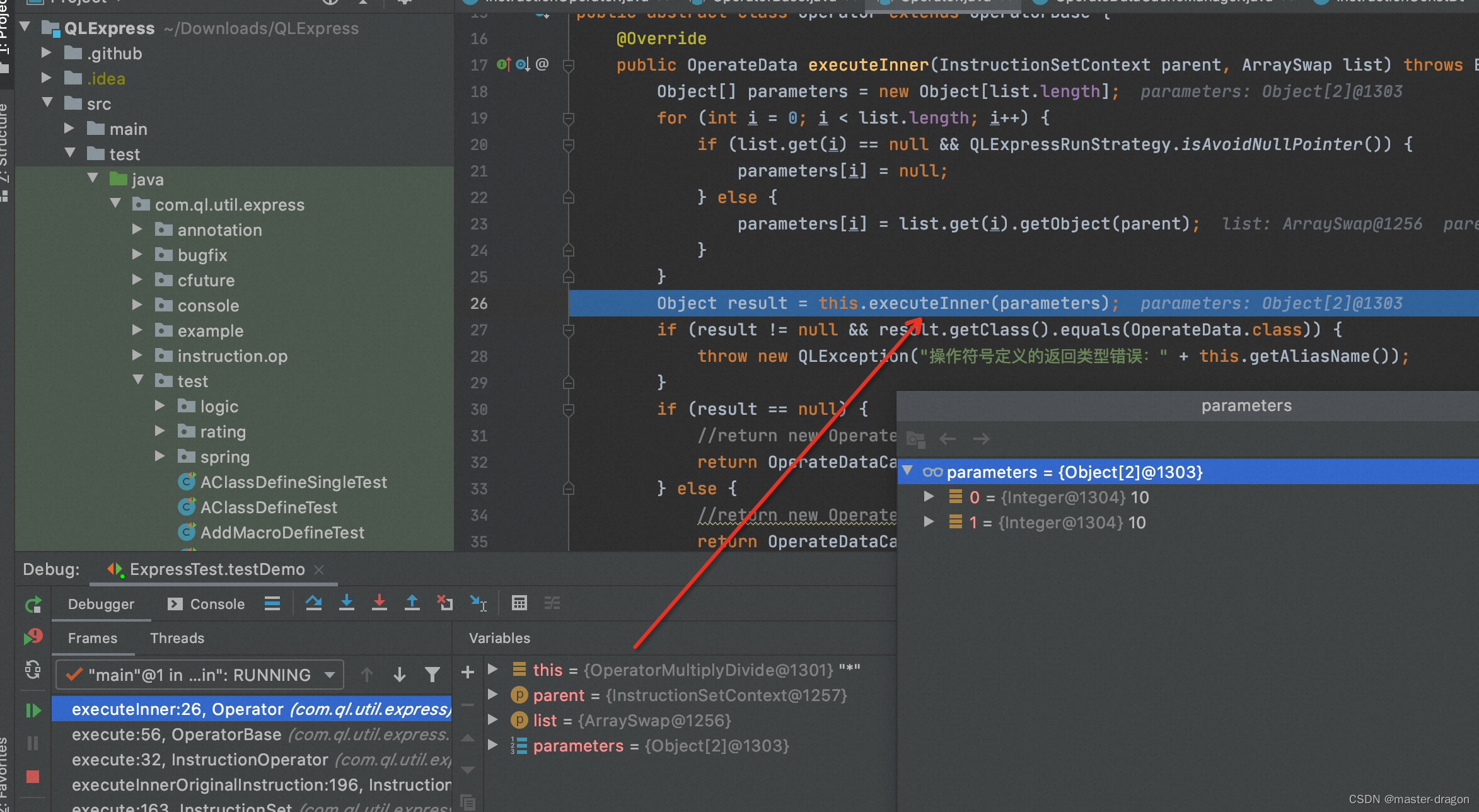
按照特定指令,取数执行
@Override
public void execute(RunEnvironment environment, List<String> errorList) throws Exception {
InstructionSetContext instructionSetContext = environment.getContext();
ArraySwap parameters = environment.popArray(this.opDataNumber);
try {
OperateData result = this.operator.execute(instructionSetContext, parameters, errorList);
environment.push(result);
environment.programPointAddOne();
} catch (QLException e) {
throw new QLException(getExceptionPrefix(), e);
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw new QLBizException(getExceptionPrefix(), t);
}
}
最后得到结果
com.ql.util.express.InstructionSetRunner#execute
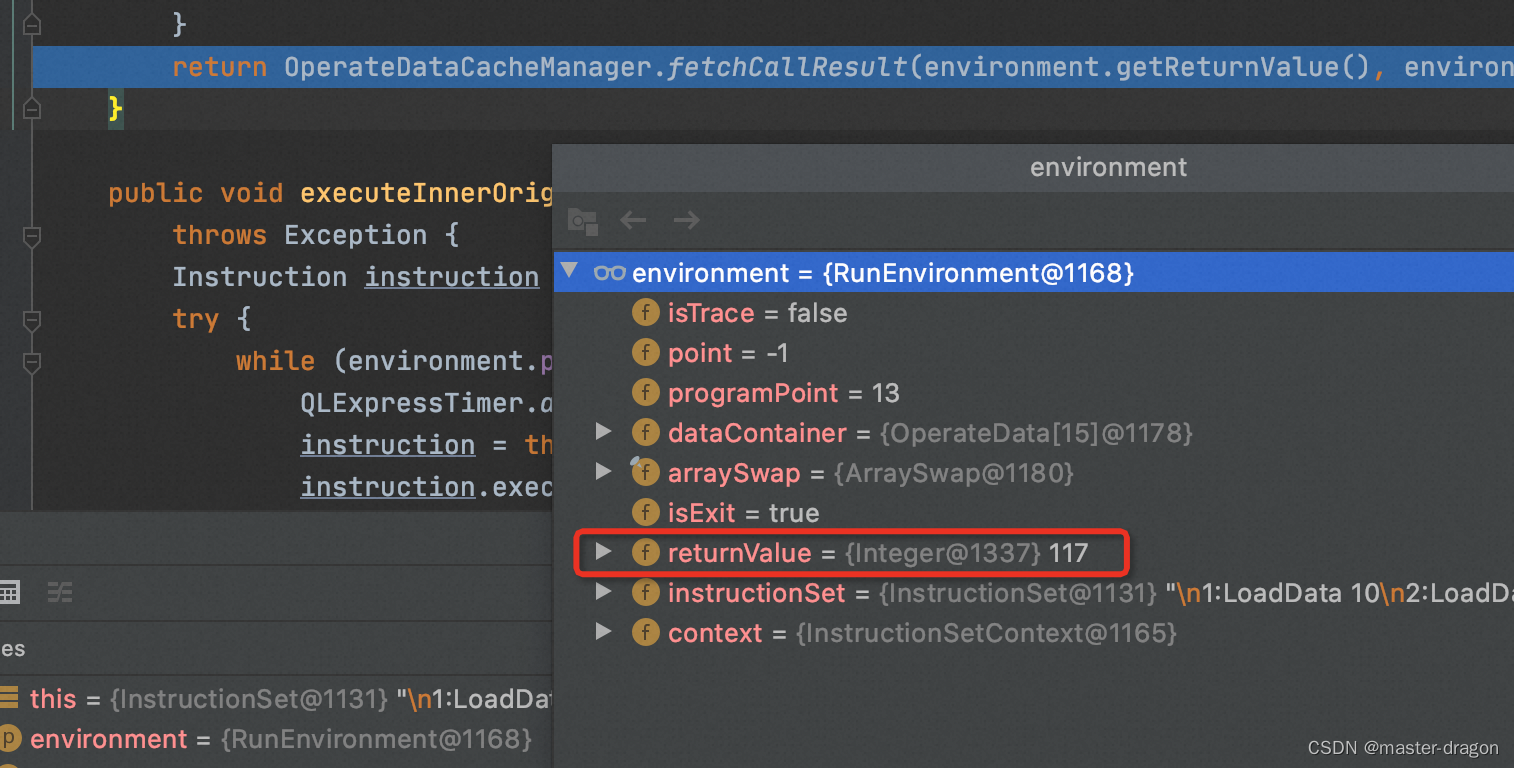
