STL常用容器:string、vector、deque
目录
一、string容器
1.string的基本概念
2.string的构造函数
- string();//创建字符串 例如:string str;
- string(const char* s);//使用字符串s初始化;
- string(const string& str)//使用一个string对象初始化另外一个string对象
- string(int n,char c)//使用n个字符c初始化
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
//容器-string构造函数
/*
string();//创建字符串 例如:string str;
string(const char* s);//使用字符串s初始化;
string(const string& str)//使用一个string对象初始化另外一个string对象
string(int n,char c)//使用n个字符c初始化
*/
void test01()
{
string s1;
const char* str = "hello world";
string s2(str);
cout << "s2 = " << s2 << endl;
string s3(s2);
cout << "s3 = " << s3 << endl;
string s4(10, 'a');
cout << "s4 = " << s4 << endl;
}
int main()
{
test01();
system("pause");
return 0;
}3.string赋值操作
- string& operator=(const char * s); //char* 类型字符串赋值给当前字符串
- string& operator=(const string &s); //把字符串s赋值给当前字符串
- string& operator=(char *s); //把字符s赋值给当前字符串
- string& assign(const char * s); //char* 类型字符串赋值给当前字符串
- string& assign(const char * s,int n); //char* 类型字符串前n个字符赋值给当前字符串
- string& assign(const string &s); //把字符串s赋值给当前字符串
- string& assign(int n,char c);//用n个字符c赋值给当前字符串
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
//容器-string赋值操作
/*
string& operator=(const char * s); //char* 类型字符串赋值给当前字符串
string& operator=(const string &s); //把字符串s赋值给当前字符串
string& operator=(char *s); //把字符s赋值给当前字符串
string& assign(const char * s); //char* 类型字符串赋值给当前字符串
string& assign(const char * s,int n); //char* 类型字符串前n个字符赋值给当前字符串
string& assign(const string &s); //把字符串s赋值给当前字符串
string& assign(int n,char c);//用n个字符c赋值给当前字符串
*/
void test01()
{
string str1;
str1 = "hello woeld";
cout << "str1 = " << str1 << endl;
string str2;
str2 = str1;
cout << "str2 = " << str2 << endl;
string str3;
str3 = 'a';
cout << "str3 = " << str3 << endl;
string str4;
str4.assign("hello c++");
cout << "str4 = " << str4 << endl;
string str5;
str5.assign("hello c++",5);
cout << "str5 = " << str5 << endl;
string str6;
str6.assign(str5);
cout << "str6 = " << str6 << endl;
string str7;
str7.assign(7, 'd');
cout << "str7 = " << str7 << endl;
}
int main()
{
test01();
system("pause");
return 0;
}4.string字符串拼接
- string &operator+=(const char *str); //重载+=操作符
- string &operator+=(const char c); //重载+=操作符
- string &operator+=(const string &str); //重载+=操作符
- string &append(const char *s); //把字符串s连接到当前字符串结尾
