http://soundfile.sapp.org/doc/WaveFormat/
The WAVE file format is a subset of Microsoft's RIFF specification for the storage of multimedia files. A RIFF file starts out with a file header followed by a sequence of data chunks. A WAVE file is often just a RIFF file with a single "WAVE" chunk which consists of two sub-chunks -- a "fmt " chunk specifying the data format and a "data" chunk containing the actual sample data. Call this form the "Canonical form". Who knows how it really all works. An almost complete description which seems totally useless unless you want to spend a week looking over it can be found at MSDN (mostly describes the non-PCM, or registered proprietary data formats).
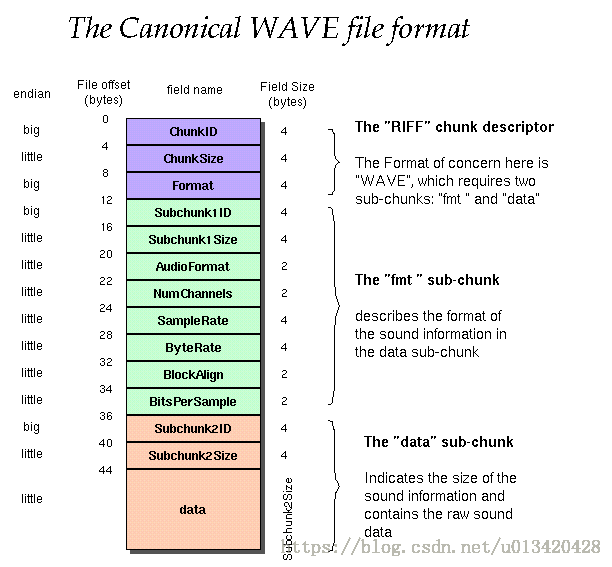
I use the standard WAVE format as created by the sox program:Offset Size Name Description
The canonical WAVE format starts with the RIFF header:
0 4 ChunkID Contains the letters "RIFF" in ASCII form
(0x52494646 big-endian form).
4 4 ChunkSize 36 + SubChunk2Size, or more precisely:
4 + (8 + SubChunk1Size) + (8 + SubChunk2Size)
This is the size of the rest of the chunk
following this number. This is the size of the
entire file in bytes minus 8 bytes for the
two fields not included in this count:
ChunkID and ChunkSize.
8 4 Format Contains the letters "WAVE"
(0x57415645 big-endian form).
The "WAVE" format consists of two subchunks: "fmt " and "data":
The "fmt " subchunk describes the sound data's format:
12 4 Subchunk1ID Contains the letters "fmt "
(0x666d7420 big-endian form).
16 4 Subchunk1Size 16 for PCM. This is the size of the
rest of the Subchunk which follows this number.
20 2 AudioFormat PCM = 1 (i.e. Linear quantization)
Values other than 1 indicate some
form of compression.
22 2 NumChannels Mono = 1, Stereo = 2, etc.
24 4 SampleRate 8000, 44100, etc.
28 4 ByteRate == SampleRate * NumChannels * BitsPerSample/8
32 2 BlockAlign == NumChannels * BitsPerSample/8
The number of bytes for one sample including
all channels. I wonder what happens when
this number isn't an integer?
34 2 BitsPerSample 8 bits = 8, 16 bits = 16, etc.
2 ExtraParamSize if PCM, then doesn't exist
X ExtraParams space for extra parameters
The "data" subchunk contains the size of the data and the actual sound:
36 4 Subchunk2ID Contains the letters "data"
(0x64617461 big-endian form).
40 4 Subchunk2Size == NumSamples * NumChannels * BitsPerSample/8
This is the number of bytes in the data.
You can also think of this as the size
of the read of the subchunk following this
number.
44 * Data The actual sound data.
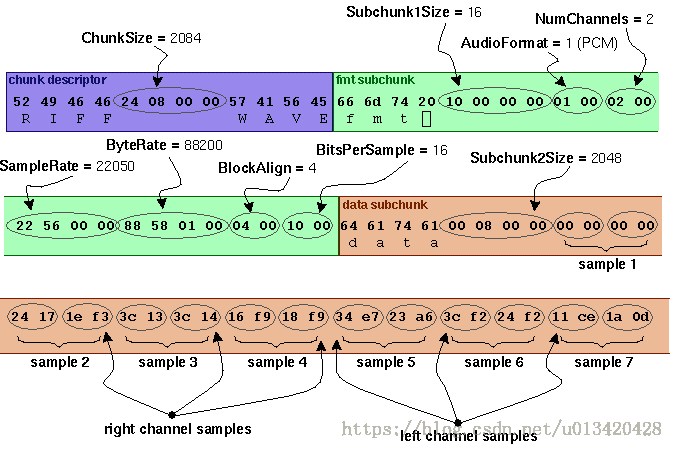
As an example, here are the opening 72 bytes of a WAVE file with bytes shown as hexadecimal numbers:
52 49 46 46 24 08 00 00 57 41 56 45 66 6d 74 20 10 00 00 00 01 00 02 00
22 56 00 00 88 58 01 00 04 00 10 00 64 61 74 61 00 08 00 00 00 00 00 00
24 17 1e f3 3c 13 3c 14 16 f9 18 f9 34 e7 23 a6 3c f2 24 f2 11 ce 1a 0d Notes:
The default byte ordering assumed for WAVE data files is little-endian. Files written using the big-endian byte ordering scheme have the identifier RIFX instead of RIFF.
