前面两篇说的有点多了,不过多了解点东西也挺好的,遇到问题时可以有更多的思路,真正驱动是从这一块开始。一般BSP的camera都是完好的,我们只用关心驱动这些就可以了。
1. V4L2
1)简介
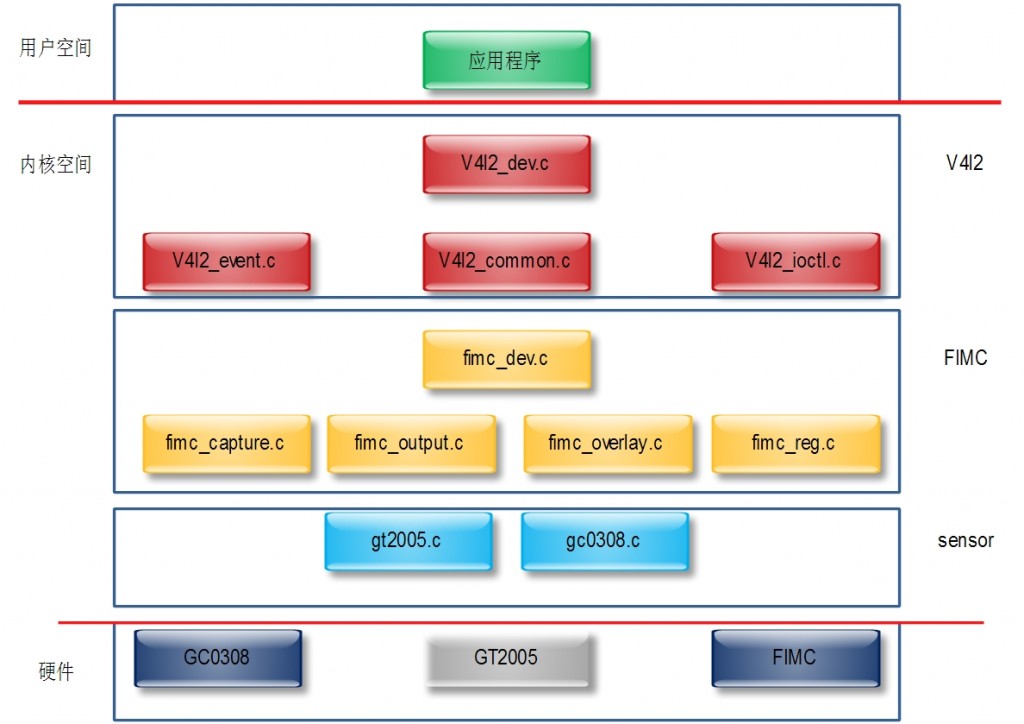
在Linux中,摄像头方面的标准化程度比较高,这个标准就是V4L2驱动程序,这也是业界比较公认的方式。
V4L全称是Video for Linux,是Linux内核中标准的关于视频驱动程序,目前使用比较多的版本是Video for Linux 2,简称V4L2。它为Linux下的视频驱动提供了统一的接口,使得应用程序可以使用统一的API操作不同的视频设备。从内核空间到用户空间,主要的数据流和控制类均由V4L2驱动程序的框架来定义。
V4L2驱动程序一般只提供Video数据的获得,而如何实现视频预览,如何向上层发送数据,如何把纯视频流和取景器、视频录制等实际业务组织起来,都是camera的硬件抽象层需要负责的工作。
V4L2驱动核心实现为如下文件:drivers/media/video/v4l2-dev.c。
V4l2-dev.h中定义的video_device是V4L2驱动程序的核心数据结构,它为具体的摄像头sensor驱动提供了接口调用。
V4l2的采集过程(应用程序):
1) 打开设备,获得文件描述符;
2) 设置图片格式;
3) 分配缓冲区;
4) 启动采集过程,读取数据;
5) 停止采集,关闭设备。
2)数据结构
V4L2的主要数据结构是video_device,定义在v4l2_dev.h中:
- struct video_device
- {
- /* device ops */
- const struct v4l2_file_operations *fops; /*接口函数指针*/
- /* sysfs */
- struct device dev; /* v4l 设备结构 */
- struct cdev *cdev; /* 字符设备结构*/
- /* Set either parent or v4l2_dev if your driver uses v4l2_device */
- struct device *parent; /* 设备父指针 */
- struct v4l2_device *v4l2_dev; /* v4l2设备指针*/
- /* device info */
- char name[32]; /*设备名称*/
- int vfl_type;
- /* 'minor' is set to -1 if the registration failed */
- int minor; /*次设备号*/
- u16 num;
- /* use bitops to set/clear/test flags */
- unsigned long flags;
- /* attribute to differentiate multiple indices on one physical device */
- int index;
- /* V4L2 file handles */
- spinlock_t fh_lock; /* Lock for all v4l2_fhs */
- struct list_head fh_list; /* List of struct v4l2_fh */
- int debug; /* debug 级别*/
- /* Video 标准变量 */
- v4l2_std_id tvnorms; /* Supported tv norms */
- v4l2_std_id current_norm; /* Current tvnorm */
- /* 回调函数 */
- void (*release)(struct video_device *vdev);
- /* ioctl 回调函数 */
- const struct v4l2_ioctl_ops *ioctl_ops;
- };
主要接口函数有:
intvideo_register_device(struct video_device *vdev, int type, int nr);
static intv4l2_ioctl(struct inode *inode, struct file *filp, unsigned int cmd, unsigned long arg);
2. FIMC
1)简介
FIMC这个模块不仅仅是一个摄像头的控制接口,它还承担着V4L2的output功能和overlay的功能。
FIMC的驱动在内核中的位置:drivers/media/video/samsung/fimc
它包含下边的文件:
fimc_regs.c
fimc_capture.c
fimc_dev.c
fimc_output.c
fimc_overlay.c
fimc_v4l2.c
它们的组织关系如下:
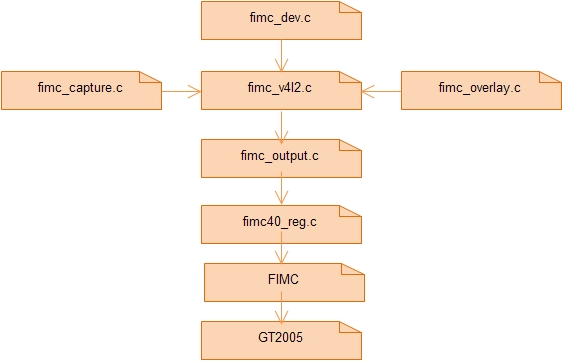
可以看到,FIMC的驱动实现了v4l2所有的接口,可以分为v4l2-input设备接口,v4l2-output设备接口以及v4l2-overlay设备接口。这里我们主要关注v4l2-input设备接口,因为摄像头属于视频输入设备。
fimc_v4l2.c里面注册了很多的回调函数,都是用于实现v4l2的标准接口的,但是这些回调函数基本上都不是在fimc_v4l2.c里面实现的,而是有相应的.c分别去实现。比如:
v4l2-input设备的操作实现:fimc_capture.c
v4l2-output设备的操作实现: fimc_output.c
v4l2-overlay设备的操作实现: fimc_overlay.c
这些代码其实都是和具体硬件操作无关的,这个驱动把所有操作硬件寄存器的代码都写到一个文件里面了,就是fimc40_regs.c。这样把硬件相关的代码和硬件无关的代码分开来实现是非常好的方式,可以最大限度的实现代码复用。
2) 数据结构
FIMC的主要数据结构fimc_control,定义在fimc.h中:
- struct fimc_control {
- int id; /* 控制器 id */
- char name[16];
- atomic_t in_use;
- void __iomem *regs; /* 寄存器 i/o */
- struct clk *clk; /* interface clock */
- struct regulator *regulator; /* pd regulator */
- struct fimc_meminfo mem; /* for reserved mem */
- /* kernel helpers */
- struct mutex lock; /* controller lock */
- struct mutex alloc_lock;
- struct mutex v4l2_lock;
- wait_queue_head_t wq;
- struct device *dev;
- int irq;
- /* v4l2 related */
- struct video_device *vd;
- struct v4l2_device v4l2_dev;
- /* fimc specific */
- struct fimc_limit *limit; /* H/W limitation */
- struct s3c_platform_camera *cam; /* activated camera */
- struct fimc_capinfo *cap; /* capture dev info */
- struct fimc_outinfo *out; /* output dev info */
- struct fimc_fbinfo fb; /* fimd info */
- struct fimc_scaler sc; /* scaler info */
- struct fimc_effect fe; /* fimc effect info */
- enum fimc_status status;
- enum fimc_log log;
- u32 ctx_busy[FIMC_MAX_CTXS];
- };
- struct video_device fimc_video_device[FIMC_DEVICES] = {
- [0] = {
- .fops = &fimc_fops,
- .ioctl_ops = &fimc_v4l2_ops,
- .release = fimc_vdev_release,
- },
- [1] = {
- .fops = &fimc_fops,
- .ioctl_ops = &fimc_v4l2_ops,
- .release = fimc_vdev_release,
- },
- [2] = {
- .fops = &fimc_fops,
- .ioctl_ops = &fimc_v4l2_ops,
- .release = fimc_vdev_release,
- },
- };
fb_ops结构体是针对v4l2设备的基本操作,定义如下:
- static const struct v4l2_file_operations fimc_fops = {
- .owner = THIS_MODULE,
- .open = fimc_open,
- .release = fimc_release,
- .ioctl = video_ioctl2,
- .read = fimc_read,
- .write = fimc_write,
- .mmap = fimc_mmap,
- .poll = fimc_poll,
- };
3)FIMC初始设置
在S5PV210中,FIMC初始设置代码在 /drivers/ arch/arm/mach-s5pv210/mach-smdkv310.c中:
- static struct s3c_platform_fimc fimc_plat = {
- .srclk_name = "mout_mpll",
- .clk_name = "sclk_fimc",
- .lclk_name = "sclk_fimc_lclk",
