第一章 需求分析
计划在Team的开源项目里加入Redis实现缓存处理,因为业务功能已经实现了一部分,通过写Redis工具类,然后引用,改动量较大,而且不可以实现解耦合,所以想到了Spring框架的AOP(面向切面编程)。
开源项目:https://github.com/u014427391/jeeplatform
欢迎star(收藏)
第二章 SpringBoot简介
Spring框架作为JavaEE框架领域的一款重要的开源框架,在企业应用开发中有着很重要的作用,同时Spring框架及其子框架很多,所以知识量很广。
SpringBoot:一款Spring框架的子框架,也可以叫微框架,是2014年推出的一款使Spring框架开发变得容易的框架。学过Spring框架的都知识,Spring框架难以避免地需要配置不少XMl,而使用SpringBoot框架的话,就可以使用注解开发,极大地简化基于Spring框架的开发。SpringBoot充分利用了JavaConfig的配置模式以及“约定优于配置”的理念,能够极大的简化基于SpringMVC的Web应用和REST服务开发。
第三章 Redis简介
3.1 Redis安装部署(Linux)
Redis安装部署的可以参考我的博客(Redis是基于C编写的,所以安装前先安装gcc编译器):http://blog.csdn.net/u014427391/article/details/71210989
3.2 Redis简介
Redis如今已经成为Web开发社区最火热的内存数据库之一,随着Web2.0的快速发展,再加上半结构数据比重加大,网站对高效性能的需求也越来越多。
而且大型网站一般都有几百台或者更多Redis服务器。Redis作为一款功能强大的系统,无论是存储、队列还是缓存系统,都有其用武之地。
SpringBoot框架入门的可以参考我之前的博客:http://blog.csdn.net/u014427391/article/details/70655332
第四章 Redis缓存实现
4.1下面结构图
项目结构图:
4.2 SpringBoot的yml文件配置
添加resource下面的application.yml配置,这里主要配置mysql,druid,redis
spring:
datasource:
# 主数据源
shop:
url: jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/jeeplatform?autoReconnect=true&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&characterSetResults=utf8&useSSL=false
username: root
password: root
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
# 连接池设置
druid:
initial-size: 5
min-idle: 5
max-active: 20
# 配置获取连接等待超时的时间
max-wait: 60000
# 配置间隔多久才进行一次检测,检测需要关闭的空闲连接,单位是毫秒
time-between-eviction-runs-millis: 60000
# 配置一个连接在池中最小生存的时间,单位是毫秒
min-evictable-idle-time-millis: 300000
# Oracle请使用select 1 from dual
validation-query: SELECT 'x'
test-while-idle: true
test-on-borrow: false
test-on-return: false
# 打开PSCache,并且指定每个连接上PSCache的大小
pool-prepared-statements: true
max-pool-prepared-statement-per-connection-size: 20
# 配置监控统计拦截的filters,去掉后监控界面sql无法统计,'wall'用于防火墙
filters: stat,wall,slf4j
# 通过connectProperties属性来打开mergeSql功能;慢SQL记录
connection-properties: druid.stat.mergeSql=true;druid.stat.slowSqlMillis=5000
# 合并多个DruidDataSource的监控数据
use-global-data-source-stat: true
jpa:
database: mysql
hibernate:
show_sql: true
format_sql: true
ddl-auto: none
naming:
physical-strategy: org.hibernate.boot.model.naming.PhysicalNamingStrategyStandardImpl
mvc:
view:
prefix: /WEB-INF/jsp/
suffix: .jsp
#Jedis配置
jedis :
pool :
host : 127.0.0.1
port : 6379
password : password
timeout : 0
config :
maxTotal : 100
maxIdle : 10
maxWaitMillis : 100000- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
编写一个配置类启动配置JedisConfig.java:
package org.muses.jeeplatform.config;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionalOnMissingBean;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import redis.clients.jedis.JedisPool;
import redis.clients.jedis.JedisPoolConfig;
@Configuration
//@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = JedisConfig.JEDIS_PREFIX )