- string &append(const char *s,int n); //把字符串s的前n个字符连接到当前字符串结尾
- string &append(const string &s); //同operator+=(const string &str)
- string &append(const string &s,int pos,int n); //字符串s中从pos开始的n个字符连接到字符串结尾
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
//容器-string+字符串拼接
/*
string &operator+=(const char *str); //重载+=操作符
string &operator+=(const char c); //重载+=操作符
string &operator+=(const string &str); //重载+=操作符
string &append(const char *s); //把字符串s连接到当前字符串结尾
string &append(const char *s,int n); //把字符串s的前n个字符连接到当前字符串结尾
string &append(const string &s); //同operator+=(const string &str)
string &append(const string &s,int pos,int n); //字符串s中从pos开始的n个字符连接到字符串结尾
*/
void test01()
{
string str1 = "我";
str1 += "爱看";
cout << "str1 = " << str1 << endl;
str1 += ':';
cout << "str1 = " << str1 << endl;
string str2 = "My Brilliant Friend";
str1 += str2;
cout << "str1 = " << str1 << endl;
string str3 = "I";
str3.append(" Love Flower!");
cout << "str3 = " << str3 << endl;
str3.append("Lily 123", 5);
cout << "str3 = " << str3 << endl;
//str3.append(str2);
//cout << "str3 = " << str3 << endl;
str3.append(str2, 3, 9);//从位置3开始 往后年截取9个字符+
cout << "str3 = " << str3 << endl;
}
int main()
{
test01();
system("pause");
return 0;
}5.string查找和替换
查找:查找指定的字符串是否存在
替换:在指定的位置替换字符串
rfind和find区别:rfind从右往左找,find从左往右找
- int find(const string& str, int pos = 0) const; //查找str第一次出现位置,从pos开始查找
- int find(const char* s, int pos = 0) const; //查找s第一次出现位置,从pos开始查找
- int find(const char* s, int pos, int n) const; //从pos位置查找s的前n个字符第一次位置
- int find(const char c, int pos = 0) const; //查找字符c第一次出现位置
- int rfind(const string& str, int pos = npos) const; //查找str最后一次位置,从pos开始查找
- int rfind(const char* s, int pos = npos) const; //查找s最后一次出现位置,从pos开始查找
- int rfind(const char* s, int pos, int n) const; //从pos查找s的前n个字符最后一次位置
- int rfind(const char c, int pos = 0) const; //查找字符c最后一次出现位置
- string& replace(int pos, int n, const string& str); //替换从pos开始n个字符替换为字符串str
- string& replace(int pos, int n,const char* s); //替换从pos开始的n个字符替换为字符串s
-
#include<iostream> using namespace std; //容器-string字符串查找和替换 void test01() { string str1 = "abcdefg"; int pos = str1.find("de");//返回3 //int pos = str1.find("df");//没有的话,返回-1 if (pos == -1) { cout << "未找到字符串!" << endl; } else { cout << "找到字符串,pos = " << pos << endl; } //rfind 和find的区别 //rfing从右往左找,find是从左往右 pos = str1.rfind("de"); cout << "rfing,pos = " << pos << endl; } //2、替换 void test02() { string str = "abcdefg"; str.replace(1, 3, "1111"); cout << "replace str = " << str << endl; } int main() { test02(); system("pause"); return 0; }