特别说明:代码执行过程中会有各种缓存,避免指令的重复生成,可提高运行效率
再看一个in表达式设置参数的执行
@Test
public void testOperatorIn() throws Exception {
String express1 = "2 in (2, 3) ";
String express2 = "2 in a";
String express3 = "2 in b";
ExpressRunner runner = new ExpressRunner(true, true);
DefaultContext<String, Object> context = new DefaultContext<>();
int[] a = {
1, 2, 3};
context.put("a", a);
List<Integer> b = new ArrayList<>();
b.add(2);
b.add(3);
context.put("b", b);
System.out.println(runner.execute(express1, context, null, false, false));
System.out.println(runner.execute(express2, context, null, false, false));
System.out.println(runner.execute(express3, context, null, false, false));
}
对于表达式"2 in b" 解析为的语法树
1: STAT_BLOCK:STAT_BLOCK STAT_BLOCK
2: STAT_SEMICOLON:STAT_SEMICOLON STAT_SEMICOLON
3: in:in in
4: 2:CONST_INTEGER CONST
4: b:ID ID
执行指令:
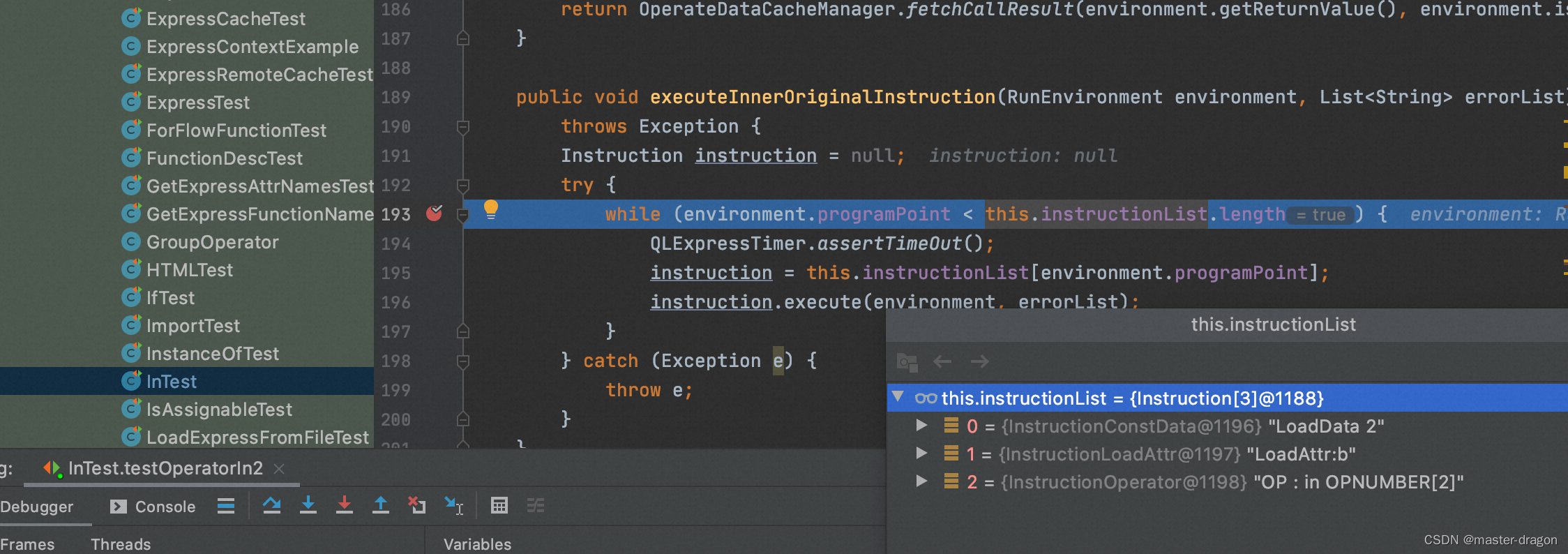
在执行in操作符时候,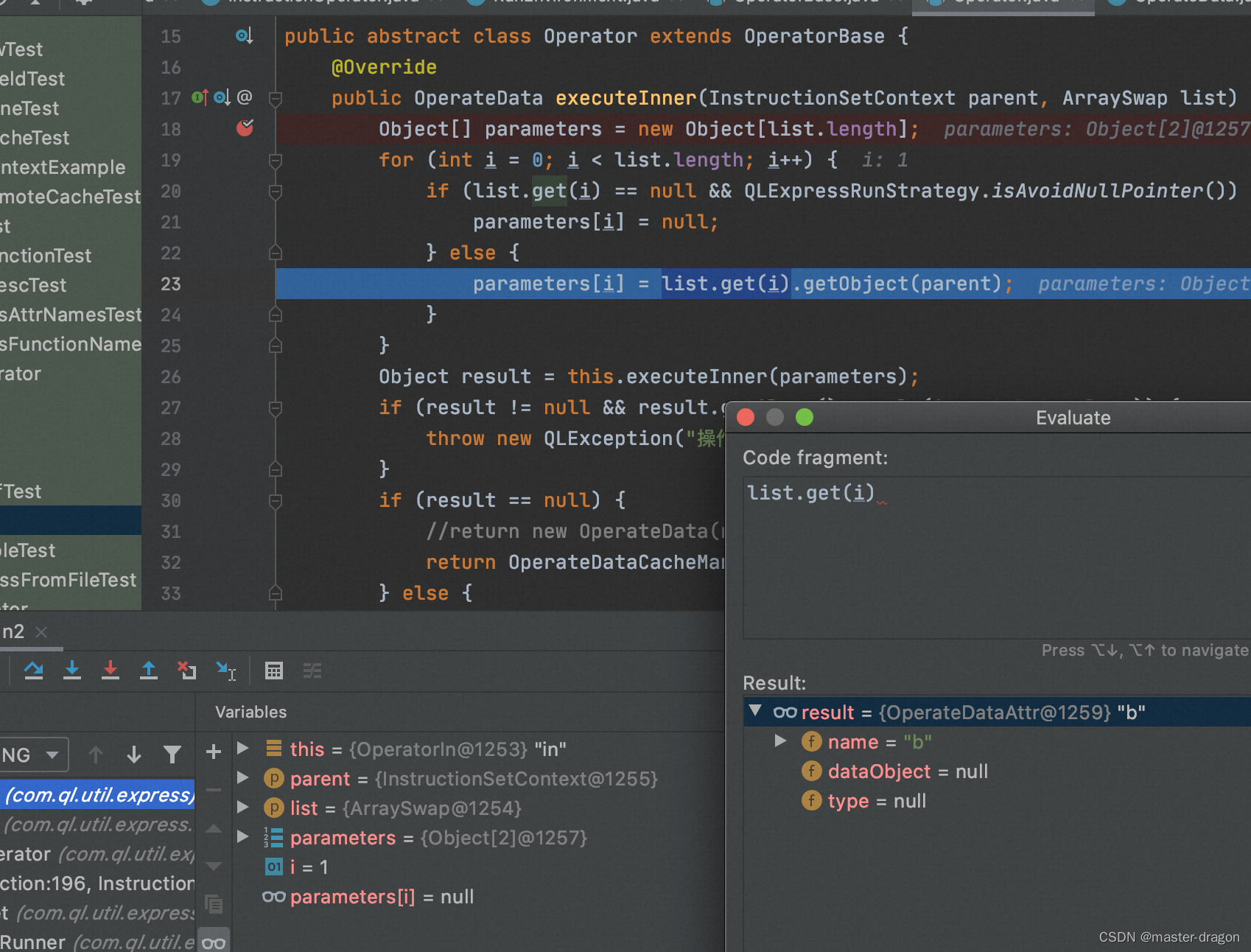
获取b参数则调用com.ql.util.express.instruction.opdata.OperateDataAttr#getObjectInner, 从context中获取值:
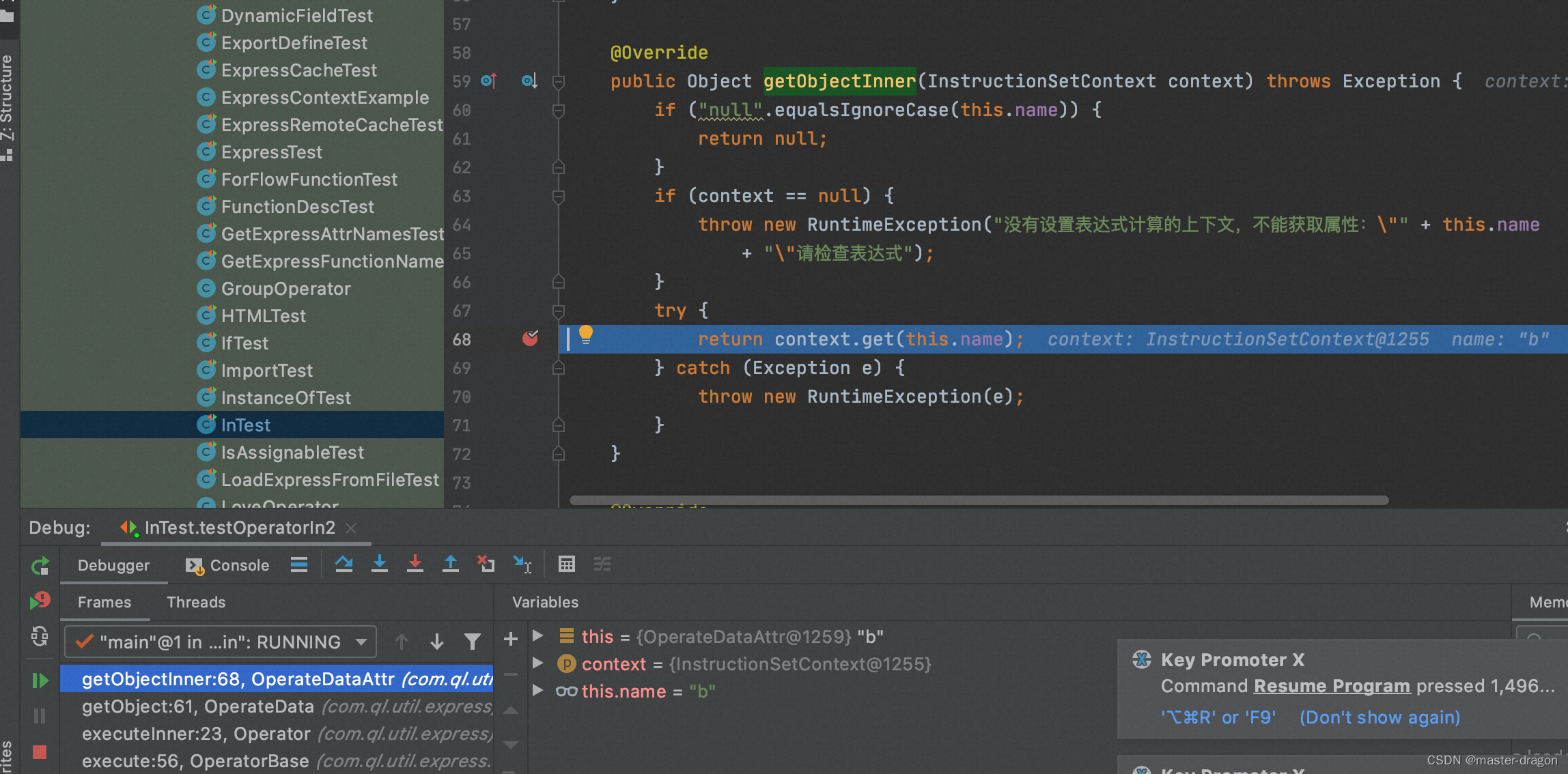
最后正确执行in指令,得到结果