public class JedisConfig {
//public static final String JEDIS_PREFIX = "jedis";
@Bean(name= "jedisPool")
@Autowired
public JedisPool jedisPool(@Qualifier("jedisPoolConfig") JedisPoolConfig config,
@Value("${spring.jedis.pool.host}")String host,
@Value("${spring.jedis.pool.port}")int port,
@Value("${spring.jedis.pool.timeout}")int timeout,
@Value("${spring.jedis.pool.password}")String password) {
return new JedisPool(config, host, port,timeout,password);
}
@Bean(name= "jedisPoolConfig")
public JedisPoolConfig jedisPoolConfig (@Value("${spring.jedis.pool.config.maxTotal}")int maxTotal,
@Value("${spring.jedis.pool.config.maxIdle}")int maxIdle,
@Value("${spring.jedis.pool.config.maxWaitMillis}")int maxWaitMillis) {
JedisPoolConfig config = new JedisPoolConfig();
config.setMaxTotal(maxTotal);
config.setMaxIdle(maxIdle);
config.setMaxWaitMillis(maxWaitMillis);
return config;
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
4.3 元注解类编写
编写一个元注解类RedisCache.java,被改注解定义的类都自动实现AOP缓存处理
package org.muses.jeeplatform.annotation;
import org.muses.jeeplatform.common.RedisCacheNamespace;
import java.lang.annotation.*;
/**
* 元注解 用来标识查询数据库的方法
*/
@Documented
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface RedisCache {
// RedisCacheNamespace nameSpace();
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
JDK 5提供的注解,除了Retention以外,还有另外三个,即Target 、Inherited 和 Documented。基于这个,我们可以实现自定义的元注解
我们设置RedisCache基于Method方法级别引用。
1.RetentionPolicy.SOURCE 这种类型的Annotations只在源代码级别保留,编译时就会被忽略
2.RetentionPolicy.CLASS 这种类型的Annotations编译时被保留,在class文件中存在,但JVM将会忽略
3.RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME 这种类型的Annotations将被JVM保留,所以他们能在运行时被JVM或其他使用反射机制的代码所读取和使用.
4.4 调用JedisPool实现Redis缓存处理
package org.muses.jeeplatform.cache;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import redis.clients.jedis.Jedis;
import redis.clients.jedis.JedisPool;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
@Component("redisCache")
public class RedisCache {
@Autowired
private JedisPool jedisPool;
private JedisPool getJedisPool(){
return jedisPool;
}
public void setJedisPool(JedisPool jedisPool){
this.jedisPool = jedisPool;
}
/**
* 从Redis缓存获取数据
* @param redisKey
* @return
*/
public Object getDataFromRedis(String redisKey){
Jedis jedis = jedisPool.getResource();
byte[] byteArray = jedis.get(redisKey.getBytes());
if(byteArray != null){
return SerializeUtil.unSerialize(byteArray);
}
return null;
}
/**
* 保存数据到Redis
* @param redisKey
*/
public String saveDataToRedis(String redisKey,Object obj){
byte[] bytes = SerializeUtil.serialize(obj);
Jedis jedis = jedisPool.getResource();
String code = jedis.set(redisKey.getBytes(), bytes);
return code;
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
对象序列化的工具类:
package org.muses.jeeplatform.cache;