- .clk_rate = 166750000,
- .default_cam = CAMERA_CSI_C,
- .camera = {
- &mt9p111,//5M back cam
- &s5k6aafx,///1.3M front cam
- },
- .hw_ver = 0x43,
- };
对于GPIO的配置代码在 /drivers/ arch/arm/mach-s5pv210/setup-fimc0.c中:
- oid s3c_fimc0_cfg_gpio(struct platform_device *pdev)
- {
- int i = 0;
- /* CAM A port(b0010) : PCLK, VSYNC, HREF, DATA[0-4] */
- for (i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
- s3c_gpio_cfgpin(S5PV210_GPE0(i), S3C_GPIO_SFN(2));
- s3c_gpio_setpull(S5PV210_GPE0(i), S3C_GPIO_PULL_NONE);
- }
- /* CAM A port(b0010) : DATA[5-7], CLKOUT(MIPI CAM also), FIELD */
- for (i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
- s3c_gpio_cfgpin(S5PV210_GPE1(i), S3C_GPIO_SFN(2));
- s3c_gpio_setpull(S5PV210_GPE1(i), S3C_GPIO_PULL_NONE);
- }
- /* CAM B port(b0011) : DATA[0-7] */
- for (i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
- s3c_gpio_cfgpin(S5PV210_GPJ0(i), S3C_GPIO_SFN(3));
- s3c_gpio_setpull(S5PV210_GPJ0(i), S3C_GPIO_PULL_NONE);
- }
- /* CAM B port(b0011) : PCLK, VSYNC, HREF, FIELD, CLCKOUT */
- for (i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
- s3c_gpio_cfgpin(S5PV210_GPJ1(i), S3C_GPIO_SFN(3));
- s3c_gpio_setpull(S5PV210_GPJ1(i), S3C_GPIO_PULL_NONE);
- }
- }
4)接口函数
FIMC的主要回调函数如下,实现在fimc_v4l2.c中:
- onst struct v4l2_ioctl_ops fimc_v4l2_ops = {
- .vidioc_querycap = fimc_querycap,
- .vidioc_reqbufs = fimc_reqbufs,
- .vidioc_querybuf = fimc_querybuf,
- .vidioc_g_ctrl = fimc_g_ctrl,
- .vidioc_s_ctrl = fimc_s_ctrl,
- .vidioc_s_ext_ctrls = fimc_s_ext_ctrls,
- .vidioc_cropcap = fimc_cropcap,
- .vidioc_g_crop = fimc_g_crop,
- .vidioc_s_crop = fimc_s_crop,
- .vidioc_streamon = fimc_streamon,
- .vidioc_streamoff = fimc_streamoff,
- .vidioc_qbuf = fimc_qbuf,
- .vidioc_dqbuf = fimc_dqbuf,
- .vidioc_enum_fmt_vid_cap = fimc_enum_fmt_vid_capture,
- .vidioc_g_fmt_vid_cap = fimc_g_fmt_vid_capture,
- .vidioc_s_fmt_vid_cap = fimc_s_fmt_vid_capture,
- .vidioc_try_fmt_vid_cap = fimc_try_fmt_vid_capture,
- .vidioc_enum_input = fimc_enum_input,
- .vidioc_g_input = fimc_g_input,
- .vidioc_s_input = fimc_s_input,
- .vidioc_g_parm = fimc_g_parm,
- .vidioc_s_parm = fimc_s_parm,
- .vidioc_queryctrl = fimc_queryctrl,
- .vidioc_querymenu = fimc_querymenu,
- .vidioc_g_fmt_vid_out = fimc_g_fmt_vid_out,
- .vidioc_s_fmt_vid_out = fimc_s_fmt_vid_out,
- .vidioc_try_fmt_vid_out = fimc_try_fmt_vid_out,
- .vidioc_g_fbuf = fimc_g_fbuf,
- .vidioc_s_fbuf = fimc_s_fbuf,
- .vidioc_try_fmt_vid_overlay = fimc_try_fmt_overlay,
- .vidioc_g_fmt_vid_overlay = fimc_g_fmt_vid_overlay,
- .vidioc_s_fmt_vid_overlay = fimc_s_fmt_vid_overlay,
- };
对于寄存器的操作,实现都在fimc_regs.c文件中,如
- int fimc_hwset_camera_source(struct fimc_control *ctrl)
- {
- struct s3c_platform_camera *cam = ctrl->cam;
- u32 cfg = 0;
- cfg |= S3C_CISRCFMT_ITU601_8BIT;
- cfg |= cam->order422;
- if (cam->type == CAM_TYPE_ITU)
- cfg |= cam->fmt;
- cfg |= S3C_CISRCFMT_SOURCEHSIZE(cam->width);
- cfg |= S3C_CISRCFMT_SOURCEVSIZE(cam->height);
- writel(cfg, ctrl->regs + S3C_CISRCFMT);
- return 0;
- }
- int fimc_hwset_enable_irq(struct fimc_control *ctrl, int overflow, int level)
- {
- u32 cfg = readl(ctrl->regs + S3C_CIGCTRL);
- cfg &= ~(S3C_CIGCTRL_IRQ_OVFEN | S3C_CIGCTRL_IRQ_LEVEL);
- cfg |= S3C_CIGCTRL_IRQ_ENABLE;
- if (overflow)
- cfg |= S3C_CIGCTRL_IRQ_OVFEN;
- if (level)
- cfg |= S3C_CIGCTRL_IRQ_LEVEL;
- writel(cfg, ctrl->regs + S3C_CIGCTRL);
- return 0;
- }
前面两篇说的有点多了,不过多了解点东西也挺好的,遇到问题时可以有更多的思路,真正驱动是从这一块开始。一般BSP的camera都是完好的,我们只用关心驱动这些就可以了。
1. V4L2
1)简介
在Linux中,摄像头方面的标准化程度比较高,这个标准就是V4L2驱动程序,这也是业界比较公认的方式。
V4L全称是Video for Linux,是Linux内核中标准的关于视频驱动程序,目前使用比较多的版本是Video for Linux 2,简称V4L2。它为Linux下的视频驱动提供了统一的接口,使得应用程序可以使用统一的API操作不同的视频设备。从内核空间到用户空间,主要的数据流和控制类均由V4L2驱动程序的框架来定义。
V4L2驱动程序一般只提供Video数据的获得,而如何实现视频预览,如何向上层发送数据,如何把纯视频流和取景器、视频录制等实际业务组织起来,都是camera的硬件抽象层需要负责的工作。
V4L2驱动核心实现为如下文件:drivers/media/video/v4l2-dev.c。
V4l2-dev.h中定义的video_device是V4L2驱动程序的核心数据结构,它为具体的摄像头sensor驱动提供了接口调用。
V4l2的采集过程(应用程序):
1) 打开设备,获得文件描述符;
2) 设置图片格式;
3) 分配缓冲区;
4) 启动采集过程,读取数据;
5) 停止采集,关闭设备。

2)数据结构
V4L2的主要数据结构是video_device,定义在v4l2_dev.h中:
- struct video_device
- {
- /* device ops */
- const struct v4l2_file_operations *fops; /*接口函数指针*/
- /* sysfs */
- struct device dev; /* v4l 设备结构 */
- struct cdev *cdev; /* 字符设备结构*/
- /* Set either parent or v4l2_dev if your driver uses v4l2_device */
- struct device *parent; /* 设备父指针 */
- struct v4l2_device *v4l2_dev; /* v4l2设备指针*/
- /* device info */
- char name[32]; /*设备名称*/
- int vfl_type;
