文章目录
Practical Deep Raw Image Denoising on Mobile Devices(huber linear regression)
code:https://github.com/MegEngine/PMRID
其他相关博客:https://blog.csdn.net/zjy_snow/article/details/124385456
1.DNG 文件处理 pipeline
关于DNG文件的处理,主要查看 SIDD 的仓库 simple-camera-pipeline.
打印bayer pattern格式
pattern = “”.join([chr(short_raw.color_desc[i]) for i in short_raw.raw_pattern.flatten()])
或者
cfa_pattern_str = “”.join([“RGB”[i] for i in cfa_pattern])
下面demo_single.py输入dng raw后,可以得到各个阶段的输出结果。
# (demo_single.py)
import glob
import os
import cv2
import numpy as np
from python.pipeline import run_pipeline_v2
from python.pipeline_utils import get_visible_raw_image, get_metadata
params = {
'input_stage': 'raw', # options: 'raw', 'normal', 'white_balance', 'demosaic', 'xyz', 'srgb', 'gamma', 'tone'
'output_stage': 'tone', # options: 'normal', 'white_balance', 'demosaic', 'xyz', 'srgb', 'gamma', 'tone'
'save_as': 'png', # options: 'jpg', 'png', 'tif', etc.
'demosaic_type': 'EA',
'save_dtype': np.uint8
}
image_path = r'D:\dataset\pratical_raw\reno10x_noise\gray_scale_chart\RAW_2020_02_20_13_11_10_787\DNG_2020_02_20_13_11_10_787_1.dng'
# raw image data
raw_image = get_visible_raw_image(image_path)
print('raw data:', raw_image.shape, raw_image.dtype, raw_image.max(), raw_image.min())
# metadata
metadata = get_metadata(image_path)
print('meta info : ', metadata)
# modify WB here
#metadata['as_shot_neutral'] = [1., 1., 1.]
# render
output_image = run_pipeline_v2(image_path, params)
#
# save
output_image_path = image_path.replace('.dng', '_{}.'.format(params['output_stage']) + params['save_as'])
max_val = 2 ** 16 if params['save_dtype'] == np.uint16 else 255
output_image = (output_image[..., ::-1] * max_val).astype(params['save_dtype'])
if params['save_as'] == 'jpg':
