这两天在学习 pytorch 的加载预训练模型和 fine tune 为了方便以后查看,特写成博客。
1. pytorch 预训练模型以及修改
pytorch中自带几种常用的深度学习网络预训练模型,torchvision.models包中包含alexnet、densenet、inception、resnet、squeezenet、vgg等常用网络结构,并且提供了预训练模型,可通过调用来读取网络结构和预训练模型(模型参数)。往往为了加快学习进度,训练的初期直接加载pretrain模型中预先训练好的参数。
加载模型有两种形式进行加载:a、加载网络结构和预训练参数;b、只加载网络结构,不加载预训练参数。两种形式怎么选择看自己的需要。
# pretrained=True 加载网络结构和预训练参数,
# pretrained=False 时代表只加载网络结构,不加载预训练参数,即不需要用预训练模型的参数来初始化
# pretrained 参数默认是False,为了代码清晰,最好还是加上参数赋值
net = models.vgg16(pretrained=True)
修改加载好的预训练模型有两种形式:
a、网络最后一层分类层fc是对1000种类型进行划分,对于自己的数据集,如果只有 2 类,只修改最后的全连接层的输出为 2。
b、增减卷积 要修改网络中的层次结构,这时只能用参数覆盖的方法,即自己先定义一个类似的网络,再将预训练中的参数提取到自己的网络中来。
两种形式怎么实现我们看代码:
# 方法一:增减卷积 要修改网络中的层次结构,这时只能用参数覆盖的方法,即自己先定义一个类似的网络,再将预训练中的参数提取到自己的网络中来
class Dgo_Cat_Net1(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_classes=2):
super(Dgo_Cat_Net1, self).__init__()
# pretrained=True 加载网络结构和预训练参数,
# pretrained=False 时代表只加载网络结构,不加载预训练参数,即不需要用预训练模型的参数来初始化
# pretrained 参数默认是False,为了代码清晰,最好还是加上参数赋值
net = models.vgg16(pretrained=True)
net.classifier = nn.Sequential() # 将分类层(fc)置空
self.features = net
self.classifier = nn.Sequential( # 定义一个卷积网络结构
nn.Linear(512*7*7, 512),
nn.ReLU(True),
nn.Dropout(),
nn.Linear(512, 128),
nn.ReLU(True),
nn.Dropout(),
nn.Linear(128, num_classes),
)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.features(x)
x = x.view(x.size(0), -1)
x = self.classifier(x)
return x
# 方法二:网络最后一层分类层fc是对1000种类型进行划分,对于自己的数据集,如果只有2类
class Dgo_Cat_Net2(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_classes=2):
super(Dgo_Cat_Net2, self).__init__()
# pretrained=True 加载网络结构和预训练参数,False 时代表只加载网络结构,不加载预训练参数,即不需要用预训练模型的参数来初始化
# pretrained 参数默认是False,为了代码清晰,最好还是加上参数赋值
self.model = models.resnet50(pretrained=True) # 调用模型
fc_features = self.model.fc.in_features # 提取 fc 层中固定的参数 in_features
self.model.fc = nn.Linear(in_features=fc_features, out_features=num_classes) # 修改 fc 层中 out_features 参数,修改分类为9
def forward(self, x):
x = self.model(x)
return x
2. pytorch fine tune 微调(冻结一部分层)
还有一种使用预训练模型的方法是对它进行部分训练。具体做法是,将模型起始的一些层的权重保持不变,冻结住,重新训练后面的层,得到新的权重。在这个过程中,可多次进行尝试,从而能够依据结果找到 frozen layers 和 retrain layers 之间的最佳搭配。
如何使用预训练模型,是由数据集大小和新旧数据集(预训练的数据集和自己要解决的数据集)之间数据的相似度来决定的。
model = Dgo_Cat_Net1(num_classes=2)
for i, param in enumerate(model.parameters()):
print(i)
if i < 27: # 前面一些参数冻结
param.requires_grad = False
工程全部代码:
main.py
import torch
from torch import nn
import torchvision.models as models
from dataload import new_test_loader, new_train_loader
import torch.optim as optim
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import time
import math
LR = 0.0005 # 设置学习率
EPOCH_NUM = 10 # 训练轮次
def time_since(since):
s = time.time() - since
m = math.floor(s/60)
s -= m*60
return '%dm %ds' % (m, s)
# 方法一:增减卷积 要修改网络中的层次结构,这时只能用参数覆盖的方法,即自己先定义一个类似的网络,再将预训练中的参数提取到自己的网络中来
class Dgo_Cat_Net1(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_classes=2):
