#导入工具包
from collections import OrderedDict
import numpy as np
import argparse
import dlib
import cv2
#https://ibug.doc.ic.ac.uk/resources/facial-point-annotations/
#http://dlib.net/files/
# 参数
ap = argparse.ArgumentParser()
ap.add_argument("-p", "--shape-predictor", required=True,
help="path to facial landmark predictor")
ap.add_argument("-i", "--image", required=True,
help="path to input image")
args = vars(ap.parse_args())
FACIAL_LANDMARKS_68_IDXS = OrderedDict([
("mouth", (48, 68)),
("right_eyebrow", (17, 22)),
("left_eyebrow", (22, 27)),
("right_eye", (36, 42)),
("left_eye", (42, 48)),
("nose", (27, 36)),
("jaw", (0, 17))
])
FACIAL_LANDMARKS_5_IDXS = OrderedDict([
("right_eye", (2, 3)),
("left_eye", (0, 1)),
("nose", (4))
])
def shape_to_np(shape, dtype="int"):
# 创建68*2
coords = np.zeros((shape.num_parts, 2), dtype=dtype)
# 遍历每一个关键点
# 得到坐标
for i in range(0, shape.num_parts):
coords[i] = (shape.part(i).x, shape.part(i).y)
return coords
def visualize_facial_landmarks(image, shape, colors=None, alpha=0.75):
# 创建两个copy
# overlay and one for the final output image
overlay = image.copy()
output = image.copy()
# 设置一些颜色区域
if colors is None:
colors = [(19, 199, 109), (79, 76, 240), (230, 159, 23),
(168, 100, 168), (158, 163, 32),
(163, 38, 32), (180, 42, 220)]
# 遍历每一个区域
for (i, name) in enumerate(FACIAL_LANDMARKS_68_IDXS.keys()):
# 得到每一个点的坐标
(j, k) = FACIAL_LANDMARKS_68_IDXS[name]
pts = shape[j:k]
# 检查位置
if name == "jaw":
# 用线条连起来
for l in range(1, len(pts)):
ptA = tuple(pts[l - 1])
ptB = tuple(pts[l])
cv2.line(overlay, ptA, ptB, colors[i], 2)