- /* 'minor' is set to -1 if the registration failed */
- int minor; /*次设备号*/
- u16 num;
- /* use bitops to set/clear/test flags */
- unsigned long flags;
- /* attribute to differentiate multiple indices on one physical device */
- int index;
- /* V4L2 file handles */
- spinlock_t fh_lock; /* Lock for all v4l2_fhs */
- struct list_head fh_list; /* List of struct v4l2_fh */
- int debug; /* debug 级别*/
- /* Video 标准变量 */
- v4l2_std_id tvnorms; /* Supported tv norms */
- v4l2_std_id current_norm; /* Current tvnorm */
- /* 回调函数 */
- void (*release)(struct video_device *vdev);
- /* ioctl 回调函数 */
- const struct v4l2_ioctl_ops *ioctl_ops;
- };
主要接口函数有:
intvideo_register_device(struct video_device *vdev, int type, int nr);
static intv4l2_ioctl(struct inode *inode, struct file *filp, unsigned int cmd, unsigned long arg);
2. FIMC
1)简介
FIMC这个模块不仅仅是一个摄像头的控制接口,它还承担着V4L2的output功能和overlay的功能。
FIMC的驱动在内核中的位置:drivers/media/video/samsung/fimc
它包含下边的文件:
fimc_regs.c
fimc_capture.c
fimc_dev.c
fimc_output.c
fimc_overlay.c
fimc_v4l2.c
它们的组织关系如下:

可以看到,FIMC的驱动实现了v4l2所有的接口,可以分为v4l2-input设备接口,v4l2-output设备接口以及v4l2-overlay设备接口。这里我们主要关注v4l2-input设备接口,因为摄像头属于视频输入设备。
fimc_v4l2.c里面注册了很多的回调函数,都是用于实现v4l2的标准接口的,但是这些回调函数基本上都不是在fimc_v4l2.c里面实现的,而是有相应的.c分别去实现。比如:
v4l2-input设备的操作实现:fimc_capture.c
v4l2-output设备的操作实现: fimc_output.c
v4l2-overlay设备的操作实现: fimc_overlay.c
这些代码其实都是和具体硬件操作无关的,这个驱动把所有操作硬件寄存器的代码都写到一个文件里面了,就是fimc40_regs.c。这样把硬件相关的代码和硬件无关的代码分开来实现是非常好的方式,可以最大限度的实现代码复用。
2) 数据结构
FIMC的主要数据结构fimc_control,定义在fimc.h中:
- struct fimc_control {
- int id; /* 控制器 id */
- char name[16];
- atomic_t in_use;
- void __iomem *regs; /* 寄存器 i/o */
- struct clk *clk; /* interface clock */
- struct regulator *regulator; /* pd regulator */
- struct fimc_meminfo mem; /* for reserved mem */
- /* kernel helpers */
- struct mutex lock; /* controller lock */
- struct mutex alloc_lock;
- struct mutex v4l2_lock;
- wait_queue_head_t wq;
- struct device *dev;
- int irq;
- /* v4l2 related */
- struct video_device *vd;
- struct v4l2_device v4l2_dev;
- /* fimc specific */
- struct fimc_limit *limit; /* H/W limitation */
- struct s3c_platform_camera *cam; /* activated camera */
- struct fimc_capinfo *cap; /* capture dev info */
- struct fimc_outinfo *out; /* output dev info */