6.string字符串比较

总结:通常比较两个字符是否相等
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
//容器-string字符串比较
void test01()
{
string str1 = "hello";
string str2 = "xello";
if (str1.compare(str2) == 0)
{
cout << "str1 等于 str2" << endl;
}
else if(str1.compare(str2) > 0)
{
cout << "str1 小于 str2" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "str1 大于 str2" << endl;
}
}
int main()
{
test01();
system("pause");
return 0;
}7.string字符存取

#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
//容器-string字符存取
void test01()
{
string str = "hello";
//1、通过[] 访问单个字符
for (int i = 0; i < str.size(); i++)
{
cout << str[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
//通过at 访问当个字符
for (int i = 0; i < str.size(); i++)
{
cout << str.at(i) << " ";
}
cout << endl;
str[0] = 'x';
cout << "str = " << str << endl;
str.at(1) = 'x';
cout << "str = " << str << endl;
}
int main()
{
test01();
system("pause");
return 0;
}8.string插入和删除

#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
//容器-string字符串插入和删除
void test01()
{
string str = "hello";
//插入
str.insert(1, "1111");
cout << "str = " << str << endl;
//删除
str.erase(1, 4);
cout << "str = " << str << endl;
string str2 = "World";
str.insert(str.size(), str2);
cout << "str = " << str << endl;
}
int main()
{
test01();
system("pause");
return 0;
}9.string 子串:从字符串中截取子串
string substr(int pos = 0, int n=npos)const ;//返回由pos开的的n个字符组成的字符串
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
//容器-string字符串插入和删除
void test01()
{
string str = "Hello World";
string subStr = str.substr(1, 3);
cout << "subStr = " << subStr << endl;
}
//实用操作
void test02()
{
string email = "[email protected]";
//从邮件地址中 获取 用户名信息
int pos = email.find("@");
cout << pos << endl;
string userName = email.substr(0, pos);
cout << "User Name = " << userName << endl;
}
int main()
{
test02();
system("pause");
return 0;
}二、vector容器
1、vector基本概念

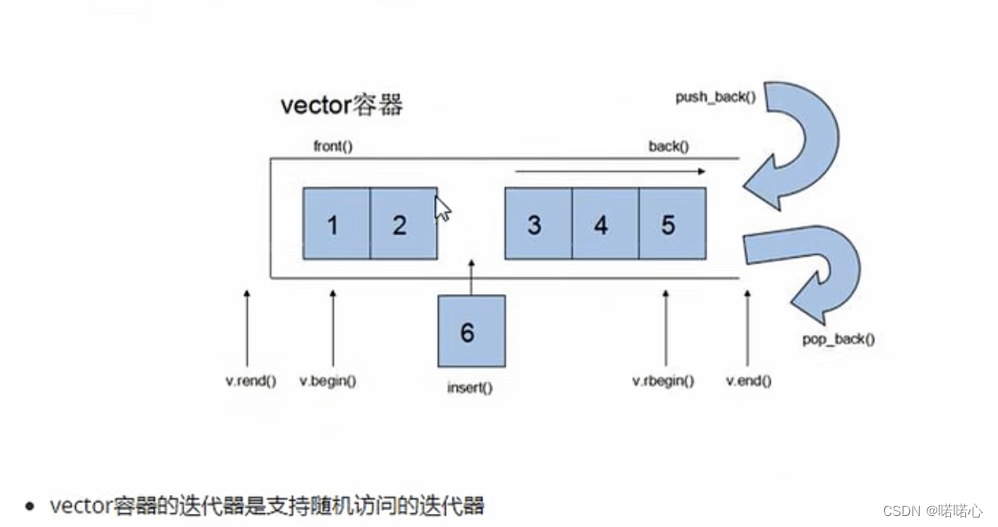
注意:
- 这v.end指定的是最后一个元素的下一个元素地址
- 单端数组:数组尾端可以插入和删除
2、vector构造函数

#include<iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
//打印
void printVector(vector<int>&v)
