简单理解一下序列化,序列化就相当于把你想要进行序列化的类的一切东西变成数据流的形式保存在文件中。比如说,打游戏的时候,需要暂停,退出,等等,你需要保存此时的游戏状态,下次玩游戏的时候直接继续游戏就可以回到当前状态了。(有些折磨人的游戏没有保存游戏功能。)也可以想象成把太阳系二维化存到一幅画里面,如果有 反二向箔 就可以重新把二维化的太阳系变成三维的太阳系。
但是想要序列化的话,首先你的这个类,它要支持序列化。也就是说,这个被序列化的东西要实现一个表示能被序列化的接口 : Serializable。序列化本身就和IO流不分家,因此需要搞清楚IO的操作。
1、序列化
package com.Unit1;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
import java.io.Serializable;
public class RunTest05 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//首先表示作为一个文件输出。
FileOutputStream outputStream = new FileOutputStream("E:\\student.txt");
ObjectOutputStream out = new ObjectOutputStream(outputStream);
//生成Student对象
Student stu = new Student("徐凤年", 21);
//将stu对象序列化并写到上面提到的文件路径中。
out.writeObject(stu);
//记得关闭流
out.close();
outputStream.close();
}
}
class Student implements Serializable {
private String name;
private int age;
public Student() {
}
public Student(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
}
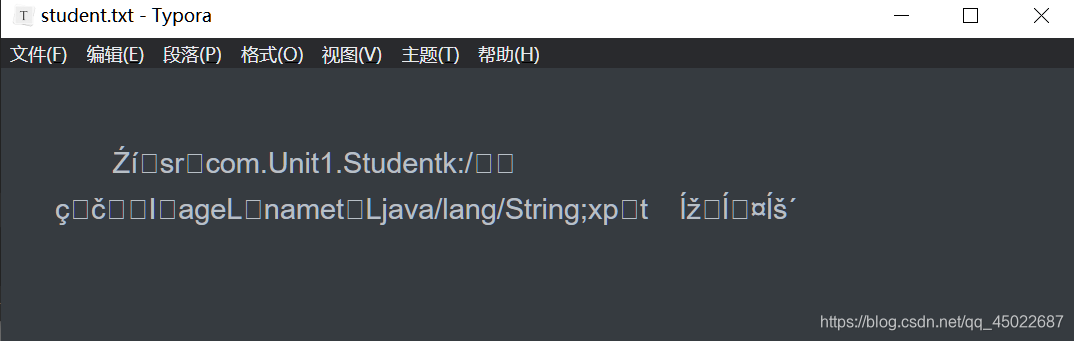
此时,我的 E:\student.txt 就自动生成了,打开后,里面就是一些乱码。

2、解序列化
那怎么读出刚才所保存的数据?我们就要用到解序列化。原理都是相同的,不过一个是写,一个是读。序列化也就是一个有点特殊的IO流操作。
解序列化就相当于从文件中取出你所保存的一些数据啊,对象啊什么的。刚才用的什么类写进去的,现在就用什么类来接收。读出来的全部是Object类。需要进行向上转型。
package com.Unit1;
import java.io.*;
public class RunTest05 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//首先指定文件路径
FileInputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream("E:\\student.txt");
ObjectInputStream in = new ObjectInputStream(inputStream);
//因为是 readObject(),所以读出来的肯定是一个Object类。我们需要进行强转
Student stu2 = (Student) in.readObject();
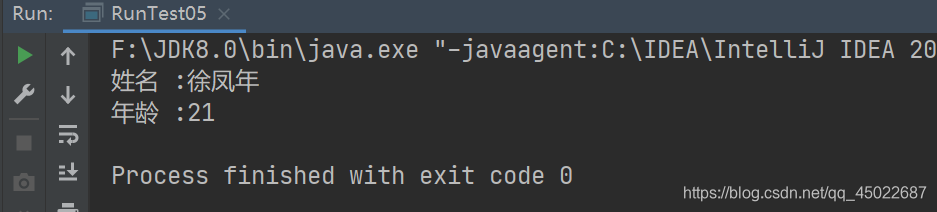
//我们读一下刚才存进去的数据,看对不对
System.out.println("姓名 :" + stu2.getName());
System.out.println("年龄 :" + stu2.getAge());
//记得关闭流
in.close();
inputStream.close();
}
}
class Student implements Serializable {
private String name;
private int age;
public Student() {
}
public Student(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
}
结果: