一、Wappalyzer介绍
Wappalyzer 是一款浏览器插件,通过 Wappalyzer 可以识别出网站采用了那种 web 技术。它能够检测出 CMS 和电子商务系统、留言板、javascript 框架,主机面板,分析统计工具和其它的一些 web 系统。The company behind Wappalyzer 还能够收集 web 程序的一些信息用于统计分析,揭示出各种 web 系统的使用率即增长情况。实际 Wappalyzer 就是一个指纹识别工具。
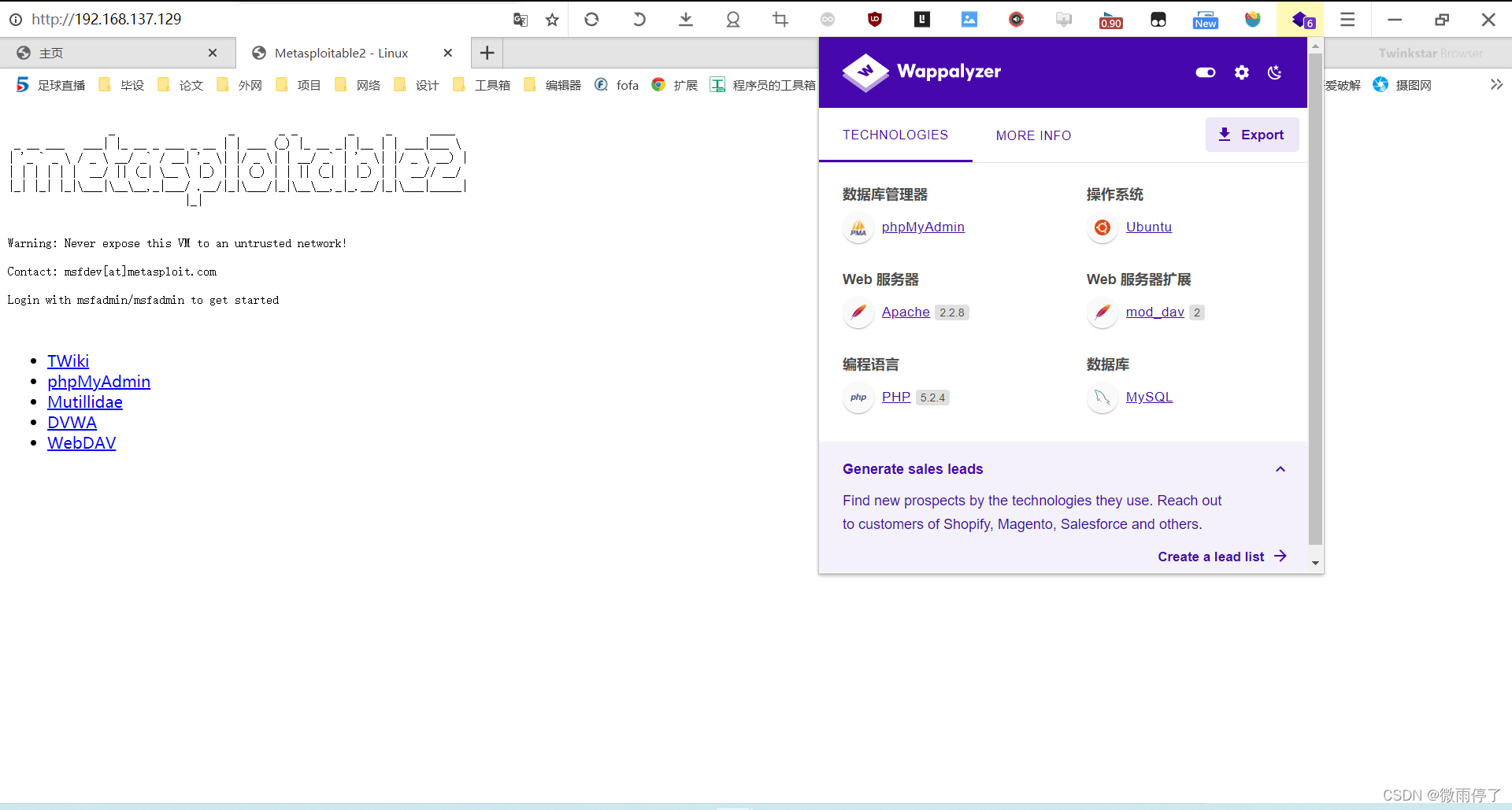
例如:
二、设计原理
系统通过构造HTTP请求与目标Web服务器交互,从其响应数据包信息中提取提取指纹特征信息,然后通过与指纹数据库(Wappalyzer)进行比对,从而获取到Web服务器及应用的组件信息和版本信息。通过发现这些特征信息并对它进行识别可以帮助我们快速地制定渗透策略,是渗透环节中关键的一步。
三、python实现代码
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
"""
作者:wyt
日期:2022年04月17日
"""
# Reference:https://github.com/jwt1399/Sec-Tools
import json
import os
import re
import requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
class Wappalyzer(object):
"""
Python Wappalyzer driver.
"""
def __init__(self, apps_file=None):
"""
Initialize a new Wappalyzer instance.
初始化一个新的Wappalyzer实例。
Parameters
----------
categories : dict
Map of category ids to names, as in apps.json.
apps : dict
Map of app names to app dicts, as in apps.json.
类别:dict类型
分类id到名称的映射,如app.json。
应用:dict类型
应用名称到应用字典的映射,如在app.json中。
"""
with open(os.path.dirname(__file__) + '/apps.json', 'rb') as fd:
obj = json.load(fd)
self.categories = obj['categories']
self.apps = obj['apps']
for name, app in self.apps.items():
self._prepare_app(app)
def _prepare_app(self, app):
"""
Normalize app data, preparing it for the detection phase.