{
for (vector<int>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void test01()
{
vector<int>v1;//默认构造 无参构造
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
v1.push_back(i);
}
printVector(v1);
//通过区间的方式进行构造
vector<int>v2(v1.begin(), v1.end());
printVector(v2);
//n个elem
vector<int>v3(10, 100);//10个100
printVector(v3);
//拷贝构造
vector<int>v4(v3);
printVector(v4);
}
int main()
{
test01();
system("pause");
return 0;
}3、vector赋值操作

#include<iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
void printVector(vector<int> &v)
{
for (vector<int>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
//vector赋值
void test01()
{
vector<int>v1;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
v1.push_back(i);
}
printVector(v1);
//赋值=
vector<int>v2 = v1;
printVector(v2);
//assign
vector<int>v3;
v3.assign(v1.begin(), v1.end());
printVector(v3);
//n个elem方式赋值
vector<int>v4;
v4.assign(10, 100);
printVector(v4);
}
int main()
{
test01();
system("pause");
return 0;
}4、vector容量和大小
#include<iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
void printVector(vector<int>v)
{
for (vector<int>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
//vector容量和大小
void test01()
{
vector<int>v1;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
v1.push_back(i);
}
printVector(v1);
if (v1.empty())//为真,代表容器为空,即v1为空
{
cout << "v1为空" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "v1 不为空" << endl;
cout << "v1的容量:" << v1.capacity() << endl;
cout << "v1的大小:" << v1.size() << endl;
}
//重新指定大小
//v1.resize(15);
//printVector(v1);//如果重写指定的长度比原来长,默认用0填充
v1.resize(15,100);//利用重载版本,可以指定默认值填充,参数2
printVector(v1);
v1.resize(5);//如果重写指定的长度比原来短,超出部分被删除
printVector(v1);
}
int main()
{
test01();
system("pause");
return 0;
}5、vector插入和删除
- push_back 尾删
- pop_back 尾插
- insert 插入
- erase 删除
- clear 清空
#include<iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
void printVector(vector<int>& v)
{
for (vector<int>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
//vector插入和删除
void test01()
{
vector<int>v;
//尾插
v.push_back(10);
v.push_back(20);
v.push_back(30);
v.push_back(40);
v.push_back(50);
printVector(v);
//尾删
v.pop_back();
printVector(v);
//插入
v.insert(v.begin(), 100);//第一个参数是迭代器
printVector(v);
v.insert(v.begin(), 2, 1000);//第一个参数是迭代器
printVector(v);
//删除
v.erase(v.begin());//也是迭代器