super(Dgo_Cat_Net1, self).__init__()
# pretrained=True 加载网络结构和预训练参数,
# pretrained=False 时代表只加载网络结构,不加载预训练参数,即不需要用预训练模型的参数来初始化
# pretrained 参数默认是False,为了代码清晰,最好还是加上参数赋值
net = models.vgg16(pretrained=True)
net.classifier = nn.Sequential() # 将分类层(fc)置空
self.features = net
self.classifier = nn.Sequential( # 定义一个卷积网络结构
nn.Linear(512*7*7, 512),
nn.ReLU(True),
nn.Dropout(),
nn.Linear(512, 128),
nn.ReLU(True),
nn.Dropout(),
nn.Linear(128, num_classes),
)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.features(x)
x = x.view(x.size(0), -1)
x = self.classifier(x)
return x
# 方法二:网络最后一层分类层fc是对1000种类型进行划分,对于自己的数据集,如果只有2类
class Dgo_Cat_Net2(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_classes=2):
super(Dgo_Cat_Net2, self).__init__()
# pretrained=True 加载网络结构和预训练参数,False 时代表只加载网络结构,不加载预训练参数,即不需要用预训练模型的参数来初始化
# pretrained 参数默认是False,为了代码清晰,最好还是加上参数赋值
self.model = models.resnet50(pretrained=True) # 调用模型
fc_features = self.model.fc.in_features # 提取 fc 层中固定的参数 in_features
self.model.fc = nn.Linear(in_features=fc_features, out_features=num_classes) # 修改 fc 层中 out_features 参数,修改分类为9
def forward(self, x):
x = self.model(x)
return x
model = Dgo_Cat_Net1(num_classes=2)
device = torch.device('cuda:0' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
model.to(device)
train_data = new_train_loader
test_data = new_test_loader
# 总共有 44 层网络,37层预加载VGG模型里面的,还有 7 层外面自己加的,我们把前面一些层预加载的模型冻结住,后面的一些层更新
para_optim = []
# for i, single_layer in enumerate(model.modules()):
# # print(i, single_layer)
# if i > 36: # 前面37层冻结
# for param in single_layer.parameters():
# para_optim.append(param)
# else: # 后面7层不冻结正常更新
# for param in single_layer.parameters():
# param.requires_grad = False
# print(f'para_optim len = {len(para_optim)}')
for i, param in enumerate(model.parameters()):
print(i)
if i < 27: # 前面一些参数冻结
param.requires_grad = False
criterion = torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
# optimizer = optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=LR)
# optimizer = optim.Adam(para_optim, lr=LR)
optimizer = optim.Adam(filter(lambda p: p.requires_grad, model.parameters()), lr=LR)
def train(epoch, loss_list):
# print(f'moduls len:{len(model.modules())} children len:{len(model.children())}')
n, m = 0, 0
for k in model.modules():
n += 1
# print(k)
print(f'n={n}')
for k in model.children():
# print(k)
m += 1
print(f'm={m}')
running_loss = 0.0
for batch_idx, data in enumerate(train_data, 0):
inputs, target = data[0], data[1]
inputs, target = inputs.to(device), target.to(device)
optimizer.zero_grad()
outputs = model(inputs)
loss = criterion(outputs, target)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
loss_list.append(loss.item())
running_loss += loss.item()
if batch_idx % 100 == 99:
print(f'[{time_since(start)}] Epoch {epoch}', end='')