- struct fimc_fbinfo fb; /* fimd info */
- struct fimc_scaler sc; /* scaler info */
- struct fimc_effect fe; /* fimc effect info */
- enum fimc_status status;
- enum fimc_log log;
- u32 ctx_busy[FIMC_MAX_CTXS];
- };
- struct video_device fimc_video_device[FIMC_DEVICES] = {
- [0] = {
- .fops = &fimc_fops,
- .ioctl_ops = &fimc_v4l2_ops,
- .release = fimc_vdev_release,
- },
- [1] = {
- .fops = &fimc_fops,
- .ioctl_ops = &fimc_v4l2_ops,
- .release = fimc_vdev_release,
- },
- [2] = {
- .fops = &fimc_fops,
- .ioctl_ops = &fimc_v4l2_ops,
- .release = fimc_vdev_release,
- },
- };
fb_ops结构体是针对v4l2设备的基本操作,定义如下:
- static const struct v4l2_file_operations fimc_fops = {
- .owner = THIS_MODULE,
- .open = fimc_open,
- .release = fimc_release,
- .ioctl = video_ioctl2,
- .read = fimc_read,
- .write = fimc_write,
- .mmap = fimc_mmap,
- .poll = fimc_poll,
- };
3)FIMC初始设置
在S5PV210中,FIMC初始设置代码在 /drivers/ arch/arm/mach-s5pv210/mach-smdkv310.c中:
- static struct s3c_platform_fimc fimc_plat = {
- .srclk_name = "mout_mpll",
- .clk_name = "sclk_fimc",
- .lclk_name = "sclk_fimc_lclk",
- .clk_rate = 166750000,
- .default_cam = CAMERA_CSI_C,
- .camera = {
- &mt9p111,//5M back cam
- &s5k6aafx,///1.3M front cam
- },
- .hw_ver = 0x43,
- };
对于GPIO的配置代码在 /drivers/ arch/arm/mach-s5pv210/setup-fimc0.c中:
- oid s3c_fimc0_cfg_gpio(struct platform_device *pdev)
- {
- int i = 0;
- /* CAM A port(b0010) : PCLK, VSYNC, HREF, DATA[0-4] */
- for (i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
- s3c_gpio_cfgpin(S5PV210_GPE0(i), S3C_GPIO_SFN(2));
- s3c_gpio_setpull(S5PV210_GPE0(i), S3C_GPIO_PULL_NONE);
- }
- /* CAM A port(b0010) : DATA[5-7], CLKOUT(MIPI CAM also), FIELD */
- for (i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
- s3c_gpio_cfgpin(S5PV210_GPE1(i), S3C_GPIO_SFN(2));
- s3c_gpio_setpull(S5PV210_GPE1(i), S3C_GPIO_PULL_NONE);
- }
- /* CAM B port(b0011) : DATA[0-7] */
- for (i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
- s3c_gpio_cfgpin(S5PV210_GPJ0(i), S3C_GPIO_SFN(3));
- s3c_gpio_setpull(S5PV210_GPJ0(i), S3C_GPIO_PULL_NONE);
- }
- /* CAM B port(b0011) : PCLK, VSYNC, HREF, FIELD, CLCKOUT */
- for (i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
- s3c_gpio_cfgpin(S5PV210_GPJ1(i), S3C_GPIO_SFN(3));
- s3c_gpio_setpull(S5PV210_GPJ1(i), S3C_GPIO_PULL_NONE);
- }
- }
4)接口函数
FIMC的主要回调函数如下,实现在fimc_v4l2.c中:
- onst struct v4l2_ioctl_ops fimc_v4l2_ops = {
- .vidioc_querycap = fimc_querycap,
- .vidioc_reqbufs = fimc_reqbufs,
- .vidioc_querybuf = fimc_querybuf,
- .vidioc_g_ctrl = fimc_g_ctrl,
- .vidioc_s_ctrl = fimc_s_ctrl,
- .vidioc_s_ext_ctrls = fimc_s_ext_ctrls,
- .vidioc_cropcap = fimc_cropcap,
- .vidioc_g_crop = fimc_g_crop,
- .vidioc_s_crop = fimc_s_crop,
- .vidioc_streamon = fimc_streamon,
- .vidioc_streamoff = fimc_streamoff,
- .vidioc_qbuf = fimc_qbuf,
- .vidioc_dqbuf = fimc_dqbuf,
- .vidioc_enum_fmt_vid_cap = fimc_enum_fmt_vid_capture,
- .vidioc_g_fmt_vid_cap = fimc_g_fmt_vid_capture,
- .vidioc_s_fmt_vid_cap = fimc_s_fmt_vid_capture,
- .vidioc_try_fmt_vid_cap = fimc_try_fmt_vid_capture,
- .vidioc_enum_input = fimc_enum_input,
- .vidioc_g_input = fimc_g_input,
- .vidioc_s_input = fimc_s_input,
- .vidioc_g_parm = fimc_g_parm,
- .vidioc_s_parm = fimc_s_parm,
- .vidioc_queryctrl = fimc_queryctrl,
- .vidioc_querymenu = fimc_querymenu,
- .vidioc_g_fmt_vid_out = fimc_g_fmt_vid_out,
- .vidioc_s_fmt_vid_out = fimc_s_fmt_vid_out,
- .vidioc_try_fmt_vid_out = fimc_try_fmt_vid_out,
- .vidioc_g_fbuf = fimc_g_fbuf,
- .vidioc_s_fbuf = fimc_s_fbuf,
- .vidioc_try_fmt_vid_overlay = fimc_try_fmt_overlay,
- .vidioc_g_fmt_vid_overlay = fimc_g_fmt_vid_overlay,
- .vidioc_s_fmt_vid_overlay = fimc_s_fmt_vid_overlay,
- };
对于寄存器的操作,实现都在fimc_regs.c文件中,如
- int fimc_hwset_camera_source(struct fimc_control *ctrl)
- {
- struct s3c_platform_camera *cam = ctrl->cam;
- u32 cfg = 0;
- cfg |= S3C_CISRCFMT_ITU601_8BIT;
- cfg |= cam->order422;
- if (cam->type == CAM_TYPE_ITU)
- cfg |= cam->fmt;
- cfg |= S3C_CISRCFMT_SOURCEHSIZE(cam->width);
- cfg |= S3C_CISRCFMT_SOURCEVSIZE(cam->height);
- writel(cfg, ctrl->regs + S3C_CISRCFMT);
- return 0;
- }
- int fimc_hwset_enable_irq(struct fimc_control *ctrl, int overflow, int level)
- {
- u32 cfg = readl(ctrl->regs + S3C_CIGCTRL);
- cfg &= ~(S3C_CIGCTRL_IRQ_OVFEN | S3C_CIGCTRL_IRQ_LEVEL);
- cfg |= S3C_CIGCTRL_IRQ_ENABLE;
- if (overflow)
- cfg |= S3C_CIGCTRL_IRQ_OVFEN;
- if (level)
- cfg |= S3C_CIGCTRL_IRQ_LEVEL;
- writel(cfg, ctrl->regs + S3C_CIGCTRL);
- return 0;
- }