参考:http://blog.csdn.net/mzpmzk/article/details/77337851
一、Tensor 之间的运算规则
- 相同大小 Tensor 之间的任何算术运算都会将运算应用到元素级
- 不同大小 Tensor(要求dimension 0 必须相同) 之间的运算叫做广播(broadcasting)
- Tensor 与 Scalar(0维 tensor) 间的算术运算会将那个标量值传播到各个元素
- Note: TensorFLow 在进行数学运算时,一定要求各个 Tensor 数据类型一致
二、常用操作符和基本数学函数
大多数运算符都进行了重载操作,使我们可以快速使用 (+ - * /) 等,但是有一点不好的是使用重载操作符后就不能为每个操作命名了。
# 算术操作符:+ - * / % tf.add(x, y, name=None) # 加法(支持 broadcasting) tf.subtract(x, y, name=None) # 减法 tf.multiply(x, y, name=None) # 乘法 tf.divide(x, y, name=None) # 浮点除法, 返回浮点数(python3 除法) tf.mod(x, y, name=None) # 取余 # 幂指对数操作符:^ ^2 ^0.5 e^ ln tf.pow(x, y, name=None) # 幂次方 tf.square(x, name=None) # 平方 tf.sqrt(x, name=None) # 开根号,必须传入浮点数或复数 tf.exp(x, name=None) # 计算 e 的次方 tf.log(x, name=None) # 以 e 为底,必须传入浮点数或复数 # 取符号、负、倒数、绝对值、近似、两数中较大/小的 tf.negative(x, name=None) # 取负(y = -x). tf.sign(x, name=None) # 返回 x 的符号 tf.reciprocal(x, name=None) # 取倒数 tf.abs(x, name=None) # 求绝对值 tf.round(x, name=None) # 四舍五入 tf.ceil(x, name=None) # 向上取整 tf.floor(x, name=None) # 向下取整 tf.rint(x, name=None) # 取最接近的整数 tf.maximum(x, y, name=None) # 返回两tensor中的最大值 (x > y ? x : y) tf.minimum(x, y, name=None) # 返回两tensor中的最小值 (x < y ? x : y) # 三角函数和反三角函数 tf.cos(x, name=None) tf.sin(x, name=None) tf.tan(x, name=None) tf.acos(x, name=None) tf.asin(x, name=None) tf.atan(x, name=None) # 其它 tf.div(x, y, name=None) # python 2.7 除法, x/y-->int or x/float(y)-->float tf.truediv(x, y, name=None) # python 3 除法, x/y-->float tf.floordiv(x, y, name=None) # python 3 除法, x//y-->int tf.realdiv(x, y, name=None) tf.truncatediv(x, y, name=None) tf.floor_div(x, y, name=None) tf.truncatemod(x, y, name=None) tf.floormod(x, y, name=None) tf.cross(x, y, name=None) tf.add_n(inputs, name=None) # inputs: A list of Tensor objects, each with same shape and type tf.squared_difference(x, y, name=None) 三、矩阵数学函数
# 矩阵乘法(tensors of rank >= 2) tf.matmul(a, b, transpose_a=False, transpose_b=False, adjoint_a=False, adjoint_b=False, a_is_sparse=False, b_is_sparse=False, name=None) # 转置,可以通过指定 perm=[1, 0] 来进行轴变换 tf.transpose(a, perm=None, name='transpose') # 在张量 a 的最后两个维度上进行转置 tf.matrix_transpose(a, name='matrix_transpose') # Matrix with two batch dimensions, x.shape is [1, 2, 3, 4] # tf.matrix_transpose(x) is shape [1, 2, 4, 3] # 求矩阵的迹 tf.trace(x, name=None) # 计算方阵行列式的值 tf.matrix_determinant(input, name=None) # 求解可逆方阵的逆,input 必须为浮点型或复数 tf.matrix_inverse(input, adjoint=None, name=None) # 奇异值分解 tf.svd(tensor, full_matrices=False, compute_uv=True, name=None) # QR 分解 tf.qr(input, full_matrices=None, name=None) # 求张量的范数(默认2) tf.norm(tensor, ord='euclidean', axis=None, keep_dims=False, name=None) # 构建一个单位矩阵, 或者 batch 个矩阵,batch_shape 以 list 的形式传入 tf.eye(num_rows, num_columns=None, batch_shape=None, dtype=tf.float32, name=None) # Construct one identity matrix. tf.eye(2) ==> [[1., 0.], [0., 1.]] # Construct a batch of 3 identity matricies, each 2 x 2. # batch_identity[i, :, :] is a 2 x 2 identity matrix, i = 0, 1, 2. batch_identity = tf.eye(2, batch_shape=[3]) # Construct one 2 x 3 "identity" matrix tf.eye(2, num_columns=3) ==> [[ 1., 0., 0.], [ 0., 1., 0.]] # 构建一个对角矩阵,rank = 2*rank(diagonal) tf.diag(diagonal, name=None) # 'diagonal' is [1, 2, 3, 4] tf.diag(diagonal) ==> [[1, 0, 0, 0] [0, 2, 0, 0] [0, 0, 3, 0] [0, 0, 0, 4]] # 其它 tf.diag_part tf.matrix_diag tf.matrix_diag_part tf.matrix_band_part tf.matrix_set_diag tf.cholesky