print('[%d, %5d] loss:%.3f' % (epoch + 1, batch_idx + 1, running_loss / 100))
running_loss = 0.0
return loss_list
def test():
correct = 0
total = 0
with torch.no_grad():
for _, data in enumerate(new_test_loader, 0):
inputs, target = data[0], data[1]
inputs, target = inputs.to(device), target.to(device)
outputs = model(inputs)
_, prediction = torch.max(outputs.data, dim=1)
total += target.size(0)
correct += (prediction == target).sum().item()
print('Accuracy on test set: (%d/%d)%d %%' % (correct, total, 100 * correct / total))
with open("test.txt", "a") as f:
f.write('Accuracy on test set: (%d/%d)%d %% \n' % (correct, total, 100 * correct / total))
if __name__ == '__main__':
start = time.time()
with open("test.txt", "a") as f:
f.write('Start write!!! \n')
loss_list = []
for epoch in range(EPOCH_NUM):
train(epoch, loss_list)
test()
torch.save(model.state_dict(), 'Model.pth')
x_ori = []
for i in range(len(loss_list)):
x_ori.append(i)
plt.title("Graph")
plt.plot(x_ori, loss_list)
plt.ylabel("Y")
plt.xlabel("X")
plt.show()
dataload.py(猫狗数据集加载)
import torch
from torchvision import transforms
from torch.utils.data import Dataset, DataLoader
import os
from PIL import Image
# 初始化根目录
train_path = 'D:\\DeapLearn Project\\Vgg16_findtune_classificate_CatDog\\CatDogData\\train\\'
test_path = 'D:\\DeapLearn Project\\Vgg16_findtune_classificate_CatDog\\CatDogData\\test\\'
# 定义读取文件的格式
# 数据集
class MyDataSet(Dataset):
def __init__(self, data_path:str, transform=None):
super(MyDataSet, self).__init__()
self.data_path = data_path
if transform is None:
self.transform = transforms.Compose(
[
transforms.Resize(size=(224, 224)),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize((0.5, 0.5, 0.5), (0.5, 0.5, 0.5)),
]
)
else:
self.transform = transforms
self.path_list = os.listdir(data_path)
def __getitem__(self, idx:int):
img_path = self.path_list[idx]
if img_path.split('.')[0] == 'dog':
label = 1
else:
label = 0
label = torch.as_tensor(label, dtype=torch.int64)
img_path = os.path.join(self.data_path, img_path)
img = Image.open(img_path)
img = self.transform(img)
return img, label
def __len__(self)->int:
return len(self.path_list)
train_ds = MyDataSet(train_path)
full_ds = train_ds
train_size = int(0.8*len(full_ds))
test_size = len(full_ds) - train_size
new_train_ds, test_ds = torch.utils.data.random_split(full_ds, [train_size, test_size])
# 数据加载
new_train_loader = DataLoader(new_train_ds, batch_size=32, shuffle=True, pin_memory=True, num_workers=0)
new_test_loader = DataLoader(test_ds, batch_size=32, shuffle=False, pin_memory=True, num_workers=0)
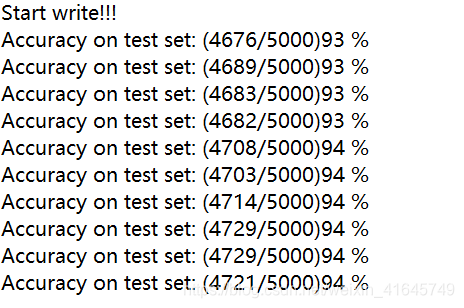
最后模型跑了 10 轮次,最大准确率为 94% ,我们可以看出来使用 pytorch 自带的预训练模型,加上自己添加的一些层,然后冻结住前面的一些预加载模型里面的参数,只更新后面一部分的参数,最终得出的模型的效果还是很不错的。
参考文章:
pytorch预训练
工程GitHub:Vgg16_findtune_classificate_CatDog
联系邮箱:[email protected]