1.XML 的特征:xml即可扩展标记语言,它可以用来标记数据、定义数据类型,是一种允许用户对自己的标记语言进行定义的源语言。从结构上,很像HTML超文本标记语言。但他们被设计的目的是不同的,超文本标记语言被设计用来显示数据,其焦点是数据的外观。它被设计用来传输和存储数据,其焦点是数据的内容
那么它有如下特征:
- 它是有标签对组成,<aa></aa>
- 标签可以有属性:<aa id='123'></aa>
- 标签对可以嵌入数据:<aa>abc</aa>
- 标签可以嵌入子标签(具有层级关系)
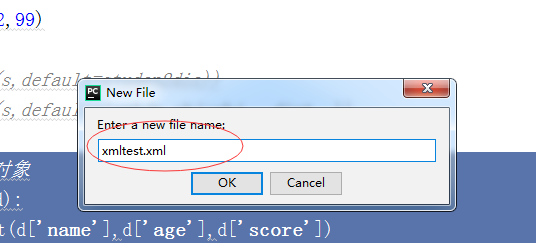
例子:创建一个XML文件
<?xml version="1.0"?> <data> <country name="Liechtenstein"> <rank updated="yes">2</rank> <year>2008</year> <gdppc>141100</gdppc> <neighbor name="Austria" direction="E"/> <neighbor name="Switzerland" direction="W"/> </country> <country name="Singapore"> <rank updated="yes">5</rank> <year>2011</year> <gdppc>59900</gdppc> <neighbor name="Malaysia" direction="N"/> </country> <country name="Panama"> <rank updated="yes">69</rank> <year>2011</year> <gdppc>13600</gdppc> <neighbor name="Costa Rica" direction="W"/> <neighbor name="Colombia" direction="E"/> </country> </data>
步骤:
【XML操作】
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET tree = ET.parse("xmltest.xml") root = tree.getroot() print(root.tag) #遍历xml文档 for child in root: print(child.tag, child.attrib) for i in child: print(i.tag,i.text) #只遍历year 节点 for node in root.iter('year'): print(node.tag,node.text) #修改和删除xml文档内容 import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET tree = ET.parse("xmltest.xml") root = tree.getroot() #修改 for node in root.iter('year'): new_year = int(node.text) + 1 node.text = str(new_year) node.set("updated","yes") tree.write("xmltest.xml") #删除node for country in root.findall('country'): rank = int(country.find('rank').text) if rank > 50: root.remove(country) tree.write('output.xml')
【自己创建xml文档】
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET new_xml = ET.Element("namelist") name = ET.SubElement(new_xml,"name",attrib={"enrolled":"yes"}) age = ET.SubElement(name,"age",attrib={"checked":"no"}) sex = ET.SubElement(name,"sex") sex.text = '33' name2 = ET.SubElement(new_xml,"name",attrib={"enrolled":"no"}) age = ET.SubElement(name2,"age") age.text = '19' et = ET.ElementTree(new_xml) #生成文档对象 et.write("test.xml", encoding="utf-8",xml_declaration=True) ET.dump(new_xml) #打印生成的格式
总结
minidom.parse(filename) 加载读取XML文件 doc.documentElement 获取XML文档对象 node.getAttribute(AttributeName) 获取XML节点属性值 node.getElementsByTagName(TagName) 获取XML节点对象集合 node.childNodes #返回子节点列表。 node.childNodes[index].nodeValue 获取XML节点值 node.firstChild #访问第一个节点。等价于pagexml.childNodes[0] doc = minidom.parse(filename) doc.toxml('UTF-8') 返回Node节点的xml表示的文本 Node.attributes["id"] a.name #就是上面的 "id" a.value #属性的值 访问元素属性