as we all know,there're three kinds of replication in MySQL nowadays.such as,asynchronous replication,(fully) synchronous replication,semisynchronous replication.what's the difference between them?first of all,let's see the intact architecture picture of MySQL replication:
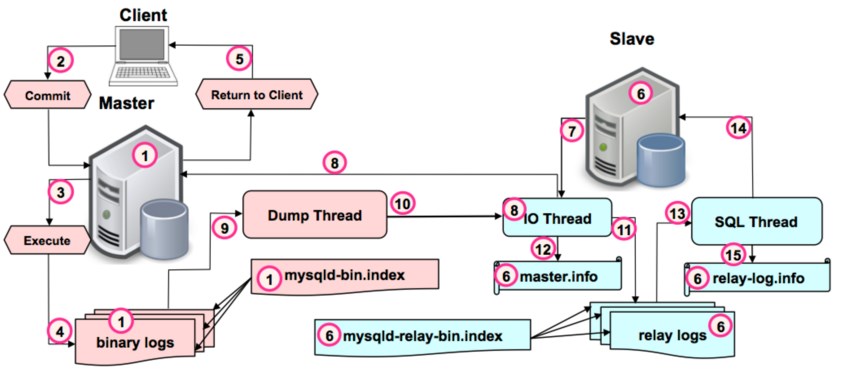
what will client do?
-
genrates transactions
-
commits transactions to master
-
returns result to client
- executes transactions
- generates binary logs
- dump thread sends contents(binary logs) to IO Thread of slave
what will slave do?
- connects to master
- IO Thread asks for data(binary logs) and gets it
- generates relay logs
- SQL Thread applies data(relay logs)
generally speaking,the data changed on master will continuously be sent to slave,so the data on slave seems the equal with the master.this mechanism is usually used to backup on slave(reduce pressure of master),construct HA architecture(failover or dispatch w/r opertions),etc.nevertheless,because of all kinds of reasons,slave frequently defers in most scenario what's often grumbled by MySQL dba.below are different kind of replication methods,let's see the detail.
- asynchronous replication
since MySQL 3.2.22,this kind of replication was supported with statement format of binlog.then,untill MySQL 5.1.5 row format of binlog was supported.the mechanism of it is that as sonn as the master dump thread has sent the binary logs to the slave,the server returns the result from client.there is nothing to guarantee the binary logs is normally received by the slave(maybe the network failure occurs simultaneously).so it's unsafe in consistency what means your transaction will lost in the replication.this is also the original replication of MySQL.here's the picture about the procedure:
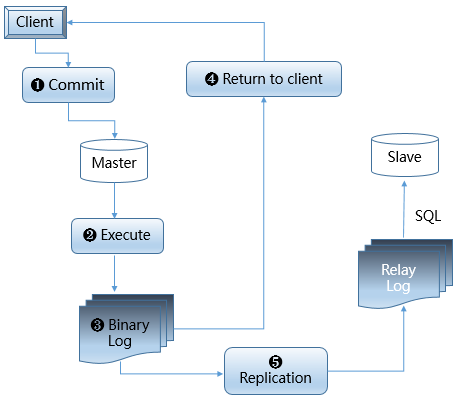
1. client send dml operations to the master meanwhile the transaction starts.
2. master execute these dml operations from client in transaction.
3. generate some binary logs which contain the transaction information.
4. master will return results to the client immediately after dump thread has sent these binary logs to slave.
5. slave receive the binary log by IO_Thread and apply the de relay log by SQL_Thread.
in step 4,master won't judge whether slave has received the binary logs (which are sent by itself) or not.if the master crashs suddenly after it has sent the binary logs,but slave does not receive them at all on account of network delay,only if the slave take over the application at this time,the committed transactions will miss which means data loss.this is not commonly acceptalbe in most important product system especially the finacial about.
- synchronous replication
synchronous replication require master returns result to client only after the transactions be committed by all the slaves(receive and apply).this method will severely lead to bad performance on master unless you can guarantee the slaves can commit immediate without any delay(infact it's tough).nowadays,the only solution of synchronous replication is still the MySQL NDB Cluser.therefore,it's not recommended to use synchronous replication method.
- semi-synchronous replication
semi-synchronous replication seems the workaround solution of above two method which can strongly increase the consistency bween master and slave.it's supported since MySQL 5.5 and enhanced in MySQL 5.7.what's the mechanism of semi-sychronouos replication?master is permitted to return the result to client merely after only one slave has received binary logs,write them to the relay logs and returns an ACK signal to master.there're two ways of it,such as after_commit & after_sync,let's see the difference or them:
after_commit(Since MySQL 5.5):
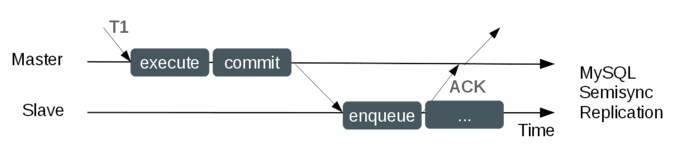
in this mechod,master performances a commit before it receives ACK signal from slave.let's suppose a scenario that once master crashs after it commits a transaction but it hasn't receive the ACK signal from slave.meanwhile,failover makes slave become the new master.how does the slave deal with then?will the transaction lost?it depends.there're two situations:
- slave has received the binary log,then turns it into relay log and applys it.there's no transaction loss.
- slave hasn't received the binary log,the transaction commited by master just now will lost,but the client will failure.
therefore,after_commit cannot guarantee lossless replication.after_commit is the default mode(actually it's the only mode can be use) which is supported by MySQL 5.5 & 5.6.
after_sync(since MySQL 5.7):
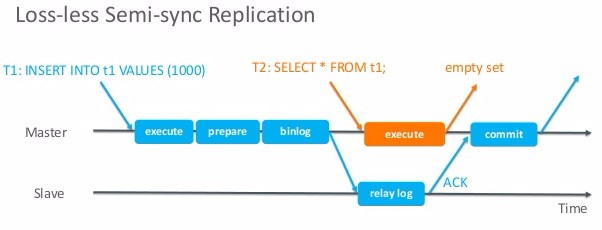
in the picture above,the t1 transaction shouldn't be lost because of the master merely commits to the storage engine after receive the ACK signal from slave.in spite of master may crash before receiving ACK signal,no transaction will lost as the master hasn't commit at all.meanwhile,the t2 transaction also get consistent query here.
in order to improve the data consistency(since after_commit has avoidless deficiency),MySQL official enhances the semi-synchronous replication which can be called "loss-less semi-synchronous replication" in MySQL 5.7 by add after_sync mode in parameter "rpl_semi_sync_master_wait_point".
caution,semi-synchronous replication may turn into asynchronous replication whenever the delay time of slave surpass the value which is specified in parameter "rpl_semi_sync_master_timeout"(default values is 10000 milliseconds).why it is permitted?i'm afraid to give consideration to performance of master.notwithstanding,you can also play a trick to prevent it from being converted over by set a infinite number in this parameter such as "10000000" or above.especially in case that your product is too important to lost data.
further more,to configure semi-sychronous replication,you should implement the optional plugin component "rpl_semi_sync_master",which can be check by using command "show plugins;"
Summary:
- commonly,semi-sync replication is strongly recommended when implements MySQL replication nowadays.
- i utterly recommend to upgrade product system to MySQL 5.7 in order to use after_sync mode which can avoid data loss.
- be careful of specify an inappropriate value in parameter "rpl_semi_sync_master_timeout" which will lead to conver semi-sync to async replication.