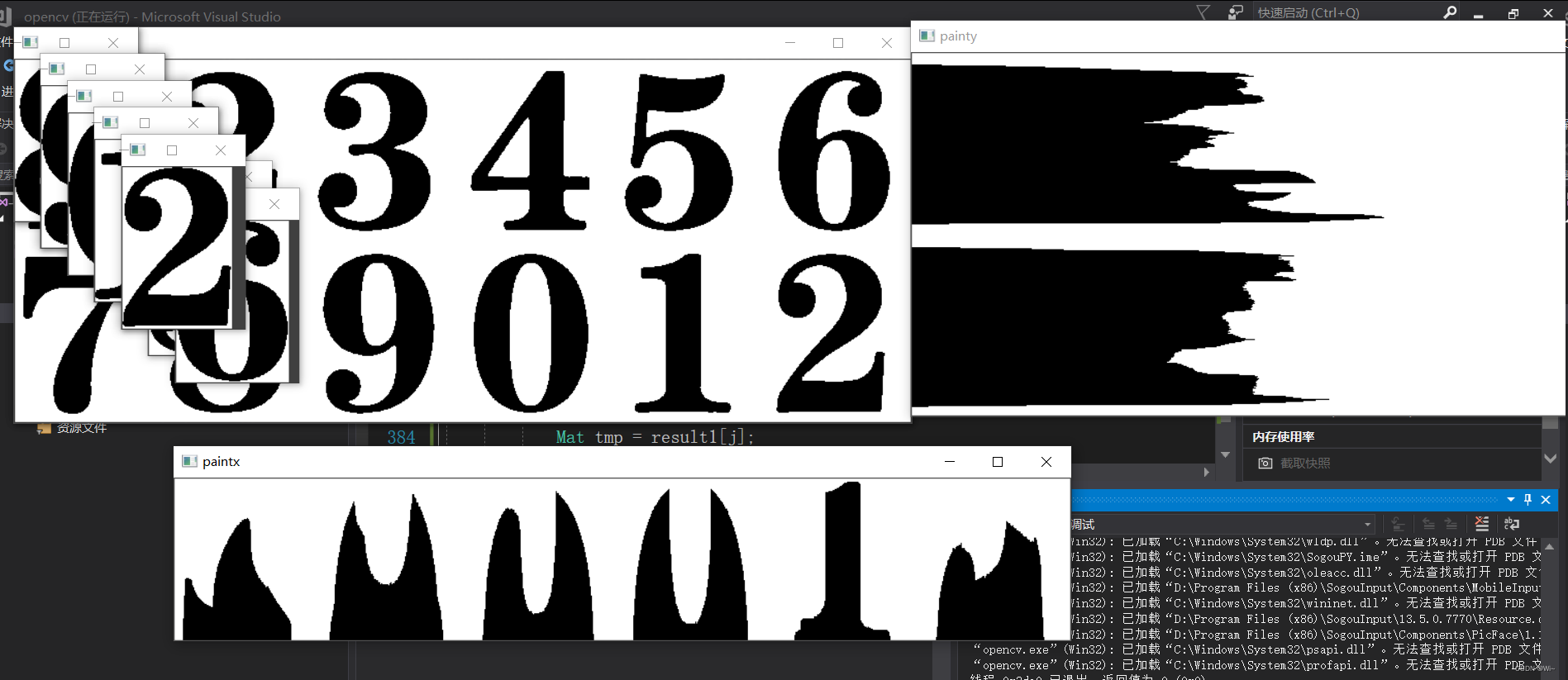
图像水平投影和垂直投影,图像分割
#include <iostream>
#include <opencv2/core/core.hpp>
#include <opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp>
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
#include <fstream>
#include <opencv2/ml.hpp>
#include <cmath>
#include <locale>
#include <codecvt>
#include <string>
using namespace cv;
using namespace std;
using namespace ml;
void thresholdIntegral(Mat inputMat, Mat& outputMat)
{
int nRows = inputMat.rows;
int nCols = inputMat.cols;
Mat sumMat;
integral(inputMat, sumMat);
int S = MAX(nRows, nCols) / 8;
double T = 0.15;
int s2 = S / 2;
int x1, y1, x2, y2, count, sum;
int* p_y1, *p_y2;
uchar* p_inputMat, *p_outputMat;
for (int i = 0; i < nRows; ++i)
{
y1 = i - s2;
y2 = i + s2;
if (y1 < 0)
{
y1 = 0;
}
if (y2 >= nRows)
{
y2 = nRows - 1;
}
p_y1 = sumMat.ptr<int>(y1);
p_y2 = sumMat.ptr<int>(y2);
p_inputMat = inputMat.ptr<uchar>(i);
p_outputMat = outputMat.ptr<uchar>(i);
for (int j = 0; j < nCols; ++j)
{
x1 = j - s2;
x2 = j + s2;
if (x1 < 0)
{
x1 = 0;
}
if (x2 >= nCols)
{
x2 = nCols - 1;
}
count = (x2 - x1)* (y2 - y1);
sum = p_y2[x2] - p_y1[x2] - p_y2[x1] + p_y1[x1];
if ((int)(p_inputMat[j] * count) < (int)(sum* (1.0 - T)))
{
p_outputMat[j] = 0;
}
else
{
p_outputMat[j] = 255;
}
}
}
}
void picshadowx(Mat binary, vector<Mat> &result)
{
Mat paintx(binary.size(), CV_8UC1, Scalar(255));
int* blackcout = new int[binary.cols];
memset(blackcout, 0, binary.cols * 4);
for (int i = 0; i < binary.rows; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < binary.cols; j++)
{
if (binary.at<uchar>(i, j) == 0)
{
blackcout[j]++;
}
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < binary.cols; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < blackcout[i]; j++)
{
paintx.at<uchar>(binary.rows - 1 - j, i) = 0;
}
}
imshow("paintx", paintx);
int startindex = 0;
int endindex = 0;
bool inblock = false;