tf.cholesky_solve tf.matrix_solve tf.matrix_triangular_solve tf.matrix_solve_ls tf.self_adjoint_eig tf.self_adjoint_eigvals四、Reduction:reduce various dimensions of a tensor
# 计算输入 tensor 所有元素的和,或者计算指定的轴所有元素的和 tf.reduce_sum(input_tensor, axis=None, keep_dims=False, name=None) # 'x' is [[1, 1, 1] # [1, 1, 1]] tf.reduce_sum(x) ==> 6 tf.reduce_sum(x, 0) ==> [2, 2, 2] tf.reduce_sum(x, 1) ==> [3, 3] tf.reduce_sum(x, 1, keep_dims=True) ==> [[3], [3]] # 维度不缩减 tf.reduce_sum(x, [0, 1]) ==> 6 # 计算输入 tensor 所有元素的均值/最大值/最小值/积/逻辑与/或 # 或者计算指定的轴所有元素的均值/最大值/最小值/积/逻辑与/或(just like reduce_sum) tf.reduce_mean(input_tensor, axis=None, keep_dims=False, name=None) tf.reduce_max(input_tensor, axis=None, keep_dims=False, name=None) tf.reduce_min(input_tensor, axis=None, keep_dims=False, name=None) tf.reduce_prod(input_tensor, axis=None, keep_dims=False, name=None) tf.reduce_all(input_tensor, axis=None, keep_dims=False, name=None) # 全部满足条件 tf.reduce_any(input_tensor, axis=None, keep_dims=False, name=None) #至少有一个满足条件 ------------------------------------------- # 分界线以上和 Numpy 中相应的用法完全一致 ------------------------------------------- # inputs 为一 list, 计算 list 中所有元素的累计和, # tf.add(x, y, name=None)只能计算两个元素的和,此函数相当于扩展了其功能 tf.accumulate_n(inputs, shape=None, tensor_dtype=None, name=None) # Computes log(sum(exp(elements across dimensions of a tensor))) tf.reduce_logsumexp(input_tensor, axis=None, keep_dims=False, name=None) # Computes number of nonzero elements across dimensions of a tensor tf.count_nonzero(input_tensor, axis=None, keep_dims=False, name=None)五、Scan:perform scans (running totals) across one axis of a tensor
# Compute the cumulative sum of the tensor x along axis tf.cumsum(x, axis=0, exclusive=False, reverse=False, name=None) # Eg: tf.cumsum([a, b, c]) # => [a, a + b, a + b + c] tf.cumsum([a, b, c], exclusive=True) # => [0, a, a + b] tf.cumsum([a, b, c], reverse=True) # => [a + b + c, b + c, c] tf.cumsum([a, b, c], exclusive=True, reverse=True) # => [b + c, c, 0] # Compute the cumulative product of the tensor x along axis tf.cumprod(x, axis=0, exclusive=False, reverse=False, name=None)六、Segmentation
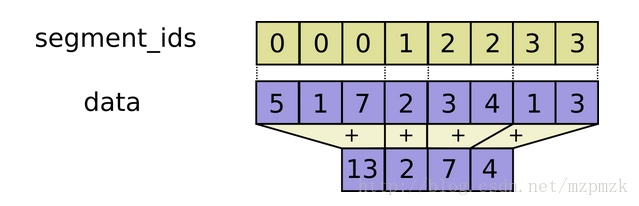
沿着第一维(x 轴)根据 segment_ids(list)分割好相应的数据后再进行操作
# Computes the sum/mean/max/min/prod along segments of a tensor tf.segment_sum(data, segment_ids, name=None) # Eg: m = tf.constant([5,1,7,2,3,4,1,3]) s_id = [0,0,0,1,2,2,3,3] s.run(tf.segment_sum(m, segment_ids=s_id)) >array([13, 2, 7, 4], dtype=int32) tf.segment_mean(data, segment_ids, name=None) tf.segment_max(data, segment_ids, name=None) tf.segment_min(data, segment_ids, name=None) tf.segment_prod(data, segment_ids, name=None) # 其它 tf.unsorted_segment_sum tf.sparse_segment_sum tf.sparse_segment_mean tf.sparse_segment_sqrt_n七、 序列比较与索引提取
# 比较两个 list 或者 string 的不同,并返回不同的值和索引 tf.setdiff1d(x, y, index_dtype=tf.int32, name=None) # 返回 x 中的唯一值所组成的tensor 和原 tensor 中元素在现 tensor 中的索引 tf.unique(x, out_idx=None, name=None) # x if condition else y, condition 为 bool 类型的,可用tf.equal()等来表示 # x 和 y 的形状和数据类型必须一致 tf.where(condition, x=None, y=None, name=None) # 返回沿着坐标轴方向的最大/最小值的索引 tf.argmax(input, axis=None, name=None, output_type=tf.int64) tf.argmin(input, axis=None, name=None, output_type=tf.int64) # x 的值当作 y 的索引,range(len(x)) 索引当作 y 的值 # y[x[i]] = i for i in [0, 1, ..., len(x) - 1] tf.invert_permutation(x, name=None) # 其它 tf.edit_distance