Android Platform Architecture 安卓平台架构
Android is an open source, Linux-based software stack created for a wide array of devices and form factors. The following diagram shows the major components of the Android platform.
Android 是一种基于 Linux 的开放源代码软件栈,为各类设备和机型而创建。下图所示为 Android 平台的主要组件。
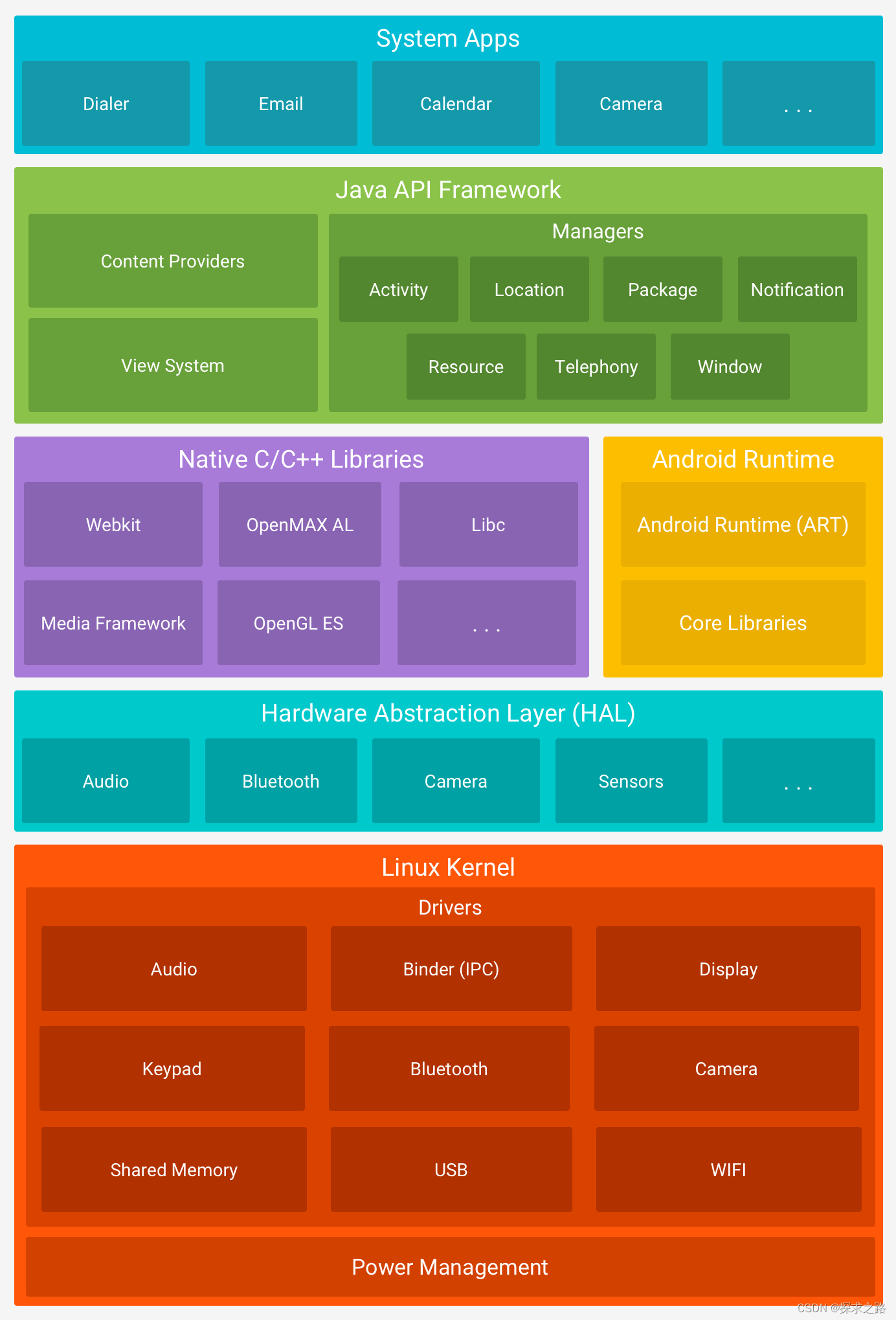
The Linux Kernel 系统驱动层
The foundation of the Android platform is the Linux kernel. For example, the Android Runtime (ART) relies on the Linux kernel for underlying functionalities such as threading and low-level memory management.
Using a Linux kernel allows Android to take advantage of key security features and allows device manufacturers to develop hardware drivers for a well-known kernel.
Android 平台的基础是 Linux 内核。例如,Android Runtime (ART) 依靠 Linux 内核来执行底层功能,例如线程和低层内存管理。
使用 Linux 内核可让 Android 利用主要安全功能,并且允许设备制造商为著名的内核开发硬件驱动程序。
Hardware Abstraction Layer (HAL) 硬件抽象层
The hardware abstraction layer (HAL) provides standard interfaces that expose device hardware capabilities to the higher-level Java API framework. The HAL consists of multiple library modules, each of which implements an interface for a specific type of hardware component, such as the camera or bluetooth module. When a framework API makes a call to access device hardware, the Android system loads the library module for that hardware component.
硬件抽象层提供标准界面,向更高级别的硬件抽象层显示设备硬件功能。HAL 包含多个库模块,其中每个模块都为特定类型的硬件组件实现一个界面,例如相机或蓝牙模块。当框架 API 要求访问设备硬件时,Android 系统将为该硬件组件加载库模块。
Android Runtime
For devices running Android version 5.0 (API level 21) or higher, each app runs in its own process and with its own instance of the Android Runtime (ART). ART is written to run multiple virtual machines on low-memory devices by executing DEX files, a bytecode format designed specially for Android that’s optimized for minimal memory footprint. Build tools, such as d8, compile Java sources into DEX bytecode, which can run on the Android platform.