import java.io.*;
public class SerializeUtil {
/**
* 序列化对象
* @param obj
* @return
*/
public static byte[] serialize(Object obj){
ObjectOutputStream oos = null;
ByteArrayOutputStream baos = null;
try{
baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
oos = new ObjectOutputStream(baos);
oos.writeObject(obj);
byte[] byteArray = baos.toByteArray();
return byteArray;
}catch(IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
/**
* 反序列化对象
* @param byteArray
* @return
*/
public static Object unSerialize(byte[] byteArray){
ByteArrayInputStream bais = null;
try {
//反序列化为对象
bais = new ByteArrayInputStream(byteArray);
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(bais);
return ois.readObject();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
这里记得Vo类都要实现Serializable
例如菜单信息VO类,这是一个JPA映射的实体类
package org.muses.jeeplatform.core.entity.admin;
import javax.persistence.*;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @description 菜单信息实体
* @author Nicky
* @date 2017年3月17日
*/
@Table(name="sys_menu")
@Entity
public class Menu implements Serializable {
/** 菜单Id**/
private int menuId;
/** 上级Id**/
private int parentId;
/** 菜单名称**/
private String menuName;
/** 菜单图标**/
private String menuIcon;
/** 菜单URL**/
private String menuUrl;
/** 菜单类型**/
private String menuType;
/** 菜单排序**/
private String menuOrder;
/**菜单状态**/
private String menuStatus;
private List<Menu> subMenu;
private String target;
private boolean hasSubMenu = false;
public Menu() {
super();
}
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy=GenerationType.IDENTITY)
public int getMenuId() {
return this.menuId;
}
public void setMenuId(int menuId) {
this.menuId = menuId;
}
@Column(length=100)
public int getParentId() {
return parentId;
}
public void setParentId(int parentId) {
this.parentId = parentId;
}
@Column(length=100)
public String getMenuName() {
return this.menuName;
}
public void setMenuName(String menuName) {
this.menuName = menuName;
}
@Column(length=30)
public String getMenuIcon() {
return this.menuIcon;
}
public void setMenuIcon(String menuIcon) {
this.menuIcon = menuIcon;
}
@Column(length=100)
public String getMenuUrl() {
return this.menuUrl;
}
public void setMenuUrl(String menuUrl) {
this.menuUrl = menuUrl;
}
@Column(length=100)
public String getMenuType() {
return this.menuType;
}
public void setMenuType(String menuType) {
this.menuType = menuType;
}
@Column(length=10)
public String getMenuOrder() {
return menuOrder;
}
public void setMenuOrder(String menuOrder) {
this.menuOrder = menuOrder;
}
@Column(length=10)
public String getMenuStatus(){
return menuStatus;
}
public void setMenuStatus(String menuStatus){
this.menuStatus = menuStatus;
}
@Transient
public List<Menu> getSubMenu() {
return subMenu;
}
public void setSubMenu(List<Menu> subMenu) {