cv2.imwrite(output_image_path, output_image, [cv2.IMWRITE_JPEG_QUALITY, 100])
else:
cv2.imwrite(output_image_path, output_image)
2.noise estimation
2.1noise model
原论文3.1中给出了简洁明了又清晰的噪声模型:
主要包括高斯噪声和泊松噪声。
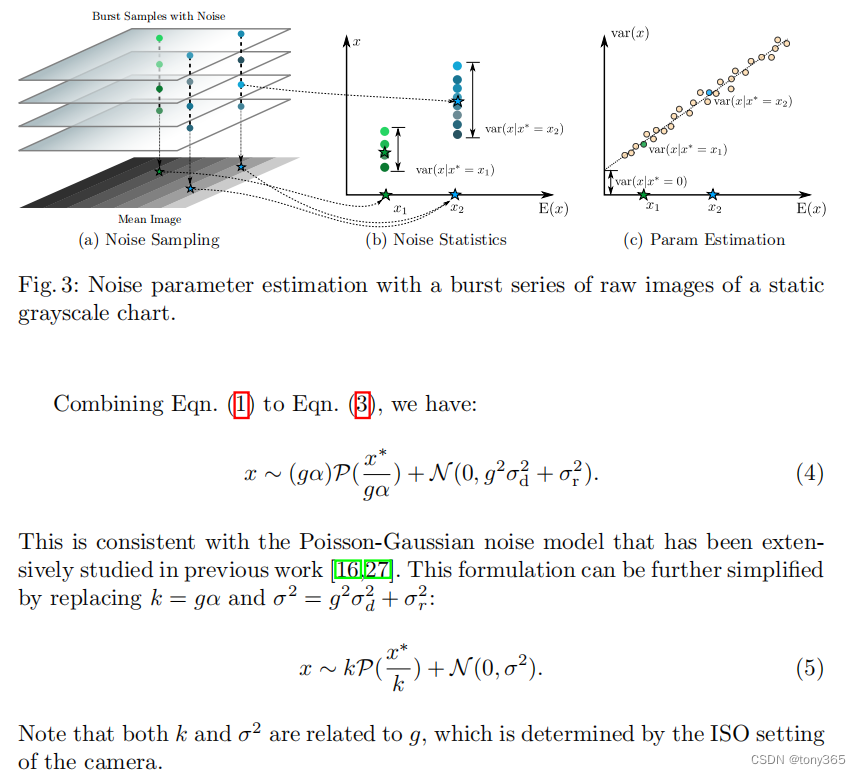
那么通过raw图的均值和方差可以得到参数k和sigma
2.2dataset
code and dataset : https://github.com/MegEngine/PMRID
- reno dataset
reno dataset 包含 [100,200,400,800,1200,1600,2400,3200,4000,4800,5600,6400]iso下的,每个iso下拍摄连续 64个raw图(注意raw图是没有经过blc的)
图像是一个会卡,光线不均匀,亮度不一
采集图像,iso变化,iso最大的时候曝光时间 设置为 固定的曝光时间。然后调节灯光亮度。
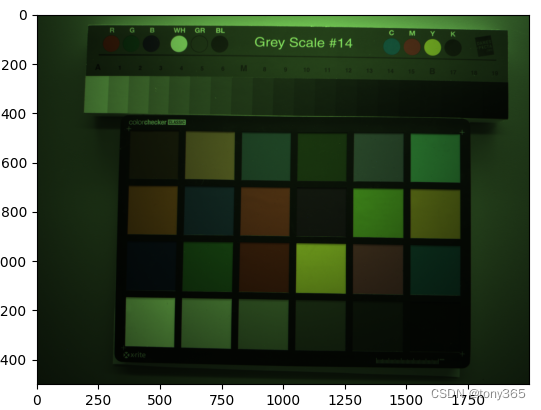
2.3noise estimation
以reno10x raw图为例,复现文章fig6
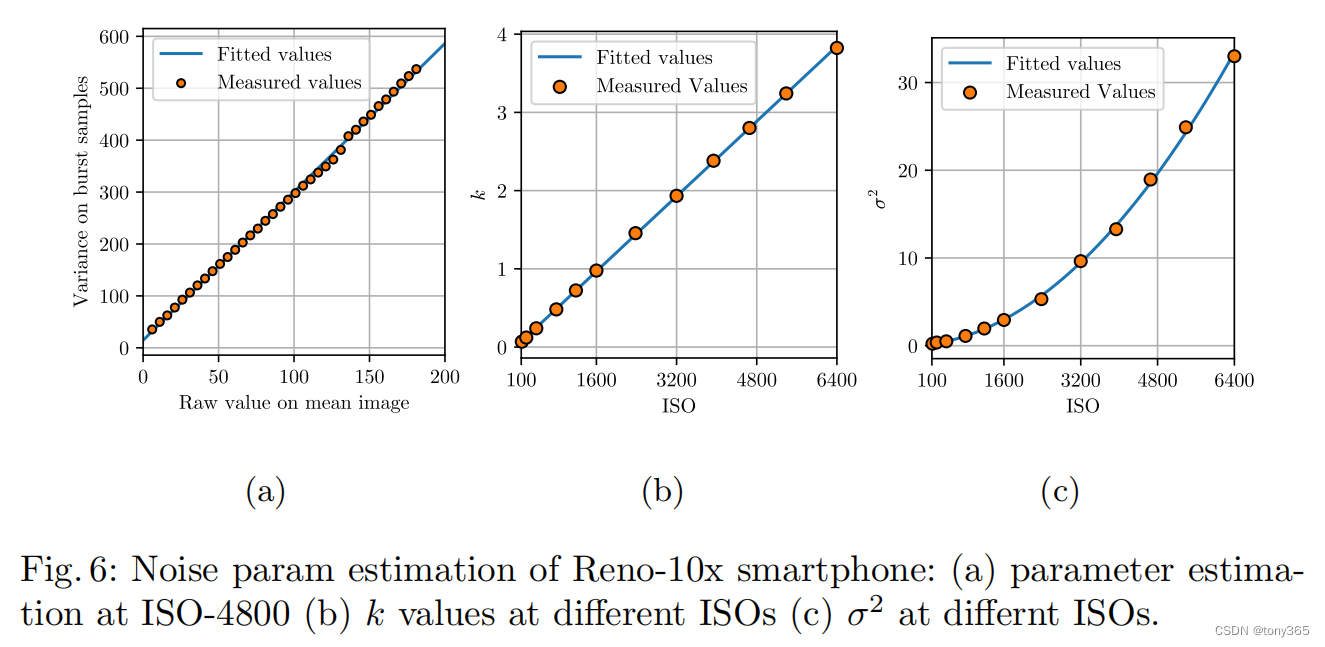
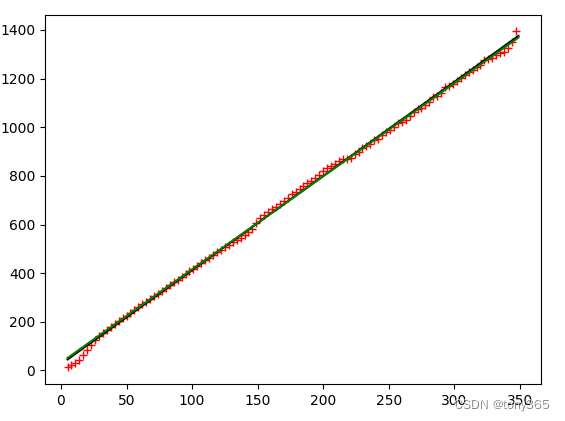
1)得到 6400 iso下的 k-sigma2图像:
import glob
import os
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
from scipy import optimize
from python.pipeline_utils import get_visible_raw_image, get_metadata
def get_rggb_mean_var(raw):
"""
:param raw: bayer raw
:return: 4个通道的均值和方差
"""
rggb = np.dstack((raw[0::2,0::2], raw[0::2,1::2], raw[1::2,0::2], raw[1::2,1::2]))
average = np.mean(rggb,axis=(0, 1))
var = np.var(rggb,axis=(0, 1))
return np.hstack((average.reshape(1, -1), var.reshape(1, -1)))
if __name__ == "__main__":
dir = r'D:\dataset\pratical_raw\reno10x_noise\gray_scale_chart\RAW_2020_02_20_13_11_10_787'
files = glob.glob(os.path.join(dir, '*.dng'))
raws = []
noise_level = []
rggb_mean_var = []
for file in files:
image_path = file # r'D:\dataset\pratical_raw\reno10x_noise\gray_scale_chart\RAW_2020_02_20_13_06_43_108\DNG_2020_02_20_13_06_43_108_1.dng'
raw_image = get_visible_raw_image(image_path) - 64
# metadata
metadata = get_metadata(image_path)
#print(' raw data:', raw_image.shape, raw_image.dtype, raw_image.max(), raw_image.min())
raws.append(raw_image)
noise = [tem[0] for tem in metadata['noise_profile']]
