目录
Protobuf详解
- 深入 ProtoBuf - 简介 - 简书 (jianshu.com)
- [索引]文章索引 - 简书 (jianshu.com)
- Protobuf3语法详解 - 望星辰大海 - 博客园 (cnblogs.com)
Python使用方式
参考:menghaocheng/hello_protobuf: python如何使用protobuf3 (github.com)
步骤:
- 下载protoc(protocol compiler)
- 编写.proto文件
- 编译(生成xxxx_pb2.py)
- 引用xxxx_pb2.py:存储、读取数据
1.下载protoc
下载地址:https://github.com/google/protobuf/releases
根据自己的平台下载对应的编译器,如win10-64位:

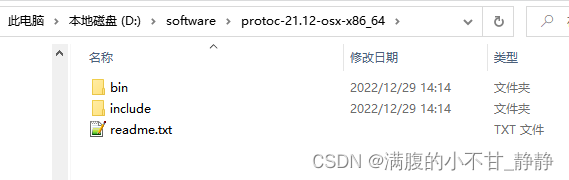
解压到指定目录下:
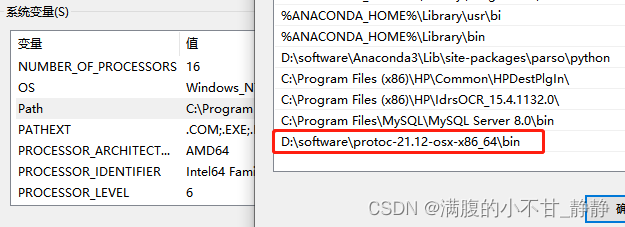
设置环境变量,使在任何地方可以使用protoc指令:
测试protoc:新打开一个命令行:输入protoc --version,如果将输出版本号,说明protoc安装好了

protoc-21.12-osx-x86_64对应的版本是3.19.1
2.编写.proto协议文件
新建一个hello_protobuf文件夹,并用pycharm打开该文件夹。
新建协议文件:在hello_protobuf/protobuf/目录下手动创建addressbook.proto文件
syntax = "proto3";
message Person {
string name = 1;
int32 id = 2;
string email = 3;
enum PhoneType {
MOBILE = 0; //私人手机
HOME = 1; //家庭电话
WORK = 2; //工作电话
}
message PhoneNumber {
string number = 1;
PhoneType type = 2;
}
repeated PhoneNumber phones = 4;
}
message AddressBook {
repeated Person people = 1;
}解释:
syntax = "proto3";指定正在使用 proto3 语法,否则 protobuf 将默认使用的是 proto2。这个指定语法行必须是文件的非空非注释的第一个行。package Test;包申明,指定命名空间(C# 中)。对于 Python,这个包声明符是被忽略的,因为Python模块是按照其在文件系统中的位置进行组织的。message是关键字,定义结构化数据。- 等号后面的数字是字段唯一编号(注意不是字段的值),用于二进制格式消息中标识字段。
protoc 是 protobuf 自带的编译器,可以将 .proto 文件编译成 java、python、go、C# 等多种语言的代码,直接引用。
3.编译Protocol buffer
打开命令行,cd到hello_protobuf/protobuf/下,执行
protoc --python_out=./ addressbook.proto或者在任意位置执行:
protoc -I=F:\hello_protobuf\protobuf --python_out=F:\hello_protobuf\protobuf addressbook.proto编译命令说明:
- -I:表示源文件(.proto 文件)所在文件夹路径。
- --python_out:表示目标语言为 python,且指定生成的 .py 文件存放目录。
- addressbook.proto 为源文件文件名,如果有多个,空格隔开。
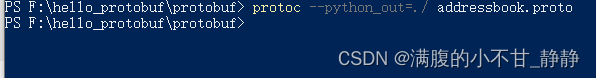
没有输出说明未出错。
新生成hello_protobuf/protobuff/addressbook_pb2.py——这是我们python最终要用的协议文件了。
4.存储/读取数据测试
(1)序列化:addressbook_test_writing.py
from protobuf import addressbook_pb2
import os
def PromptForAddress(person):
person.id = 1
person.name = "mc.meng"
person.email = "[email protected]"
phone_number = person.phones.add()
phone_number.number = "18565772445"
phone_number.type = addressbook_pb2.Person.MOBILE
def write_test():
address_book = addressbook_pb2.AddressBook()
address_book_file = "./data/addressbook.txt"
if not os.path.exists(address_book_file):
os.mkdir(address_book_file)
# 读取文本初始内容
try:
f = open(address_book_file, "rb")
address_book.ParseFromString(f.read())
f.close()
except IOError:
print(address_book_file + ": Could not open file. Creating a new one.")
PromptForAddress(address_book.people.add())
# 追加新内容
f = open(address_book_file, "wb")
f.write(address_book.SerializeToString())
f.close()
if __name__ == "__main__":
write_test()hello_protobuf/data/目录用于存放数据
执行addressbook_test_writing.py后,在hello_protobuf/data/下生成了addressbook.txt文件:

(2)反序列化:address_test_reading.py
import protobuf.addressbook_pb2 as addressbook_pb2
def ListPeople(address_book):
for person in address_book.people:
print("Person ID:", person.id)
print(" Name:", person.name)
print(" E-mail address:", person.email)
for phone_number in person.phones:
if phone_number.type == addressbook_pb2.Person.MOBILE:
print(" Mobile phone #: ", end='')
elif phone_number.type == addressbook_pb2.Person.HOME:
print(" Home phone #: ", end='')
elif phone_number.type == addressbook_pb2.Person.WORK:
print(" Work phone #: ", end='')
print(phone_number.number)
def read_test():
address_book = addressbook_pb2.AddressBook()
address_book_file = "./data/addressbook.txt"
f = open(address_book_file, "rb")
address_book.ParseFromString(f.read())
f.close()
ListPeople(address_book)
if __name__ == "__main__":
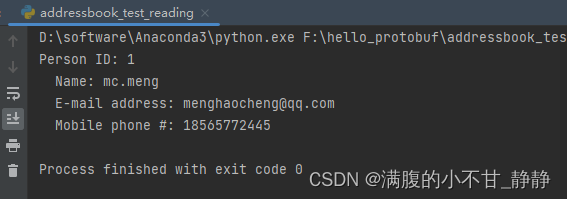
read_test()
运行结果: