一.信号的基本概念
信号是系统响应某个条件而产生的事件,进程接收到信号会执行相应的操作。
与信号调用有关的系统调用在“ signal.h”头文件中有声明。
二.信号的引发
- 键盘事件 ctrl +c ctrl +\
- 非法内存 如果内存管理出错,系统就会发送一个信号进行处理
- 硬件故障 同样的,硬件出现故障系统也会产生一个信号
- 环境切换 比如说从用户态切换到其他态,状态的改变也会发送一个信号,这个信号会告知给系统。
三.常见信号主要功能与对应的值
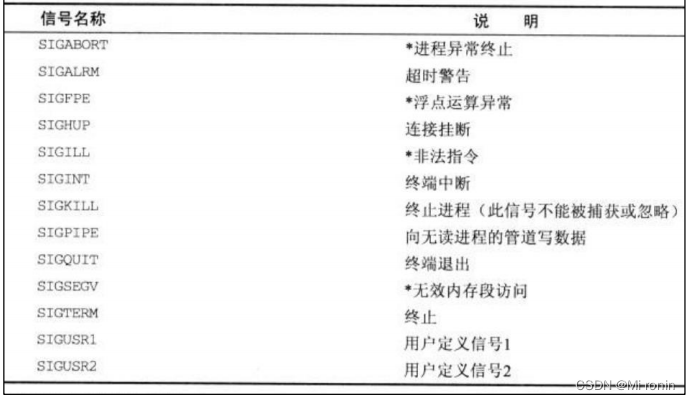
#define SIGHUP 1
#define SIGINT 2 //键盘按下 Ctrl+c 时,会产生该信号
#define SIGQUIT 3
#define SIGILL 4
#define SIGTRAP 5
#define SIGABRT 6
#define SIGIOT 6
#define SIGBUS 7
#define SIGFPE 8
#define SIGKILL 9 //该信号的响应方式不允许改变
#define SIGUSR1 10
#define SIGSEGV 11
#define SIGUSR2 12
#define SIGPIPE 13 //读端关闭的描述符,写端写入时产生,该信号会终止程序
#define SIGALRM 14
#define SIGTERM 15 //系统 kill 命令默认发送的信号
#define SIGSTKFLT 16
#define SIGCHLD 17 //子进程结束后,会默认给父进程发送该信号
#define SIGCONT 18
#define SIGSTOP 19
#define SIGTSTP 20
#define SIGTTIN 21
#define SIGTTOU 22
#define SIGURG 23
四.修改信号的相应方式——signal()
利用signal()可以将指定的信号进行修改
忽略信号:SIG_IGN
默认处理:SIG_DFL
自定义的:自己写的信号处理函数
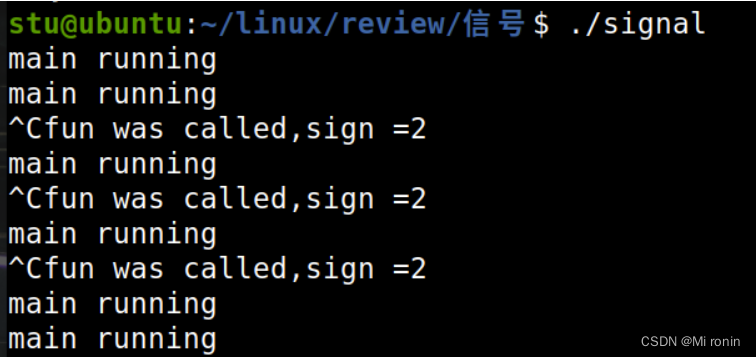
在键盘上按下 Ctrl+c 时,会给当前终端前台执行的进程发送 SIGINT 信号,用 signal 修 改 SIGINT 信号的响应方式示例代码如下:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<assert.h>
void fun(int sign)
{
printf("fun was called, sign = %d\n", sign);
}
int main()
{
signal(SIGINT, fun);
while(1)
{
sleep(1);
printf("main running\n");
}
exit(0);
}
运行结果:
五.发送信号 – kill()
kill() 可以向指定的进程发送指定的信号‘
int kill(pid_t pid,int sig);
pid > 0 指定将信号发送个那个进程
pid == 0 信号被发送到和当前进程在同一个进程组的进程
pid == -1 将信号发送给系统上有权限发送的所有的进程
pid < -1 将信号发送给进程组 id 等于 pid 绝对值,并且有权限发送的所有的进程。
sig 指定发送信号的类型。
附64个信号类型及作用详细说明
> root@myj:/usr/include/x86_64-linux-gnu/bits# cat signum-generic.h /*
> Signal number constants. Generic template. Copyright (C) 1991-2018
> Free Software Foundation, Inc. This file is part of the GNU C
> Library.
