self.lstm = nn.LSTM(input_size=n_class, hidden_size=n_hidden, num_layers=n_layers)
输入网络的维度数:26,隐层维度:128,lstm层数:n_layers:1
LSTM: 单向LSTM,D=1
input:[3, 10, 26] sequence len=3, batch=10, input_size=26
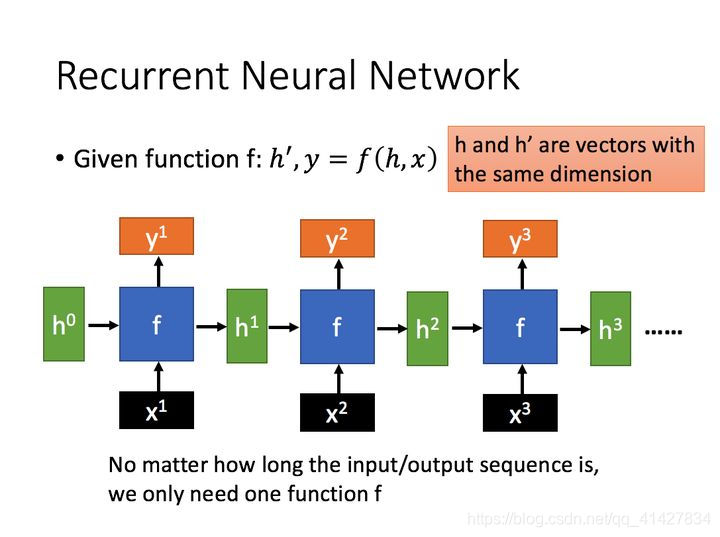
# 可以理解为,sequence length有多长就有几个上图中的F
h0:[1, 10, 128] n_layers = 1, batch=10, hidden_size=128
c0:[1, 10, 128] n_layers = 1, batch=10, hidden_size=128
输入,3个细胞单元作为输入,每个细胞单元接收26维的输入,一个batch为10条数据
输出:output, (h_n, c_n)
output: [3, 10, 128],3个细胞单元,一批次10个数据,隐层维度为128,输出最后一层每个细胞单元的隐层输出;
output保存了最后一层,每个time step的输出h
h_n保存每一层,最后一个time-step的输出h
c_n保存每一层,最后一个time-step的输出c
官方给定实例:
# Examples::
# 初始化模型
rnn = nn.LSTM(10, 20, 2) # 输入特征的维度:10,隐层维度:20 ,LSTM层数:2
# 输入数据格式
input = torch.randn(5, 3, 10) # 句子长度:5,batch_size:3,输入特征的维度:10
# 隐层结构
h0 = torch.randn(2, 3, 20) # LSTM层:2,batch_size:3,隐层参数维度:20
# 细胞单元结构
c0 = torch.randn(2, 3, 20) # 同上
# 输出结构
output, (hn, cn) = rnn(input, (h0, c0))
"""
output:LSTM最后一层隐状态的输出,维度:(5, 3, 20)
hn:最后一个timestep的隐状态结果,维度:(1, 3, 20)
cn:最后一个timestep的细胞单元的结果,维度:(1, 3, 20)
"""BiLSTM-torch调用:
# 单层变双层,单向变为双向
# 举例解决:
# 单层Bilstm, 输入数据,一个batch包含26条数据,每条数据为27x27,类别数为27,每个单元包含隐藏单元为5
# 定义BiLSTM时:
bilstm = nn.LSTM(input_size=27, hidden_size=5, bidirectional=True)
# 输入input维度应为:[sequence length, batch size, input_size]即需通过torch.transpose(0, 1)改变维度
inputs shape: [27, 26, 27]
# 隐藏定义:[Bilstm:2 x 层数默认:1, batch_size:26, 每个单元包含隐藏单元:5]
h0 shape: [2x1, 26, 5]
c0 shape: [2x1, 26, 5] #细胞状态同上
output, (h_n, c_n) = bilstm(inputs, (h0, c0)
#同lstm,output包含最后一层所有细胞的隐层输出,
# [sequence length, batch size, H_{out}*2]
output shape: [27, 26, 5*2]
# h_n 包含最后一个细胞的最后一个时间步的隐层输出
# [D * num_layers, batch size, H_{out}]
h_n shape: [2, 26, 5]
# c_n同上
c_n shape: [2, 26, 5]
pytorch实现LSTM例子:
import numpy as np
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from torch.nn.modules import loss, module
import torch.optim as optim
def make_batch():
input_batch, target_batch = [], []
for seq in seq_data:
input = [word_dict[n] for n in seq[:-1]] #到最后一个字母
target = word_dict[seq[-1]] # 最后一个标签,预测最后一个单词
input_batch.append(np.eye(n_class)[input])
target_batch.append(target)
print("input:{}, target:{}".format(input, target))
return input_batch, target_batch
"""
np.eye(3):代表一个维度为3的单位矩阵
np.eye(x)[N]: 代表取出维度为x的单位矩阵的第N行,用于构造one-hot表示
x.transpose(0, 1):交换0,1两个维度
例:x为[10, 3, 26] x.transpose(0, 1)为[3, 10 ,26] # 有啥意义
Examples::
>>> rnn = nn.LSTM(10, 20, 2) #
input_size: The number of expected features in the input `x`
hidden_size: The number of features in the hidden state `h`
num_layers: Number of recurrent layers. E.g., setting ``num_layers=2``
>>> input = torch.randn(5, 3, 10) : N,L,H_{in}或L,N,H_{in}
输入向量的长度, 一次传入多少条数据,单词向量的维度
L ={} & \text{sequence length} \\
N ={} & \text{batch size} \\
H_{in} ={} & \text{input\_size} \\
>>> h0 = torch.randn(2, 3, 20)
(D * \text{num\_layers}, N, H_{out}), BiLSTM: D=2, LSTM: D=1
H_{out} ={} & \text{proj\_size if } \text{proj\_size}>0 \text{ otherwise hidden\_size} \\\end{aligned}
>>> c0 = torch.randn(2, 3, 20)