noise_level.append(noise)
print(get_rggb_mean_var(raw_image).reshape(-1))
rggb_mean_var.append(get_rggb_mean_var(raw_image).reshape(-1))
noise_level = np.dstack(noise_level)
noise_level = np.mean(noise_level, axis=-1)
print('noise_level:', noise_level)
rggb_mean_var = np.dstack(rggb_mean_var)
rggb_mean_var = np.mean(rggb_mean_var.reshape(8, -1), axis=-1)
print('rggb_mean_var:', rggb_mean_var)
raws = np.dstack(raws)
print(raws.dtype, raws.shape)
raw_mean = np.mean(raws, axis=-1).astype(np.uint16)
mm = np.arange(metadata['white_level'][0]+1)
uu = []
for i in range(metadata['white_level'][0]+1):
data = raws[raw_mean == i]
if data is None or len(data) == 0:
uu.append(-1)
else:
#print(data.shape, i, data.min(), data.max())
uu.append((data.var())) # 这里如果筛选出 异常的数据,计算会更精确
uu = np.array(uu)
print(mm, uu, mm.dtype, mm.shape, uu.dtype, uu.shape)
mask = np.logical_and(uu >= 0, mm < 350)
mm = mm[mask]
uu = uu[mask]
m_u = np.hstack((mm.reshape(-1, 1), uu.reshape(-1, 1))).astype(np.float32)
# method1
z1 = np.polyfit(mm[uu>=0], uu[uu>=0], 1) # 用3次多项式拟合,输出系数从高到0
p1 = np.poly1d(z1) # 使用系数合成多项式
r_y = p1(mm[uu > 0])
print('z1:',z1)
# method2
def huber_loss(theta, x, y, delta=0.8):
diff = abs(y - (theta[1] + theta[0] * x))
return ((diff < delta) * diff ** 2 / 2 + (diff >= delta) * delta * (diff - delta / 2)).sum()
z2 = optimize.fmin(huber_loss, x0=(0, 0), args=(mm[uu>0], uu[uu>0]), disp=False)
print('z2', z2)
p1 = np.poly1d(z2) # 使用系数合成多项式
r_y2 = p1(mm[uu >= 0])
plt.figure()
plt.plot(mm[uu >= 0][::3], uu[uu >= 0][::3], 'r+')
plt.plot(mm[uu > 0], r_y, 'k-')
plt.plot(mm[uu > 0], r_y2, 'g-')
plt.show()
save_dir = r'D:\dataset\pratical_raw\reno10x_noise\gray_scale_chart'
np.savetxt(os.path.join(save_dir, dir[-27:]+'_k1_sigma2.txt'), np.round(z2, 5), fmt='%.5f')
np.savetxt(os.path.join(save_dir, dir[-27:] + '_m_var.txt'), np.round(m_u, 2), fmt='%.2f')
np.savetxt(os.path.join(save_dir, dir[-27:] + '_noise.txt'), np.round(noise_level.reshape(-1), 9), fmt='%.9f')
np.savetxt(os.path.join(save_dir, dir[-27:] + '_rggb_mean_var.txt'), np.round(rggb_mean_var.reshape(-1), 2), fmt='%.2f')
print(dir)
2)各个iso下的 k, sigma2:
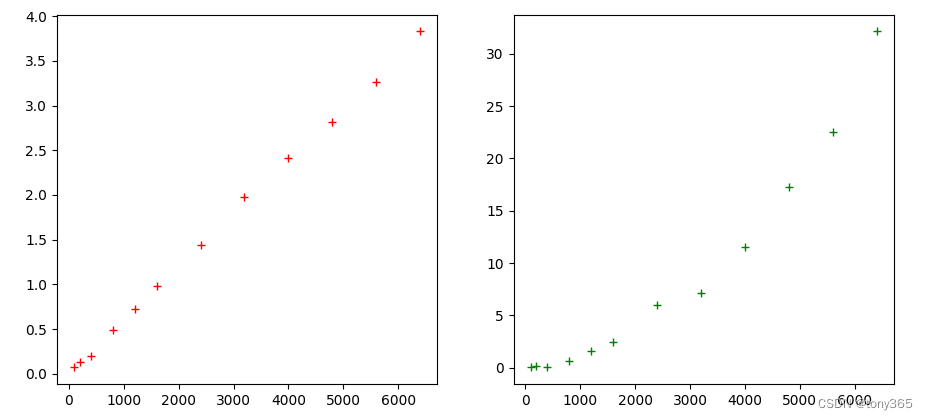
基本和文章fig6一致。
import glob
import os
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
from scipy import optimize
if __name__ == "__main__":
iso = [100,200,400,800,1200,1600,2400,3200,4000,4800,5600,6400]
dir = r'D:\dataset\pratical_raw\reno10x_noise\gray_scale_chart'
k1_sigma2s = []
files = glob.glob(os.path.join(dir, '*k1_sigma2.txt'))
for file in files:
k1_sigma2 = np.loadtxt(file)
print(k1_sigma2)
k1_sigma2s.append(k1_sigma2)
k1_sigma2s = np.array(k1_sigma2s)
k = k1_sigma2s[..., 0]
sigma2 = k1_sigma2s[..., 1]
# print('norm k:', k / k[0])
plt.figure()
plt.subplot(121)
plt.plot(iso, k, 'r+')
plt.subplot(122)
plt.plot(iso, sigma2, 'g+')
plt.show()
# 各iso下图像均值变化不大,方差随着iso增大而增大。
rggb_mean_vars = []
files = glob.glob(os.path.join(dir, '*rggb_mean_var.txt'))
for file in files:
rggb_mean_var = np.loadtxt(file)
print(rggb_mean_var)
rggb_mean_vars.append(rggb_mean_var)
rggb_mean_vars = np.array(rggb_mean_vars)
print('rggb ratio:\n', rggb_mean_vars / rggb_mean_vars[0])
# 打印DNG meta记录的 noise level
print('\n\n noise level in meta:')
noises = []
files = glob.glob(os.path.join(dir, '*noise.txt'))
for file in files:
noise = np.loadtxt(file)
print(noise)
noises.append(noise[:2])
noises = np.array(noises).reshape(-1, 2)
plt.figure()
plt.subplot(121)
plt.plot(iso, noises[:,0]*(1023-64), 'r+')
plt.subplot(122)
plt.plot(iso, noises[:,1]*(959*959), 'g+')
plt.show()
3.论文中的测试集
拍了五个场景,每个场景两种光源调节bright和dark.