printVector(v);
//类似于清空
//v.erase(v.begin(),v.end());//也是迭代器
v.clear();
printVector(v);
}
int main()
{
test01();
system("pause");
return 0;
}6、vector数据存取操作

#include<iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
//vector数据存取
void test01()
{
vector<int>v;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
v.push_back(i);
}
//利用[]访问数组中的元素
for (int i = 0; i < v.size(); i++)
{
cout << v[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
//利用at方式访问元素
for (int i = 0; i < v.size(); i++)
{
cout << v.at(i) << " ";
}
cout << endl;
//获取第一个元素
cout << "第一个元素:" << v.front() << endl;
//获取最后一个元素
cout << "最后一个元素:" << v.back() << endl;
}
int main()
{
test01();
system("pause");
return 0;
}7、vector互换元素
函数原型:swap(vec);//将vec与本身的元素互换
#include<iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
//vector互换
void printVector(vector<int>&v)
{
for (vector<int>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
//1、基本使用
void test01()
{
vector<int>v1;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
v1.push_back(i);
}
cout<<"交换前:" << endl;
printVector(v1);
vector<int>v2;
for (int i = 10; i > 0; i--)
{
v2.push_back(i);
}
printVector(v2);
//交换后
cout<<"交换后:" << endl;
v1.swap(v2);
printVector(v1);
printVector(v2);
}
//2、实际使用
//巧用swap可以收缩内存空间
void test02()
{
vector<int>v;
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++)
{
v.push_back(i);
}
cout << "v的容量为:" << v.capacity() << endl;
cout << "v的大小为:" << v.size() << endl;
v.resize(3);
cout << "resize v的容量为:" << v.capacity() << endl;
cout << "resize v的大小为:" << v.size() << endl;
vector<int>(v).swap(v); //vector<int>(v)是匿名对象 系统在执行完成该句之后 释放
cout << "swap v的容量为:" << v.capacity() << endl;
cout << "swap v的大小为:" << v.size() << endl;
}
int main()
{
test02();
system("pause");
return 0;
}sawp收缩内存的原因:匿名对象在执行完后,系统自动释放
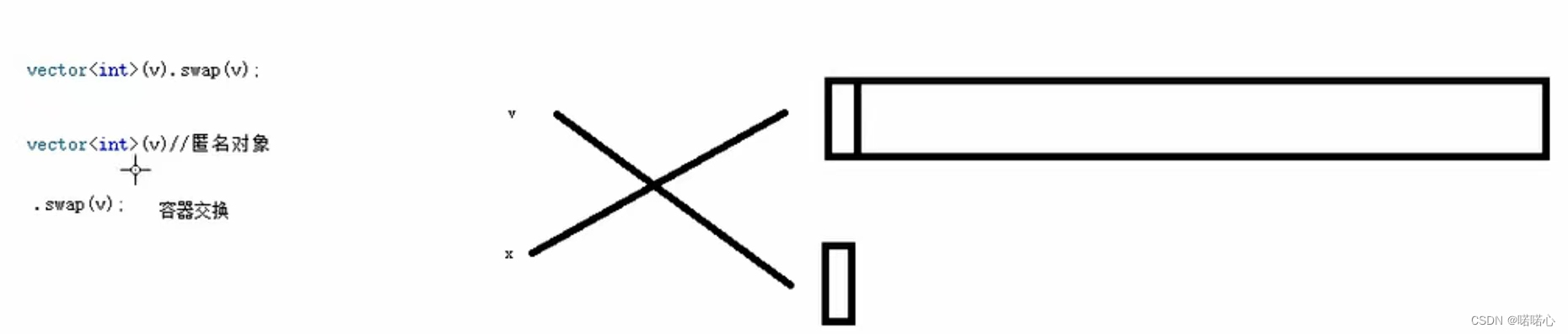
8、vector预留空间
功能描述:减少vector在动态扩展容量时的扩展次数
函数原型:reserve(int,len);//容器预留len个元素长度,预留位置不初始化,元素不可访问
#include<iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
//vector预留空间
void test01()
{
vector<int>v;
//利用reserve预留空间
v.reserve(100000);
int num = 0;
int* p = NULL;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
v.push_back(i);
//每次开辟新内存 都会使得首地址变化
if (p != &v[0])
{
p = &v[0];
num++;
}
}
cout << "num = " << num << endl;
}
int main()
{
test01();
system("pause");
return 0;