Some of the major features of ART include the following:
- Ahead-of-time (AOT) and just-in-time (JIT) compilation
- Optimized garbage collection (GC)
- On Android 9 (API level 28) and higher, conversion of an app package’s Dalvik Executable format (DEX) files to more compact machine code.
- Better debugging support, including a dedicated sampling profiler, detailed diagnostic exceptions and crash reporting, and the ability to set watchpoints to monitor specific fields
Prior to Android version 5.0 (API level 21), Dalvik was the Android runtime. If your app runs well on ART, then it should work on Dalvik as well, but the reverse may not be true.
Android also includes a set of core runtime libraries that provide most of the functionality of the Java programming language, including some Java 8 language features, that the Java API framework uses.
对于运行 Android 5.0(API 级别 21)或更高版本的设备,每个应用都在其自己的进程中运行,并且有其自己的 Android Runtime (ART) 实例。ART 编写为通过执行 DEX 文件在低内存设备上运行多个虚拟机,DEX 文件是一种专为 Android 设计的字节码格式,经过优化,使用的内存很少。编译工具链(例如 Jack)将 Java 源代码编译为 DEX 字节码,使其可在 Android 平台上运行。
ART 的部分主要功能包括:
- 预先 (AOT) 和即时 (JIT) 编译
- 优化的垃圾回收 (GC)
- 在 Android 9(API 级别 28)及更高版本的系统中,支持将应用软件包中的 Dalvik Executable 格式 (DEX) 文件转换为更紧凑的机器代码。
- 更好的调试支持,包括专用采样分析器、详细的诊断异常和崩溃报告,并且能够设置观察点以监控特定字段
在 Android 版本 5.0(API 级别 21)之前,Dalvik 是 Android Runtime。如果您的应用在 ART 上运行效果很好,那么它应该也可在 Dalvik 上运行,但反过来不一定。
Android 还包含一套核心运行时库,可提供系统框架层所使用的 Java 编程语言中的大部分功能,包括一些 Java 8 语言功能。
Native C/C++ Libraries 本地共享库
Many core Android system components and services, such as ART and HAL, are built from native code that require native libraries written in C and C++. The Android platform provides Java framework APIs to expose the functionality of some of these native libraries to apps. For example, you can access OpenGL ES through the Android framework’s Java OpenGL API to add support for drawing and manipulating 2D and 3D graphics in your app.
If you are developing an app that requires C or C++ code, you can use the Android NDK to access some of these native platform libraries directly from your native code.
许多核心 Android 系统组件和服务(例如 ART 和 HAL)构建自原生代码,需要以 C 和 C++ 编写的原生库。Android 平台提供系统框架层以向应用显示其中部分原生库的功能。例如,您可以通过 Android 框架的 Java OpenGL API 访问 OpenGL ES,以支持在应用中绘制和操作 2D 和 3D 图形。
如果开发的是需要 C 或 C++ 代码的应用,可以使用 Android NDK 直接从原生代码访问某些原生平台库。
Java API Framework 系统框架层
The entire feature-set of the Android OS is available to you through APIs written in the Java language. These APIs form the building blocks you need to create Android apps by simplifying the reuse of core, modular system components and services, which include the following:
- A rich and extensible View System you can use to build an app’s UI, including lists, grids, text boxes, buttons, and even an embeddable web browser
- A Resource Manager, providing access to non-code resources such as localized strings, graphics, and layout files
- A Notification Manager that enables all apps to display custom alerts in the status bar
- An Activity Manager that manages the lifecycle of apps and provides a common navigation back stack
- Content Providers that enable apps to access data from other apps, such as the Contacts app, or to share their own data
Developers have full access to the same framework APIs that Android system apps use.
您可通过以 Java 语言编写的 API 使用 Android OS 的整个功能集。这些 API 形成创建 Android 应用所需的构建块,它们可简化核心模块化系统组件和服务的重复使用,包括以下组件和服务:
- 丰富、可扩展的视图系统,可用以构建应用的 UI,包括列表、网格、文本框、按钮甚至可嵌入的网络浏览器
- 资源管理器,用于访问非代码资源,例如本地化的字符串、图形和布局文件
- 通知管理器,可让所有应用在状态栏中显示自定义提醒
- Activity 管理器,用于管理应用的生命周期,提供常见的导航返回栈
- 内容提供程序,可让应用访问其他应用(例如“联系人”应用)中的数据或者共享其自己的数据
开发者可以完全访问 Android 系统应用使用的框架 API。
System Apps 系统应用层
Android comes with a set of core apps for email, SMS messaging, calendars, internet browsing, contacts, and more. Apps included with the platform have no special status among the apps the user chooses to install. So a third-party app can become the user’s default web browser, SMS messenger, or even the default keyboard (some exceptions apply, such as the system’s Settings app).
The system apps function both as apps for users and to provide key capabilities that developers can access from their own app. For example, if your app would like to deliver an SMS message, you don’t need to build that functionality yourself—you can instead invoke whichever SMS app is already installed to deliver a message to the recipient you specify.
Android 随附一套用于电子邮件、短信、日历、互联网浏览和联系人等的核心应用。平台随附的应用与用户可以选择安装的应用一样,没有特殊状态。因此第三方应用可成为用户的默认网络浏览器、短信 Messenger 甚至默认键盘(有一些例外,例如系统的“设置”应用)。
系统应用可用作用户的应用,以及提供开发者可从其自己的应用访问的主要功能。例如,如果您的应用要发短信,您无需自己构建该功能,可以改为调用已安装的短信应用向您指定的接收者发送消息。