每种光源条件又用了5中iso+expo time.
import glob
import os
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
'''
process PMRID dataset
'''
if __name__ == "__main__":
dir_ori = r'D:\dataset\pratical_raw\PMRID\Scene4\dark'
dirs = glob.glob(os.path.join(dir_ori, 'RAW*'))
print(dirs)
for dir in dirs:
files = glob.glob(os.path.join(dir, "*.raw"))
for file in files:
print(file)
data = np.fromfile(file, dtype=np.uint16)
data = data.reshape(3000, 4000)
rgb = np.dstack((data[1::2,1::2], data[1::2,0::2], data[0::2,0::2]))
plt.figure()
plt.imshow(rgb / rgb.max())
plt.show()
4.论文总结
- 提出根据raw图泊松高斯噪声估计模型,即各种iso下的噪声参数
- 根据噪声参数可以生成泛化能力强的噪声图片
- 提出k-sigma转换处理 input 和 output, 可以使网络学习 iso-independent space, 因此不需要扩大网络模型,就可以训练一个能处理各种iso噪声的轻量化模型,且效果很好。
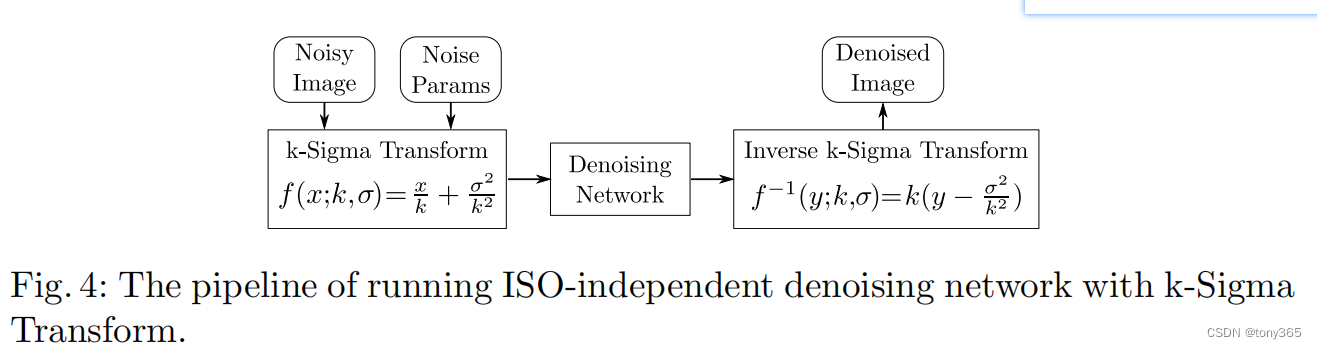
5.net
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from collections import OrderedDict
import numpy as np
def Conv2D(
in_channels: int, out_channels: int,
kernel_size: int, stride: int, padding: int,
is_seperable: bool = False, has_relu: bool = False,
):
modules = OrderedDict()
if is_seperable:
modules['depthwise'] = nn.Conv2d(
in_channels, in_channels, kernel_size, stride, padding,
groups=in_channels, bias=False,
)
modules['pointwise'] = nn.Conv2d(
in_channels, out_channels,
kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=True,
)
else:
modules['conv'] = nn.Conv2d(
in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride, padding,
bias=True,
)
if has_relu:
modules['relu'] = nn.ReLU()
return nn.Sequential(modules)
class EncoderBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels: int, mid_channels: int, out_channels: int, stride: int = 1):
super().__init__()
self.conv1 = Conv2D(in_channels, mid_channels, kernel_size=5, stride=stride, padding=2, is_seperable=True, has_relu=True)
self.conv2 = Conv2D(mid_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=5, stride=1, padding=2, is_seperable=True, has_relu=False)
self.proj = (
nn.Identity()
if stride == 1 and in_channels == out_channels else
Conv2D(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=3, stride=stride, padding=1, is_seperable=True, has_relu=False)
)
self.relu = nn.ReLU()
def forward(self, x):
proj = self.proj(x)
x = self.conv1(x)
x = self.conv2(x)
x = x + proj
return self.relu(x)
def EncoderStage(in_channels: int, out_channels: int, num_blocks: int):
blocks = [
EncoderBlock(
in_channels=in_channels,
mid_channels=out_channels//4,
out_channels=out_channels,
stride=2,
)
]
for _ in range(num_blocks-1):
blocks.append(
EncoderBlock(
in_channels=out_channels,
mid_channels=out_channels//4,
out_channels=out_channels,
stride=1,
)
)
return nn.Sequential(*blocks)
class DecoderBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels: int, out_channels: int, kernel_size: int = 3):
super().__init__()
padding = kernel_size // 2
