目录
方法1-栈
将一个个数据推入栈区,然后再一个个弹出来。注意点:弹出完成之后,要把最后一个节点的next指向null,否则链表就闭环了。
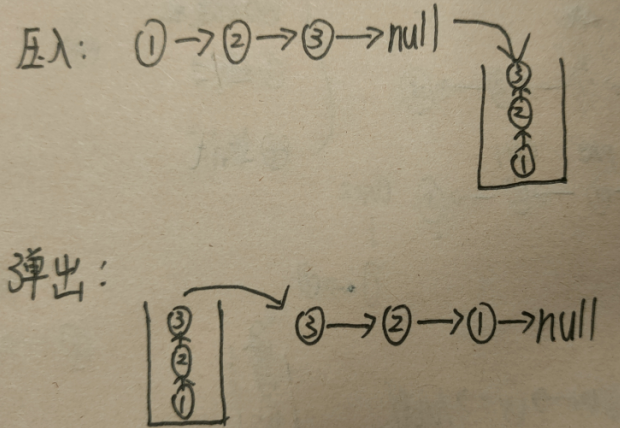
/*
struct ListNode {
int val;
struct ListNode *next;
ListNode(int x) :
val(x), next(NULL) {
}
};*/
#include<stack>
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* ReverseList(ListNode* pHead) {
stack<ListNode*> stack_temp;
ListNode* cur = pHead;
while (cur != NULL) {
stack_temp.push(cur);
cur = cur->next;
}
ListNode* pHead2=new ListNode(0);
ListNode* cur2 = pHead2;
while (stack_temp.empty()!=true) {
cur2->next=stack_temp.top();
stack_temp.pop();
cur2 = cur2->next;
}
cur2->next = NULL;
return pHead2->next;
}
};方法2-双链表(和迭代法是一个意思)
建立链表1和链表2,循环遍历链表1,在每一个循环内部,将链表1的当前节点接入到链表2的头节点。图中是两种图形描述,代码是一样的,图形化理解方式不一样。


/*
struct ListNode {
int val;
struct ListNode *next;
ListNode(int x) :
val(x), next(NULL) {
}
};*/
#include<stack>
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* ReverseList(ListNode* pHead) {
ListNode* cur2 = NULL;
ListNode* cur1 = pHead;
while (cur1 != NULL) {
ListNode* temp = cur1->next;//备份cur1下一个节点
cur1->next = cur2;//将cur1的节点连接到cur2的节点
cur2 = cur1;//更新cur2的头节点
cur1 = temp;//cur1往后移动一位
}
return cur2;
}
};
方法3-递归
递归(深度优先)遍历到最底层,然后逐级往上进行反转,每一次递归内部,将当前节点的next节点的next节点指向自身,同时将自身的next节点指向NULL(为了在最后一次递归时候,不让链表形成闭环)。

/*
struct ListNode {
int val;
struct ListNode *next;
ListNode(int x) :
val(x), next(NULL) {
}
};*/
#include<stack>
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* ReverseList(ListNode* pHead) {
//终止条件
if (pHead==NULL||pHead->next == NULL){
return pHead;
}
//递归调用
ListNode* ans = ReverseList(pHead->next);
pHead->next->next = pHead;
pHead->next = NULL;
return ans;
}
};