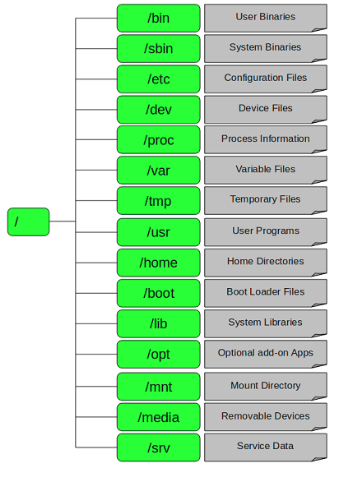
1、目录结构
2、文件类型
LINUX有四种基本文件系统类型:普通文件、目录文件、连接文件和特殊文件,可用file命令来识别。
普通文件:如文本文件、C语言元代码、SHELL脚本、二进制的可执行文件等,可用cat、less、more、vi、emacs来察看内容,用mv来改名。
目录文件:包括文件名、子目录名及其指针。它是LINUX储存文件名的唯一地方,可用ls列出目录文件。
连接文件:是指向同一索引节点的那些目录条目。用ls来查看是,连接文件的标志用l开头,而文件面后以"->"指向所连接的文件。
特殊文件:LINUX的一些设备如磁盘、终端、打印机等都在文件系统中表示出来,则一类文件就是特殊文件,常放在/dev目录内。例如,软驱A称为/dev/fd0。LINUX无C:的概念,而是用/dev/had来自第一硬盘。
3、详细说明
1、根目录:/
This is the root directory. The mothership. The home field. The one and only top directory for your whole computer. Everything, and I mean EVERYTHING starts here.
When you type ‘/home’ what you’re really saying is “start at / and then go to the home directory.”
这就是根目录。对你的电脑来说,有且只有一个根目录。所有的东西,我是说所有的东西都是从这里开始。举个例子:当你在终端里输入“/home”,你其实是在告诉电脑,先从/(根目录)开始,再进入到home目录。
2、 /root
This is where the root user lives. The root user is the god of your system. Root can do anything, up to and including removing your entire filesystem. So be careful using root.
这是系统管理员(root user)的目录。对于系统来说,系统管理员就好比是上帝,它能对系统做任何事情,甚至包括删除你的文件。因此,请小心使用root帐号
3、/bin
Here’s where your standard linux utilities(read programs) live — things like “ls” and “vi” and “more”. Generally this directory is included in your path. What this means is that if you type ‘ls’,
/bin is one of the places your shell will look to see if ‘ls’ means anything.
这里存放了标准的(或者说是缺省的)linux的工具,比如像“ls”、“vi”还有“more”等等。通常来说,这个目录已经包含在你的“path”系 统变量里面了。什么意思呢?就是:当你在终端里输入ls,
系统就会去/bin目录下面查找是不是有ls这个程序