The sample data must end on an even byte boundary. Whatever that means.
8-bit samples are stored as unsigned bytes, ranging from 0 to 255. 16-bit samples are stored as 2’s-complement signed integers, ranging from -32768 to 32767.
There may be additional subchunks in a Wave data stream. If so, each will have a char[4] SubChunkID, and unsigned long SubChunkSize, and SubChunkSize amount of data.
RIFF stands for Resource Interchange File Format.
General discussion of RIFF files:
Multimedia applications require the storage and management of a wide variety of data, including bitmaps, audio data, video data, and peripheral device control information. RIFF provides a way to store all these varied types of data. The type of data a RIFF file contains is indicated by the file extension. Examples of data that may be stored in RIFF files are:
Audio/visual interleaved data (.AVI)
Waveform data (.WAV)
Bitmapped data (.RDI)
MIDI information (.RMI)
Color palette (.PAL)
Multimedia movie (.RMN)
Animated cursor (.ANI)
A bundle of other RIFF files (.BND)
NOTE: At this point, AVI files are the only type of RIFF files that have been fully implemented using the current RIFF specification. Although WAV files have been implemented, these files are very simple, and their developers typically use an older specification in constructing them.
For more info see http://www.ora.com/centers/gff/formats/micriff/index.htm
References:
http://www.ora.com/centers/gff/formats/micriff/index.htm (good).
http://premium.microsoft.com/msdn/library/tools/dnmult/d1/newwave.htm
http://www.lightlink.com/tjweber/StripWav/WAVE.html
wav头数据:
typedef struct
{
unsigned int riff_id;
unsigned int riff_size;
unsigned int riff_format;
} RIFF_HEADER;
typedef struct
{
unsigned int format_id;
unsigned int format_size;
unsigned short format_tag;
unsigned short channels;
unsigned int sample_rate;
unsigned int bytes_rate;
unsigned short block_align;
unsigned short bits;
} WAVE_FORMAT;
typedef struct
{
unsigned int data_tag;
unsigned int data_size;
} WAVE_DATA_INFO;
// http://soundfile.sapp.org/doc/WaveFormat/
#define SAMPLE_BITS 16
static FILE* _WriteWaveHeader(const char *path,
unsigned int channel_num,
unsigned int sample_rate,
unsigned int sample_num)
{
FILE* file = fopen(path, "wb");
if (file == NULL)
return NULL;
RIFF_HEADER riff_header;
WAVE_FORMAT wave_format;
WAVE_DATA_INFO wave_data_info;
riff_header.riff_id = 0x46464952ul;
riff_header.riff_size = (sample_num * channel_num * SAMPLE_BITS / 8 + sizeof(wave_format) + 8);
riff_header.riff_format = 0x45564157ul;
wave_format.format_id = 0x20746D66ul;
wave_format.format_size = sizeof(wave_format) - 8;
wave_format.format_tag = 1;
wave_format.channels = channel_num;
wave_format.sample_rate = sample_rate;
wave_format.bytes_rate = sample_rate * channel_num * SAMPLE_BITS / 8;
wave_format.block_align = channel_num * SAMPLE_BITS / 8;
wave_format.bits = SAMPLE_BITS;
wave_data_info.data_tag = 0x61746164ul;
wave_data_info.data_size= sample_num * channel_num * SAMPLE_BITS / 8;
fwrite(&riff_header, sizeof(riff_header), 1, file);
fwrite(&wave_format, sizeof(wave_format), 1, file);
fwrite(&wave_data_info, sizeof(wave_data_info), 1, file);
return file;
}
//创建output.wav文件并写入wav格式头数据
char option_output_path[1024] = "output.wav";
FILE *output_file = _WriteWaveHeader(option_output_path, channel_num, info.sample_rate, channel_size * context_num);
if (output_file == NULL) {
fprintf (stderr, "Failed to create output file:%s!\n", option_output_path);
return -1;
}