(D * \text{num\_layers}, N, H_{cell})
H_{cell} ={} & \text{hidden\_size} \\
>>> output, (hn, cn) = rnn(input, (h0, c0))
output保存了最后一层,每个time step的输出h,如果是双向LSTM,每个time step的输出h = [h正向, h逆向] (同一个time step的正向和逆向的h连接起来)。
h_n保存了每一层,最后一个time step的输出h,如果是双向LSTM,单独保存前向和后向的最后一个time step的输出h。
c_n与h_n一致,只是它保存的是c的值。
output是一个三维的张量,第一维表示序列长度,第二维表示一批的样本数(batch),第三维是 hidden_size(隐藏层大小) * num_directions
"""
class TextLSTM(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(TextLSTM, self).__init__()
self.lstm = nn.LSTM(input_size=n_class, hidden_size=n_hidden)
# input_size:26
# hidden_size:128
# mode:'LSTM'
# num_layers:1
self.W = nn.Linear(
n_hidden, n_class, bias=False
) #LSTM+一个线性层加偏置,最后softmax输出 # out_features:26 # in_features:128
self.b = nn.Parameter(torch.ones(
[n_class])) # P的大小写有何影响,nn.parameter报错,必须得是nn.Parameter
def forward(self, x):
# print('x:{}, x_size:{}'.format(
# x, x.size())) # shape:torch.Size([10, 3, 26])
input = x.transpose(0, 1) # torch.Size([3, 10, 26]) ****有何意义
# print('input:{}, input_size:{}'.format(input, input.size()))
hidden_state = torch.zeros(1, len(x),
n_hidden) # shape:torch.Size([1, 10, 128])
cell_state = torch.zeros(1, len(x),
n_hidden) # shape:torch.Size([1, 10, 128])
# 为啥少了一个维度啊????
outputs, (_, _) = self.lstm(input, (hidden_state, cell_state))
# _1,2: torch.Size([1, 10, 128])
# print("outputs_size:{}".format(
# outputs.size())) # torch.Size([3, 10, 128])
outputs = outputs[-1] # outputs: torch.Size([10, 128])
# 使用outputs的原因:保留最后一层所有隐层的输出,可以尽可能包含所有的局部信息,减少RNN的梯度消失、最后输出的向量与较后的cell有关
model = self.W(
outputs
) + self.b # shape:torch.Size([10, 26]) batch_size, n_class
# print("model:{}".format(model))
return model
if __name__ == '__main__':
n_step = 3
n_hidden = 128
char_arr = [c for c in 'abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz']
word_dict = {w: i for i, w in enumerate(char_arr)}
number_dict = {i: w for i, w in enumerate(char_arr)}
print(number_dict)
# print(word_dict)
n_class = len(word_dict)
seq_data = [
'make', 'need', 'coal', 'word', 'love', 'hate', 'live', 'home', 'hash',
'star'
]
model = TextLSTM()
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer = optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=0.001)
input_batch, target_batch = make_batch() # 原本shape[10, 3], [10]
input_batch = torch.FloatTensor(
input_batch
) # shape:torch.Size([10, 3, 26]) 10条数据,每条数据长度为3,one-hot表示维度为26
target_batch = torch.LongTensor(target_batch)
for epoch in range(1000):
optimizer.zero_grad()
output = model(input_batch)
loss1 = criterion(output, target_batch)
if (epoch + 1) % 100 == 0:
print('Epoch:', '%04d' % (epoch + 1), 'cost =',
'{:.6f}'.format(loss1))
loss1.backward()
optimizer.step()
inputs = input_batch[:4]
# inputs = inputs.unsqueeze(0)
print('inputs:{}, inputs_size:{}'.format(inputs, np.shape(inputs)))
print("mdoel:{}".format(model)) #model就是一个输入26维,输出128维的lstm
print("mdoel(inputs):{}".format(model(inputs)))
predict = model(inputs).data.max(1, keepdim=True)[1]
# output = model(input_batch)
print("predict:{}".format(predict))