# 计算凸包
else:
hull = cv2.convexHull(pts)
cv2.drawContours(overlay, [hull], -1, colors[i], -1)
# 叠加在原图上,可以指定比例
cv2.addWeighted(overlay, alpha, output, 1 - alpha, 0, output)
return output
# 加载人脸检测与关键点定位
detector = dlib.get_frontal_face_detector()
predictor = dlib.shape_predictor(args["shape_predictor"])
# 读取输入数据,预处理
image = cv2.imread(args["image"])
(h, w) = image.shape[:2]
width=500
r = width / float(w)
dim = (width, int(h * r))
image = cv2.resize(image, dim, interpolation=cv2.INTER_AREA)
gray = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
# 人脸检测
rects = detector(gray, 1)
# 遍历检测到的框
for (i, rect) in enumerate(rects):
# 对人脸框进行关键点定位
# 转换成ndarray
shape = predictor(gray, rect)
shape = shape_to_np(shape)
# 遍历每一个部分
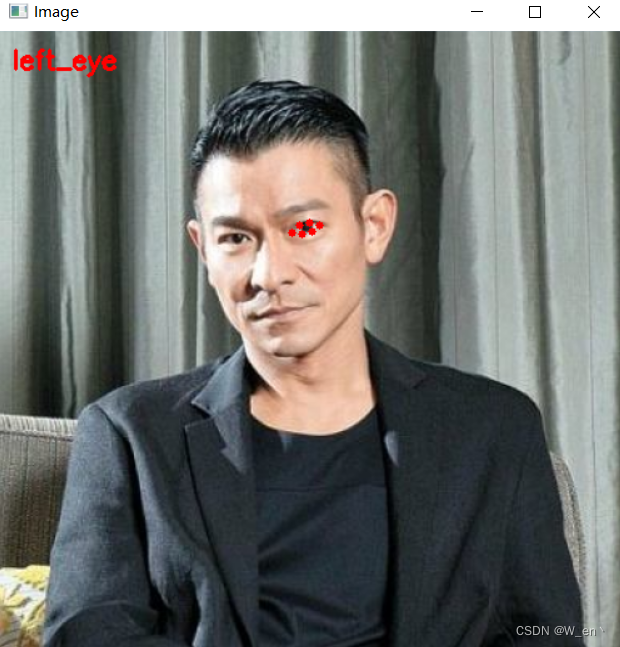
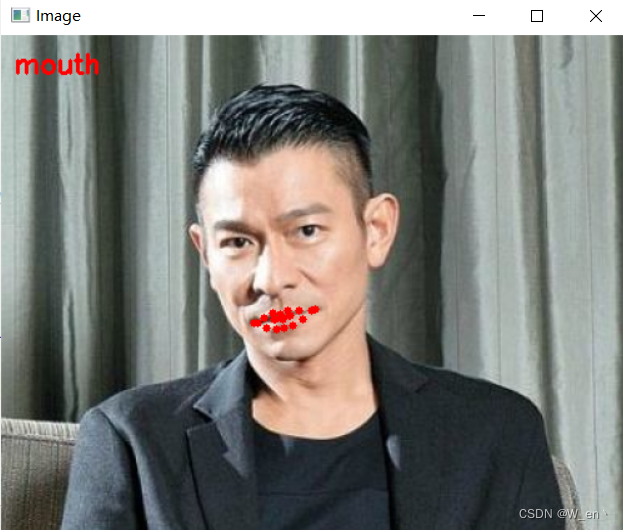
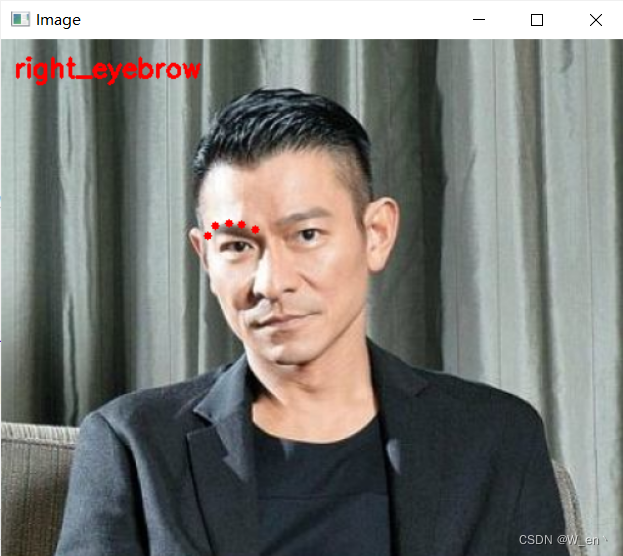
for (name, (i, j)) in FACIAL_LANDMARKS_68_IDXS.items():
clone = image.copy()
cv2.putText(clone, name, (10, 30), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX,
0.7, (0, 0, 255), 2)
# 根据位置画点
for (x, y) in shape[i:j]:
cv2.circle(clone, (x, y), 3, (0, 0, 255), -1)
# 提取ROI区域
(x, y, w, h) = cv2.boundingRect(np.array([shape[i:j]]))
roi = image[y:y + h, x:x + w]
(h, w) = roi.shape[:2]
width=250
r = width / float(w)
dim = (width, int(h * r))
roi = cv2.resize(roi, dim, interpolation=cv2.INTER_AREA)
# 显示每一部分
cv2.imshow("ROI", roi)
cv2.imshow("Image", clone)
cv2.waitKey(0)
# 展示所有区域
output = visualize_facial_landmarks(image, shape)
cv2.imshow("Image", output)
cv2.waitKey(0)