>
> The GNU C Library is free software; you can redistribute it and/or
> modify it under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public License
> as published by the Free Software Foundation; either version 2.1 of
> the License, or (at your option) any later version.
>
> The GNU C Library is distributed in the hope that it will be
> useful, but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty
> of MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
> GNU Lesser General Public License for more details.
>
> You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public
> License along with the GNU C Library; if not, see
> <http://www.gnu.org/licenses/>. */
>
> #ifndef _BITS_SIGNUM_GENERIC_H
> #define _BITS_SIGNUM_GENERIC_H 1
>
> #ifndef _SIGNAL_H
> #error "Never include <bits/signum-generic.h> directly; use <signal.h> instead."
> #endif
>
> /* Fake signal functions. */
>
> #define SIG_ERR ((__sighandler_t) -1) /* Error return. */
> #define SIG_DFL ((__sighandler_t) 0) /* Default action. */
> #define SIG_IGN ((__sighandler_t) 1) /* Ignore signal. */
>
> #ifdef __USE_XOPEN
> # define SIG_HOLD ((__sighandler_t) 2) /* Add signal to hold mask. */
> #endif
>
> /* We define here all the signal names listed in POSIX (1003.1-2008);
> as of 1003.1-2013, no additional signals have been added by POSIX.
> We also define here signal names that historically exist in every
> real-world POSIX variant (e.g. SIGWINCH).
>
> Signals in the 1-15 range are defined with their historical
> numbers. For other signals, we use the BSD numbers. There are
> two unallocated signal numbers in the 1-31 range: 7 and 29. Signal
> number 0 is reserved for use as kill(pid, 0), to test whether a
> process exists without sending it a signal. */
>
> /* ISO C99 signals. */
> #define SIGINT 2 /* Interactive attention signal. */
> #define SIGILL 4 /* Illegal instruction. */
> #define SIGABRT 6 /* Abnormal termination. */
> #define SIGFPE 8 /* Erroneous arithmetic operation. */
> #define SIGSEGV 11 /* Invalid access to storage. */
> #define SIGTERM 15 /* Termination request. */
>
> /* Historical signals specified by POSIX. */
> #define SIGHUP 1 /* Hangup. */
> #define SIGQUIT 3 /* Quit. */
> #define SIGTRAP 5 /* Trace/breakpoint trap. */
> #define SIGKILL 9 /* Killed. */
> #define SIGBUS 10 /* Bus error. */
> #define SIGSYS 12 /* Bad system call. */
> #define SIGPIPE 13 /* Broken pipe. */
> #define SIGALRM 14 /* Alarm clock. */
>
> /* New(er) POSIX signals (1003.1-2008, 1003.1-2013). */
> #define SIGURG 16 /* Urgent data is available at a socket. */
> #define SIGSTOP 17 /* Stop, unblockable. */
> #define SIGTSTP 18 /* Keyboard stop. */
> #define SIGCONT 19 /* Continue. */
> #define SIGCHLD 20 /* Child terminated or stopped. */
> #define SIGTTIN 21 /* Background read from control terminal. */
> #define SIGTTOU 22 /* Background write to control terminal. */
> #define SIGPOLL 23 /* Pollable event occurred (System V). */
> #define SIGXCPU 24 /* CPU time limit exceeded. */
> #define SIGXFSZ 25 /* File size limit exceeded. */
> #define SIGVTALRM 26 /* Virtual timer expired. */
> #define SIGPROF 27 /* Profiling timer expired. */
> #define SIGUSR1 30 /* User-defined signal 1. */
> #define SIGUSR2 31 /* User-defined signal 2. */
>
> /* Nonstandard signals found in all modern POSIX systems (including
> both BSD and Linux). */