this.subMenu = subMenu;
}
public void setTarget(String target){
this.target = target;
}
@Transient
public String getTarget(){
return target;
}
public void setHasSubMenu(boolean hasSubMenu){
this.hasSubMenu = hasSubMenu;
}
@Transient
public boolean getHasSubMenu(){
return hasSubMenu;
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
4.5 Spring AOP实现监控所有被@RedisCache注解的方法缓存
先从Redis里获取缓存,查询不到,就查询MySQL数据库,然后再保存到Redis缓存里,下次查询时直接调用Redis缓存
package org.muses.jeeplatform.cache;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* AOP实现Redis缓存处理
*/
@Component
@Aspect
public class RedisAspect {
private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(RedisAspect.class);
@Autowired
@Qualifier("redisCache")
private RedisCache redisCache;
/**
* 拦截所有元注解RedisCache注解的方法
*/
@Pointcut("@annotation(org.muses.jeeplatform.annotation.RedisCache)")
public void pointcutMethod(){
}
/**
* 环绕处理,先从Redis里获取缓存,查询不到,就查询MySQL数据库,
* 然后再保存到Redis缓存里
* @param joinPoint
* @return
*/
@Around("pointcutMethod()")
public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint){
//前置:从Redis里获取缓存
//先获取目标方法参数
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
String applId = null;
Object[] args = joinPoint.getArgs();
if (args != null && args.length > 0) {
applId = String.valueOf(args[0]);
}
//获取目标方法所在类
String target = joinPoint.getTarget().toString();
String className = target.split("@")[0];
//获取目标方法的方法名称
String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
//redis中key格式: applId:方法名称
String redisKey = applId + ":" + className + "." + methodName;
Object obj = redisCache.getDataFromRedis(redisKey);
if(obj!=null){
LOGGER.info("**********从Redis中查到了数据**********");
LOGGER.info("Redis的KEY值:"+redisKey);
LOGGER.info("REDIS的VALUE值:"+obj.toString());
return obj;
}
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
LOGGER.info("Redis缓存AOP处理所用时间:"+(endTime-startTime));
LOGGER.info("**********没有从Redis查到数据**********");
try{
obj = joinPoint.proceed();
}catch(Throwable e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
LOGGER.info("**********开始从MySQL查询数据**********");
//后置:将数据库查到的数据保存到Redis
String code = redisCache.saveDataToRedis(redisKey,obj);
if(code.equals("OK")){
LOGGER.info("**********数据成功保存到Redis缓存!!!**********");
LOGGER.info("Redis的KEY值:"+redisKey);
LOGGER.info("REDIS的VALUE值:"+obj.toString());
}
return obj;
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
然后调用@RedisCache实现缓存
/**
* 通过菜单Id获取菜单信息
* @param id
* @return
*/
@Transactional
@RedisCache
public Menu findMenuById(@RedisCacheKey int id){
return menuRepository.findMenuByMenuId(id);
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
登录系统,然后加入@RedisCache注解的方法都会实现Redis缓存处理
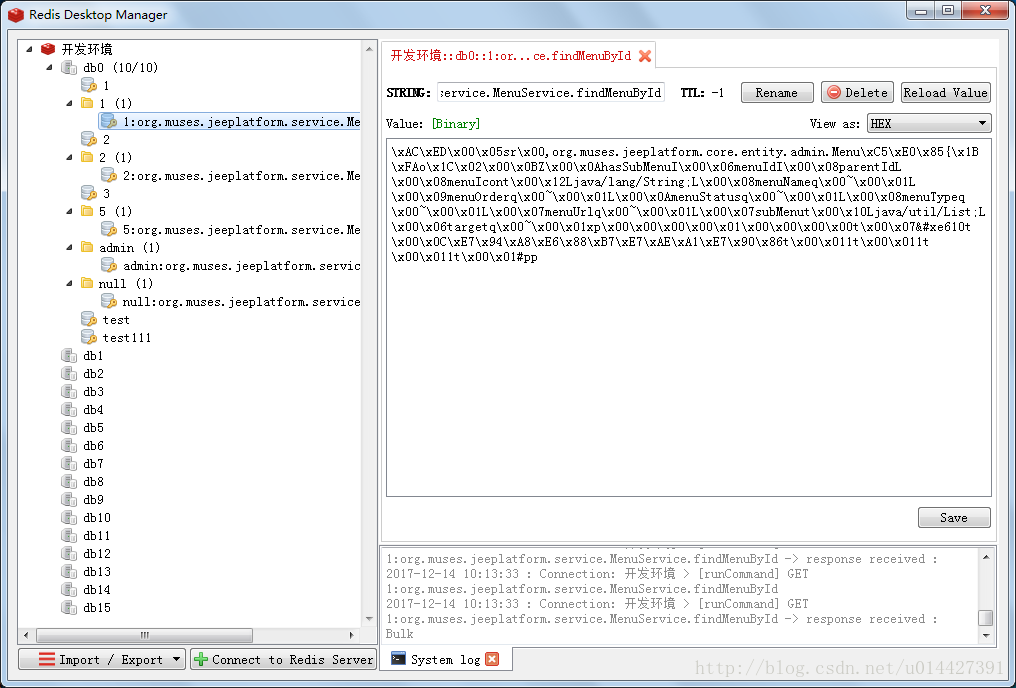
可以看到Redis里保存到了缓存
项目代码:https://github.com/u014427391/jeeplatform,欢迎去github上star(收藏)