for (int i = 0; i < paintx.cols; i++)
{
if (!inblock&&blackcout[i] != 0)
{
inblock = true;
startindex = i;
cout << "startindex:" << startindex << endl;
}
if (inblock&&blackcout[i] == 0)
{
endindex = i;
inblock = false;
Mat roi = binary.colRange(startindex, endindex + 1);
result.push_back(roi);
}
}
delete blackcout;
}
void picshadowy(Mat binary,vector<Mat> &result)
{
Mat painty(binary.size(), CV_8UC1, Scalar(255));
int* pointcount = new int[binary.rows];
memset(pointcount, 0, binary.rows * 4);
for (int i = 0; i < binary.rows; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < binary.cols; j++)
{
if (binary.at<uchar>(i, j) == 0)
{
pointcount[i]++;
}
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < binary.rows; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < pointcount[i]; j++)
{
painty.at<uchar>(i, j) = 0;
}
}
imshow("painty", painty);
int startindex = 0;
int endindex = 0;
bool inblock = false;
for (int i = 0; i < painty.rows; i++)
{
if (!inblock&&pointcount[i] != 0)
{
inblock = true;
startindex = i;
cout << "startindex:" << startindex << endl;
}
if (inblock&&pointcount[i] == 0)
{
endindex = i;
inblock = false;
Mat roi = binary.rowRange(startindex, endindex + 1);
result.push_back(roi);
}
}
delete pointcount;
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
Mat src = cv::imread("test_number.jpg");
if (src.empty())
{
cerr << "Problem loading image!!!" << endl;
return -1;
}
imshow("in", src);
Mat gray;
if (src.channels() == 3)
{
cv::cvtColor(src, gray,COLOR_BGR2GRAY);
}
else
{
gray = src;
}
Mat bw2 = Mat::zeros(gray.size(), CV_8UC1);
thresholdIntegral(gray, bw2);
cv::imshow("binary integral", bw2);
vector<Mat> result;
picshadowy(bw2, result);
for (int i = 0; i < result.size(); i++)
{
vector<Mat> result1;
picshadowx(result[i], result1);
for (int j = 0; j < result1.size(); j++)
{
Mat tmp = result1[j];
imshow("test" + to_string(i) + to_string(j), tmp);
}
}
waitKey(0);
return 0;
}