}总结:如果数据量很大,可以一开始就利用resreve预留出空间
三、deque容器
1、deque容器基本概念
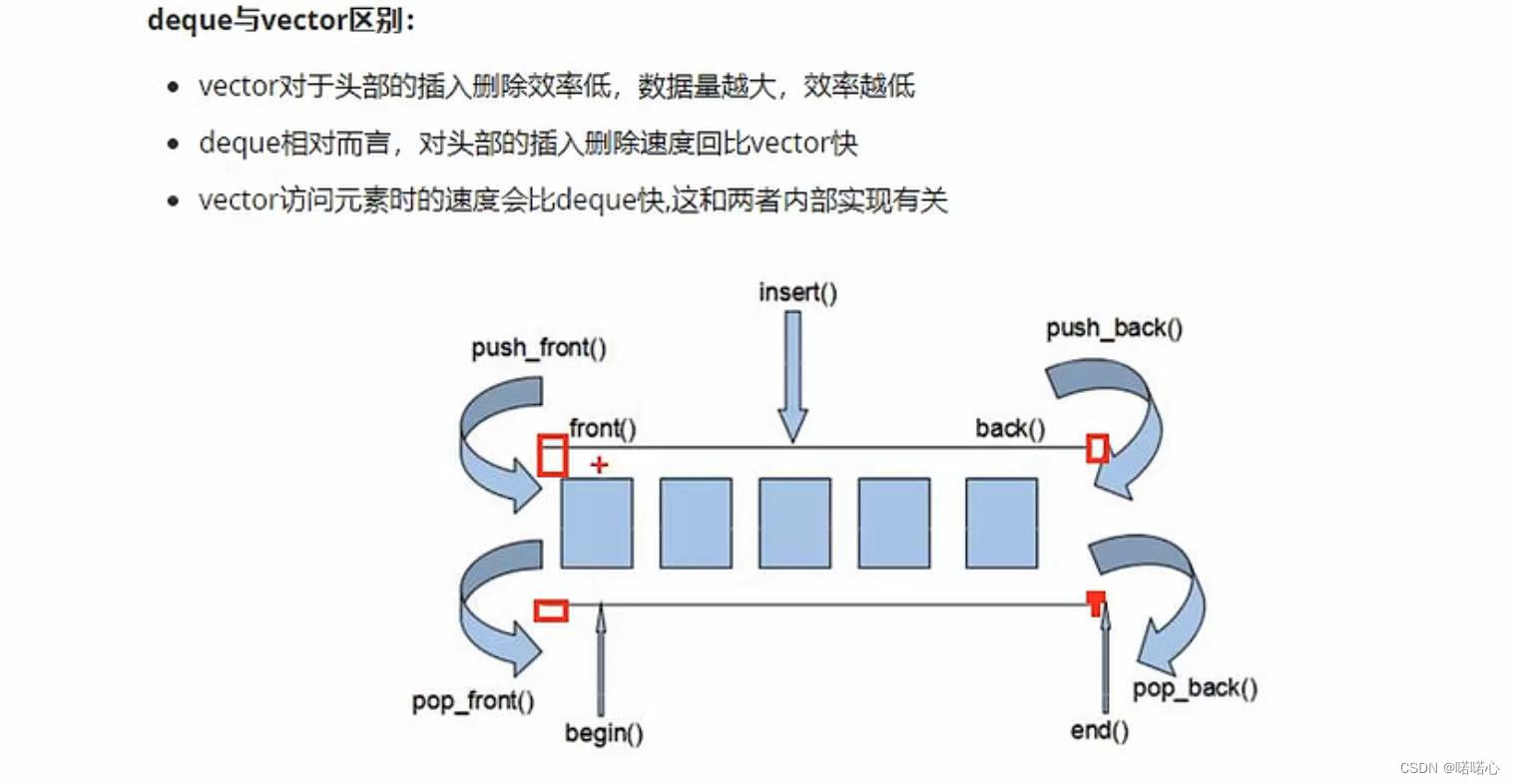
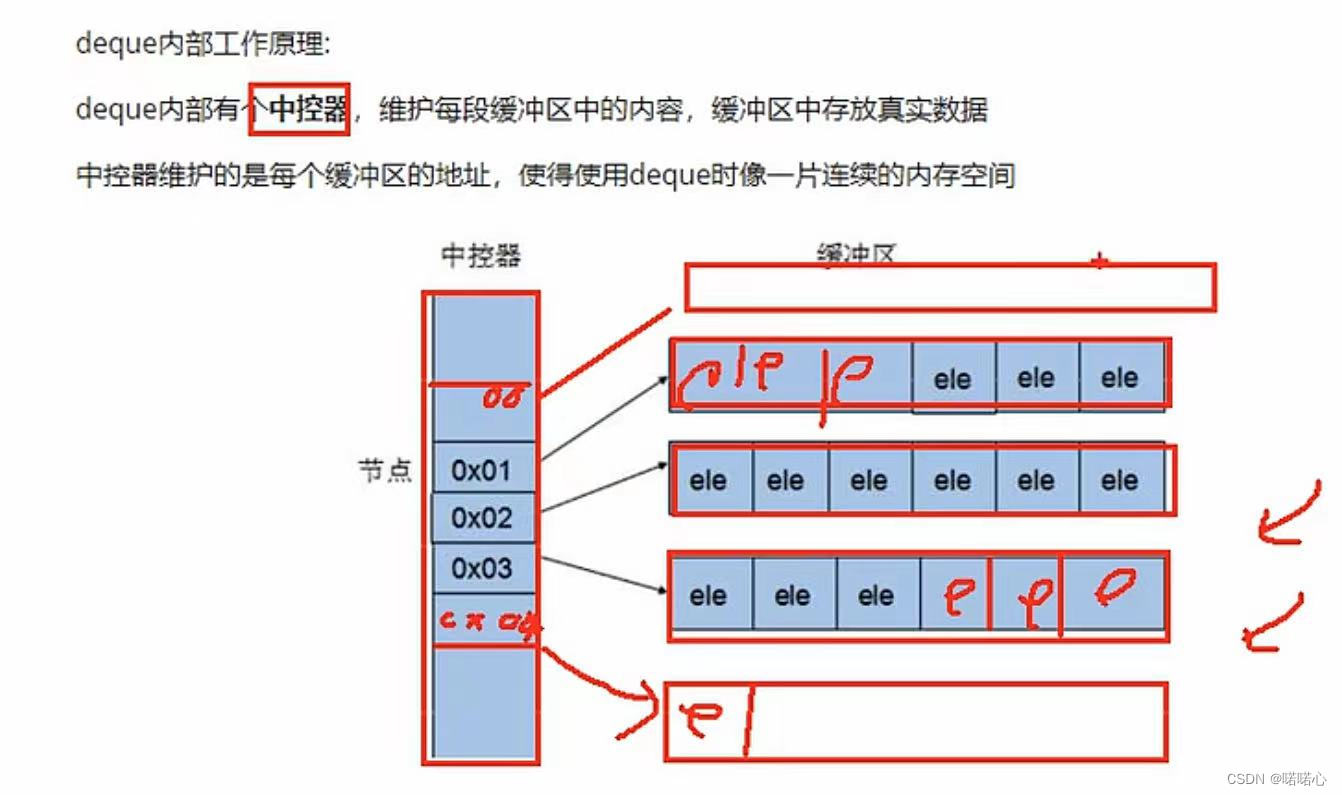
- 插入和删除比vector快,但是访问比vector慢,因为vector要先访问地址再访问元素
- deque容器的迭代器也支持随机访问
2、deque构造函数

#include<iostream>
#include <deque>
using namespace std;
void printDeque(const deque<int>& d)//加const只读容器
{
for (deque<int>::const_iterator it = d.begin(); it != d.end(); it++)
{
//*it = 100;//加const只读容器 容器中的数据不可以修改
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
//deque构造函数
void test01()
{
deque<int>d1;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
d1.push_back(i);
}
printDeque(d1);
deque<int>d2(d1.begin(), d1.end());
printDeque(d2);
deque<int>d3(10, 100);
printDeque(d3);
deque<int>d4(d3);
printDeque(d4);
}
int main()
{
test01();
system("pause");
return 0;
}3、deque赋值操作
#include<iostream>
#include <deque>
using namespace std;
void printDeque(deque<int>&d)
{
for (deque<int>::iterator it = d.begin(); it != d.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
//deque赋值操作
void test01()
{
deque<int>d1;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
d1.push_back(i);
}
printDeque(d1);
//operator= 赋值
deque<int>d2;
d2 = d1;
printDeque(d2);
//assign
deque<int>d3;
d3.assign(d1.begin(), d1.end());
printDeque(d3);
deque<int>d4(10, 100);
printDeque(d4);
}
int main()
{
test01();
system("pause");
return 0;
}4、deque大小操作
deque容器没有容量限制,可以无限扩展
#include<iostream>
#include <deque>
using namespace std;
void printDeque(deque<int>& d)
{
for (deque<int>::iterator it = d.begin(); it != d.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
//deque大小操作
void test01()
{
deque<int>d1;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
d1.push_back(i);
}
printDeque(d1);
if (d1.empty())
{
cout << "d1为空" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "d1不为空" << endl;
cout << "d1容量:" << d1.size()<<endl;
//deque没有容量的概念
}
d1.resize(15);
//printDeque(d1);
d1.resize(15, 1);
printDeque(d1);
d1.resize(5);
printDeque(d1);
}
int main()
{
test01();
system("pause");
return 0;
}5、deque插入删除

#include<iostream>
#include <deque>
using namespace std;
void printDeque(const deque<int>& d)//const只读迭代器
{
for (deque<int>::const_iterator it = d.begin(); it != d.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
//deque大小操作
void test01()
{
deque<int>d1;
//尾插
d1.push_back(10);
d1.push_back(20);
//头插 200 100 10 20
d1.push_front(100);
d1.push_front(200);
printDeque(d1);
//尾删
d1.pop_back();
//头删
d1.pop_front();
printDeque(d1);
}
//插入insert
void test02()
{
deque<int> d1;
d1.push_back(10);
d1.push_back(20);
d1.push_front(100);
d1.push_front(200);
//200 100 10 20
printDeque(d1);
d1.insert(d1.begin(),1000);
//1000 200 100 10 20
printDeque(d1);
d1.insert(d1.begin(), 2, 11);
//11 11 1000 200 100 10 20
printDeque(d1);
deque<int>d2;
d2.push_back(1);
d2.push_back(2);
d2.push_back(3);
d1.insert(d1.begin(), d2.begin(), d2.end());
//1 2 3 11 11 1000 200 100 10 20
printDeque(d1);
}
void test03()
{
deque<int> d1;
d1.push_back(10);
d1.push_back(20);
d1.push_front(100);
d1.push_front(200);
//删除
deque<int>::iterator it = d1.begin();
it++;
d1.erase(it);
printDeque(d1);
//区间方式删除
//类似于清空
//d1.erase(d1.begin(), d1.end());
//printDeque(d1);
//清空
d1.clear();
printDeque(d1);
}
int main()
{
test03();
system("pause");
return 0;
}6、deque数据存储

#include<iostream>
#include <deque>
using namespace std;
void printDeque(const deque<int>& d)//const只读迭代器
{
for (deque<int>::const_iterator it = d.begin(); it != d.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
//deque大小操作
void test01()
{
deque<int>d;
d.push_back(10);
d.push_back(20);
d.push_back(30);
d.push_front(100);
d.push_front(200);
d.push_front(300);
//通过[]方式访问元素
//300 200 100 10 20 30
for (int i = 0; i < d.size(); i++)
{
cout << d[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
//通过at的方式
for (int i = 0; i < d.size(); i++)
{
cout << d.at(i) << " ";
}
cout << endl;
cout << "第一个元素为:" << d.front() << endl;
cout << "最后一个元素为:" << d.back() << endl;
}
int main()
{
test01();
system("pause");
return 0;
}7、deque排序
#include<iostream>
#include <deque>
using namespace std;
#include<algorithm>
void printDeque(const deque<int>& d)//const只读迭代器
{
for (deque<int>::const_iterator it = d.begin(); it != d.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
//deque大小操作
void test01()
{
deque<int>d;
d.push_back(10);
d.push_back(20);
d.push_back(30);
d.push_front(100);
d.push_front(200);
d.push_front(300);
//300 200 100 10 20 30
printDeque(d);
//排序 默认排序规则 升序
//对于支持随机访问的迭代器,都可以利用sort算法之间进行排序
//vector容器也可以利用sort排序
sort(d.begin(), d.end());
cout << "排序后结果:" << endl;
printDeque(d);
}
int main()
{
test01();
system("pause");
return 0;
}