self.conv0 = Conv2D(
in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=kernel_size, padding=padding,
stride=1, is_seperable=True, has_relu=True,
)
self.conv1 = Conv2D(
out_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=kernel_size, padding=padding,
stride=1, is_seperable=True, has_relu=False,
)
def forward(self, x):
inp = x
x = self.conv0(x)
x = self.conv1(x)
x = x + inp
return x
class DecoderStage(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels: int, skip_in_channels: int, out_channels: int):
super().__init__()
self.decode_conv = DecoderBlock(in_channels, in_channels, kernel_size=3)
self.upsample = nn.ConvTranspose2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0)
self.proj_conv = Conv2D(skip_in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1, is_seperable=True, has_relu=True)
# M.init.msra_normal_(self.upsample.weight, mode='fan_in', nonlinearity='linear')
def forward(self, inputs):
inp, skip = inputs
x = self.decode_conv(inp)
x = self.upsample(x)
y = self.proj_conv(skip)
return x + y
class Network(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.conv0 = Conv2D(in_channels=4, out_channels=16, kernel_size=3, padding=1, stride=1, is_seperable=False, has_relu=True)
self.enc1 = EncoderStage(in_channels=16, out_channels=64, num_blocks=2)
self.enc2 = EncoderStage(in_channels=64, out_channels=128, num_blocks=2)
self.enc3 = EncoderStage(in_channels=128, out_channels=256, num_blocks=4)
self.enc4 = EncoderStage(in_channels=256, out_channels=512, num_blocks=4)
self.encdec = Conv2D(in_channels=512, out_channels=64, kernel_size=3, padding=1, stride=1, is_seperable=True, has_relu=True)
self.dec1 = DecoderStage(in_channels=64, skip_in_channels=256, out_channels=64)
self.dec2 = DecoderStage(in_channels=64, skip_in_channels=128, out_channels=32)
self.dec3 = DecoderStage(in_channels=32, skip_in_channels=64, out_channels=32)
self.dec4 = DecoderStage(in_channels=32, skip_in_channels=16, out_channels=16)
self.out0 = DecoderBlock(in_channels=16, out_channels=16, kernel_size=3)
self.out1 = Conv2D(in_channels=16, out_channels=4, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1, is_seperable=False, has_relu=False)
def forward(self, inp):
conv0 = self.conv0(inp)
conv1 = self.enc1(conv0)
conv2 = self.enc2(conv1)
conv3 = self.enc3(conv2)
conv4 = self.enc4(conv3)
conv5 = self.encdec(conv4)
up3 = self.dec1((conv5, conv3))
up2 = self.dec2((up3, conv2))
up1 = self.dec3((up2, conv1))
x = self.dec4((up1, conv0))
x = self.out0(x)
x = self.out1(x)
pred = inp + x
return pred
if __name__ == "__main__":
net = Network()
# img = mge.tensor(np.random.randn(1, 4, 64, 64).astype(np.float32))
img = torch.randn(1, 4, 64, 64, device=torch.device('cpu'), dtype=torch.float32)
out = net(img)
import IPython; IPython.embed()
# vim: ts=4 sw=4 sts=4 expandtab