标准化应用程序数据,为检测阶段做好准备。
"""
# Ensure these keys' values are lists
# 确保这些键的值是列表
for key in ['url', 'html', 'script', 'implies']:
value = app.get(key)
if value is None:
app[key] = []
else:
if not isinstance(value, list):
app[key] = [value]
# Ensure these keys exist
# 确保这些键存在
for key in ['headers', 'meta']:
value = app.get(key)
if value is None:
app[key] = {
}
# Ensure the 'meta' key is a dict
# 确保“meta”键是一个字典
obj = app['meta']
if not isinstance(obj, dict):
app['meta'] = {
'generator': obj}
# Ensure keys are lowercase
# 确保键是小写的
for key in ['headers', 'meta']:
obj = app[key]
app[key] = {
k.lower(): v for k, v in obj.items()}
# Prepare regular expression patterns
# 准备正则表达式模式
for key in ['url', 'html', 'script']:
app[key] = [self._prepare_pattern(pattern) for pattern in app[key]]
for key in ['headers', 'meta']:
obj = app[key]
for name, pattern in obj.items():
obj[name] = self._prepare_pattern(obj[name])
def _prepare_pattern(self, pattern):
"""
Strip out key:value pairs from the pattern and compile the regular
expression.
从模式中删除键:值对,并编译正则表达式。
"""
regex, _, rest = pattern.partition('\\;')
try:
return re.compile(regex, re.I)
except re.error as e:
# regex that never matches:
# 从不匹配的正则表达式:
# http://stackoverflow.com/a/1845097/413622
return re.compile(r'(?!x)x')
def _has_app(self, app, webpage):
"""
Determine whether the web page matches the app signature.
判断web页面是否与应用程序签名匹配。
"""
# Search the easiest things first and save the full-text search of the
# HTML for last
for regex in app['url']:
if regex.search(webpage.url):
return True
for name, regex in app['headers'].items():
if name in webpage.headers:
content = webpage.headers[name]
if regex.search(content):
return True
for regex in app['script']:
for script in webpage.scripts:
if regex.search(script):
return True
for name, regex in app['meta'].items():
if name in webpage.meta:
content = webpage.meta[name]
if regex.search(content):
return True
for regex in app['html']:
if regex.search(webpage.html):
return True
def _get_implied_apps(self, detected_apps):
"""
Get the set of apps implied by `detected_apps`.
获取' detected_apps '隐含的一组应用程序。
"""
def __get_implied_apps(apps): # app
_implied_apps = set()
try:
for app in apps:
if 'implies' in self.apps[app]:
_implied_apps.update(set(self.apps[app]['implies']))
return _implied_apps
except:
pass
implied_apps = __get_implied_apps(detected_apps)
all_implied_apps = set()
# Descend recursively until we've found all implied apps
# 递归查询,直到我们找到所有隐含的应用
try:
while not all_implied_apps.issuperset(implied_apps):
all_implied_apps.update(implied_apps)
implied_apps = __get_implied_apps(all_implied_apps)
except:
pass
return all_implied_apps
def get_categories(self, app_name):
"""
Returns a list of the categories for an app name.
返回应用程序名称的类别列表。
"""
cat_nums = self.apps.get(app_name, {
}).get("cats", [])
cat_names = [
self.categories.get("%s" % cat_num, "") for cat_num in cat_nums
]
return cat_names
def analyze(self, webpage):
"""
Return a list of applications that can be detected on the web page.
返回可以在网页上检测到的应用程序列表。
"""
detected_apps = set()
for app_name, app in self.apps.items():
if self._has_app(app, webpage):
detected_apps.add(app_name)
detected_apps |= self._get_implied_apps(detected_apps)
return detected_apps # {'mod_dav', 'PHP', 'Ubuntu', 'Apache'}
def analyze_with_categories(self, webpage):
detected_apps = self.analyze(webpage)
categorised_apps = {
}
for app_name in detected_apps:
cat_names = self.get_categories(app_name)
categorised_apps[app_name] = {
"categories": cat_names}
return categorised_apps
# 初始化一个cms类
class cms(object):
def __init__(self, url, html, headers):
self.url = url
self.html = html
soup = BeautifulSoup(self.html, "html.parser") # 只有经bs4.BeautifulSoup方法解析成的soup才有“soup.title”方法
self.title = soup.title.string if soup.title else 'None' # title
self.headers = headers
self.meta = {
meta['name'].lower(): meta['content'] for meta in
soup.findAll('meta', attrs=dict(name=True, content=True))
}
self.scripts = [script['src'] for script in soup.findAll('script', src=True)]
wappalyzer = Wappalyzer() # 实例化一个Wappalyzer类
self.apps = wappalyzer.analyze(self) # 利用定义好的Wappalyzer方法分析传入对象,返回Wappalyzer中analyze方法识别结果
self.result = ';'.join(self.apps)
# print(self.result)
def info(self):
result = self.result.split(';')
return {
"apps": list(set(result)),
}
if __name__ == '__main__':
url = "http://192.168.137.129/"
headers = {
'user-agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; WOW64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/39.0.2171.71 Safari/537.36'
}
html = requests.get(url=url, headers=headers, timeout=4)
cms = cms(html.url, html.text, html.headers).info()
print(cms)
apps.json部分截图:

python返回结果:
{'apps': ['mod_dav', 'Apache', 'Ubuntu', 'PHP']}
Wappalyzer网页插件分析结果: