步骤:
- 需求与分析
- 创建测试JavaBean
- 创建配置文件
- 创建BeanConfig
- 解析Properties
- 使用BeanConfig数据
- 整合
创建测试JavaBean
package bull07.domain;
public class User implements java.io.Serializable {
private String userName;
private String userPasswd;
private String userId;
public User() {
}
public User(String userName,String userPasswd,String userId) {
this.userName = userName;
this.userPasswd = userPasswd;
this.userId = userId;
}
public String getUserName() {
return userName;
}
public void setUserName(String userName) {
this.userName = userName;
}
public String getUserPasswd() {
return userPasswd;
}
public void setUserPasswd(String userPasswd) {
this.userPasswd = userPasswd;
}
public String getUserId() {
return userId;
}
public void setUserId(String userId) {
this.userId = userId;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User [userName=" + userName + ", userPasswd=" + userPasswd
+ ", userId=" + userId + "]";
}
}
创建配置文件
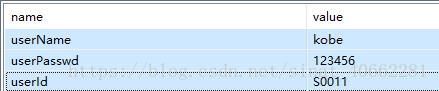
- bean.properties

- data.properties
创建BeanConfig
package bull07.domain;
import java.util.Properties;
public class BeanConfig {
private String id;
private String className;
private Properties prop = new Properties();
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getClassName() {
return className;
}
public void setClassName(String className) {
this.className = className;
}
public Properties getProp() {
return prop;
}
public void setProp(Properties prop) {
this.prop = prop;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "BeanConfig [id=" + id + ", className=" + className + ", prop="
+ prop + "]";
}
}
package bull07.ReflectTest
import org.junit.Test
import bull07.domain.BeanConfig
public class Demo1 {
@Test
public void method() {
//模拟数据
BeanConfig beanConfig = new BeanConfig()
beanConfig.setId("moni001")
beanConfig.setClassName("bull07.domain.User")
//beanConfih.getProp()其实就是获取了Properties对象,因为BeanConfig里有创建Properties对象。
beanConfig.getProp().setProperty("userName", "moniName")
beanConfig.getProp().setProperty("userPasswd", "moniPasswd")
beanConfig.getProp().setProperty("userId", "moniId")
System.out.println(beanConfig)
}
}
解析Properties
package bull07.ReflectTest;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException;
import java.util.Properties;
import org.junit.Test;
import bull07.domain.BeanConfig;
public class PropertiesDemo_02 {
private static final int UTF = 0;
@Test
public void method() throws UnsupportedEncodingException, FileNotFoundException, IOException {
BeanConfig beanConfig = new BeanConfig();
Properties beanProp = new Properties();
beanProp.load(new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("bean.properties"),"UTF-8"));
beanConfig.setId(beanProp.getProperty("id"));
beanConfig.setClassName(beanProp.getProperty("className"));
Properties dataProp = new Properties();
dataProp.load(new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("data.properties"),"UTF-8"));
for (String key : dataProp.stringPropertyNames()) {
String value = dataProp.getProperty(key);
beanConfig.getProp().setProperty(key, value);
}
System.out.println(beanConfig);
}
}
结果:
BeanConfig [id=id001, className=bull07.domain.User, prop={userId=S0011, userPasswd=123456, userName=kobe}]
使用BeanConfig数据
package bull07.ReflectTest
import java.lang.reflect.Method
import org.junit.Test
import bull07.domain.BeanConfig
public class BeanConfigUse {
@Test
public void method() throws Exception {
//创建BeanConfig对象
BeanConfig beanConfig = new BeanConfig()
//配置beanConfig数据
beanConfig.setId("mo001")
beanConfig.setClassName("bull07.domain.User")
//配置User数据
beanConfig.getProp().setProperty("userName", "moni002")
beanConfig.getProp().setProperty("userPasswd", "moniPasswd2")
beanConfig.getProp().setProperty("userId", "moniId2")
//使用数据创建JavaBean实例,并为JavaBean封装具体事例
//创建实例,使用反射.beanConfig.getClassName()就是bull07.domain.User.
Class clazz = Class.forName(beanConfig.getClassName())
Object obj = clazz.newInstance()
//beanConfig.getProp().stringPropertyNames()先获取所有的key集合
for (String key : beanConfig.getProp().stringPropertyNames()) {
//获取value
String value = beanConfig.getProp().getProperty(key)
//获取方法.substring(0,1)意思是获取第0个字符,substring(1)意思是获取第1以及以后的字符。
String methodName = "set" + key.substring(0, 1).toUpperCase() + key.substring(1)
Method method = clazz.getMethod(methodName, String.class)
//给属性赋上value值
method.invoke(obj, value)
}
System.out.println(obj)
}
}
结果:
User [userName=moni002, userPasswd=moniPasswd2, userId=moniId2]
整合
package bull07.ReflectTest
import java.io.FileInputStream
import java.io.FileNotFoundException
import java.io.IOException
import java.io.InputStreamReader
import java.lang.reflect.Method
import java.util.Properties
import org.junit.Test
import bull07.domain.BeanConfig
public class CompleteDemo {
//注意这里就不用写@Test了,这个方法下面setBean()会调用。
public BeanConfig getBean() throws Exception, FileNotFoundException, IOException {
//创建BeanConfig对象
BeanConfig beanConfig = new BeanConfig()
//读取bean.properties文件
//创建Properties对象
Properties beanProp = new Properties()
//采用流方式读取bean.properties文件
beanProp.load(new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("bean.properties"),"UTF-8"))
beanConfig.setId(beanProp.getProperty("id"))
beanConfig.setClassName(beanProp.getProperty("className"))
//读取data.peoperties文件
//创建Properties对象
Properties dataProp = new Properties()
dataProp.load(new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("data.properties"),"UTF-8"))
//for循环先获取dataProp对象的key集合
for (String key : dataProp.stringPropertyNames()) {
//获取key对应的属性值value
String value = dataProp.getProperty(key)
//beanConfig.getProp()相当于一个对象。这里为对应的属性赋值。
beanConfig.getProp().setProperty(key, value)
}
return beanConfig
}
@Test
public void setBean() throws FileNotFoundException, IOException, Exception {
BeanConfig beanConfig = getBean()
//创建实例,使用反射。beanConfig.getClassName()就是bull07.domain.User.
Class clazz = Class.forName(beanConfig.getClassName())
Object obj = clazz.newInstance()
//beanConfig.getProp()是一个对象,BeanConfig里面有new一个Properties对象。
for (String key : beanConfig.getProp().stringPropertyNames()) {
String value = beanConfig.getProp().getProperty(key)
//获取方法
String methodName = "set" + key.substring(0,1).toUpperCase() + key.substring(1)
Method method = clazz.getMethod(methodName, String.class)
//给对应的属性赋上value值。
method.invoke(obj, value)
}
System.out.println(obj)
}
}
结果:
User [userName=kobe, userPasswd=123456, userId=S0011]