> #define SIGWINCH 28 /* Window size change (4.3 BSD, Sun). */
>
> /* Archaic names for compatibility. */
> #define SIGIO SIGPOLL /* I/O now possible (4.2 BSD). */
> #define SIGIOT SIGABRT /* IOT instruction, abort() on a PDP-11. */
> #define SIGCLD SIGCHLD /* Old System V name */
>
> /* Not all systems support real-time signals. bits/signum.h indicates
> that they are supported by overriding __SIGRTMAX to a value greater
> than __SIGRTMIN. These constants give the kernel-level hard limits,
> but some real-time signals may be used internally by glibc. Do not
> use these constants in application code; use SIGRTMIN and SIGRTMAX
> (defined in signal.h) instead. */
> #define __SIGRTMIN 32
> #define __SIGRTMAX __SIGRTMIN
>
> /* Biggest signal number + 1 (including real-time signals). */
> #define _NSIG (__SIGRTMAX + 1)
>
> #endif /* bits/signum-generic.h. */
> #define SIG_ERR ((__sighandler_t) -1) /* Error return. /
> #define SIG_DFL ((__sighandler_t) 0) / Default action. /
> #define SIG_IGN ((__sighandler_t) 1) / Ignore signal. */
/* Signals. */
#define SIGHUP 1 /* Hangup (POSIX). 终端连接断开信号*/
#define SIGINT 2 /* Interrupt (ANSI). 中断信号,终端中输入ctrl+c,可中断前台进程*/
#define SIGQUIT 3 /* Quit (POSIX). 退出信号,终端中输入ctrl+\,可退出前台进程,同时产生core文件*/
#define SIGILL 4 /* Illegal instruction (ANSI). 非法指令信号,4.3BSD的abort函数产生该信号 */
#define SIGTRAP 5 /* Trace trap (POSIX). 调试信号,当在程序中设置断点后,该信号使得调试程序获得控制权*/
#define SIGABRT 6 /* Abort (ANSI). 程序异常终止信号,abort函数产生该信号 */
#define SIGIOT 6 /* IOT trap (4.2 BSD). 功能同SIGABRT*/
#define SIGBUS 7 /* BUS error (4.2 BSD). 程序访问不存在的内存区域时,产生该信号*/
#define SIGFPE 8 /* Floating-point exception (ANSI). 算术异常,如除以0*/
#define SIGKILL 9 /* Kill, unblockable (POSIX). 不能被忽略,非阻塞,可杀死任意一个运行中的进程*/
#define SIGUSR1 10 /* User-defined signal 1 (POSIX). 用户自定义1*/
#define SIGSEGV 11 /* Segmentation violation (ANSI). 当程序访问没有访问权限的内存区域,或者访问非可读的内存区域时,产生该信号,如数组越界 */
#define SIGUSR2 12 /* User-defined signal 2 (POSIX). 用户自定义2 */
#define SIGPIPE 13 /* Broken pipe (POSIX). 当管道读端已关闭,继续往管道中写,产生该信号 */
#define SIGALRM 14 /* Alarm clock (POSIX). alarm函数超时时产生该信号,默认动作是程序终止 */
#define SIGTERM 15 /* Termination (ANSI). 终止程序信号,命令kill默认使用该参数*/
#define SIGSTKFLT 16 /* Stack fault. */
#define SIGCLD SIGCHLD /* Same as SIGCHLD (System V). */
#define SIGCHLD 17 /* Child status has changed (POSIX). 子进程终止或停止时,产生该信号,默认被忽略*/
#define SIGCONT 18 /* Continue (POSIX). */
#define SIGSTOP 19 /* Stop, unblockable (POSIX). 停止一个作业控制进程*/
#define SIGTSTP 20 /* Keyboard stop (POSIX). ctrl+z产生该信号,改信号使得前台进程挂起*/
#define SIGTTIN 21 /* Background read from tty (POSIX). */
#define SIGTTOU 22 /* Background write to tty (POSIX). */
#define SIGURG 23 /* Urgent condition on socket (4.2 BSD). */
#define SIGXCPU 24 /* CPU limit exceeded (4.2 BSD). 进程超过了CPU软限制产生该信号*/
#define SIGXFSZ 25 /* File size limit exceeded (4.2 BSD). 进程超过了文件大小软限制产生该信号*/
#define SIGVTALRM 26 /* Virtual alarm clock (4.2 BSD). */
#define SIGPROF 27 /* Profiling alarm clock (4.2 BSD). */
#define SIGWINCH 28 /* Window size change (4.3 BSD, Sun). */
#define SIGPOLL SIGIO /* Pollable event occurred (System V). */
#define SIGIO 29 /* I/O now possible (4.2 BSD). */
#define SIGPWR 30 /* Power failure restart (System V). */
#define SIGSYS 31 /* Bad system call. */
#define SIGUNUSED 31
#define _NSIG 65 /* Biggest signal number + 1
(including real-time signals). */
#define SIGRTMIN (__libc_current_sigrtmin ())
#define SIGRTMAX (__libc_current_sigrtmax ())